Opinion
When black roofs cost more and most negatively affect our health, why are we installing them?

We are into construction season and summer and the heat is starting to be an issue. We will have some heat waves and we will notice the “Urban Heat Island Effect”.
The city will seem hotter than the county, but we will also notice differences in temperature between light coloured vehicles and darker coloured vehicles, and even the coolness of a white fence.
During heat waves some of the most vulnerable people are those living on the top floor of a building with a black roof.
My biggest question is why are we still putting black roofs on our buildings? Black roofs do not absorb heat in the winter under a foot of white snow. They absorb heat during the hot days making it hotter.
Let’s start at the beginning, by hitting the Google button.
What is the Heat Island Effect?
The elevated temperature in urban areas as compared to rural, less developed areas is referred to as the urban heat island effect. As cities grow and develop, more buildings and people are added. The process of urban development leads to this phenomenon.
What are the Implications of Heat Islands?
Heat islands are considered a form of local climate change as opposed to global climate change. The effects of heat islands are confined to specific areas, and do not have a larger impact on climate change. Despite being confined to a certain locality, heat islands can still make a significant impact.
Of course, one of the most noticeable impacts on urban dwellers is an increase in hot, summer weather. On particularly clear and hot days, when the heat island effect is at its worst, inhabitants of larger cities will notice hotter and more uncomfortable temperatures. When people are hot, they often crank up their air conditioners. Increases in air conditioning use not only results in more heat being released into the air, this also contributes to air pollution, as more greenhouse gas emissions are discharged. This negatively impacts air quality and can also lead to a surge in urban smog.
How Can We Reduce the Heat Island?
Since the impact of heat islands is mostly negative, scientists and researchers are searching for ways to reduce and reverse the effects. Dark roof surfaces are one of the major culprits of temperature increases. One popular technique for combating the heat island effect is installing green roofs on urban buildings. Green roofs, which are lined with soil and certain types of vegetation, can actually help cities regain some of the cooling and evaporative effects that the natural landscape once provided. As this idea becomes more popular, there is more and more scientific evidence that green roofs can reduce heat in urban areas.
Dark building surfaces that absorb more heat account for some of the rising temperatures in urban areas. One simple method for reducing this effect is to paint buildings with light or white colors that do not absorb nearly as much heat. Some cities are also using paint treatments that reflect light to combat the heat island effect. White, Green or Black Roofs? Berkeley Lab Report Compares Economic Payoffs
Looking strictly at the economic costs and benefits of three different roof types—black, white and “green” (or vegetated)—Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) researchers have found in a new study that white roofs are the most cost-effective over a 50-year time span. While the high installation cost of green roofs sets them back in economic terms, their environmental and amenity benefits may at least partially mitigate their financial burden.
A new report titled “Economic Comparison of White, Green, and Black Flat Roofs in the United States” by Julian Sproul, Benjamin Mandel, and Arthur Rosenfeld of Berkeley Lab, and Man Pun Wan of Nanyang Technological University in Singapore, provides a direct economic comparison of these three roof types. The study will appear in the March 2014 volume of Energy and Buildings and has just been published online. “White roofs win based on the purely economic factors we included, and black roofs should be phased out,” said study co-author Rosenfeld, a Berkeley Lab Distinguished Scientist Emeritus and former Commissioner of the California Energy Commission
The study analyzes 22 commercial flat roof projects in the United States in which two or more roof types were considered. The researchers conducted a 50-year life cycle cost analysis, assuming a 20-year service life for white and black roofs and a 40-year service life for green roofs.
A green roof, often called vegetated roofs or rooftop gardens, has become an increasingly popular choice for aesthetic and environmental reasons. Rosenfeld acknowledges that their economic analysis does not capture all of the benefits of a green roof. For example rooftop gardens provide storm water management, an appreciable benefit in cities with sewage overflow issues, while helping to cool the roof’s surface as well as the air. Green roofs may also give building occupants the opportunity to enjoy green space where they live or work.
Berkeley Lab Distinguished Scientist Emeritus Art Rosenfeld
“We leave open the possibility that other factors may make green roofs more attractive or more beneficial options in certain scenarios,” said Mandel, a graduate student researcher at Berkeley Lab. “The relative costs and benefits do vary by circumstance.”
However, unlike white roofs, green roofs do not offset climate change. White roofs are more reflective than green roofs, reflecting roughly three times more sunlight back into the atmosphere and therefore absorbing less sunlight at earth’s surface. By absorbing less sunlight than either green or black roofs, white roofs offset a portion of the warming effect from greenhouse gas emissions.
“Both white and green roofs do a good job at cooling the building and cooling the air in the city, but white roofs are three times more effective at countering climate change than green roofs,” said Rosenfeld.
White roofs are most cost-effective
The costs and benefits difference stack that has the highest net present value shows the roof type that is most cost-effective.
The 50-year life-cycle cost analysis found that even the most inexpensive kind of green roof (with no public access and consisting of only sedum, or prairie grass) costs $7 per square foot more than black roofs over 50 years, while white roofs save $2 per square foot compared to black roofs. In other words, white roofs cost $9 per square foot less than green roofs over 50 years, or $0.30 per square foot each year.
The researchers acknowledge that their data are somewhat sparse but contend that their analysis is valuable in that it is the first to compare the economic costs and energy savings benefits of all three roof types. “When we started the study it wasn’t obvious that white roofs would still be more cost-effective over the long run, taking into account the longer service time of a green roof,” Mandel said.
Furthermore while the economic results are interesting, it also highlights the need to include factors such health and environment in a more comprehensive analysis. “We’ve recognized the limitations of an analysis that’s only economic,” Mandel said. “We would want to include these other factors in any future study.”
Black roofs pose health risk
For example, black roofs pose a major health risk in cities that see high temperatures in the summer. “In Chicago’s July 1995 heat wave a major risk factor in mortality was living on the top floor of a building with a black roof,” Rosenfeld said.
For that reason, he believes this latest study points out the importance of government policymaking. “White doesn’t win out over black by that much in economic terms, so government has a role to ban or phase out the use of black or dark roofs, at least in warm climates, because they pose a large negative health risk,” he said.
Rosenfeld, who started at Berkeley Lab in the 1950s, is often called California’s godfather of energy efficiency for his pioneering work in the area. He was awarded a National Medal of Technology and Innovation by President Obama in 2012, one of the nation’s highest honours.
Rosenfeld has been a supporter of solar-reflective “cool” roofs, including white roofs, as a way to reduce energy costs and address global warming. He was the co-author of a 2009 study in which it was estimated that making roofs and pavements around the world more reflective could offset 44 billion tons of CO2 emissions. A later study using a global land surface model found similar results: cool roofs could offset the emissions of roughly 300 million cars for 20 years.
So if black roofs are detrimental to our health, contribute to the issue of Urban Heat Island Effect and costs more, why are we still building black roofs?
Daily Caller
AI Needs Natural Gas To Survive


