National
Paul Wells: The Second Finance Ministers Club
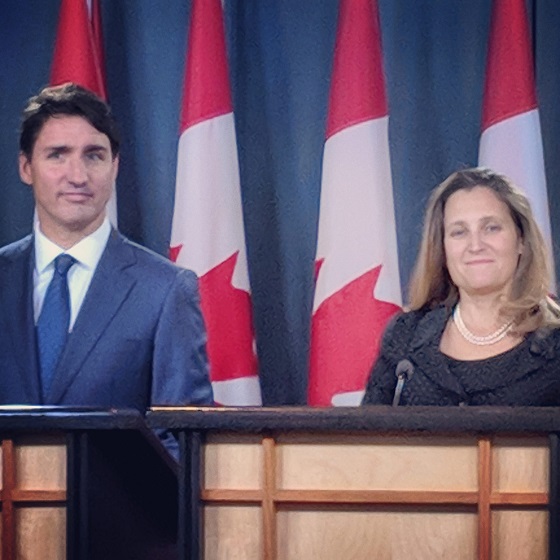

I want to write 5,000 words of narrative in the wake of Chrystia Freeland’s resignation, but we’re still in the middle of the story. Thoughts kind of pour out. I found myself telling La Presse, “‘What the f—k?’ has replaced ‘Hello’ as the standard greeting in Ottawa since Monday.” We’ll see whether they use that quote.
Here are some thoughts, from different angles. I don’t know whether Freeland’s resignation will blow over, the way Justin Trudeau’s last 20 messes did, because I don’t have a crystal ball, but I think Justin Trudeau hopes it’ll blow over. Because he always hopes it’ll blow over. I hear, as you do, rumours that the PM will resign.
On Monday night at the Laurier Club he didn’t look like he’d received the memo yet. On Tuesday his staff cancelled his year-end interviews, something I’ve never seen in 30 years in Ottawa. We’ll see.
Meanwhile, some thoughts.
1. A very British resignation
A standard conversational gambit in Ottawa this week is to point out that nobody’s ever seen a resignation letter like Freeland’s — I’ve given it some thought, and I’ve decided you’re a dink. (I paraphrase, barely.) Except that’s not quite true. Millions of people have seen dozens of resignation letters like it, because you see them every few weeks in the United Kingdom. And Chrystia Freeland was an editor in London for the Financial Times for years.
Canada is in some ways an unhealthily reticent country. I once covered an international summit where the only reason I knew anything the Canadian delegation had done was that I was sitting next to the journalists from France and I could overhear the French government’s briefings. Resignation letters here follow suit: it’s been a privilege, more time with my family, and out. You’re often left wondering, if you loved the boss so much, why leave?
But in England…
Rosie Duffield to Keir Starmer: “How dare you take our longed-for victory, the electorate’s sacred and precious trust, and throw it back in their individual faces and the faces of dedicated and hardworking Labour MPs?! The sleaze, nepotism and apparent avarice are off the scale. I am so ashamed of what you and your inner circle have done to tarnish and humiliate our once proud party.”
John Glen to Boris Johnson: “I can no longer reconcile my commitment to the role and to the financial services sector with the complete lack of confidence I have in your continuing leadership of our country… [R]ecent events concerning the handling of the appointment of the former Deputy Chief Whip, and the poor judgement you have shown, have made it impossible for me to square continued service with my conscience. The country deserves better…”
Nadine Dorries to Rishi Sunak: “You flashed your gleaming smile in your Prada shoes and Savile Row suit from behind a camera, but you just weren’t listening… But worst of all has been the spectacle of a prime minister demeaning his office by opening the gates to whip up a public frenzy against one of his own MPs…Since you took office a year ago, the country is run by a zombie Parliament where nothing meaningful has happened. What exactly has been done or have you achieved?”
This newsletter is my full-time job. Paid subscriptions at $5 a month or $50 a year are a great way to read all my work here.
2. The Zoom call
I resist biography as an analytical tool. People outgrow their backgrounds all the time.
But just about everybody who follows politics has been wondering how Trudeau could fire his most loyal lieutenant by a Zoom call three days before he needed her to deliver a crucial fall economic statement. If the Globe’s latest story is true, and he told her Mark Carney would take the job without knowing whether Carney will take the job, that’s even wilder. Who does that?
The short answer is, somebody who is used to getting his way. Then you look at Trudeau’s life and you think, why wouldn’t he expect to get his way?
