Canadian Energy Centre
Top 10 good news stories about Canadian energy in 2024

From the Canadian Energy Centre
Record oil production, more Indigenous ownership and inching closer to LNG
It’s likely 2024 will go down in history as a turning point for Canadian energy, despite challenging headwinds from federal government policy.
Here’s some of the good news.
10. New carbon capture and storage (CCS) projects to proceed
In June, Shell announced it will proceed with the Polaris and Atlas CCS projects, expanding emissions reduction at the company’s Scotford energy and chemicals park near Edmonton.
Polaris is designed to capture approximately 650,000 tonnes of CO2 per year, or the equivalent annual emissions of about 150,000 gasoline-powered cars. The CO2 will be transported by a 22-kilometre pipeline to the Atlas underground storage hub.
The projects build on Shell’s experience at the Quest CCS project, also located at the Scotford complex. Since 2015, Quest has stored more than eight million tonnes of CO2. Polaris and Atlas are targeted for startup in 2028.
Meanwhile, Entropy Inc. announced in July it will proceed with its Glacier Phase 2 CCS project. Located at the Glacier gas plant near Grande Prairie, the project is expected onstream in mid-2026 and will capture 160,000 tonnes of emissions per year.
Since 2015, CCS operations in Alberta have safely stored roughly 14 million tonnes of CO2, or the equivalent emissions of more than three million cars.
9. Canada’s U.S. oil exports reach new record

Expanded export capacity at the Trans Mountain Westridge Terminal. Photo courtesy Trans Mountain Corporation
Canada’s exports of oil and petroleum products to the United States averaged a record 4.6 million barrels per day in the first nine months of 2024, according to the U.S. Energy Information Administration.
Demand from Midwest states increased, along with the U.S. Gulf Coast, the world’s largest refining hub. Canadian sales to the U.S. West Coast also increased, enabled by the newly completed Trans Mountain Pipeline Expansion.
8. Alberta’s oil production never higher
In early December, ATB Economics analyst Rob Roach reported that Alberta’s oil production has never been higher, averaging 3.9 million barrels per day in the first 10 months of the year.
This is about 190,000 barrels per day higher than during the same period in 2023, enabled by the Trans Mountain expansion, Roach noted.
7. Indigenous energy ownership spreads

Communities of Wapiscanis Waseskwan Nipiy Limited Partnership in December 2023. Photo courtesy Alberta Indigenous Opportunities Corporation
In September, the Bigstone Cree Nation became the latest Indigenous community to acquire an ownership stake in an Alberta energy project.
Bigstone joined 12 other First Nations and Métis settlements in the Wapiscanis Waseskwan Nipiy Holding Limited Partnership, which holds 85 per cent ownership of Tamarack Valley Energy’s Clearwater midstream oil and gas assets.
The Alberta Indigenous Opportunities Corporation (AIOC) is backstopping the agreement with a total $195 million loan guarantee.
In its five years of operations, the AIOC has supported more than 60 Indigenous communities taking ownership of energy projects, with loan guarantees valued at more than $725 million.
6. Oil sands emissions intensity goes down
A November report from S&P Global Commodity said that oil sands production growth is beginning to rise faster than emissions growth.
While oil sands production in 2023 was nine per cent higher than in 2019, total emissions rose by just three per cent.
“This is a notable, significant change in oil sands emissions,” said Kevin Birn, head of S&P Global’s Centre for Emissions Excellence.
Average oil sands emissions per barrel, or so-called “emissions intensity” is now 28 per cent lower than it was in 2009.
5. Oil and gas producers beat methane target, again
Data released by the Alberta Energy Regulator in November 2024 confirmed that methane emissions from conventional oil and gas production in the province continue to go down, exceeding government targets.
In 2022, producers reached the province’s target to reduce methane emissions by 45 per cent compared to 2014 levels by 2025 three years early.
The new data shows that as of 2023, methane emissions have been reduced by 52 per cent.
4. Cedar LNG gets the green light to proceed