From the Daily Caller News Foundation
By David Blackmon
As recent studies project a big rise in power generation demand from the big datacenters that are proliferating around the United States, the big question continues to focus in on what forms of generation will rise to meet the new demand. Most datacenters have plans to initially interconnect into local power grids, but the sheer magnitude of their energy needs threatens to outstrip the ability of grid managers to expand supply fast enough.
This hunger for more affordable, 24/7 baseload capacity is leading to a variety of proposed solutions, including President Donald Trump’s new executive orders focused on reviving the nation’s coal industry, scheduled to be signed Tuesday afternoon. But efforts to restart the permitting of new coal-fired power plants in the US will require additional policy changes, efforts which will take time and could ultimately fail. In the meantime, datacenter developers find themselves having to delay construction and completion dates until firm power supply can be secured.
Datacenters specific to AI technology require ever-increasing power loads. For instance, a single AI query can consume nearly ten times the power of a traditional internet search, and projections suggest that U.S. data center electricity consumption could double or even triple by 2030, rising from about 4-5% of total U.S. electricity today to as much as 9-12%. Globally, data centers could see usage climb from around 536 terawatt-hours (TWh) in 2025 to over 1,000 TWh by 2030. In January, a report from the American Security Project estimated that datacenters could consume about 12% of all U.S. power supply.
Obviously, the situation calls for innovative solutions. A pair of big players in the natural gas industry, Liberty Energy and Range Resources, announced on April 8 plans to diversify into the power generation business with the development of a major new natural gas power plant to be located in the Pittsburgh area. Partnering with Imperial Land Corporation (ILC), Liberty and Range will locate the major power generation plant in the Fort Cherry Development District, a Class A industrial park being developed by ILC.
“The strategic collaboration between Liberty, ILC, and Range will focus on a dedicated power generation facility tailored to meet the energy demands of data centers, industrial facilities, and other high-energy-use businesses in Pennsylvania,” the companies said in a joint release.
Plans for this new natural gas power project follows closely on the heels of the March 22 announcement for plans to transform the largest coal-fired power plant in Pennsylvania, the Homer City generating station, into a new gas-fired facility. The planned revitalized plant would house 7 natural gas turbines with a combined capacity of 4.5 GW, enough power 3 million homes.
Both the Homer City station and the Fort Cherry plant will use gas produced out of the Appalachia region’s massive Marcellus Shale formation, the most prolific gas basin in North America. But plans like these by gas companies to invest in their own products for power needs aren’t isolated to Pennsylvania.
In late January, big Permian Basin oil and gas producer Diamondback Energy told investors that it is seeking equity partners to develop a major gas-fired plan on its own acreage in the region. The facility would primarily supply electricity to data centers, which are expected to proliferate in Texas due to the AI boom, while also providing power for Diamondback’s own field operations. This dual-purpose approach could lower the company’s power costs and create a new revenue stream by selling excess electricity.
Prospects for expansion of gas generation in the U.S. received a big boost in January when GE Vernova announced plans for a $600 million expansion of its manufacturing capacity for gas turbines and other products in the U.S. GE Vernova is the main supplier of turbines for U.S. power generation needs. The company plans to build 37 gas power turbines in 2025, with a potential increase to over 70 by 2027, to meet rising energy demands.
The bottom line on these and other recent events is this: Natural gas is quickly becoming the power generation fuel of choice to feed the needs of the expanding datacenter industry through 2035, and potentially beyond. Given that reality, the smart thing to do for these and other companies in the natural gas business is to put down big bets on themselves.
David Blackmon is an energy writer and consultant based in Texas. He spent 40 years in the oil and gas business, where he specialized in public policy and communications.
2025 Federal Election
‘Sadistic’ Canadian murderer claiming to be woman denied transfer to female prison

