Energy
Net Zero’s days are numbered? Why Europeans are souring on the climate agenda

From LifeSiteNews
By Frank Wright
Dr. Benny Peiser recently spoke about how the E.U. and various European nations have started a ‘rollback’ of their climate agendas due to ‘increasing costs and increasing hostility from the public.’
A recent presentation given in Canada brings welcome news to the reality-based community: Net Zero’s days are numbered. The costs of the “utopian” green agenda have been realized, and the public are not buying it any more.
This is the message of Dr. Benny Peiser of the Global Warming Policy Foundation, who was in Calgary on April 9 to speak about “Europe’s Net Zero rebellion and the implications for Canada.”
“The game is over for anyone who is willing to commit industrial suicide through the implementation of Net Zero policies,” he says, going on to cite public opinion and political decisions which are driving the political agenda of the future.
Peiser shows how the European Union and the nations of Sweden, France, Germany, Britain, and Italy have started this “rollback” – due to “increasing costs and increasing hostility from the public.”
Saying that Canada, where he spoke, is “maybe five years” behind the Net Zero rollback in Europe, he said the agenda was in retreat there as its “astronomical” costs have now been grasped by the public.
“This is direct,” he says.
We have been telling [the public] for 15 years this will be very expensive … and your energy bills are going up because of the renewables.
This is all far too abstract for people. They don’t get that.
Citing reports which show that Net Zero will cost over a trillion euros a year, every year, he says:
This they get directly – the car they can’t drive, the way they heat their homes. What they’re allowed to do.
That has caused huge opposition and a lot of headache for governments.
Peiser says political parties across Europe have realized that they face being swept from power in the forthcoming elections in June.
Politics pivots back to reality
The headaches Peiser cites include the near collapse of the German government late last year over a policy to make heat pumps compulsory. A week after Peiser’s talk, news came that the Scottish coalition government has collapsed, with the Greens withdrawing support from the ruling SNP after the abandonment of climate change targets.
Politicians are faced with a choice between electoral oblivion and public opinion, and Peiser says this has led to structural change in European policy.
Peiser believes that the enormous public support behind the farmer protests, coupled with green policies creating crisis in the German government, has made the E.U. think again.
“As a result of these protests governments and the European Commission itself have begun to cave in,” Peiser said. “They are not just losing farmers but a large chunk of the public at the same time.”
Peiser is aware that election cycles see politicians shelve unpopular policies – only to resume them after the votes have been counted. Yet he notes a structural change in priorities.
“The E.U. in its draft agenda for the next five years has decided to relegate climate and shift to defense,” he continued, saying that the European Union is shifting from the green agenda to the “real agenda.”
This pivot to reality is one that is long overdue. As Peiser points out, the case for Net Zero is one that is made out of words, not of facts. To take one example, that of electric vehicles, he says “the biggest fear in Europe is not climate change. The biggest fear is cheap electric vehicles from China.”
The E.U.’s recent Net Zero Industry Act (NZIA) has been shaded by economic and industrial concerns, as well as fear from the climate lobby that it too is a rollback of Net Zero commitments.
Passed on April 25, its name alone would suggest business as usual for the climate agenda.
However, in a press conference introducing the Act last November, German “conservative” MEP Christian Ehler was keen to anticipate criticism from the Green lobby, saying “this is not an attempt to scrap social achievements or environmental law.”
Ehler’s emphasis here was on industry and whether Europe will have an economic and industrial future – or not.
Ehler stressed the need to keep industry “on our side” and that the past practices of regulation threatens the economic future of European industry,
It’s simply reflecting the very fact that our industry is burdened by regulation in a way that we can’t expect them to succeed – if we really want to have them on our side – and if we really have to have an economic future for the European industry.
READ: New documentary exposes climate agenda as ‘scam’ to increase globalist power and profit
An act in name only
This may explain why, according to two experts, the Act is in fact just words. Yet it is not only the threat of Green-inspired regulation which faces European industry.
