Energy
World’s Most Populous Nation Has Put Solar Out To Pasture. Other Countries Should Follow Suit

 From the Daily Caller News Foundation
From the Daily Caller News Foundation
During his debate with former President Donald Trump, President Joe Biden claimed: “The only existential threat to humanity is climate change.” What if I told you that it is not climate change but climate policies that are the real existential threat to billions across our planet?
The allure of a green utopia masks the harsh realities of providing affordable and reliable electricity. Americans could soon wake up to a dystopian future if the proposed Net Zero and Build Back Better initiatives — both aimed at an illogical proliferation of unreliable renewables and a clamp down on dependable fossil fuels — are implemented.
Nowhere is this better reflected than in remote regions of India where solar panels — believed to provide clean and green energy — ultimately resulted in being used to construct cattle sheds.
The transformation of Dharnai in the state of Bihar into a “solar village” was marked by great enthusiasm and high expectations. Villagers were told the solar micro-grid would provide reliable electricity for agriculture, social activities and daily living. The promise engendered a naïve trust in a technology that has failed repeatedly around the world.
The news of this Greenpeace initiative quickly spread as international news media showcased it as a success story for “renewable” energy in a third world country. CNN International’s “Connect the World” said Dharnai’s micro-grid provided a continuous supply of electricity. For an unaware viewer sitting in, say, rural Kentucky, solar energy would have appeared to be making great strides as a dependable energy source.
But the Dharnai system would end up on the long list of grand solar failures.
“As soon as we got solar power connections, there were also warnings to not use high power electrical appliances like television, refrigerator, motor and others,” said a villager. “These conditions are not there if you use thermal power. Then what is the use of such a power? The solar energy tariff was also higher compared to thermal power.”
A village shopkeeper said: “But after three years, the batteries were exhausted and it was never repaired. … No one uses solar power anymore here.” Hopefully, the solar panels will last longer as shelter for cows.
Eventually, the village was connected to the main grid, which provided fully reliable coal-powered electricity at a third of the price of the solar power.
Dharnai is not an isolated case. Several other large-scale solar projects in rural India have had a similar fate. Writing for the publication Mongabay, Mainsh Kumar said: “Once (grid) electricity reaches unelectrified villages, the infrastructure and funds used in installation of such off-grid plants could prove futile.”
While green nonprofits and liberal mainstream media have the embarrassment of a ballyhooed solar project being converted to cattle shed, conventional energy sources like coal continue to power India’s over 1.3 billion people and the industries their economies depend on.
India saw a record jump in electricity demand this year, partly due to increased use of air conditioning units and other electrical appliances as more of the population achieved the financial wherewithal to afford them. During power shortages, coal often has come to the rescue. India allows its coal plants to increase coal stockpiles and import additional fuel without restrictions.
India will add more than 15 gigawatts in the year ending March 2025 (the most in nine years) and aims to add a total of 90 gigawatts of coal-fired capacity by 2032.
Energy reality is inescapable in a growing economy like India’s, and only sources such as coal, oil and natural gas can meet the demand. Fossil fuels can be counted on to supply the energy necessary for modern life, and “green” sources cannot.
India’s stance is to put economic growth ahead of any climate-based agenda to reduce the use of fossil fuels. This was reaffirmed when the country refused to set an earlier target for its net zero commitment, delaying it until 2070.
The story of Dharnai serves as a cautionary tale for the implementation of renewable energy projects in rural India, where pragmatism is the official choice over pie in the sky.
Vijay Jayaraj is a Research Associate at the CO2 Coalition, Arlington, Virginia. He holds a master’s degree in environmental sciences from the University of East Anglia, UK.
Daily Caller
AI Needs Natural Gas To Survive