Haisla Nation Chief Councillor Crystal Smith and Pembina Pipeline Corporation CEO Scott Burrows announce the Cedar LNG positive final investment decision on June 25, 2024. Photo courtesy Cedar LNG
The world’s first Indigenous majority-owned liquefied natural gas (LNG) project is now under construction on the coast of Kitimat, B.C., following a positive final investment decision in June.
Cedar LNG is a floating natural gas export terminal owned by the Haisla Nation and Pembina Pipeline Corporation. It will have capacity to produce 3.3 million tonnes of LNG per year for export overseas, primarily to meet growing demand in Asia.
The $5.5-billion project will receive natural gas through the Coastal GasLink pipeline. Peak construction is expected in 2026, followed by startup in late 2028.
3. Coastal GasLink Pipeline goes into service
The countdown is on to Canada’s first large-scale LNG exports, with the official startup of the $14.5-billion Coastal GasLink Pipeline in November.
The 670-kilometre pipeline transports natural gas from near Dawson Creek, B.C. to the LNG Canada project at Kitimat, where it will be supercooled and transformed into LNG.
LNG Canada will have capacity to export 14 million tonnes of LNG per year to overseas markets, primarily in Asia, where it is expected to help reduce emissions by displacing coal-fired power.
The terminal’s owners – Shell, Petronas, PetroChina, Mitsubishi and Korea Gas Corporation – are ramping up natural gas production to record rates, according to RBN Energy.
RBN analyst Martin King expects the first shipments to leave LNG Canada by early next year, setting up for commercial operations in mid-2025.
2. Construction starts on $8.9 billion net zero petrochemical plant
In April, construction commenced near Edmonton on the world’s first plant designed to produce polyethylene — a widely used, recyclable plastic — with net zero scope 1 and 2 emissions.
Dow Chemicals’ $8.9 billion Path2Zero project is an expansion of the company’s manufacturing site in Fort Saskatchewan. Using natural gas as a feedstock, it will incorporate CCS to reduce emissions.
According to business development agency Edmonton Global, the project is spurring a boom in the region, with nearly 200 industrial projects worth about $96 billion now underway or nearing construction.
Dow’s plant is scheduled for startup in 2027.
1. Trans Mountain Pipeline Expansion completed

The “Golden Weld” marked mechanical completion of construction for the Trans Mountain Expansion Project on April 11, 2024. Photo courtesy Trans Mountain Corporation
The long-awaited $34-billion Trans Mountain Pipeline Expansion officially went into service in May, in a game-changer for Canadian energy with ripple effects around the world.
The 590,000 barrel-per-day expansion for the first time gives customers outside the United States access to large volumes of Canadian oil, with the benefits flowing to Canada’s economy.
According to the Canada Energy Regulator, exports to non-U.S. locations more than doubled following the expansion startup, averaging 420,000 barrels per day compared to about 130,000 barrels per day in 2023.
The value of Canadian oil exports to Asia has soared from effectively zero to a monthly average of $515 million between June and October, according to ATB Economics.
Canadian Energy Centre
Saskatchewan Indigenous leaders urging need for access to natural gas

Piapot First Nation near Regina, Saskatchewan. Photo courtesy Piapot First Nation/Facebook
From the Canadian Energy Centre
By Cody Ciona and Deborah Jaremko
“Come to my nation and see how my people are living, and the struggles that they have day to day out here because of the high cost of energy, of electric heat and propane.”
Indigenous communities across Canada need access to natural gas to reduce energy poverty, says a new report by Energy for a Secure Future (ESF).
It’s a serious issue that needs to be addressed, say Indigenous community and business leaders in Saskatchewan.
“We’re here today to implore upon the federal government that we need the installation of natural gas and access to natural gas so that we can have safe and reliable service,” said Guy Lonechild, CEO of the Regina-based First Nations Power Authority, on a March 11 ESF webinar.
Last year, 20 Saskatchewan communities moved a resolution at the Assembly of First Nations’ annual general assembly calling on the federal government to “immediately enhance” First Nations financial supports for “more desirable energy security measures such as natural gas for home heating.”
“We’ve been calling it heat poverty because that’s what it really is…our families are finding that they have to either choose between buying groceries or heating their home,” Chief Christine Longjohn of Sturgeon Lake First Nation said in the ESF report.
“We should be able to live comfortably within our homes. We want to be just like every other homeowner that has that choice to be able to use natural gas.”
At least 333 First Nations communities across Canada are not connected to natural gas utilities, according to the Canada Energy Regulator (CER).
ESF says that while there are many federal programs that help cover the upfront costs of accessing electricity, primarily from renewable sources, there are no comparable ones to support natural gas access.
“Most Canadian and Indigenous communities support actions to address climate change. However, the policy priority of reducing fossil fuel use has had unintended consequences,” the ESF report said.
“Recent funding support has been directed not at improving reliability or affordability of the energy, but rather at sustainability.”
Natural gas costs less than half — or even a quarter — of electricity prices in Alberta, British Columbia, Ontario, Manitoba and Saskatchewan, according to CER data.
“Natural gas is something NRCan [Natural Resources Canada] will not fund. It’s not considered a renewable for them,” said Chief Mark Fox of the Piapot First Nation, located about 50 kilometres northeast of Regina.
“Come to my nation and see how my people are living, and the struggles that they have day to day out here because of the high cost of energy, of electric heat and propane.”
According to ESF, some Indigenous communities compare the challenge of natural gas access to the multiyear effort to raise awareness and, ultimately funding, to address poor water quality and access on reserve.
“Natural gas is the new water,” Lonechild said.
Alberta
The beauty of economic corridors: Inside Alberta’s work to link products with new markets