Chinese dominance of the market has rendered E.U. Net Zero measures to create a “sustainable” industry producing “green technology” such as solar panels mere “paper tigers,” according to one analyst.
Simone Tagliapietra, a senior fellow at think-tank Bruegel said this in response to the E.U.’s new Act.
His comments, reported by Euractiv on April 26, included an explanation why the legislation “doesn’t change anything.”
A second analyst, Nils Redeker of the Berlin-based Jacques Delors Centre, agreed according to Euractiv that the new measures “could, in practice, and will most likely, be ignored.”
The green lights are going out all over Europe, most obviously in what was once its industrial and economic powerhouse.
Germany in crisis
Following a budget crisis which also threatened the survival of the German government’s “Red/Green/Yellow” or “traffic light” coalition last November, the former E.U. paymaster of Germany was said to be “likely in recession.”
The February 19 report by the Daily Telegraph noted the resulting “uncertainty” over Net Zero implementation. This is another sign of the impact of reality on the deeply unpopular policies of what Peiser called the “utopia” imagined by the Green lobby.
The Daily Telegraph also reported that the German central bank had warned of “no end in sight” for the “ongoing weakness” of Europe’s largest economy.
The Bundesbank added that “uncertainty regarding climate and transformation policy remains elevated.”
In his analysis of the electoral cost of Net Zero, Peiser seems to have read the room very well. The political climate has changed.
As the British government is faced with power cuts over soaring demand for electricity, its refusal to build more gas-fired power stations may see the actual lights go out as well as the figurative beacon of an agenda the Conservative Party have greenlit for years.
U.K. climate chief quits
The outgoing head of the U.K.’s climate change committee has conceded that Net Zero is a toxic brand:
Net Zero has definitely become a slogan that I feel occasionally is now unhelpful, because it’s so associated with the campaigns against it.
Chris Stark, who looks exactly as you would imagine he would, blamed a minority faction of imaginary “culture warriors” whilst saying on April 22 in The Guardian that the cost of living was effectively irrelevant.
“It’s the culture warriors who have really taken against it,” said Stark. “A small group of politicians or political voices has moved in to say that net zero is something that you can’t afford, net zero is something that you should be afraid of … But we’ve still got to reduce emissions. In the end, that’s all that matters.”
Stark’s missionary zeal is untouched by a Europe-wide survey cited by in Peiser’s presentation. According to the survey, conducted in January by the European Council on Foreign Relations (ECFR), it is the climate zealots themselves who are the minority.
With a sample from 12 European nations, it shows a clear majority in 10 countries for “reducing energy bills” over “reducing carbon emissions.” In Germany, support for lower energy costs is more than twice that for the higher ones promised by “reducing emissions.”
Peiser explained, “What [the survey] tells you is that a clear minority of Europeans are prioritizing the climate issue over their energy cost issue.”
READ: Climate expert warns against extreme ‘weather porn’ from alarmists pushing ‘draconian’ policies
Describing the clear majority of European citizens against the cost of Net Zero, he says “that is the most dramatic change I’ve seen in the last 20 years.”
This “realization of cost moment” is one which Peiser shows had been predicted in the 1970s by Anthony Downs, whose “issue attention cycle” predicted public understanding of the true cost as the point beyond which climate policies will no longer enjoy public support.
The graph roughly charts the interest and support of the public, which moves from ignorance of the “problem” to generate public support through a sense of alarm. This enthusiasm steeply fades as the public realizes the price of the product they have been sold.
Yet this process is based on the common sense to the common man. The U.K.’s former climate change chief Christopher Stark is immune to this determining factor.
He displays the alarming detachment from reality which typifies the Net Zero zealot, and which Peiser warns is proving electorally – and industrially – suicidal.
Speaking of the implementation of Net Zero, Stark claimed, against rapid deindustrialization, soaring energy prices, and former measures to restrict cars and home heating to costly and inferior alternatives, that “the lifestyle change that goes with this is not enormous at all.”
This also ignores the likely “power cuts” that Britain will face, given a massive upsurge in Net Zero-driven electricity demand.