The rich kid always knows the normies will cover for him. If he needs a ride, some kid with stars in his eyes will wave his keys and volunteer. If he’s hung over he can borrow the lecture notes. He shows up in racist makeup to yet another party — forcing every other person in the venue to decide how to respond — and once again nobody stands up to him or makes a fuss. Indeed, when the record of that behaviour threatens his political career decades later, there’ll be plenty of volunteers to criticize anyone who mentions the record, rather than criticizing the guy who acted like that.
He runs for the leadership of a national political party on a platform of “I’ll tell you what I stand for after I win.” He mentions carbon pricing precisely one time at his first national leaders’ debate. He dumps his electoral-reform promise at the first hurdle, and later, when asked about it, he blames the person who asks. He gaslights Canada’s first Indigenous attorney-general for months, but he is not particularly kinder to her replacement, who is ejected from Cabinet because, I don’t know, it’s Wednesday or whatever. He lets a 72-year-old man run for re-election and only after it’s over does he let the guy know he’s getting dumped from Cabinet.
He fires the Clerk of the Privy Council by news release while travelling.
In particular, if there’s anyone in the world he might have expected to tolerate the kind of high-handedness we’re hearing about Friday’s Zoom call, it’s Chrystia Freeland. Her eagerness to endorse him in the immediate aftermath of his latest cockup has been such a reliable feature of Canadian public life it’s devolved into a kind of shtick. SNC-Lavalin, 2019: “she has absolute confidence.” Blackface, six months later: “tremendous confidence.” WE Charity, 10 months after that: “The prime minister has my complete confidence.”
Perhaps only Jagmeet Singh has shown more confidence than Freeland, over the years, in Trudeau’s leadership. Given that record — and his own much longer record of taking advantage of others’ generosity — it’s not too much of a stretch to think that at some point he decided his deputy prime minister was just another easy mark.
Turns out that’s the kind of mistake he only needed to make once.
3. Speaking of Jagmeet Singh
He’ll qualify for his pension in 70 days. After his astonishing scrum on Monday, he might as well put it on a T-shirt.
4. After Trudeau
Say he quits. What next?
Here’s something I’m starting to hear from Liberals. I don’t believe I’m the first to write about it, but it hasn’t received enough attention yet.
Can the party ensure the legitimacy of its leadership succession process?
I suspect some large number of the presumed candidates for his succession won’t run. They haven’t exactly been a bold lot so far. But assume for the sake of argument that there are four or five candidates, and none has an insurmountable advantage.
The Liberal Party transformed its leadership-selection process for the 2013 race: preferential vote among “supporters.” Supporters didn’t need any record of involvement with the party, didn’t need to pledge any support, didn’t need to pay a dime in return for voting rights. Whee! Populist rush: 300,000 people registered as supporters, 130,000 voted. Trudeau won overwhelmingly on the first ballot. Of course: he was the only candidate most people voting in the contest had ever heard of.
After a big defeat, or with such a defeat looming, figure far less than half as many people would be involved next time. Say, very generously, 40,000 supporters.
How hard would it be to rig that contest for mischievous purposes or worse? Probably not hard enough. In a vote open to every random “supporter,” it would take only a few thousand, or tens of thousands, of supporters to capture a major national political party for any cause or faction that might want one.
I traded emails with a former senior Liberal organizer about all this today. Without prompting, this veteran of many leadership contests mentioned the need to “ensure… that groups not Liberal-friendly are not organizing to disrupt the democratic process within the Party.” Those groups could include supporters of one side in the Israel-Hamas dispute. Or proxies for a hostile regime. Or pro-life or anti-MAID or anti-vaccine groups. Or practical jokers: Could the process as currently constituted block a write-in campaign for Doris Day?
This newsletter is my full-time job. Paid subscriptions at $5 a month
or $50 a year are a great way to read all my work here.

