Economy
Taxpayer watchdog slams Trudeau gov’t for increasing debt ceiling: ‘Put down the credit card’

From LifeSiteNews
Canadian Finance Minister Chrystia Freeland authorized an additional $73 billion in borrowing this fiscal year.
After Canadian Finance Minister Chrystia Freeland gave herself and the government the authority to borrow an additional $73 billion this fiscal year, the head of the nation’s leading taxpayer watchdog group said the federal government needs to “put down the credit card” and return to common-sense spending.
Freeland, as per a February 15 cabinet order made under the Financial Administration Act, allowed the extra borrowing to take place.
The government has set “$517 billion to be the maximum aggregate principal amount of money that may be borrowed” before April 1. Before this cabinet order, however, the maximum amount was $444 billion.
Despite Freeland claiming that the increase in borrowing is “in no way a blank cheque,” Canadian Taxpayers Federation federal director Franco Terrazzano said the borrowing needs to end.
“The Trudeau government needs to put down the credit card and pick up some scissors,” Terrazzano told LifeSiteNews.
“The government should be cutting spending and balancing the budget, not racking up more debt for years to come.”
In 2021, Canada’s Parliament raised the federal debt borrowing amount by a whopping 56% under the Borrowing Authority Act. The amount went from $1.168 trillion to $1.831 trillion.
“What it does is set a ceiling for how much the government can spend,” Freeland said at the time.
Terrazzano told LifeSiteNews that the Trudeau government should be cutting spending and balancing the budget, not racking up more debt for years to come.
“More debt means more money wasted on interest charges and less room to cut taxes,” he noted.
Terrazzano observed that in the coming year the Trudeau government will be spending “more money on debt interest charges than it sends to the provinces in health transfers.”
“In a handful of years, every penny collected from the GST (Goods and Service Tax) will go toward paying interest on the debt,” he noted.
Under Prime Minister Justin Trudeau, due to excessive COVID money printing, inflation has skyrocketed.
Last month, LifeSiteNews reported that fast-rising food costs in Canada have led to many people feeling a sense of “hopelessness and desperation” with nowhere to turn for help, according to the Canadian government’s own National Advisory Council on Poverty.
Last year, the Bank of Canada acknowledged that Trudeau’s federal “climate change” programs, which have been deemed “extreme” by some provincial leaders, are indeed helping to fuel inflation.
Terrazzano told LifeSiteNews that Trudeau should “completely scrap his carbon tax,” which is making everything more expensive.
Conservatives blast increased debt
Conservative Party of Canada (CPC) MPs have been critical of the raised debt ceiling. “You’re simply saying, ‘Give me a blank cheque and then trust me,’” MP Ed Fast said.
Freeland claimed that the “characterization of the borrowing authority limit as a blank cheque is simply false.”
CPC leader Pierre Poilievre recently asked, “Is there a dollar figure to which she would limit the debt?”
She replied that the government is “mindful that limits exist.”
During a February 13 Senate national finance committee meeting, Budget Officer Yves Giroux noted how Trudeau’s cabinet plans in terms of spending are not clear.
“We don’t know exactly what the government plans on spending or doing in terms of new spending or potential spending,” he said when asked by Senator Elizabeth Marshall if the new borrowing limits are “still realistic.”
Marshall added, “As it stands now, do you think it looks reasonable?”
“It looks sufficient, but the government always wants to give itself some room to maneuver in case there are unforeseen events that require borrowing on short notice,” Giroux replied.
A report from September 5, 2023, by Statistics Canada shows food prices are rising faster than headline inflation at a rate of between 10% and 18% per year.
According to a recent Statistics Canada survey of supermarket prices, Canadians are paying 12% more for carrots, 14% more for hamburger (ground meat), and 27% more for baby formula.
Business
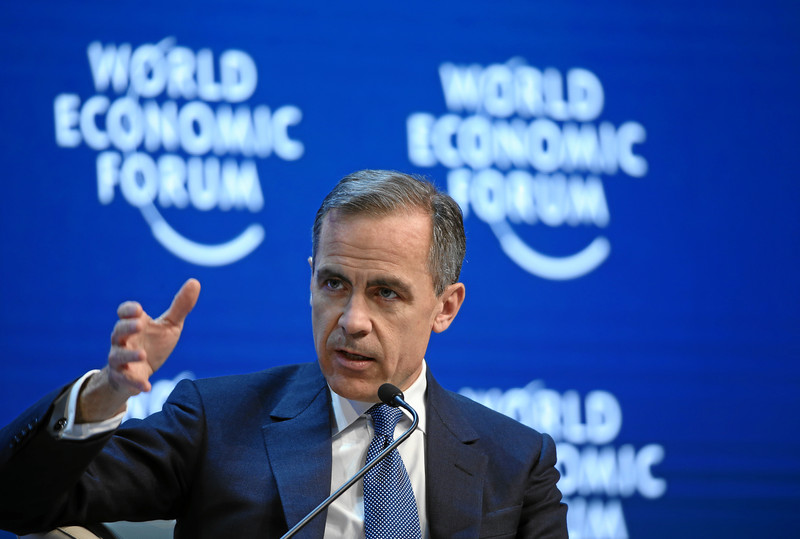
Carney and other world leaders should recognize world’s dependence on fossil fuels