The Daily Telegraph, reporting accusations from the Green lobby that Rishi Sunak was “abandoning” Net Zero, said on March 17 that without more gas fired power generation, support for Net Zero “would collapse.”
The report continued that “the U.K. would almost certainly endure power cuts, causing civic and commercial havoc, without more gas-fired baseload in place.”
The piece concludes with a verdict which is now becoming a theme: “And then the case for tackling climate change, already increasingly questioned, would become politically toxic.”
The rule of law – or the rule of lawyers
As Peiser notes, this toxification has weakened the power of politics itself, with the rule of law being replaced by the rule of lawyers. He notes a recent ruling by the European Court of Human Rights, which condemned the Swiss government for “violations of the Convention [on Human Rights] for failing to implement sufficient measures to combat climate change.”
Peiser said the ruling showed that democratic majorities do not have the legal power to refuse an agenda enforced by activist judges. He went on:
The judges in their in their ruling said it’s kind of naive to think that democracy would work just with majorities in Parliament and that only judges can rule or decide what makes legal sense – that’s why it’s so important for judges to tell parliaments what they should do.
That’s essentially what they were saying today.
Peiser was speaking on the same day the ruling was announced, which according to a Swiss report will “have a direct impact on the Council of Europe’s 46 member states” and that “its ramifications will extend to the whole world.”
This element of legal insurrection is one direct example of how the sovereignty of democracy is being undermined. In this case, a group of elderly female climate campaigners received a sympathetic hearing from the ECHR’s presiding judge, Siofra O’Leary. Her judgment overruled the Swiss courts’ dismissal of the case. It read:
The Court found that the national courts had not provided convincing reasons as to why they had considered it unnecessary to examine the merits of the complaints. They had failed to take into consideration the compelling scientific evidence concerning climate change and had not taken the association’s complaints seriously.
As Peiser warns, we are ruled by Science Followers, whose emotional enthusiasm for the climate panic talks past the costs of the sale of this agenda. It is a product which most people now recognize promises the permanent collapse of living standards in the West, and is taking democracy down with cries for climate “justice.”
Suicidal policy vs. ‘populism’
Peiser says Net Zero is already “suicidal” – and not in name only. Changing the branding will not wash with voters, Peiser says, as the impact of cost and on freedom is “direct.”
This, he says, is what is driving the beginning of the end of Net Zero.
“Europeans have been told that this Net Zero issue and renewables and so on will make life easier for people.” Instead, he says, “the opposite has happened.”
They’ve been told that energy costs would go down. They’ve gone up.
He observes a factor which could apply to practically any of the policies he also claims are driving “populism.”
So people are beginning to realize that what they’ve been told hasn’t actually materialized.
The opposite has materialized.
Peiser himself notes that this “opposite effect” is driving the rise of “populist parties … skeptical of mass immigration, of Net Zero and of other mainstream policies.”
He says, “I don’t know exactly why they’re called populist but something makes them popular.”
Yet his own presentation shows a simple explanation. What is called “populism” is simply a reaction to the insanity of the policies of national suicide presented as wisdom. The emergence of these parties is the opposite reaction to a political system whose every argument is a contradiction of reality.
Peiser says that this political correction is coming, and soon.
The mainstream parties are concerned that they will hemorrhaging voters.
That’s what the prospects are for the elections in June.
His assessment is shared by the European Council on Foreign Relations, which predicted a “sharp right turn” in the forthcoming E.U. Parliament elections.
He says that for Europe “there might be – for the first time – a center right populist majority in Parliament. If that were to happen of course all bets are off.”
What is more, Peiser concludes that political climate change is coming home – to yours:
That’s the situation in Europe which sooner or later will come to a theater close to you.
Energy
‘War On Coal Is Finally Over’: Energy Experts Say Trump Admin’s Deregulation Agenda Could Fuel Coal’s ‘Revival’


From the Daily Caller News Foundation
By Audrey Streb
Within the first months of his second administration, President Donald Trump has prioritized “unleashing” American energy and has already axed several of what he considers to be burdensome regulations on the coal industry, promising it’s “reinvigoration.”