From LifeSiteNews
The logical decision to house the male murderer with men flies in the face of the Liberal Party’s official stance, which is to incarcerate prisoners according to their ‘self-identified’ gender.
A Canadian man who butchered his family and now claims to be a woman will not be allowed to transfer to a female prison.
On April 8, Correctional Services Canada (CSC) announced that Mohamad Al Ballouz, who brutally murdered his wife and two children, will be sent to a men’s prison, despite claiming to be a woman, according to CTV News.
“When there are overriding health and safety concerns, the request is denied and alternatives are put in place to meet the offender’s gender‑related needs at the institution where they are incarcerated,” the CSC statement reads.
Following an assessment of Al Ballouz request, CSC confirmed that he “will be incarcerated in a men’s institution.”
On December 16, Al Ballouz, a 38-year-old from Quebec, was found guilty second-degree murder of his wife Synthia Bussières, first-degree murder of five-year-old Eliam and two-year-old Zac, and one count of attempted arson.
Crown prosecutor Éric Nadeau revealed that the murder took place in September 2022 when Al Ballouz slaughtered his family at their Brossard apartment. He stabbed his wife 23 times before suffocated his children and trying to set the apartment on fire. He then ingested windshield washer fluid, which is believed to have been a suicide attempt.
During the trial, Quebec Superior Justice Eric Downs described Al Ballouz, as having a “sadistic character” and being “deeply narcissistic.” He was sentenced to life imprisonment with no chance of parole for 25 years.
Throughout the trial, Al Ballouz, a biological male, claimed to be a woman and demanded that he be referred to as “Levana,” a change which was made after he was charged for his crimes. Notably, the Canadian Broadcasting Report’s (CBC’s) report of the case refers to the convicted murder as “she” and uses his fake name.
Following his sentencing, the murderer requested to be sent to the Joliette Institution for Women; however, Downs responded that is a decision for Correctional Service Canada.
Currently under the Liberal Party, the policy is to place prisoners according to their “self-identified” gender, not according to biology. As a result, male rapists and murderers can be sent to prison with females.
However, Al Ballouz’s case caused an uproar on social media as many pointed out that putting the murderer in a women’s prison would pose a danger to female inmates.
Conservative Party leader Pierre Poilievre has condemned the Liberal policy and promised that he would end this practice if elected.
“Surreal: A man who killed his wife and two kids now claims he is a woman to go to a female prison,” he wrote in a December 22 post on X.
“I can’t believe I have to say this: but when I’m PM, there will be no male prisoners in female jails,” Poilievre continued. “Period.”
-

