National
People’s Party of Canada releases audited financial report ahead of election call

They’re a small party with big ambitions and not much to hide apparently. In the lead up to an expected election call Maxime Bernier’s People’s Party of Canada has released a few highlights from the party’s 2020 audited financial report. This short read sheds some interesting light. For example, leader Maxime Bernier has disclosed that he’s taking a salary of just over $100,000. Would be nice to see the same from Canada’s major parties.
From a release of the People’s Party of Canada
The People’s Party of Canada recently filed its 2020 audited financial report with Elections Canada, in accordance with regulations. That report covers the 12-month period between January 1 and December 31, 2020.
We would like to highlight the main items in this report so that you aware of the Party’s financial situation as a member, dedicated volunteer, supporter, or as a donor or potential donor. You can read the full report here.
REVENUES
In 2020, the Party raised $963,059 in donations and $64,407 in membership fees. After adding transfers and interest income, total revenues for 2020 amounted to $1,146,607.
SALARIES AND PROFESSIONAL FEES
The Party’s main item of expenses in 2020 was salaries and benefits, at $395,690. The Party’s had four full-time employees at the beginning of the year and six at the end of the year, including the Leader. Mr. Bernier did not receive any salary or compensation from the Party in 2018 and 2019, as he was then receiving a salary as a Member of Parliament. He only started receiving a salary at the beginning of 2020 and his salary for the year was $104,000.
Contrary to other parties, the Party did not apply for the federal government’s COVID-19 wage subsidy program. The Party also paid $73,428 in professional fees to non-staffers.
LAWYER FEES
The Party spent $61,366 in legal fees in 2020 to defend itself in various lawsuits launched against it. The costs of the current defamation lawsuit against Warren Kinsella are not paid by the Party but by Mr. Bernier himself.
VARIOUS EXPENSES
In 2020, the Party also spent the following amounts on:
- Advertising = $45,226
- Travel = $32,454
- Office supply = $29,301
- Database = $40,382
- Telecommunications = $7,182
- Interest and bank charges = $28,338
- Rent = $19,284
The Party transferred $42,280 to candidates for the October 2020 by-elections in Toronto Centre and York Centre.
Note that following the outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic, and in order to reduce costs during these uncertain times, the Party closed its Gatineau office in June 2020 and only reopened one in Ottawa in July 2021 in preparation for the general election. All staffers worked remotely during that period.
SURPLUS
The Party manages its finances in a responsible manner, did not borrow any money to run its election campaign in the fall of 2019, and does not have any debt. Thanks to the generosity of our donors, we finished the year 2020 with $431,635 in cash and cash equivalents. This will serve as a cushion for the snap election expected in the fall of 2021.
CONCLUSION
Running a party necessitates the work of thousands of volunteers, but also involves unavoidable costs. We are proud of what has been accomplished by the People’s Party of Canada so far and we thank the generous donors who made it possible. If you want to help the Party be better financially prepared to sell its bold Canada First platform and fight for Freedom, Responsibility, Fairness and Respect in the next election, please donate here.
Many thanks,
The PPC Team
August 11, 2021
2025 Federal Election
PRC-Linked Disinformation Claims Conservatives Threaten Chinese Diaspora Interests, Take Aim at PM Carney’s Debate Remark
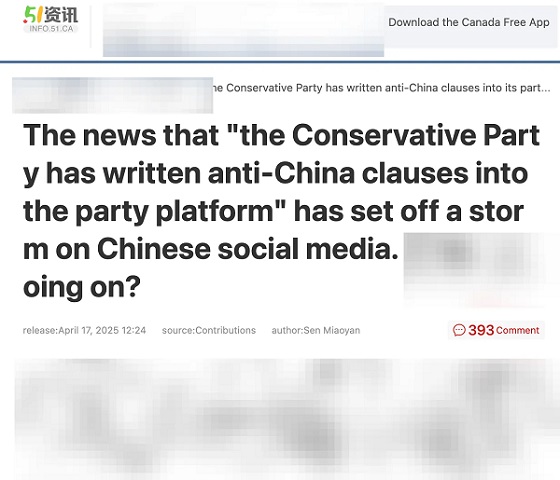
As polls tighten in Canada’s pivotal federal election, a Chinese-language website has published multiple editorials suggesting that a Pierre Poilievre government could threaten Chinese Canadian interests with so-called “anti-China” policy clauses—claiming it could bring “inconvenience to the lives of Chinese people, such as restrictions on the use of social media, reductions in return air tickets, etc.”
During the 2021 federal election, then-Conservative leader Erin O’Toole and MP Kenny Chiu were widely attacked with similar arguments across Chinese-language news and social media. CSIS reporting from 2022, cited exclusively by The Bureau, warned that Chinese-language media in Canada is effectively controlled by Beijing and weaponized during election periods to spread Chinese Communist Party-aligned narratives.
One of the new articles also criticizes Prime Minister Mark Carney’s debate remark that Beijing poses the greatest threat to Canada’s national security—a comment that prompted the Chinese-language editorial to question whether Carney’s statement was “a gimmick to attract attention.”
The articles, published Thursday and Friday by 51.ca, have raised deep concern among some community members. One longtime Chinese Canadian journalist, who requested anonymity due to fear of retaliation, told The Bureau they were alarmed by the messaging and suspected the coverage was driven by election-interference motives.
One of the pieces claimed that “the Conservative Party has written anti-China clauses into the party platform,” referencing a prior story that quickly circulated on Chinese-language social media and triggered fearful discussion.
Citing WeChat commentary on the same article, the journalist pointed specifically to a politically connected figure previously associated with CSIS investigations into election interference networks in the Greater Toronto Area—allegedly tied to clandestine funding channels linked to the Chinese Consulate in Toronto.
Sharing a WeChat forum screen-picture, the diaspora journalist noted:
“The writer said, according to the Conservative’s campaign platform, China’s definition is ‘enemy.’ So what is the impact on Chinese Canadians’ daily life? Facing more discrimination? Fewer flights going back to China? How about using social media? If there is a war, what will happen to Chinese Canadians—like Japanese people were sent to the concentration camps or deported?”
The journalist said the messaging is not only inflammatory, but dangerously manipulative—casting the Conservative Party as a threat to the civil rights and safety of Chinese Canadians, while exploiting historical trauma to provoke fear.
The same 51.ca article—while quoting from the Conservative Party’s platform documents—shifts sharply into misleading commentary. It contrasts the party’s current positions with historical discrimination enacted by the Liberal government of the 1920s.
One of the recent 51.ca articles warns that the Conservative Party’s stance “can easily cause ethnic tensions and even exacerbate anti-China sentiment.”
A second article delivers a similar critique of Conservative policy while also taking aim at Prime Minister Mark Carney, who, in last night’s nationally televised debate, stated:
“I think the biggest security threat to Canada is China.”
That comment, consistent with assessments from Canadian intelligence services and allied Five Eyes partners, was immediately seized upon by 51.ca’s editorial board.
“Carney blurted out that China is Canada’s biggest threat. Is this a deep-rooted idea or a gimmick to attract attention? It is not known yet. But what is certain is that when other party leaders are talking about how to deal with the problems facing Canada itself, Carney is talking about China being the enemy. I really don’t know what’s going on in his mind.”
Both 51.ca articles strategically focus their sharpest criticism on the Conservative Party, portraying its platform as existentially dangerous, while the second treats Carney’s one-line debate comment as a moment of rhetorical overreach.
The Bureau is a reader-supported publication.
To receive new posts and support my work, consider becoming a free or paid subscriber.
Invite your friends and earn rewards
Canadian Energy Centre
First Nations in Manitoba pushing for LNG exports from Hudson’s Bay

