Taxpayers
Police admit Canadian bribery scandal was nixed without talking to Trudeau, reviewing records

From LifeSiteNews
The Royal Canadian Mounted Police believed there was political pressure to dismiss a government bribery case against engineering firm SNC-Lavalin in 2019 but claimed there was insufficient evidence to proceed.
The Royal Canadian Mounted Police (RCMP) confirmed that it never talked with Prime Minister Justin Trudeau or was able to view secret cabinet records before dismissing charges in a bribery scandal involving the large engineering firm SNC-Lavalin.
The RCMP’s admission came after intense questioning before the House of Commons ethics committee late last month.
As per Blacklock’s Reporter, RCMP commissioner Michael Duheme testified, “No one is above the law,” adding that there was “insufficient evidence to proceed” with the investigation.
In a 2021 memo titled RCMP Assessment Report: Obstruction of Justice SNC-Lavalin Affair obtained from Access to Information requests last October by Democracy Watch, the RCMP noted that it did not doubt there was indeed political pressure to stop criminal prosecution of SNC-Lavalin.
“However, for it to be an offence under the Criminal Code, there must be more than a technical violation,” the 2021 memo read.
During the House of Commons ethics committee meeting in February, Duheme said he had considered the SNC-Lavalin case routine, noting, “We approach every investigation in the same manner.”
Staff Sergeant Frédéric Pincince, who serves as a director of investigations, admitted that the RCMP never questioned Trudeau in the SNC-Lavalin case but gave no reason.
“He was not interviewed,” testified Pincince, to which Conservative MP Larry Brock asked, “Was there at least an attempt to interview Justin Trudeau?”
“No,” Pincince replied.
SNC-Lavalin, which now goes by the name “AtkinsRéalis,” in 2019 pleaded guilty to fraud in a Québec Provincial Court and was hit with a $280 million fine. Company executives also admitted that they had paid $47.7 million in bribes to get contracts in Libya.
In October 2023, Canadian Liberal MPs on the ethics committee voted to stop the RCMP from testifying about the SNC-Lavalin bribery scandal.
In June 2023, LifeSiteNews reported that the RCMP denied it was looking into whether Trudeau and his cabinet committed obstruction of justice concerning the SNC-Lavalin bribery scandal.
SNC-Lavalin was faced with changes of corruption and fraud concerning about $48 million in payments made to Libyan government officials between 2001 and 2011. The company had hoped to be spared a trial and prosecution deferred prosecution agreement.
However, then-Attorney General Jody Wilson-Raybould did not go along with Trudeau’s plan, which would have allegedly appeared to help SNC-Lavalin. In 2019, she contended that both Trudeau and his top Liberal officials had inappropriately applied pressure on her for four months to directly intervene in the criminal prosecution of Montreal-based global engineering firm SNC-Lavalin relating to its scandal involving corruption and bribery charges connected to government contracts it once had in Libya.
Commissioner mum on whether there was ‘reluctance’ to charge a sitting PM
During the ethics committee meeting, Brock asked Duheme if there was an “overall general reluctance in charging a sitting Prime Minister?”
“I would say to that, we follow the evidence and if the evidence warrants charges, we charge,” Duheme replied.
Brock then asked if the RCMP obtained “all relevant documents to further the investigation?”
Duheme admitted that “we were limited with the information that we had access to.”
Brock pressed him, asking, “Is that a yes or no, sir?” to which Duheme replied, “I don’t know,” adding, “We didn’t know.”
“We don’t know, we still don’t know to this day all the information that is out there,” Duheme responded.
Brock then pressed Duheme, asking why the RCMP did not “exercise its absolute statutory right under the Criminal Code to obtain a production order or search warrant from a justice to obtain those cabinet documents?”
Duheme said the RCMP were not “able to obtain enough information or evidence.”
As for the initial investigation concerning SNC-Lavalin, Wilson-Raybould testified in early 2019 to Canada’s justice committee that she believed she was moved from her then-justice cabinet posting to veterans’ affairs due to the fact she did not grant a request from SNC-Lavalin for a deferred prosecution agreement rather than a criminal trial.
Of note is that a criminal conviction would have banned the company from landing any government contracts for 10 years.
Trudeau flat-out denied it was being investigated by the RCMP.
Less than four years ago, Trudeau was found to have broken the federal ethics laws, or Section 9 of the Conflict of Interest Act, for his role in pressuring Wilson-Raybould.
On February 12, 2019, Wilson-Raybould resigned from her veterans’ affairs post and Treasury Board president Jane Philpott quit in March 2019. They both cited a lack of confidence in the Liberal government’s handling of the scandal.
Then, in April 2019, Trudeau turfed Wilson-Raybould and Philpott from his caucus, meaning they were no longer part of the Liberal Party.
Internet
US government gave $22 million to nonprofit teaching teens about sex toys: report