 Alberta2 days ago
Alberta2 days agoAlberta takes big step towards shorter wait times and higher quality health care
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoStocks soar after Trump suspends tariffs
-

 COVID-192 days ago
COVID-192 days agoBiden Admin concealed report on earliest COVID cases from 2019
-

 2025 Federal Election1 day ago
2025 Federal Election1 day agoResearchers Link China’s Intelligence and Elite Influence Arms to B.C. Government, Liberal Party, and Trudeau-Appointed Senator
-
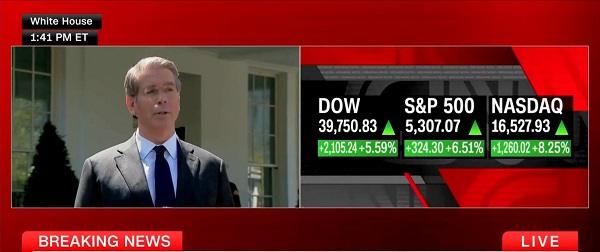
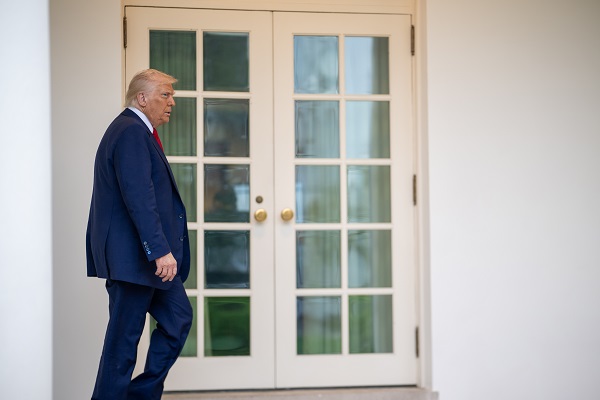
 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoScott Bessent Says Trump’s Goal Was Always To Get Trading Partners To Table After Major Pause Announcement
-

 Energy2 days ago
Energy2 days agoTrump signs four executive orders promoting coal industry
-
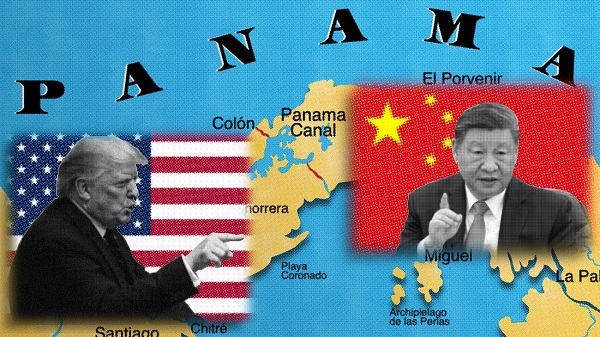
 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoTimeline: Panama Canal Politics, Policy, and Tensions
-

 COVID-191 day ago
COVID-191 day agoFauci, top COVID officials have criminal referral requests filed against them in 7 states