From the Fraser Institute
By Julio Mejía and Elmira Aliakbari
Simply put, despite trillions invested in the energy transition, the world is more dependent on fossil fuels today than when the United Nations launched its first COP. No wonder that ahead of COP30, leading voices of the net-zero-by-2050 agenda, including Bill Gates, are acknowledging both the vital role of fossil fuels on the planet and the failure of efforts to cut them.
On the heels of his first federal budget, which promises more spending to promote a “green economy,” Prime Minister Carney will soon fly to Brazil for COP30, the 30th United Nations climate summit. Like the former Trudeau government, the Carney government has pledged to achieve “net-zero” emissions in Canada—and compel other countries to pursue net-zero—by 2050. To achieve a net-zero world, it’s necessary to phase out fossil fuels—oil, natural gas, coal—or offset their CO2 emissions with technologies such as “carbon capture” or large-scale tree planting.
But after trillions of dollars spent in pursuit of that goal, it appears more unrealistic than ever. It’s time for world leaders, including Canada’s policymakers, to face reality and be honest about the costly commitments they make on behalf of their citizens.
For starters, carbon capture—the process of trapping and storing carbon dioxide so it’s unable to affect the atmosphere—is a developing technology not yet capable of large-scale deployment. And planting enough trees to offset global emissions would require vast amounts of land, take decades to absorb significant CO2 and risk unpredictable losses from wildfires and drought. Due to these constraints, in their net-zero quest governments and private investors have poured significant resources into “clean energy” such as wind and solar to replace fossil fuels.
According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), from 2015 to 2024, the world’s public and private investment in clean energy totalled and estimated US$14.6 trillion (inflation-adjusted). Yet from 1995 (the first COP year) to 2024, global fossil fuel consumption increased by more than 64 per cent. Specifically, oil consumption grew by 39 per cent, natural gas by 96 per cent and coal by 76 per cent. As of 2024, fossil fuels accounted for 80.6 per cent of global energy consumption, slightly lower than the 85.6 per cent in 1995.
The Canadian case shows an even greater mismatch between Ottawa’s COP commitments and its actual results. Despite billions spent by the federal government on the low-carbon economy (electric vehicle subsidies, tax credits to corporations, etc.), fossil fuel consumption in our country has increased by 23 per cent between 1995 and 2024. Over the same period, the share of fossil fuels in Canada’s total energy consumption climbed from 62.0 to 66.3 per cent.
Simply put, despite trillions invested in the energy transition, the world is more dependent on fossil fuels today than when the United Nations launched its first COP. No wonder that ahead of COP30, leading voices of the net-zero-by-2050 agenda, including Bill Gates, are acknowledging both the vital role of fossil fuels on the planet and the failure of efforts to cut them.
Why has this massive effort, which includes many countries and trillions of dollars, failed to transition humanity away from fossil fuels?
As renowned scholar Vaclav Smil explains, it can take centuries—not decades—for an energy source to become globally predominant. For thousands of years, humanity relied on wood, charcoal, dried dung and other traditional biomass fuels for heating and cooking, with coal only becoming a major energy source around 1900. It took oil 150 years after its introduction into energy markets to account for one-quarter of global fossil fuel consumption, a milestone reached only in the 1950s. And for natural gas, it took about 130 years after its commercial development to reach 25 per cent of global fossil fuel consumption at the end of the 20th century.
Yet, coal, oil and natural gas didn’t completely replace traditional biomass to meet the surging energy demand as the modern world developed. As of 2020, nearly three billion people in developing countries still relied on charcoal, straw and dried dung to supply their basic energy needs. In light of these facts, the most vocal proponents of the global energy transition seem, at the very least, out of touch.
The world’s continued reliance on fossil fuels should prompt world leaders at COP30 to exercise caution before pushing the same unrealistic commitments of the past. And Prime Minister Carney, in particular, should be careful not to keep leading Canadians into costly ventures that lead nowhere near their intended results.
Business
Ottawa should stop using misleading debt measure to justify deficits

