Artificial Intelligence
Poll: Despite global pressure, Americans want the tech industry to slow down on AI
From The Deep View
| A little more than a year ago, the Future of Life Institute published an open letter calling for a six-month moratorium on the development of AI systems more powerful than GPT-4. Of course, the pause never happened (and we didn’t seem to stumble upon superintelligence in the interim, either) but it did elicit a narrative from the tech sector that, for a number of reasons, a pause would be dangerous. | |
|
|
| As the Pause AI organization themselves put it: “We might end up in a world where the first AGI is developed by a non-cooperative actor, which is likely to be a bad outcome.” | |
| But new polling shows that American voters aren’t buying it. | |
| The details: A recent poll conducted by the Artificial Intelligence Policy Institute (AIPI) — and first published by Time — found that Americans would rather fall behind in that global race than skimp on regulation. | |
|
|
| The polling additionally found that 50% of voters surveyed think the U.S. should use its position in the AI race to prevent other countries from building powerful AI systems by enforcing “safety restrictions and aggressive testing requirements.” | |
| Only 23% of Americans polled believe that the U.S. should eschew regulation in favor of being the first to build a more powerful AI. | |
|
|
| This comes as federal regulatory efforts in the U.S. remain stalled, with the focus shifting to uneven state-by-state regulation. | |
| Previous polling from the AIPI has found that a vast majority of Americans want AI to be regulated and wish the tech sector would slow down on AI; they don’t trust tech companies to self-regulate. | |
| Colson has told me in the past that the American public is hyper-focused on security, safety and risk mitigation; polling published in May found that “66% of U.S. voters believe AI policy should prioritize keeping the tech out of the hands of bad actors, rather than providing the benefits of AI to all.” | |
|
|
| Underpinning all of this is a layer of hype and an incongruity of definition. It is not clear what “extremely powerful” AI means, or how it would be different from current systems. | |
| Unless artificial general intelligence is achieved (and agreed upon in some consensus definition by the scientific community), I’m not sure how you measure “more powerful” systems. As current systems go, “more powerful” doesn’t mean much more than predicting the next word at slightly greater speeds. | |
|
|
| Do people want development to slow down, or deployment? | |
| To once again call back Helen Toner’s comment of a few weeks: how is AI affecting your life, and how do you want it to affect your life? | |
| Regulating a hypothetical is going to be next to impossible. But if we establish the proper levels of regulation to address the issues at play today, we’ll be in a better position to handle that hypothetical if it ever does come to pass. |
Artificial Intelligence
Apple faces proposed class action over its lag in Apple Intelligence

News release from The Deep View
| Apple, already moving slowly out of the gate on generative AI, has been dealing with a number of roadblocks and mounting delays in its effort to bring a truly AI-enabled Siri to market. The problem, or, one of the problems, is that Apple used these same AI features to heavily promote its latest iPhone, which, as it says on its website, was “built for Apple Intelligence.” |
| Now, the tech giant has been accused of false advertising in a proposed class action lawsuit that argues that Apple’s “pervasive” marketing campaign was “built on a lie.” |
| The details: Apple has — if reluctantly — acknowledged delays on a more advanced Siri, pulling one of the ads that demonstrated the product and adding a disclaimer to its iPhone 16 product page that the feature is “in development and will be available with a future software update.” |
|
| Apple did not respond to a request for comment. |
| The lawsuit was first reported by Axios, and can be read here. |
| This all comes amid an executive shuffling that just took place over at Apple HQ, which put Vision Pro creator Mike Rockwell in charge of the Siri overhaul, according to Bloomberg. |
| Still, shares of Apple rallied to close the day up around 2%, though the stock is still down 12% for the year. |
Artificial Intelligence
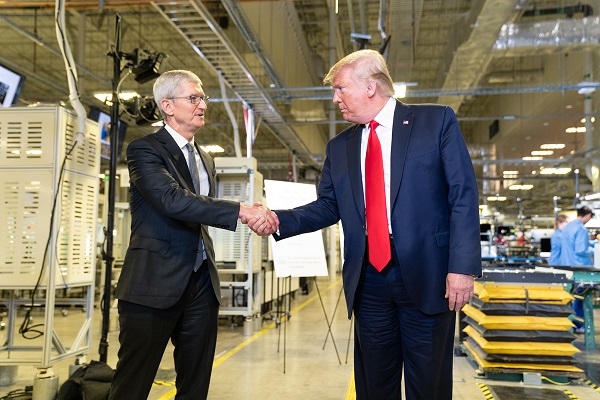
Apple bets big on Trump economy with historic $500 billion U.S. investment

Diving Deeper:
Apple’s unprecedented $500 billion investment marks what the company calls “an extraordinary new chapter in the history of American innovation.” The tech giant plans to establish an advanced AI server manufacturing facility near Houston and significantly expand research and development across several key states, including Michigan, Texas, California, and Arizona.
Apple CEO Tim Cook highlighted the company’s confidence in the U.S. economy, stating, “We’re proud to build on our long-standing U.S. investments with this $500 billion commitment to our country’s future.” He noted that the expansion of Apple’s Advanced Manufacturing Fund and investments in cutting-edge technology will further solidify the company’s role in American innovation.
President Trump was quick to highlight Apple’s announcement as a testament to his administration’s economic policies. In a Truth Social post Monday morning, he wrote:
“APPLE HAS JUST ANNOUNCED A RECORD 500 BILLION DOLLAR INVESTMENT IN THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA. THE REASON, FAITH IN WHAT WE ARE DOING, WITHOUT WHICH, THEY WOULDN’T BE INVESTING TEN CENTS. THANK YOU TIM COOK AND APPLE!!!”
Trump previously hinted at the investment during a White House meeting Friday, revealing that Cook had committed to investing “hundreds of billions of dollars” in the U.S. economy. “That’s what he told me. Now he has to do it,” Trump quipped.
Apple’s expansion will include 20,000 new jobs, with a strong focus on artificial intelligence, silicon engineering, and machine learning. The company also aims to support workforce development through training programs and partnerships with educational institutions.
With Apple’s announcement, the U.S. economy stands to benefit from a major influx of investment into high-tech manufacturing and innovation—further underscoring the tech industry’s continued growth under Trump’s economic agenda.
-

 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoTrump: China’s tariffs to “come down substantially” after negotiations with Xi
-

 2025 Federal Election2 days ago
2025 Federal Election2 days agoMark Carney Wants You to Forget He Clearly Opposes the Development and Export of Canada’s Natural Resources
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoHudson’s Bay Bid Raises Red Flags Over Foreign Influence
-

 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoTrump considers $5K bonus for moms to increase birthrate
-

 2025 Federal Election2 days ago
2025 Federal Election2 days agoCanada’s pipeline builders ready to get to work
-

 2025 Federal Election1 day ago
2025 Federal Election1 day agoPolice Associations Endorse Conservatives. Poilievre Will Shut Down Tent Cities
-

 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoChinese firm unveils palm-based biometric ID payments, sparking fresh privacy concerns
-

 2025 Federal Election2 days ago
2025 Federal Election2 days agoCanada’s press tries to turn the gender debate into a non-issue, pretend it’s not happening