From the Canadian Energy Centre
Q&A with Devin Dreeshen, Minister of Transport and Economic Corridors
CEC: How have recent developments impacted Alberta’s ability to expand trade routes and access new markets for energy and natural resources?
Dreeshen: With the U.S. trade dispute going on right now, it’s great to see that other provinces and the federal government are taking an interest in our east, west and northern trade routes, something that we in Alberta have been advocating for a long time.
We signed agreements with Saskatchewan and Manitoba to have an economic corridor to stretch across the prairies, as well as a recent agreement with the Northwest Territories to go north. With the leadership of Premier Danielle Smith, she’s been working on a BC, prairie and three northern territories economic corridor agreement with pretty much the entire western and northern block of Canada.
There has been a tremendous amount of work trying to get Alberta products to market and to make sure we can build big projects in Canada again.
CEC: Which infrastructure projects, whether pipeline, rail or port expansions, do you see as the most viable for improving Alberta’s global market access?
Dreeshen: We look at everything. Obviously, pipelines are the safest way to transport oil and gas, but also rail is part of the mix of getting over four million barrels per day to markets around the world.
The beauty of economic corridors is that it’s a swath of land that can have any type of utility in it, whether it be a roadway, railway, pipeline or a utility line. When you have all the environmental permits that are approved in a timely manner, and you have that designated swath of land, it politically de-risks any type of project.
CEC: A key focus of your ministry has been expanding trade corridors, including an agreement with Saskatchewan and Manitoba to explore access to Hudson’s Bay. Is there any interest from industry in developing this corridor further?
Dreeshen: There’s been lots of talk [about] Hudson Bay, a trade corridor with rail and port access. We’ve seen some improvements to go to Churchill, but also an interest in the Nelson River.
We’re starting to see more confidence in the private sector and industry wanting to build these projects. It’s great that governments can get together and work on a common goal to build things here in Canada.
CEC: What is your vision for Alberta’s future as a leader in global trade, and how do economic corridors fit into that strategy?
Dreeshen: Premier Smith has talked about C-69 being repealed by the federal government [and] the reversal of the West Coast tanker ban, which targets Alberta energy going west out of the Pacific.
There’s a lot of work that needs to be done on the federal side. Alberta has been doing a lot of the heavy lifting when it comes to economic corridors.
We’ve asked the federal government if they could develop an economic corridor agency. We want to make sure that the federal government can come to the table, work with provinces [and] work with First Nations across this country to make sure that we can see these projects being built again here in Canada.
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoStocks soar after Trump suspends tariffs
-

 COVID-192 days ago
COVID-192 days agoBiden Admin concealed report on earliest COVID cases from 2019
-
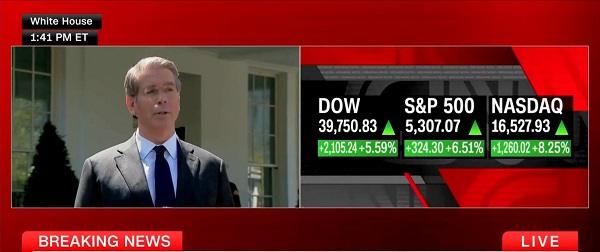
 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoScott Bessent Says Trump’s Goal Was Always To Get Trading Partners To Table After Major Pause Announcement
-

 2025 Federal Election1 day ago
2025 Federal Election1 day agoResearchers Link China’s Intelligence and Elite Influence Arms to B.C. Government, Liberal Party, and Trudeau-Appointed Senator
-
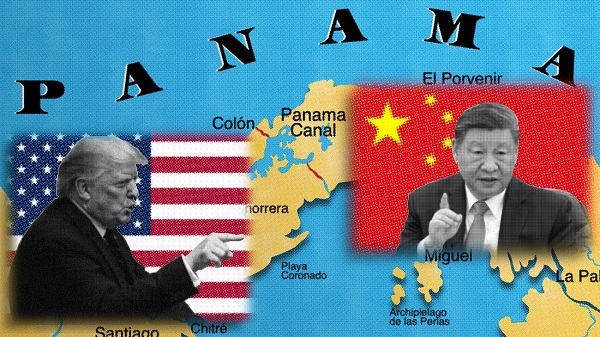
 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoTimeline: Panama Canal Politics, Policy, and Tensions
-

 COVID-191 day ago
COVID-191 day agoFauci, top COVID officials have criminal referral requests filed against them in 7 states
-

 2025 Federal Election2 days ago
2025 Federal Election2 days agoRCMP memo warns of Chinese interference on Canadian university campuses to affect election
-

 2025 Federal Election2 days ago
2025 Federal Election2 days agoThe status quo in Canadian politics isn’t sustainable for national unity












