Canadian Energy Centre
Terra Nova back producing oil, benefits to flow for Atlantic Canada communities and world energy security

The Terra Nova floating production, storage and offloading (FPSO) vessel. Photo courtesy Suncor Energy
From the Canadian Energy Centre
By Will Gibson
‘You should see it start to make a real impact on the market by 2025’
The Terra Nova offshore oil project sits about 350 kilometres southeast of St. John’s in the deep blue waters of the Atlantic.
And even though St. John’s Mayor Danny Breen can’t see the field and its massive floating, production, storage and offloading (FPSO) vessel from his office at city hall, he’s pleased it’s back to producing oil.
“There’s lots of numbers you could use to demonstrate Terra Nova’s contribution to our province and community, from the royalties and taxes it generates for governments or the jobs and contracts it provides to people and businesses,” says Breen.
“But it’s important for our psyche to see the FPSO back in production. To see it come back after some delays is great news for the province and the offshore industry.”
Suncor Energy CEO Rich Kruger announced in late November that Terra Nova’s FPSO vessel had restarted production after undergoing an extensive makeover in Spain to improve reliability and extend its life.
The massive vessel — standing 18 stories high and three football fields long — first started operating in 2002 and has produced more than 425 million barrels of oil, or enough to meet world oil demand at current levels for just over four years.
While the FPSO was in Spain, additional subsea work took place in the middle of the Atlantic to extend the Terra Nova field’s life, including replacing two million kilograms of mooring chain that anchors the ship to the underwater drilling system.
The project is forecast to extend the life of the Terra Nova project by 10 years and produce an additional 70 million barrels.
Phil Skolnick, Eight Capital’s managing director of research, sees Europe and Asia as potential destinations for those barrels when the project ramps up to full production.
Asian oil demand is rising, and Europe is now taking higher volumes of oil imports from countries other than Russia, its primary supplier before the start of the war in Ukraine.
“You should see it start to make a real impact on the market by 2025, when Terra Nova is expected to get back to producing 180,000 barrels per day,” he says.
“It will have a big impact for the Newfoundland economy.”
Even when the FPSO was in drydock in Spain, Terra Nova continued to provide benefits to the community at home.
In the third quarter of 2023, the latest period available, the project reported it spent $173.8 million in operational and capital expenditures.
This included $52.2 million in procuring goods and services, with 62 per cent spent with suppliers in the province and 94 per cent with Canadian vendors.
Terra Nova provides 710 direct jobs with 90 per cent of its workforce residing in Newfoundland and Labrador. The project is a partnership operated by Suncor, which holds a 48 per cent stake. The other partners are Cenovus Energy (34 per cent) and Murphy Oil (18 per cent).
While wind, hydrogen and other energy projects have been proposed in Newfoundland and Labrador, Breen sees the offshore oil industry as a crucial part of the province’s economy now and in the future.
He believes Terra Nova and the other three producing oil fields in the province — Hibernia, Hebron and White Rose — will assume added importance for the local economy and global energy security.
“Oil is going to be around for a long time, even if demand decreases, because it is an essential part of so many products we use today. And that’s important for us because the offshore industry supports many families across Newfoundland and Labrador today,” Breen says.
“The industry has been under a lot of scrutiny and has faced a lot of challenges, particularly in the approval for new projects. Keeping the production from approved supplies is going to be vital. That’s why it’s good to see the investment in Terra Nova and the return to production. That bodes well for the future.”
Alberta
The beauty of economic corridors: Inside Alberta’s work to link products with new markets