Trump signed an executive order on April 8 to revive the coal industry, and shortly after moved to exempt several coal plants from Biden-era regulations. Though it has become a primary target of many climate activists, coal has been historically regarded as readily available and affordable, and several energy policy experts who spoke with Daily Caller News Foundation believe Trump has the cards necessary to strengthen the industry.
“When utility bills are skyrocketing or blackouts are happening in winter, people are going to want reliable power back,” Amy Cooke, co-founder and president of Always on Energy Research and the director of the Energy and Environmental Policy Center told the DCNF. “The beauty of coal is that it allows for affordable, reliable power, which is absolutely crucial to economic prosperity, and in particular, innovation.”
“I think the number one, most significant threat to humanity is no power,” Cooke said, adding that coal is a vital contributor to the nation’s “baseload power.”
Following his executive order, Trump in early April granted a two-year exemption for nearly 70 coal plants from a Biden-era rule on air pollution that required them to reduce certain air pollutants. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) said that the move would “bolster coal-fired electricity generation, ensuring that our nation’s grid is reliable, that electricity is affordable for the American people, and that EPA is helping to promote our nation’s energy security.”
Shortly after, skepticism swirled surrounding whether or not the coal industry would be able to experience a revival, and whether it would be economically savvy to pursue one.
Energy generated from burning coal only powers roughly 16% of the U.S., though 40 states are dependent on coal, according to data from America’s Power. Energy generation through coal reached a record low in 2023, a Rhodium Group study reported. In 2021, however, coal was the primary source of energy for 15 states, according to the U.S. Energy Information Administration.
“We can lead the world in innovation,” Cook told the DCNF, referencing developments in natural gas and nuclear power as beneficial. “But you have to have coal. It has to be part of the mix.”
“It’s insane that we would shut down any base load power right now, when the demand for power is so high,” Cooke added. She further referenced the North American Electric Reliability Corporation’s 2024 report and research from Always on Energy Research that have projected rolling blackouts to begin across the U.S. by 2028.
As American energy demand continues to climb, the odds of impending blackouts would increase if the supply fails to grow at the same rate. The push toward renewable energy sources, in addition to stringent environmental regulations approved under former President Joe Biden, may have contributed to the slower growth of energy supply currently being experienced in the U.S.
Immediately after returning to the White House, Trump declared a national energy emergency, stating that “the integrity and expansion of our Nation’s energy infrastructure” is “an immediate and pressing priority for the protection of the United States’ national and economic security.”
“We looked at it and predict that there will be periods of blackouts of 24 hours or more,” Cook told the DCNF.
She further noted that “the cheapest power is the power you’ve already paid for,” arguing for the continuation of existing coal plants and the reopening of ones that have been closed.
“The only people who think coal is bad are those who view it through the lens of carbon emissions only, and that is no way to do energy policy,” Cooke said, arguing that it is necessary to adopt a “holistic” approach to energy generation, given the nation’s projected energy crisis.
“The American people need more energy, and the Department of Energy is helping to meet this demand by unleashing supply of affordable, reliable, secure energy sources – including coal,” Department of Energy Secretary Chris Wright said in an April 9 statement. “Coal is essential for generating 24/7 electricity,” he added, “but misguided policies from previous administrations have stifled this critical American industry. With President Trump’s leadership, we are cutting the red tape and bringing back common sense.”
The president has also said that he envisions greater job opportunities for coal miners with the industry’s expansion, stating during an April 8 press conference that the workers are “really well-deserving and great American patriots.”
“For years, people would just bemoan this industry and decimate the industry for absolutely no reason,” Trump added.
“Miners can wake up today for the first time in a decade and their spouses and families will realize they have a job tomorrow,” reporter Bob Aaron said in a video shared on X. They can “hear a president of the country announce that the war on coal is over.”
“I really anticipate a revival in the coal industry in the United States under Trump,” David Blackmon, an energy and policy writer who spent 40 years in the oil and gas business told the DCNF. He pointed to the Trump administration loosening restrictions on coal, adding that the Biden administration made it “near impossible” to build new coal plants due to aggressive climate rules.
