Freedom Convoy
Trudeau’s use of Emergencies Act has cost taxpayers $73 million thus far

From LifeSiteNews
Expenses for the Emergencies Act, the use of which a federal court ruled ‘not justified,’ included $17.5 million for a judicial inquiry, $400,000 for charter flights and $1.3 million for hotel rooms for out-of-town RCMP officers.
The Liberal government’s use of the Emergencies Act against the 2022 Freedom Convoy has cost Canadian taxpayers over $73 million thus far.
According to newly released records obtained by Blacklock’s Reporter, Prime Minister Justin Trudeau’s enactment of the Emergencies Act, the use of which has since been ruled “not justified” by a federal court, to drive out Freedom Convoy protestors from Ottawa in 2022, cost the Department of Public Safety $73,550,568.
According to Blacklock’s Reporter, the $73 million figure was part of records released by the department at the request of Conservative MP Ziad Aboultaif, and despite its high number, is not the final account.
“With regard to enactment of the Emergencies Act in 2022, what was the cost burden for the government?” Conservative MP Ziad Aboultaif asked.
“Cost associated with fiscal year 2023-2024 are still to be determined,” the department responded.
According to the Department of Public Safety, most of the public safety expenses were attributed to local authorities in Ottawa and Windsor, Ontario.
“It should be noted additional funding allocated by the government to Ottawa and its partners as well as Windsor were not specifically as a result of the Emergencies Act invocation but meant to compensate both municipalities for the extraordinary expenses incurred during and after the protracted blockades,” the report said.
Other expenses included $17.5 million for a judicial inquiry, $400,000 for charter flights, and $1.3 million for hotel rooms for out-of-town RCMP officers.
The costs were incurred after Trudeau enacted the Act on February 14, 2022 to shut down the Freedom Convoy protest which took place in Ottawa.
The popular protest featured thousands of Canadians calling for an end to COVID mandates by camping outside Parliament in Ottawa. Measures taken under the Act included freezing the bank accounts of Canadians who donated to the protest.
At the time, the use of the Act was justified by claims that the protest was “violent,” a claim that has still gone unsubstantiated.
In fact, videos of the protest against COVID regulations and vaccine mandates show Canadians from across the country gathering outside Parliament engaged in dancing, street hockey, and other family-friendly activities.
Indeed, the only acts of violence caught on video were carried out against the protesters after the Trudeau government directed police to end the protest. One such video showed an elderly women being trampled by a police horse.
Recently, Federal Court Justice Richard Mosley ruled that Trudeau was “not justified” in invoking the Emergencies Act.
However, the Trudeau government has doubled down on its heavy-handed response to citizen protesters, filing an appeal with the Federal Court of Appeal – a court where 10 of the 15 sitting judges were appointed by Trudeau.
COVID-19
Chris Barber asks Court to stay proceedings against him
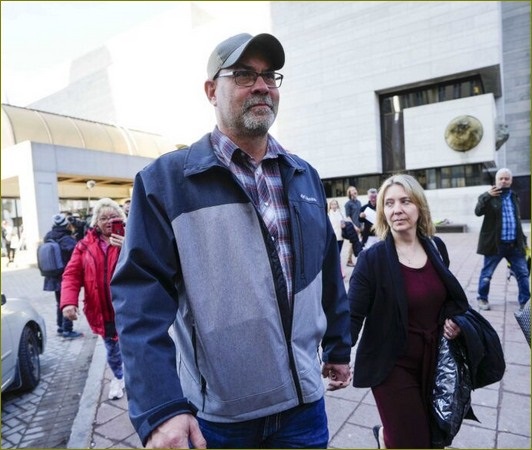

