Business
Netflix in Canada—All in the name of ‘modernizing’ broadcasting: Peter Menzies

From the MacDonald Laurier Institute
By Peter Menzies
Canada’s content czars are stuck in the past and trying to drag everyone back with them
Next week, the Canadian Radio-television and Telecommunications Commission (CRTC) will go live with its efforts to wrestle the internet and those who stream upon it into submission. Whether it fully understands the risks remains unclear.
There are 127 parties scheduled to appear before a panel of commissioners at a public hearing in Gatineau starting November 20. The tone-setting opening act will be Pierre-Karl Peladeau’s always-scrappy Quebecor while the UFC will throw the final punches before the curtain drops three weeks later.
The list of presenters consists mostly of what those of us who have experienced these mind-numbing hearings refer to as “the usual suspects”—interests whose business plans are built around the Broadcasting Act and the requirements of related funding agencies.
The largest Canadian companies will ask the CRTC to reduce its demands upon them when it comes to feeding and watering Big Cancon: the producers, directors, actors, writers, and other tradespeople who make certified Canadian content.
Quebecor, for instance, will be arguing for its contribution to be reduced from 30 percent of its revenue to 20 percent—a draw it proposes be applied to designated streamers. More money from foreign companies and less from licensed domestic broadcasters will be a recurring theme.
But there will also be a new slate of actors—those with business models designed to entertain and attract consumers in a free market—who will be staring down the barrel of CRTC Chair Vicky Eatrides’ stifling regulatory gun for the first time.
Disney+ is set to take the stage on November 29. Meta, the Big Tech bete noire that refused to play along with the Online News Act, is up on December 5.
But the big day will almost certainly be November 30 when Netflix locks horns with the Commission and what appear to be its dangerously naive assumptions.
More than half the streamer’s 30-page submission is dedicated to detailing what it is already contributing to Canada.
Some examples:
- $3.5 billion in investment;
- Thousands of jobs created;
- Consumers are 1.8 times more likely to watch a Canadian production on Netflix than they are on a licensed TV network;
- Le Guide de la Famille Parfaite—one of many Quebec productions it funded—was in Netflix’s global top 10 for non-English productions for two weeks.
Netflix is insisting on credit for what it already contributes. It has no interest in writing a cheque to the Canada Media Fund and takes serious umbrage with the CRTC’s assumption it will.
“The (hearing) notice could be understood to suggest that the Commission has made a preliminary determination to establish an ‘initial base contribution’ requirement for online undertakings,” Netflix states in its submission. “The only question for consideration would appear not to be whether, but rather what funds would be the possible recipients of contributions.
“Netflix submits that this is not an appropriate starting point.”
It gets worse. The CRTC is considering applying some of the non-financial obligations it imposes on licensed broadcasters such as CTV and Global to the streaming world.
Executive Director of Broadcasting Scott Shortliffe told the National Post recently that “Netflix is clearly producing programming that is analogous…to traditional broadcasters” and that it could be expected to “contribute” in terms of the shape of its content as well as how it spends its money.
In other words, the CRTC’s idea of “modernizing” broadcasting appears heavily weighted in favour of applying its 1990s way of doing things to the online world of 2023.
If that’s the case, the Commission is entirely unprepared to deal with the harsh truth that offshore companies don’t have to play by its rules. For decades, primary CRTC hearing participants have been dependent on the regulator. In the case of broadcasters like CTV and cable companies such as Rogers, their existence is at stake. Without a license, they are done. Which means they have to do what the Commission wants. But if the regulatory burden the CRTC places upon the offshore streamers doesn’t make business sense to them, they are free to say, “Sorry Canada, the juice just isn’t worth the squeeze. We’re outta here.”
This is most likely to occur among the smaller, niche services at the lower end of the subscription scale. The CRTC has to date exempted only companies with Canadian revenues of less than $10 million. Any company just over that line would almost certainly not bother to do business in Canada —a relatively small and increasingly confusing market—if the regulatory ask is anything close to the 20 percent commitment being suggested.
Ditto if the CRTC goes down the road Shortliffe pointed to. It would be absurd to impose expectations on unlicensed streamers that are similar to those applied to licensed broadcasters. For the latter, the burden is balanced by benefits such as market protection granted by the CRTC.