From the Canadian Energy Centre
Q&A with Devin Dreeshen, Minister of Transport and Economic Corridors
CEC: How have recent developments impacted Alberta’s ability to expand trade routes and access new markets for energy and natural resources?
Dreeshen: With the U.S. trade dispute going on right now, it’s great to see that other provinces and the federal government are taking an interest in our east, west and northern trade routes, something that we in Alberta have been advocating for a long time.
We signed agreements with Saskatchewan and Manitoba to have an economic corridor to stretch across the prairies, as well as a recent agreement with the Northwest Territories to go north. With the leadership of Premier Danielle Smith, she’s been working on a BC, prairie and three northern territories economic corridor agreement with pretty much the entire western and northern block of Canada.
There has been a tremendous amount of work trying to get Alberta products to market and to make sure we can build big projects in Canada again.
CEC: Which infrastructure projects, whether pipeline, rail or port expansions, do you see as the most viable for improving Alberta’s global market access?
Dreeshen: We look at everything. Obviously, pipelines are the safest way to transport oil and gas, but also rail is part of the mix of getting over four million barrels per day to markets around the world.
The beauty of economic corridors is that it’s a swath of land that can have any type of utility in it, whether it be a roadway, railway, pipeline or a utility line. When you have all the environmental permits that are approved in a timely manner, and you have that designated swath of land, it politically de-risks any type of project.
CEC: A key focus of your ministry has been expanding trade corridors, including an agreement with Saskatchewan and Manitoba to explore access to Hudson’s Bay. Is there any interest from industry in developing this corridor further?
Dreeshen: There’s been lots of talk [about] Hudson Bay, a trade corridor with rail and port access. We’ve seen some improvements to go to Churchill, but also an interest in the Nelson River.
We’re starting to see more confidence in the private sector and industry wanting to build these projects. It’s great that governments can get together and work on a common goal to build things here in Canada.
CEC: What is your vision for Alberta’s future as a leader in global trade, and how do economic corridors fit into that strategy?
Dreeshen: Premier Smith has talked about C-69 being repealed by the federal government [and] the reversal of the West Coast tanker ban, which targets Alberta energy going west out of the Pacific.
There’s a lot of work that needs to be done on the federal side. Alberta has been doing a lot of the heavy lifting when it comes to economic corridors.
We’ve asked the federal government if they could develop an economic corridor agency. We want to make sure that the federal government can come to the table, work with provinces [and] work with First Nations across this country to make sure that we can see these projects being built again here in Canada.
Alberta
Alberta’s massive oil and gas reserves keep growing – here’s why

From the Canadian Energy Centre
Q&A with Mike Verney, executive vice-president, McDaniel & Associates
New analysis commissioned by the Alberta Energy Regulator has increased the province’s natural gas reserves by 440 per cent, bumping Canada into the global top 10.
Alberta’s oil reserves – already fourth in the world – also increased by seven billion barrels.
The report was conducted by Calgary-based consultancy McDaniel & Associates. Executive vice-president Mike Verney explains what it means.
CEC: What are “reserves” and why do they matter?
Verney: Reserves are commercial quantities of oil and gas to be recovered in the future. They are key indicators of future production potential.
For companies, that’s a way of representing the future value of their operations. And for countries, it’s important to showcase the runway they have in terms of the future of their oil and gas.
Some countries that have exploited a lot of their resource in the past have low reserves remaining. Canada is in a position where we still have a lot of meat on the bone in terms of those remaining quantities.
CEC: How long has it been since Alberta’s oil and gas reserves were comprehensively assessed?
Verney: Our understanding is the last fully comprehensive review was over a decade ago.
CEC: Does improvement in technology and innovation increase reserves?
Verney: Technological advancements and innovation play a crucial role in increasing reserves. New technologies such as advanced drilling techniques (e.g., hydraulic fracturing, horizontal drilling), enhanced seismic imaging and improved extraction methods enable companies to discover and access previously inaccessible reserves.
As these reserves get developed, the evolution of technology helps companies develop them better and better every year.
CEC: Why have Alberta’s natural gas reserves increased?
Verney: Most importantly, hydraulic fracturing has unlocked material volume, and that’s one of the principal reasons why the new gas estimate is so much higher than what it was in the past.
The performance of the wells that are being drilled has also gotten better since the last comprehensive study.
The Montney competes with every American tight oil and gas play, so we’re recognizing the future potential of that with the gas reserves that are being assigned.
In addition, operators continue to expand the footprint of the Alberta Deep Basin.
CEC: Why have Alberta’s oil reserves increased?
Verney: We discovered over two billion barrels of oil reserves associated with multilateral wells, which is a new technology. In a multilateral well, you drill one vertical well to get to the zone and then once you hit the zone you drill multiple legs off of that one vertical spot. It has been a very positive game-changer.
Performance in the oil sands since the last comprehensive update has also gone better than expected. We’ve got 22 thermal oil sands projects that are operating, and in general, expectations in terms of recovery are higher than they were a decade ago.
Oil sands production has grown substantially in the past decade, up 70 per cent, from two million to 3.4 million barrels per day. The growth of several projects has increased confidence in the commercial viability of developing additional lands.
CEC: What are the implications of Alberta’s reserves in terms of the province’s position as a world energy supplier?
Verney: We’re seeing LNG take off in the United States, and we’re seeing lots of demand from data centers. Our estimate is that North America will need at least 30 billion cubic feet per day of more gas supply in the next few years, based on everything that’s been announced. That is a very material number, considering the United States’ total natural gas production is a little over 100 billion cubic feet per day.
In terms of oil, since the shale revolution in 2008 there’s been massive growth from North America, and the rest of the world hasn’t grown oil production. We’re now seeing that the tight plays in the U.S. aren’t infinite and are showing signs of plateauing.
Specifically, when we look at the United States’ largest oil play, the Permian, it has essentially been flat at 5.5 million barrels per day since December 2023. Flat production from the Permian is contrary to the previous decade, where we saw tight oil production grow by half a million barrels per day per year.
Oil demand has gone up by about a million barrels a day per year for the past several decades, and at this point we do expect that to continue, at the very least in the near term.
Given the growing demand for oil and the stagnation in supply growth since the shale revolution, it’s expected that Alberta’s oil sands reserves will become increasingly critical. As global oil demand continues to rise, and with limited growth in production from other sources, oil sands reserves will be relied upon more heavily.
-