Chris Barber leaves the courthouse in Ottawa after the verdict was delivered in his trial with fellow Freedom Convoy organizer Tamara Lich, on Thursday, April 3, 2025. (Photo credit: THE CANADIAN PRESS/Justin Tang)
“Chris Barber consistently followed the legal advice that he received from police officers, lawyers, and a Superior Court judge.”
The Justice Centre for Constitutional Freedoms announces that Chris Barber has asked the Ontario Court of Justice for a stay of proceedings against him. He argues that the legal advice given to him by police officers, lawyers, and a Superior Court judge during the Freedom Convoy was erroneous and that, as a result, the Crown is not entitled to convict him.
On April 3, 2025, Justice Heather Perkins-McVey of the Ontario Court of Justice found Mr. Barber guilty of mischief and of counselling others to breach a court order. That decision followed upon a lengthy 45-day trial stretching from September 2023 to September 2024.
Diane Magas, Chris Barber’s lawyer, filed a Stay of Proceedings Application with the Court on April 16, 2025. In that Application, Mr. Barber and his legal team argue that he did, in fact, seek legal advice regarding his actions during the Freedom Convoy protest.
For example, he followed Ottawa Police Services directions on where to park trucks in downtown Ottawa. When an officer asked him to move his truck, “Big Red,” from downtown Ottawa, he moved it. On February 7 and 16, 2022, his lawyer at the time advised him that Justice Maclean of the Superior Court had confirmed that the protest could continue so long as it continued to be peaceful and safe.
In essence, Chris Barber and his legal team are now arguing that he followed all legal advice that was given to him in 2022, but that some of the legal advice he was given turned out to be erroneous.
His Application argues for a stay of proceedings against him on the grounds that “he sought advice from lawyers, police officers, and a Superior Court Judge on the legality of the protest he was involved in.”
This Application was filed one day after Chris Barber was informed that the Crown was pursuing a two-year prison sentence against him. In an April 15 Facebook post, Mr. Barber wrote, “My family got bad news today. The Crown prosecutor wants to lock Tamara Lich and me in prison for two years-for standing up for freedom. They also want to [seize] my truck, Big Red, and crush her like she’s just scrap metal or sell it at auction.”
If the Application is successful, Mr. Barber would not see prison time, nor would his truck be seized.
“Throughout the peaceful Freedom Convoy, Chris Barber did what any law-abiding Canadian would do: seeking out and acting upon the best legal advice available to him,” stated John Carpay, President of the Justice Centre. “Chris Barber consistently followed the legal advice that he received from police officers, lawyers, and a Superior Court judge.”
“To hold a well-meaning man behind bars for two years and to confiscate his property, as is now demanded by the Crown, would bring the administration of justice into disrepute,” Mr. Carpay continued. “Crown prosecutors are painting a portrait of a dangerous criminal, even while Chris Barber sought out and followed legal advice when participating in the Freedom Convoy in Ottawa in 2022. Chris worked within the law when peacefully exercising his Charter freedoms of expression, assembly and association.”
COVID-19
Tamara Lich and Chris Barber trial update: The Longest Mischief Trial of All Time continues..

Here are the last two posts on Tamara Lich’s Substack posted April 16 and April 17:
April 17:
We weren’t able to secure a date yesterday for the sentencing hearing and instead another ‘speak to’ was set for April 28. In addition to time needed to enter numerous impact statements (coincidentally and conveniently comprised of individuals suing us for $300,000,000.00), the Crown has added a forfeiture order to seize Big Red which will add significant time to argue. Therefore I suspect all parties will need to find 4-5 days in their schedules for the sentencing hearing.
The Crown is also seeking two years in federal prison for each of us.
Three days were tentatively set aside at the end of May for a Stay of Proceedings application put forth yesterday by Ms. Magus on Chris’ behalf.
And so The Longest Mischief Trial of All Time continues to plod along, still no end in sight.
April 16:
In our trial, the longest mischief trial of all time, we set hearing dates to set hearing dates.
There will be a ‘speak to’ this afternoon to set a date for the sentencing hearing which we think will take 3-4 days. Following that hearing, Chris and I will return to Ottawa again for the actual sentence.
The Crown is seeking 2 years in a federal penitentiary for both of us, plus they have decided to file an application to confiscate Big Red. Funny, there hasn’t been a single other convoy case in which the Crown demanded that persons property or vehicle, yet they seem to want Big Red. You need to ask yourself why.
Chris raised his children in that truck, changed their diapers in that truck, had his old dog, Buddy, put to sleep in the passenger seat when his time came because that was Buddy’s favourite place in the world.
This is not about the rule of law.
It’s about crushing a Canadian symbol of Hope, Pride & Unity
-

 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoIs Government Inflation Reporting Accurate?
-

 2025 Federal Election2 days ago
2025 Federal Election2 days agoConservatives promise to ban firing of Canadian federal workers based on COVID jab status
-

 2025 Federal Election1 day ago
2025 Federal Election1 day agoCarney’s Hidden Climate Finance Agenda
-

 Environment2 days ago
Environment2 days agoExperiments to dim sunlight will soon be approved by UK government: report
-

 International2 days ago
International2 days agoPope Francis Got Canadian History Wrong
-

 2025 Federal Election1 day ago
2025 Federal Election1 day agoWhen it comes to pipelines, Carney’s words flow both ways
-

 2025 Federal Election1 day ago
2025 Federal Election1 day agoStudy links B.C.’s drug policies to more overdoses, but researchers urge caution
-

 Censorship Industrial Complex2 days ago
Censorship Industrial Complex2 days agoIs free speech over in the UK? Government censorship reaches frightening new levels