Automotive
Parliament Forces Liberals to Release Stellantis Contracts After $15-Billion Gamble Blows Up In Taxpayer Faces

After betting taxpayer billions on a green-industry deal that collapsed under U.S. tariffs, MPs move to expose what Ottawa promised Stellantis and what Canadians actually got for the money.
Parliament just blew the lid off one of the biggest corporate giveaways in Canadian history.
For years, Ottawa and Queen’s Park have bragged about “historic investments” in green manufacturing. What they didn’t say is that $15 billion of your money went to Stellantis, the Dutch auto conglomerate behind Chrysler, Jeep, and Ram, only for the company to announce it’s cutting 3,000 jobs in Brampton and shipping them south to the United States.
That betrayal is what triggered a heated meeting of the House of Commons Government Operations Committee on October 21. What started as routine procedure turned into a full-scale reckoning over how billions were handed to a foreign corporation with almost no strings attached.
Conservative MP Garnett Genuis opened with a blunt motion: produce every contract, memorandum of understanding, or side deal the government signed with Stellantis and its affiliates since 2015. Every page, every clause, in both official languages, “without redaction.” The demand wasn’t symbolic, it was about finding out if Trudeau’s government ever required the company to keep those Canadian jobs it was paid to “protect.”
Liberals scrambled to block it. MP Jenna Sudds proposed an amendment that would let bureaucrats black out whatever they deemed “sensitive.” In practice, that meant hiding anything embarrassing — from cabinet discussions to corporate fine print. Opposition MPs called it exactly what it was: a cover-up clause. It failed.
The committee floor turned into open warfare. The Bloc Québécois tried a softer sub-amendment giving the House Law Clerk power to vet redactions. Conservatives countered with their own version forcing departments to hand over unredacted contracts and justify any blackouts in writing. After a suspension and some backroom wrangling, a rare thing happened: compromise.
The motion passed unanimously. Even the Liberals couldn’t vote against it once the light was on.
The debate itself revealed how badly Ottawa has lost control of its own economic agenda. Conservatives pressed officials on why Canadians were paying billions for “job creation” only to see Stellantis pack up for Illinois once U.S. tariffs came down. Liberals blamed Trump, tariffs, and “global conditions,” the excuses were almost comical. Liberal members blamed Donald Trump —yes, really— for Stellantis abandoning Canada. According to them, Trump’s tariffs and “America First” trade policy scared the company into moving production south.
But here’s what they didn’t say: Trump announced his 2024 presidential campaign on November 15, 2022, promising to rip up Joe Biden’s green industrial agenda and bring manufacturing back to U.S. soil. Everyone heard it. Everyone knew it. And yet, on July 6, 2023, more than half a year later, Ottawa proudly unveiled its $15-billion subsidy for Stellantis and LG Energy Solution — a deal built entirely on the assumption that Trump wouldn’t win.
So let’s be clear about what happened here. They didn’t just hand billions to a foreign automaker. They gambled that the next U.S. president wouldn’t change course. They bet the house —your tax dollars— on a political outcome in another country.
Think about that. Fifteen billion dollars of public money wagered on a campaign prediction. They bet on black, and it landed on red.
Even if the gamble had gone their way — even if Trump had lost and Biden’s green subsidy regime had survived untouched — the deal would still have been a terrible bargain.
During the committee meeting, the Bloc Québécois pointed to the 2023 Parliamentary Budget Officer’s report, which projected that the combined federal and Ontario subsidies to Stellantis and Volkswagen, roughly $28 billion total, including Stellantis’s $15 billion share, wouldn’t even break even for twenty years. That means taxpayers would have to wait until the mid-2040s just to recover what Ottawa spent.
So imagine the “best-case scenario”: the U.S. keeps its green-industry incentives, the plant stays in Canada, and production runs at full capacity. Even then, ordinary Canadians don’t see a financial return for two decades. There are no guaranteed profits, no guaranteed jobs, and no repayment. It was a long-odds bet on a global policy trend, financed entirely with public money.
In other words, whether the roulette wheel landed on black or red, the house still lost because the government put your chips on the table in a game it never controlled.
Behind the numbers, the story is brutally simple: Ottawa slid its chips across the table, wrote the cheques, and Stellantis walked away with the winnings. When MPs tried to see the receipts, the government grabbed for the cover of secrecy — no sunlight, no scrutiny, just “trust us.”
Now, for the first time, Parliament is about to peek under the table. The committee will finally see the real contracts — not the press releases, not the slogans, but the fine print that tells Canadians what they actually paid for. The review will happen behind closed doors at first, but the pressure to show the public what’s inside will be enormous.
Because if those documents confirm what MPs already suspect —that there were no job guarantees, no clawbacks, and no consequences —then this isn’t just a bad hand. It’s a rigged table.
Ottawa didn’t just gamble with taxpayer money; it gambled against the odds, and the dealer —in this case, Stellantis— already knew the outcome. Even if the wheel had landed on black, taxpayers were still stuck covering a twenty-year “break-even” fantasy, as the Bloc reminded everyone.
The next two weeks will show Canadians whether their government actually bought jobs or just bought headlines. One thing is certain: the high-rollers in Ottawa have been playing roulette with your money, and the wheel’s finally slowing down.
Subscribe to The Opposition with Dan Knight .
For the full experience, upgrade your subscription.
Business
Canada Revenue Agency found a way to hit “Worse Than Rock Bottom”