 2025 Federal Election2 days ago
2025 Federal Election2 days agoJoe Tay Says He Contacted RCMP for Protection, Demands Carney Fire MP Over “Bounty” Remark
-
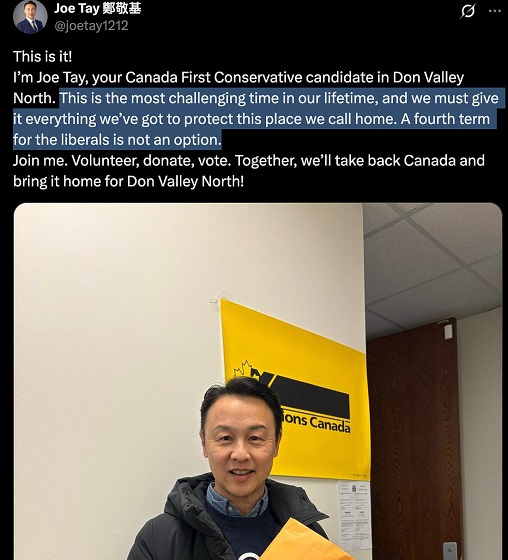
 2025 Federal Election2 days ago
2025 Federal Election2 days agoHong Kong-Canadian Groups Demand PM Carney Drop Liberal Candidate Over “Bounty” Remark Supporting CCP Repression
-

 2025 Federal Election2 days ago
2025 Federal Election2 days agoPoilievre To Create ‘Canada First’ National Energy Corridor
-

 2025 Federal Election2 days ago
2025 Federal Election2 days agoAlcohol tax and MP pay hike tomorrow (April 1)
-

 2025 Federal Election2 days ago
2025 Federal Election2 days agoChinese Election Interference – NDP reaction to bounty on Conservative candidate
-

 2025 Federal Election1 day ago
2025 Federal Election1 day agoChina Election Interference – Parties Received Security Briefing Days Ago as SITE Monitors Threats to Conservative Candidate Joe Tay
-

 2025 Federal Election1 day ago
2025 Federal Election1 day agoFixing Canada’s immigration system should be next government’s top priority
-

 2025 Federal Election1 day ago
2025 Federal Election1 day agoPoilievre, Conservatives receive election endorsement from large Canadian trade union