Frontier Centre for Public Policy
We should follow New Zealand on housing and free up more land for growth

From the Frontier Centre for Public Policy
By Wendell Cox
Attempts to contain ‘urban sprawl’ have driven land prices sky-high. It’s time to abandon densification strategies.
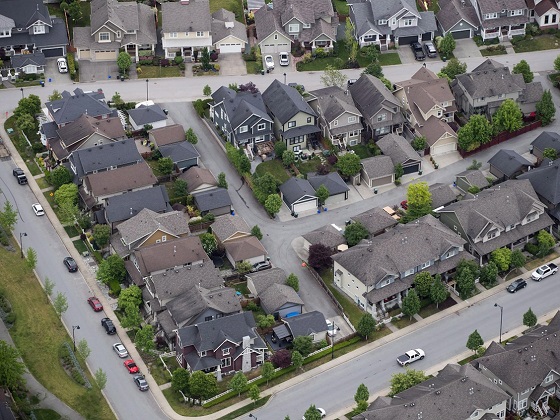
Not so long ago, house prices tended to be around three times household incomes in most housing markets in Canada, the U.S., the U.K., Ireland, Australia and New Zealand. But over the past half-century, many local and provincial governments have tried to stop the expansion of urban areas (so-called “sprawl”) by means of urban growth boundaries, greenbelts and other containment strategies.
Though pleasing to planners, the results have been disastrous for middle- and lower-income households, sending housing prices through the roof, lowering living standards and even increasing poverty. International research has associated urban containment with escalating the underlying price of land, not only on the urban fringe where the city meets rural areas, but also throughout the contained area.
Canada’s current housing affordability crisis is centred in “census metropolitan areas” that have tried containment. Vancouver, which routinely places second or third least affordable of 94 major metropolitan areas in the annual Demographia International Housing Affordability report, has experienced a tripling of house prices compared to incomes. In the third quarter of last year, the median house price was 12.3 times median household income. In less than two decades, the Toronto CMA has experienced a doubling of its house price/income ratio, to 9.3.
Not surprisingly, both CMAs are seeing huge net departures, principally to less expensive markets nearby, such as Kitchener-Waterloo, Guelph, London, Nanaimo, Chilliwack and Kelowna. But these areas are also experiencing vanishing affordability as they too impose Vancouver- and Toronto-like policies.
In recent years, Canadian governments have adopted densification strategies — on the assumption that making cities more crowded will restore housing affordability. But evidence of that is limited. Yonah Freemark of the Urban Institute characterizes the literature as indicating “that upzonings offer mixed success in terms of housing production, reduced costs, and social integration in impacted neighborhoods; outcomes depend on market demand, local context, housing types, and timing.”
Like Canada, New Zealand has seen its house prices grow much faster than household incomes, also mainly because of urban containment policies. Auckland routinely ranks as one of the world’s least affordable markets. But in what may be a watershed moment for housing policy worldwide, New Zealand’s recently elected coalition government is giving up on densification and instead, with its Going for Housing Growth program, is aiming at the heart of the issue by addressing the cost of land.
Under new proposals, local governments will be required to zone enough land for 30 years of projected growth and make it available for immediate development. According to the government, local governments’ deliberate decision to restrain growth on their fringes has “driven up the price of land, which has flowed through to house prices,” and it cites research indicating that “urban growth boundaries add NZ$600,000 (C$500,000) to the cost of land for houses in Auckland’s fringes.”
The new policy will rely on a 2020 act allowing public agencies and private developers to establish “Special Purpose Vehicles” — corporations established for financing housing-related infrastructure, with the costs to be repaid by homeowners over up to 50 years. This removes the infrastructure burden from governments, as has also been done in “municipal utility districts” (MUDs) in Texas and Colorado. MUDs are independent entities empowered to issue bonds and collect fees to finance and manage local infrastructure for new developments.
New Zealand’s government believes guaranteeing plentiful access to land will result in an increased supply “inside and at the edge of our cities … so that land prices are not inflated by artificial planning restrictions.” The same strategy could help here. Unlike most urban planners, most Canadians do not want higher population density. A 2019 survey of younger Canadian households by the Mustel Group and Sotheby’s found that on average across four metropolitan areas (Toronto, Montreal, Vancouver and Calgary) 83 per cent of such families preferred detached houses, though only 56 per cent had actually bought one.
Households that move from the big city to Kitchener-Waterloo, say, or Chilliwack not only want to save money, they also want more house and probably a yard. Detached housing predominates in these affordability sanctuaries, compared to the Vancouver and Toronto CMAs.
Urban planners continue to complain about urban expansion, but that is how organic urban growth occurs. Toronto and Vancouver show that the cost of taming expansion is unacceptably high: inflated house prices, higher rents and, for increasing numbers of people, poverty. It is time to prioritize the well-being of Canadian households, not urban planners.
Wendell Cox, a senior fellow at the Frontier Centre for Public Policy, is author of the Centre’s annual Demographia International Housing Affordability report.
2025 Federal Election
The Cost of Underselling Canadian Oil and Gas to the USA