From the Daily Caller News Foundation
By David Blackmon
As recent studies project a big rise in power generation demand from the big datacenters that are proliferating around the United States, the big question continues to focus in on what forms of generation will rise to meet the new demand. Most datacenters have plans to initially interconnect into local power grids, but the sheer magnitude of their energy needs threatens to outstrip the ability of grid managers to expand supply fast enough.
This hunger for more affordable, 24/7 baseload capacity is leading to a variety of proposed solutions, including President Donald Trump’s new executive orders focused on reviving the nation’s coal industry, scheduled to be signed Tuesday afternoon. But efforts to restart the permitting of new coal-fired power plants in the US will require additional policy changes, efforts which will take time and could ultimately fail. In the meantime, datacenter developers find themselves having to delay construction and completion dates until firm power supply can be secured.
Datacenters specific to AI technology require ever-increasing power loads. For instance, a single AI query can consume nearly ten times the power of a traditional internet search, and projections suggest that U.S. data center electricity consumption could double or even triple by 2030, rising from about 4-5% of total U.S. electricity today to as much as 9-12%. Globally, data centers could see usage climb from around 536 terawatt-hours (TWh) in 2025 to over 1,000 TWh by 2030. In January, a report from the American Security Project estimated that datacenters could consume about 12% of all U.S. power supply.
Obviously, the situation calls for innovative solutions. A pair of big players in the natural gas industry, Liberty Energy and Range Resources, announced on April 8 plans to diversify into the power generation business with the development of a major new natural gas power plant to be located in the Pittsburgh area. Partnering with Imperial Land Corporation (ILC), Liberty and Range will locate the major power generation plant in the Fort Cherry Development District, a Class A industrial park being developed by ILC.
“The strategic collaboration between Liberty, ILC, and Range will focus on a dedicated power generation facility tailored to meet the energy demands of data centers, industrial facilities, and other high-energy-use businesses in Pennsylvania,” the companies said in a joint release.
Plans for this new natural gas power project follows closely on the heels of the March 22 announcement for plans to transform the largest coal-fired power plant in Pennsylvania, the Homer City generating station, into a new gas-fired facility. The planned revitalized plant would house 7 natural gas turbines with a combined capacity of 4.5 GW, enough power 3 million homes.
Both the Homer City station and the Fort Cherry plant will use gas produced out of the Appalachia region’s massive Marcellus Shale formation, the most prolific gas basin in North America. But plans like these by gas companies to invest in their own products for power needs aren’t isolated to Pennsylvania.
In late January, big Permian Basin oil and gas producer Diamondback Energy told investors that it is seeking equity partners to develop a major gas-fired plan on its own acreage in the region. The facility would primarily supply electricity to data centers, which are expected to proliferate in Texas due to the AI boom, while also providing power for Diamondback’s own field operations. This dual-purpose approach could lower the company’s power costs and create a new revenue stream by selling excess electricity.
Prospects for expansion of gas generation in the U.S. received a big boost in January when GE Vernova announced plans for a $600 million expansion of its manufacturing capacity for gas turbines and other products in the U.S. GE Vernova is the main supplier of turbines for U.S. power generation needs. The company plans to build 37 gas power turbines in 2025, with a potential increase to over 70 by 2027, to meet rising energy demands.
The bottom line on these and other recent events is this: Natural gas is quickly becoming the power generation fuel of choice to feed the needs of the expanding datacenter industry through 2035, and potentially beyond. Given that reality, the smart thing to do for these and other companies in the natural gas business is to put down big bets on themselves.
David Blackmon is an energy writer and consultant based in Texas. He spent 40 years in the oil and gas business, where he specialized in public policy and communications.
Bjorn Lomborg
The stupidity of Net Zero | Bjorn Lomborg on how climate alarmism leads to economic crisis

From spiked on YouTube
Note: This interview is focused on Europe and the UK. It very much applies to Canada. The 2025 Federal Election which will see Canadians choose between a more common sense approach, and spending the next 4 years continuing down the path of pursuing “The Stupidity of Net Zero”.
European industry is in freefall, and Net Zero is to blame.
Here, climate economist Bjorn Lomborg – author of Best Things First and False Alarm – explains how panic over climate change is doing far more damage than climate change itself. Swapping cheap and dependable fossil fuels for unreliable and expensive renewables costs our economies trillions, but for little environmental gain, Lomborg says.
Plus, he tackles the myth of the ‘climate apocalypse’ and explains why there are more polar bears than ever.
Support spiked: https://www.spiked-online.com/support/
Sign up to spiked’s newsletters: https://www.spiked-online.com/newslet…
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoStocks soar after Trump suspends tariffs
-

 COVID-192 days ago
COVID-192 days agoBiden Admin concealed report on earliest COVID cases from 2019
-
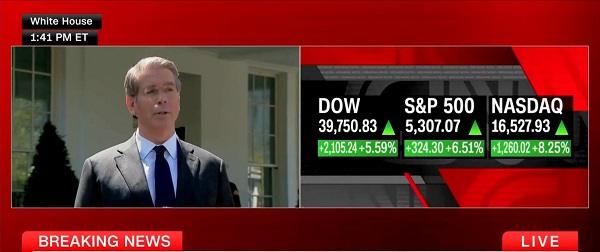
 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoScott Bessent Says Trump’s Goal Was Always To Get Trading Partners To Table After Major Pause Announcement
-

 2025 Federal Election1 day ago
2025 Federal Election1 day agoResearchers Link China’s Intelligence and Elite Influence Arms to B.C. Government, Liberal Party, and Trudeau-Appointed Senator
-
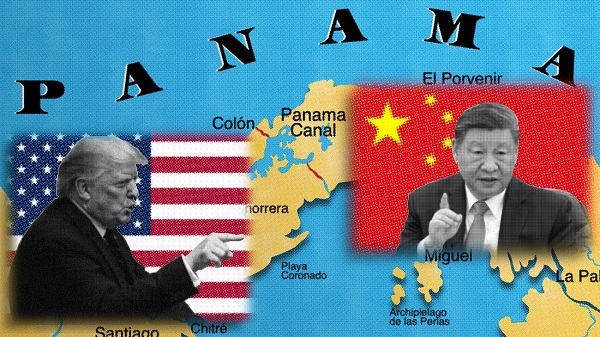
 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoTimeline: Panama Canal Politics, Policy, and Tensions
-

 COVID-191 day ago
COVID-191 day agoFauci, top COVID officials have criminal referral requests filed against them in 7 states
-

 2025 Federal Election2 days ago
2025 Federal Election2 days agoRCMP memo warns of Chinese interference on Canadian university campuses to affect election
-

 2025 Federal Election2 days ago
2025 Federal Election2 days agoThe status quo in Canadian politics isn’t sustainable for national unity