From the Fraser Institute
By Jake Fuss and Grady Munro
Based on the rhetoric, the Carney government’s first budget was a “transformative” new plan that will meet and overcome the “generational” challenges facing Canada. Of course, in reality this budget is nothing new, and delivers the same approach to fiscal and economic policy that has been tried and failed for the last decade.
First, let’s dispel the idea that the Carney government plans to manage its finances any differently than its predecessor. According to the budget, the Carney government plans to spend more, borrow more, and accumulate more debt than the Trudeau government had planned. Keep in mind, the Trudeau government was known for its recklessly high spending, borrowing and debt accumulation.
While the Carney government has tried to use different rhetoric and a new accounting framework to obscure this continued fiscal mismanagement, it’s also relied on an overused and misleading talking point about Canada’s debt as justification for higher spending and continued deficits. The talking point goes something like, “Canada has the lowest net debt-to-GDP ratio in the G7” and this “strong fiscal position” gives the government the “space” to spend more and run larger deficits.
Technically, the government is correct—Canada’s net debt (total debt minus financial assets) is the lowest among G7 countries (which include France, Germany, Italy, Japan, the United Kingdom and the United States) when measured as a share of the overall economy (GDP). The latest estimates put Canada’s net debt at 13 per cent of GDP, while net debt in the next lowest country (Germany) is 49 per cent of GDP.
But here’s the problem. This measure assumes Canada can use all of its financial assets to offset debt—which is not the case.
When economists measure Canada’s net debt, they include the assets of the Canada Pension Plan (CPP) and the Quebec Pension Plan (QPP), which were valued at a combined $890 billion as of mid-2025. But obviously Canada cannot use CPP and QPP assets to pay off government debt without compromising the benefits of current and future pensioners. And we’re one of the only industrialized countries where pension assets are accounted in such a way that it reduces net debt. Simply put, by falsely assuming CPP and QPP assets could pay off debt, Canada appears to have a stronger fiscal position than is actually the case.
A more accurate measure of Canada’s indebtedness is to look at the total level of debt.
Based on the latest estimates, Canada’s total debt (as a share of the economy) ranked 5th-highest among G7 countries at 113 per cent of GDP. That’s higher than the total debt burden in the U.K. (103 per cent) and Germany (64 per cent), and close behind France (117 per cent). And over the last decade Canada’s total debt burden has grown faster than any other G7 country, rising by 25 percentage points. Next closest, France, grew by 17 percentage points. Keep in mind, G7 countries are already among the most indebted, and continue to take on some of the most debt, in the industrialized world.
In other words, looking at Canada’s total debt burden reveals a much weaker fiscal position than the government claims, and one that will likely only get worse under the Carney government.
Prior to the budget, Prime Minister Mark Carney promised Canadians he will “always be straight about the challenges we face and the choices that we must make.” If he wants to keep that promise, his government must stop using a misleading measure of Canada’s indebtedness to justify high spending and persistent deficits.
-

 armed forces1 day ago
armed forces1 day agoIt’s time for Canada to remember, the heroes of Kapyong
-

 Digital ID1 day ago
Digital ID1 day agoCanada moves forward with digital identification for federal benefits seekers
-

 Daily Caller1 day ago
Daily Caller1 day agoUS Nuclear Bomber Fleet Shares Fence With Trailer Park Linked To Chinese Intel-Tied Fraudster
-

 Alberta1 day ago
Alberta1 day agoSchool defunding petition in Alberta is a warning to parents
-

 Daily Caller1 day ago
Daily Caller1 day agoLaura Ingraham Presses Trump On Allowing Flood Of Chinese Students Into US
-

 Opinion2 days ago
Opinion2 days agoThe Germans called her the ‘White Mouse’ for her elusiveness
-

 Agriculture2 days ago
Agriculture2 days agoBovaer Backlash Update: Danish Farmers Get Green Light to Opt Out as UK Arla Trial Abruptly Ends!
-
 espionage1 day ago
espionage1 day agoChinese-Owned Trailer Park Beside U.S. Stealth Bomber Base Linked to Alleged Vancouver Repression Case