From the Frontier Centre for Public Policy
Canadians can now track in real time how much revenue the country is forfeiting to the United States by selling its oil at discounted prices, thanks to a new online tracker from the Frontier Centre for Public Policy. The tracker shows the billions in revenue lost due to limited access to distribution for Canadian oil.
At a time of economic troubles and commercial tensions with the United States, selling our oil at a discount to U.S. middlemen who then sell it in the open markets at full price will rob Canada of nearly $19 billion this year, said Marco Navarro-Genie, the VP of Research at the Frontier Centre for Public Policy.
Navarro-Genie led the team that designed the counter.
The gap between world market prices and what Canada receives is due to the lack of Canadian infrastructure.
According to a recent analysis by Ian Madsen, senior policy analyst at the Frontier Centre, the lack of international export options forces Canadian producers to accept prices far below the world average. Each day this continues, the country loses hundreds of millions in potential revenue. This is a problem with a straightforward remedy, said David Leis, the Centre’s President. More pipelines need to be approved and built.
While the Trans Mountain Expansion (TMX) pipeline has helped, more is needed. It commenced commercial operations on May 1, 2024, nearly tripling Canada’s oil export capacity westward from 300,000 to 890,000 barrels daily. This expansion gives Canadian oil producers access to broader global markets, including Asia and the U.S. West Coast, potentially reducing the price discount on Canadian crude.
This is more than an oil story. While our oil price differential has long been recognized, there’s growing urgency around our natural gas exports. The global demand for cleaner energy, including Canadian natural gas, is climbing. Canada exports an average of 12.3 million GJ of gas daily. Yet, we can still not get the full value due to infrastructure bottlenecks, with losses of over $7.3 billion (2024). A dedicated counter reflecting these mounting gas losses underscores how critical this issue is.
“The losses are not theoretical numbers,” said Madsen. “This is real money, and Canadians can now see it slipping away, second by second.”
The Frontier Centre urges policymakers and industry leaders to recognize the economic urgency and ensure that infrastructure projects like TMX are fully supported and efficiently utilized to maximize Canada’s oil export potential. The webpage hosting the counter offers several examples of what the lost revenue could buy for Canadians. A similar counter for gas revenue lost through similarly discounted gas exports will be added in the coming days.
What Could Canada Do With $25.6 Billion a Year?
Without greater pipeline capacity, Canada loses an estimated (2025) $25.6 billion by selling our oil and gas to the U.S. at a steep discount. That money could be used in our communities — funding national defence, hiring nurses, supporting seniors, building schools, and improving infrastructure. Here’s what we’re giving up by underselling these natural resources.

342,000 Nurses
The average annual salary for a registered nurse in Canada is about $74,958. These funds could address staffing shortages and improve patient care nationwide.
Source

39,000 New Housing Units
At an estimated $472,000 per unit (excluding land costs, based on Toronto averages), $25.6 billion could fund nearly 94,000 affordable housing units.
Source
About the Frontier Centre for Public Policy
The Frontier Centre for Public Policy is an independent Canadian think-tank that researches and analyzes public policy issues, including energy, economics and governance.
Business
Hudson’s Bay Bid Raises Red Flags Over Foreign Influence