From the Canadian Energy Centre
By Will Gibson
NeeStaNan project would use port location selected by Canadian government more than 100 years ago
Building a port on Hudson’s Bay to ship natural resources harvested across Western Canada to the world has been a long-held dream of Canadian politicians, starting with Sir Wilfred Laurier.
Since 1931, a small deepwater port has operated at Churchill, Manitoba, primarily shipping grain but more recently expanding handling of critical minerals and fertilizers.
A group of 11 First Nations in Manitoba plans to build an additional industrial terminal nearby at Port Nelson to ship liquefied natural gas (LNG) to Europe and potash to Brazil.
Robyn Lore, a director with project backer NeeStaNan, which is Cree for “all of us,” said it makes more sense to ship Canadian LNG to Europe from an Arctic port than it does to send Canadian natural gas all the way to the U.S. Gulf Coast to be exported as LNG to the same place – which is happening today.
“There is absolutely a business case for sending our LNG directly to European markets rather than sending our natural gas down to the Gulf Coast and having them liquefy it and ship it over,” Lore said. “It’s in Canada’s interest to do this.”
Over 100 years ago, the Port Nelson location at the south end of Hudson’s Bay on the Nelson River was the first to be considered for a Canadian Arctic port.
In 1912, a Port Nelson project was selected to proceed rather than a port at Churchill, about 280 kilometres north.
The Port Nelson site was earmarked by federal government engineers as the most cost-effective location for a terminal to ship Canadian resources overseas.
Construction started but was marred by building challenges due to violent winter storms that beached supply ships and badly damaged the dredge used to deepen the waters around the port.
By 1918, the project was abandoned.
In the 1920s, Prime Minister William Lyon MacKenzie King chose Churchill as the new location for a port on Hudson’s Bay, where it was built and continues to operate today between late July and early November when it is not iced in.
Lore sees using modern technology at Port Nelson including dredging or extending a floating wharf to overcome the challenges that stopped the project from proceeding more than a century ago.
He said natural gas could travel to the terminal through a 1,000-kilometre spur line off TC Energy’s Canadian Mainline by using Manitoba Hydro’s existing right of way.
A second option proposes shipping natural gas through Pembina Pipeline’s Alliance system to Regina, where it could be liquefied and shipped by rail to Port Nelson.
The original rail bed to Port Nelson still exists, and about 150 kilometers of track would have to be laid to reach the proposed site, Lore said.
“Our vision is for a rail line that can handle 150-car trains with loads of 120 tonnes per car running at 80 kilometers per hour. That’s doable on the line from Amery to Port Nelson. It makes the economics work for shippers,” said Lore.
Port Nelson could be used around the year because saltwater ice is easier to break through using modern icebreakers than freshwater ice that impacts Churchill between November and May.
Lore, however, is quick to quell the notion NeeStaNan is competing against the existing port.
“We want our project to proceed on its merits and collaborate with other ports for greater efficiency,” he said.
“It makes sense for Manitoba, and it makes sense for Canada, even more than it did for Laurier more than 100 years ago.”
-