From Conservative Part Communications
Last month, Carney’s Minister responsible for the Canada Revenue Agency (CRA) debuted their new slogan: “It can’t get much worse than it is now.” Today, the Auditor General reported that under the Liberals, it has.
Over the 2024/25 period, only 18 per cent of callers were able to reach a CRA agent within 15 minutes, a far cry from the target of 65 per cent of callers. In June, the numbers plunged to just 5 per cent of callers able to get through within the service standard of 15 minutes.
The average wait time took over half an hour, double what it was the year prior. And that was if you were even given the option of getting help. Nearly nine million calls were “deflected” by an automated voice telling Canadians to figure it out themselves, with no option to speak with an agent.
Wait times are so bad that over 7.6 million calls were disconnected before callers were able to reach an agent or be provided automated service. As wait times continue to get worse and worse, Canadians have just given up, evidenced by 2.4 million more abandoned calls over the previous year.
Even when Canadians manage to get hold of an agent, employees regularly fail to provide correct information about personal and business taxes. Auditors found the call centre gave incorrect information 83 per cent of the time when asked general individual tax questions.
Non-specific questions about benefits, including about eligibility, were wrong 44 per cent of the time. Meanwhile, the CRA’s automated chatbot “Charlie”, meant to relieve the call centre, answered only two of six tax-related questions correctly.
“How is it that an organization so important to the smooth functioning of the country is failing to serve Canadians and, as the Auditor General notes, places greater importance on adhering to shift schedules and breaks than on the accuracy and completeness of the information provided?” asked Gérard Deltell, Conservative Shadow Minister for Revenue.
It’s no surprise that complaints about the CRA’s contact centre increased 145 per cent from 2021/22 to 2024/25. Despite this, the Liberals announced they will begin auto-filing taxes for 5.5 million Canadians, automatically enrolling people in benefits the CRA is regularly unable to provide accurate information about.
Worse of all, the cost of the CRA’s call centre has ballooned from $50 million over 10 years in 2015 to $190 million. The total cost is projected to continue rising to $214 million over the next two years, a more than 320 per cent increase from the original contracted amount.
Meanwhile, Auditors found “there was no process documented or followed to ensure that amounts invoiced … were accurate and reflected the services received,” and that there was “little evidence that invoice details were appropriately reviewed and approved by … the Canada Revenue Agency prior to issuing payment.”
The Liberals have delivered higher taxes and higher costs with worse service for Canadians. We deserve better than continued Liberal failures. Conservatives will continue holding Carney accountable and fight to cut taxes and waste so Canadians keep more of what they earn.
-

 Alberta2 days ago
Alberta2 days agoBusting five myths about the Alberta oil sands
-

 Frontier Centre for Public Policy2 days ago
Frontier Centre for Public Policy2 days agoOttawa Should Think Twice Before Taxing Churches
-

 Health1 day ago
Health1 day agoNew report warns WHO health rules erode Canada’s democracy and Charter rights
-
 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoUS government buys stakes in two Canadian mining companies
-

 Business7 hours ago
Business7 hours agoEmission regulations harm Canadians in exchange for no environmental benefit
-

 Business7 hours ago
Business7 hours agoQuebecers want feds to focus on illegal gun smuggling not gun confiscation
-

 Energy1 day ago
Energy1 day agoMinus Forty and the Myth of Easy Energy
-

 Courageous Discourse5 hours ago
Courageous Discourse5 hours agoNo Exit Wound – EITHER there was a very public “miracle” OR Charlie Kirk’s murder is not as it appears