From the Frontier Centre for Public Policy
A billionaire’s retail ambition might also serve Beijing’s global influence strategy. Canada must look beyond the storefront
When B.C. billionaire Weihong Liu publicly declared interest in acquiring Hudson’s Bay stores, it wasn’t just a retail story—it was a signal flare in an era where foreign investment increasingly doubles as geopolitical strategy.
The Hudson’s Bay Company, founded in 1670, remains an enduring symbol of Canadian heritage. While its commercial relevance has waned in recent years, its brand is deeply etched into the national identity. That’s precisely why any potential acquisition, particularly by an investor with strong ties to the People’s Republic of China (PRC), deserves thoughtful, measured scrutiny.
Liu, a prominent figure in Vancouver’s Chinese-Canadian business community, announced her interest in acquiring several Hudson’s Bay stores on Chinese social media platform Xiaohongshu (RedNote), expressing a desire to “make the Bay great again.” Though revitalizing a Canadian retail icon may seem commendable, the timing and context of this bid suggest a broader strategic positioning—one that aligns with the People’s Republic of China’s increasingly nuanced approach to economic diplomacy, especially in countries like Canada that sit at the crossroads of American and Chinese spheres of influence.
This fits a familiar pattern. In recent years, we’ve seen examples of Chinese corporate involvement in Canadian cultural and commercial institutions, such as Huawei’s past sponsorship of Hockey Night in Canada. Even as national security concerns were raised by allies and intelligence agencies, Huawei’s logo remained a visible presence during one of the country’s most cherished broadcasts. These engagements, though often framed as commercially justified, serve another purpose: to normalize Chinese brand and state-linked presence within the fabric of Canadian identity and daily life.
What we may be witnessing is part of a broader PRC strategy to deepen economic and cultural ties with Canada at a time when U.S.-China relations remain strained. As American tariffs on Canadian goods—particularly in aluminum, lumber and dairy—have tested cross-border loyalties, Beijing has positioned itself as an alternative economic partner. Investments into cultural and heritage-linked assets like Hudson’s Bay could be seen as a symbolic extension of this effort to draw Canada further into its orbit of influence, subtly decoupling the country from the gravitational pull of its traditional allies.
From my perspective, as a professional with experience in threat finance, economic subversion and political leveraging, this does not necessarily imply nefarious intent in each case. However, it does demand a conscious awareness of how soft power is exercised through commercial influence, particularly by state-aligned actors. As I continue my research in international business law, I see how investment vehicles, trade deals and brand acquisitions can function as instruments of foreign policy—tools for shaping narratives, building alliances and shifting influence over time.
Canada must neither overreact nor overlook these developments. Open markets and cultural exchange are vital to our prosperity and pluralism. But so too is the responsibility to preserve our sovereignty—not only in the physical sense, but in the cultural and institutional dimensions that shape our national identity.
Strategic investment review processes, cultural asset protections and greater transparency around foreign corporate ownership can help strike this balance. We should be cautious not to allow historically Canadian institutions to become conduits, however unintentionally, for geopolitical leverage.
In a world where power is increasingly exercised through influence rather than force, safeguarding our heritage means understanding who is buying—and why.
Scott McGregor is the managing partner and CEO of Close Hold Intelligence Consulting.
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoIs Government Inflation Reporting Accurate?
-

 2025 Federal Election2 days ago
2025 Federal Election2 days agoStudy links B.C.’s drug policies to more overdoses, but researchers urge caution
-

 2025 Federal Election2 days ago
2025 Federal Election2 days agoPolls say Canadians will give Trump what he wants, a Carney victory.
-

 2025 Federal Election2 days ago
2025 Federal Election2 days agoPoilievre’s Conservatives promise to repeal policy allowing male criminals in female jails
-

 2025 Federal Election2 days ago
2025 Federal Election2 days agoCarney Liberals pledge to follow ‘gender-based goals analysis’ in all government policy
-

 2025 Federal Election2 days ago
2025 Federal Election2 days agoTrump Has Driven Canadians Crazy. This Is How Crazy.
-

 Entertainment1 day ago
Entertainment1 day agoPedro Pascal launches attack on J.K. Rowling over biological sex views
-

 2025 Federal Election1 day ago
2025 Federal Election1 day agoPoilievre Campaigning To Build A Canadian Economic Fortress