From LifeSiteNews
The Center for Innovative Public Health Research’s website suggests teenage girls make their ‘own decisions’ about sex and not let their parents know if they don’t want to.
For almost a decade, the U.S. government funded a group that actively works to teach kids how to use sex toys and then keep them hidden from their parents to the tune of $22 million.
According to investigative reporter Hannah Grossman at the Manhattan Institute, The Center for Innovative Public Health Research (CIPHR) has been educating minors about sex toys with public funds.
Records show that the millions given to the group since 2016, according to its website, go toward “health education programs” that “promote positive human development.”
However, the actual contents of the programs, as can be seen from comments from CIPHR CEO Michele Ybarra, seem to suggest that its idea of “human” development is skewed toward radical sex education doctrine.
In 2017, CIPHR launched Girl2Girl, which is funded by federal money to promote “sex-ed program just for teen girls who are into girls.” Its website lets users, who are girls between ages 14 and 16, sign up for “daily text messages … about things like sex with girls and boys.”
The actual content of some of the messages is very concerning. Its website notes that some of the texts talk about “lube and sex toys” as well as “the different types of sex and ways to increase pleasure.”
The website actively calls upon teenage girls to make their “own decisions” and not let their parents know if they don’t want to.
Grossman shared a video clip on X of Ybarra explaining how they educate minors about the use of “sex toys” and dealing with their parents if they are found out.
The clip, from a 2022 Brown University webinar, shows Ybarra telling researchers how to prepare “young person(s)” for her research.
She said if they are doing “focus groups,” she will ask them, “Okay, so what happens if somebody comes into the room and sees words like penis and sex toys on your screen — on your computer screen or on your phone? What if it’s your mom?’”
In 2023, CIPHR launched Transcendent Health, which is a sex-education program for minors who are gender confused. This initiative received $1.3 million of federal grant money that expired last month.
Grossman observed that the federal government “should not fund programs that send sexually explicit messages to minors and encourage them to conceal these communications from parents.”
She noted that in order to protect children and “prevent further harm,” U.S. President Donald Trump’s Department of Health and Human Services “should immediately cancel CIPHR’s active contract and deny its future grant applications.”
“By doing so, the Trump administration can send a clear message: Taxpayers will no longer foot the bill for perverted ‘research’ projects,” she noted.
The Trump administration has thus far, through the Department of Government Efficiency (DOGE), exposed billions in government waste and fraud. Many such uses of taxpayer dollars are currently under review by the administration, including pro-abortion and pro-censorship activity through USAID, “Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion and neo-Marxist class warfare propaganda” through the National Science Foundation, and billions to left-wing “green energy” nonprofits through the Environmental Protection Agency.
2025 Federal Election
Carney needs to cancel gun ban and buyback

 Gage Haubrich
Gage Haubrich
The Canadian Taxpayers Federation is calling on Liberal Leader Mark Carney to stop the gun ban and buyback after he announced he would continue with the scheme.
“Carney needs to scrap this plan and stop wasting taxpayer’s money on it,” said Gage Haubrich, CTF Prairie Director. “Planning to spend potentially billions of dollars on a program that is not going to make Canadians safer is a waste of money.
“Carney needs to be cancelling this wasteful plan, not doubling down on it.”
Conservative Leader Pierre Poilievre is promising to get rid of Ottawa’s gun bans.
The government said the buyback would cost taxpayers $200 million in 2019. Only buying back the guns could cost up to $756 million, according to the Parliamentary Budget Officer. Government documents show that the buyback is now likely to cost almost $2 billion.
The banned gun list includes more than 2,000 different types of firearms.
Every year since the gun ban was announced in 2020, violent gun crime in Canada has increased.
New Zealand conducted a similar, but more extensive, gun ban and buyback in 2019. New Zealand had 1,216 violent firearm offenses in 2023. That’s 349 more offences than the year before the buyback.
Experts also agree that the buyback won’t make Canadians any safer.
The National Police Federation, the union representing the RCMP, says Ottawa’s buyback “diverts extremely important personnel, resources, and funding away from addressing the more immediate and growing threat of criminal use of illegal firearms.”
“Buyback programs are largely ineffective at reducing gun violence, in large part because the people who participate in such programs are not likely to use those guns to commit violence,” said University of Toronto professor Jooyoung Lee
“Experts say that this gun ban and buyback won’t do anything to make Canadians safer,” Haubrich said. “Carney needs to listen to the experts and commit to cancelling this scheme before it costs taxpayers any more money.”
-

 Also Interesting2 days ago
Also Interesting2 days agoMortgage Mayhem: How Rising Interest Rates Are Squeezing Alberta Homeowners
-

 Justice2 days ago
Justice2 days agoCanadian government sued for forcing women to share spaces with ‘transgender’ male prisoners
-

 Alberta2 days ago
Alberta2 days agoAlberta takes big step towards shorter wait times and higher quality health care
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoStocks soar after Trump suspends tariffs
-

 COVID-192 days ago
COVID-192 days agoBiden Admin concealed report on earliest COVID cases from 2019
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoTrump raises China tariffs to 125%, announces 90-day pause for countries who’ve reached out to negotiate
-
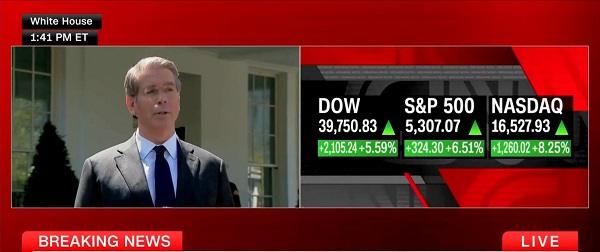
 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoScott Bessent Says Trump’s Goal Was Always To Get Trading Partners To Table After Major Pause Announcement
-

 2025 Federal Election1 day ago
2025 Federal Election1 day agoResearchers Link China’s Intelligence and Elite Influence Arms to B.C. Government, Liberal Party, and Trudeau-Appointed Senator