For streamers, no such regulatory “bargain” exists. Too much burden without benefits would make it far cheaper for many to leave and sell their most popular shows to a domestic streamer or television network.
The Online Streaming Act (Bill C-11), which led to this tussle, was originally pitched as making sure web giants “contraibute” their “fair share.”
So, as it turns out, was the Online News Act (Bill C-18).
That legislation resulted in Meta/Facebook getting out of the news business and Google may yet do the same. As a consequence, news organizations will lose hundreds of millions of dollars. Many won’t survive.
Eatrides and her colleagues, if they overplay their hand, are perfectly capable of achieving a similarly catastrophic outcome for the film and television industry.
Peter Menzies is a Senior Fellow with the Macdonald-Laurier Institute, a former newspaper executive, and past vice chair of the CRTC.
Business
China, Mexico, Canada Flagged in $1.4 Billion Fentanyl Trade by U.S. Financial Watchdog
 Sam Cooper
Sam Cooper
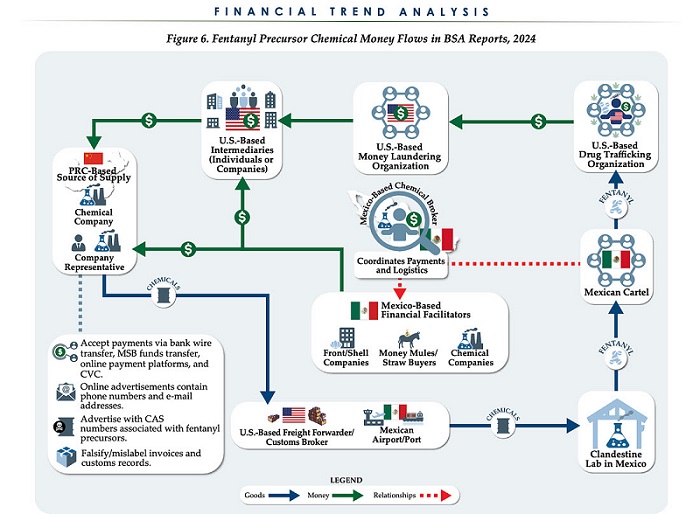
The U.S. Treasury’s Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN) has identified $1.4 billion in fentanyl-linked suspicious transactions, naming China, Mexico, Canada, and India as key foreign touchpoints in the global production and laundering network. The analysis, based on 1,246 Bank Secrecy Act filings submitted in 2024, tracks financial activity spanning chemical purchases, trafficking logistics, and international money laundering operations.
The data reveals that Mexico and the People’s Republic of China were the two most frequently named foreign jurisdictions in financial intelligence gathered by FinCEN. Most of the flagged transactions originated in U.S. cities, the report notes, due to the “domestic nature” of Bank Secrecy Act data collection. Among foreign jurisdictions, Mexico, China, Hong Kong, and Canada were cited most often in fentanyl-related financial activity.
The FinCEN report points to Mexico as the epicenter of illicit fentanyl production, with Mexican cartels importing precursor chemicals from China and laundering proceeds through complex financial routes involving U.S., Canadian, and Hong Kong-based actors.
The findings also align with testimony from U.S. and Canadian law enforcement veterans who have told The Bureau that Chinese state-linked actors sit atop a decentralized but industrialized global fentanyl economy—supplying precursors, pill presses, and financing tools that rely on trade-based money laundering and professional money brokers operating across North America.
“Filers also identified PRC-based subjects in reported money laundering activity, including suspected trade-based money laundering schemes that leveraged the Chinese export sector,” the report says.
A point emphasized by Canadian and U.S. experts—including former U.S. State Department investigator Dr. David Asher—that professional Chinese money laundering networks operating in North America are significantly commanded by Chinese Communist Party–linked Triad bosses based in Ontario and British Columbia—is not explored in detail in this particular FinCEN report.¹
Chinese chemical manufacturers—primarily based in Guangdong, Zhejiang, and Hebei provinces—were repeatedly cited for selling fentanyl precursors via wire transfers and money service businesses. These sales were often facilitated through e-commerce platforms, suggesting that China’s global retail footprint conceals a lethal underground market—one that ultimately fuels a North American public health crisis. In many cases, the logistics were sophisticated: some Chinese companies even offered delivery guarantees and customs clearance for precursor shipments, raising red flags for enforcement officials.
While China’s industrial base dominates the global fentanyl supply chain, Mexican cartels are the next most prominent state-like actors in the ecosystem—but the report emphasizes that Canada and India are rising contributors.
“Subjects in other foreign countries—including Canada, the Dominican Republic, and India—highlight the presence of alternative suppliers of precursor chemicals and fentanyl,” the report says.
“Canada-based subjects were primarily identified by Bank Secrecy Act filers due to their suspected involvement in drug trafficking organizations allegedly sourcing fentanyl and other drugs from traditional drug source countries, such as Mexico,” it explains, adding that banking intelligence “identified activity indicative of Canada-based individuals and companies purchasing precursor chemicals and laboratory equipment that may be related to the synthesis of fentanyl in Canada. Canada-based subjects were primarily reported with addresses in the provinces of British Columbia and Ontario.”
FinCEN also flagged activity from Hong Kong-based shell companies—often subsidiaries or intermediaries for Chinese chemical exporters. These entities were used to obscure the PRC’s role in transactions and to move funds through U.S.-linked bank corridors.