 2025 Federal Election2 days ago
2025 Federal Election2 days agoNeil Young + Carney / Freedom Bros
-
 Business1 day ago
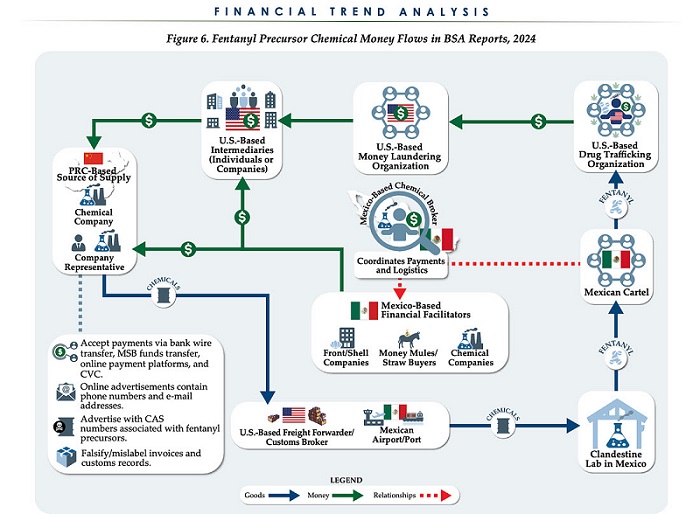
Business1 day agoChina, Mexico, Canada Flagged in $1.4 Billion Fentanyl Trade by U.S. Financial Watchdog
-

 2025 Federal Election2 days ago
2025 Federal Election2 days agoTucker Carlson Interviews Maxime Bernier: Trump’s Tariffs, Mass Immigration, and the Oncoming Canadian Revolution
-

 espionage1 day ago
espionage1 day agoEx-NYPD Cop Jailed in Beijing’s Transnational Repatriation Plot, Canada Remains Soft Target
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoDOGE Is Ending The ‘Eternal Life’ Of Government
-

 2025 Federal Election2 days ago
2025 Federal Election2 days agoCanada drops retaliatory tariffs on automakers, pauses other tariffs
-

 2025 Federal Election1 day ago
2025 Federal Election1 day agoBREAKING from THE BUREAU: Pro-Beijing Group That Pushed Erin O’Toole’s Exit Warns Chinese Canadians to “Vote Carefully”
-
 Daily Caller1 day ago
Daily Caller1 day agoDOJ Releases Dossier Of Deported Maryland Man’s Alleged MS-13 Gang Ties