Breaking down the fascinating and deadly world of Chinese underground banking used to move fentanyl profits from American cities back to producers, the report explains how Chinese nationals in North America are quietly enlisted to move large volumes of cash across borders—without ever triggering traditional wire transfers.
These networks, formally known as Chinese Money Laundering Organizations (CMLOs), operate within a global underground banking system that uses “mirror transfers.” In this system, a Chinese citizen with renminbi in China pays a local broker, while the U.S. dollar equivalent is handed over—often in cash—to a recipient in cities like Los Angeles or New York who may have no connection to the original Chinese depositor aside from their role in the laundering network. The renminbi, meanwhile, is used inside China to purchase goods such as electronics, which are then exported to Mexico and delivered to cartel-linked recipients.
FinCEN reports that US-based money couriers—often Chinese visa holders—were observed depositing large amounts of cash into bank accounts linked to everyday storefront businesses, including nail salons and restaurants. Some of the cash was then used to purchase cashier’s checks, a common method used to obscure the origin and destination of the funds. To banks, the activity might initially appear consistent with a legitimate business. However, modern AI-powered transaction monitoring systems are increasingly capable of flagging unusual patterns—such as small businesses conducting large or repetitive transfers that appear disproportionate to their stated operations.
On the Mexican side, nearly one-third of reports named subjects located in Sinaloa and Jalisco, regions long controlled by the Sinaloa Cartel and Cartel Jalisco Nueva Generación. Individuals in these states were often cited as recipients of wire transfers from U.S.-based senders suspected of repatriating drug proceeds. Others were flagged as originators of payments to Chinese chemical suppliers, raising alarms about front companies and brokers operating under false pretenses.
The report outlines multiple cases where Mexican chemical brokers used generic payment descriptions such as “goods” or “services” to mask wire transfers to China. Some of these transactions passed through U.S.-based intermediaries, including firms owned by Chinese nationals. These shell companies were often registered in unrelated sectors—like marketing, construction, or hardware—and exhibited red flags such as long dormancy followed by sudden spikes in large transactions.
Within the United States, California, Florida, and New York were most commonly identified in fentanyl-related financial filings. These locations serve as key hubs for distribution and as collection points for laundering proceeds. Cash deposits and peer-to-peer payment platforms were the most cited methods for fentanyl-linked transactions, appearing in 54 percent and 51 percent of filings, respectively.
A significant number of flagged transactions included slang terms and emojis—such as “blues,” “ills,” or blue dots—in memo fields. Structured cash deposits were commonly made across multiple branches or ATMs, often linked to otherwise legitimate businesses such as restaurants, salons, and trucking firms.
FinCEN also tracked a growing number of trade-based laundering schemes, in which proceeds from fentanyl sales were used to buy electronics and vaping devices. In one case, U.S.-based companies owned by Chinese nationals made outbound payments to Chinese manufacturers, using funds pooled from retail accounts and shell companies. These goods were then shipped to Mexico, closing the laundering loop.
Another key laundering method involved cryptocurrency. Nearly 10 percent of all fentanyl-related reports involved virtual currency, with Bitcoin the most commonly cited, followed by Ethereum and Litecoin. FinCEN flagged twenty darknet marketplaces as suspected hubs for fentanyl distribution and cited failures by some digital asset platforms to catch red-flag activity.
Overall, FinCEN warns that fentanyl-linked funds continue to enter the U.S. financial system through loosely regulated or poorly monitored channels, even as law enforcement ramps up enforcement. The Drug Enforcement Administration reported seizures of over 55 million counterfeit fentanyl pills in 2024 alone.
The broader pattern is unmistakable: precursor chemicals flow from China, manufacturing occurs in Mexico, Canada plays an increasing role in chemical acquisition and potential synthesis, and drugs and proceeds flood into the United States, supported by global financial tools and trade structures. The same infrastructure that enables lawful commerce is being manipulated to sustain the deadliest synthetic drug crisis in modern history.
The Bureau is a reader-supported publication.
To receive new posts and support my work, consider becoming a free or paid subscriber.
Invite your friends and earn rewards
2025 Federal Election
Canada drops retaliatory tariffs on automakers, pauses other tariffs

 MxM News
MxM News
Quick Hit:
Canada has announced it will roll back retaliatory tariffs on automakers and pause several other tariff measures aimed at the United States. The move, unveiled by Finance Minister François-Philippe Champagne, is designed to give Canadian manufacturers breathing room to adjust their supply chains and reduce reliance on American imports.
Key Details:
- Canada will suspend 25% tariffs on U.S. vehicles for automakers that maintain production, employment, and investment in Canada.
- A broader six-month pause on tariffs for other U.S. imports is intended to help Canadian sectors transition to domestic sourcing.
- A new loan facility will support large Canadian companies that were financially stable before the tariffs but are now struggling.
Diving Deeper:
Ottawa is shifting its approach to the escalating trade war with Washington, softening its economic blows in a calculated effort to stabilize domestic manufacturing. On Tuesday, Finance Minister François-Philippe Champagne outlined a new set of trade policies that provide conditional relief from retaliatory tariffs that have been in place since March. Automakers, the hardest-hit sector, will now be eligible to import U.S. vehicles duty-free—provided they continue to meet criteria that include ongoing production and investment in Canada.
“From day one, the government has reacted with strength and determination to the unjust tariffs imposed by the United States on Canadian goods,” Champagne stated. “We’re giving Canadian companies and entities more time to adjust their supply chains and become less dependent on U.S. suppliers.”
The tariff battle, which escalated in April with Canada slapping a 25% tax on U.S.-imported vehicles, had caused severe anxiety within Canada’s auto industry. John D’Agnolo, president of Unifor Local 200, which represents Ford employees in Windsor, warned the BBC the situation “has created havoc” and could trigger a recession.
Speculation about a possible Honda factory relocation to the U.S. only added to the unrest. But Ontario Premier Doug Ford and federal officials were quick to tamp down the rumors. Honda Canada affirmed its commitment to Canadian operations, saying its Alliston facility “will operate at full capacity for the foreseeable future.”
Prime Minister Mark Carney reinforced the message that the relief isn’t unconditional. “Our counter-tariffs won’t apply if they (automakers) continue to produce, continue to employ, continue to invest in Canada,” he said during a campaign event. “If they don’t, they will get 25% tariffs on what they are importing into Canada.”
Beyond the auto sector, Champagne introduced a six-month tariff reprieve on other U.S. imports, granting time for industries to explore domestic alternatives. He also rolled out a “Large Enterprise Tariff Loan Facility” to support big businesses that were financially sound prior to the tariff regime but have since been strained.
While Canada has shown willingness to ease its retaliatory measures, there’s no indication yet that the U.S. under President Donald Trump will reciprocate. Nevertheless, Ottawa signaled its openness to further steps to protect Canadian businesses and workers, noting that “additional measures will be brought forward, as needed.”
-

 2025 Federal Election1 day ago
2025 Federal Election1 day agoRCMP Whistleblowers Accuse Members of Mark Carney’s Inner Circle of Security Breaches and Surveillance
-

 Autism2 days ago
Autism2 days agoAutism Rates Reach Unprecedented Highs: 1 in 12 Boys at Age 4 in California, 1 in 31 Nationally
-

 Health2 days ago
Health2 days agoTrump admin directs NIH to study ‘regret and detransition’ after chemical, surgical gender transitioning
-

 Bjorn Lomborg2 days ago
Bjorn Lomborg2 days agoGlobal Warming Policies Hurt the Poor
-
 Autism1 day ago
Autism1 day agoRFK Jr. Exposes a Chilling New Autism Reality
-

 2025 Federal Election2 days ago
2025 Federal Election2 days agoAI-Driven Election Interference from China, Russia, and Iran Expected, Canadian Security Officials Warn
-

 Also Interesting1 day ago
Also Interesting1 day agoBetFury Review: Is It the Best Crypto Casino?
-

 2025 Federal Election1 day ago
2025 Federal Election1 day agoBureau Exclusive: Chinese Election Interference Network Tied to Senate Breach Investigation