Under Biden’s signature climate bill, the Inflation Reduction Act, the U.S. prioritized renewable energy generation and subsidization, resulting in a hefty price tag for taxpayers who had to foot the bill for several environmental initiatives, including hundreds of millions of dollars for solar panel construction in some of the nation’s least-sunny locations.
“The cheapest, the most affordable thing to do is to keep our current infrastructure online,” André Béliveau, Senior Manager of Energy Policy at the Commonwealth Foundation, told the DCNF. “Coal remains one of, if not, the most affordable energy source we have.”
“You’re forcing retirement of full-time energy sources and trying to replace them with part-time energy sources, and that’s not going to work,” Béliveau continued, referencing renewable energy avenues such as wind and solar. “We can’t run a full-time economy on part-time energy.”
Canadian Energy Centre
First Nations in Manitoba pushing for LNG exports from Hudson’s Bay

From the Canadian Energy Centre
By Will Gibson
NeeStaNan project would use port location selected by Canadian government more than 100 years ago
Building a port on Hudson’s Bay to ship natural resources harvested across Western Canada to the world has been a long-held dream of Canadian politicians, starting with Sir Wilfred Laurier.
Since 1931, a small deepwater port has operated at Churchill, Manitoba, primarily shipping grain but more recently expanding handling of critical minerals and fertilizers.
A group of 11 First Nations in Manitoba plans to build an additional industrial terminal nearby at Port Nelson to ship liquefied natural gas (LNG) to Europe and potash to Brazil.
Robyn Lore, a director with project backer NeeStaNan, which is Cree for “all of us,” said it makes more sense to ship Canadian LNG to Europe from an Arctic port than it does to send Canadian natural gas all the way to the U.S. Gulf Coast to be exported as LNG to the same place – which is happening today.
“There is absolutely a business case for sending our LNG directly to European markets rather than sending our natural gas down to the Gulf Coast and having them liquefy it and ship it over,” Lore said. “It’s in Canada’s interest to do this.”
Over 100 years ago, the Port Nelson location at the south end of Hudson’s Bay on the Nelson River was the first to be considered for a Canadian Arctic port.
In 1912, a Port Nelson project was selected to proceed rather than a port at Churchill, about 280 kilometres north.
The Port Nelson site was earmarked by federal government engineers as the most cost-effective location for a terminal to ship Canadian resources overseas.
Construction started but was marred by building challenges due to violent winter storms that beached supply ships and badly damaged the dredge used to deepen the waters around the port.
By 1918, the project was abandoned.
In the 1920s, Prime Minister William Lyon MacKenzie King chose Churchill as the new location for a port on Hudson’s Bay, where it was built and continues to operate today between late July and early November when it is not iced in.
Lore sees using modern technology at Port Nelson including dredging or extending a floating wharf to overcome the challenges that stopped the project from proceeding more than a century ago.
He said natural gas could travel to the terminal through a 1,000-kilometre spur line off TC Energy’s Canadian Mainline by using Manitoba Hydro’s existing right of way.
A second option proposes shipping natural gas through Pembina Pipeline’s Alliance system to Regina, where it could be liquefied and shipped by rail to Port Nelson.
The original rail bed to Port Nelson still exists, and about 150 kilometers of track would have to be laid to reach the proposed site, Lore said.
“Our vision is for a rail line that can handle 150-car trains with loads of 120 tonnes per car running at 80 kilometers per hour. That’s doable on the line from Amery to Port Nelson. It makes the economics work for shippers,” said Lore.
Port Nelson could be used around the year because saltwater ice is easier to break through using modern icebreakers than freshwater ice that impacts Churchill between November and May.
Lore, however, is quick to quell the notion NeeStaNan is competing against the existing port.
“We want our project to proceed on its merits and collaborate with other ports for greater efficiency,” he said.
“It makes sense for Manitoba, and it makes sense for Canada, even more than it did for Laurier more than 100 years ago.”
-
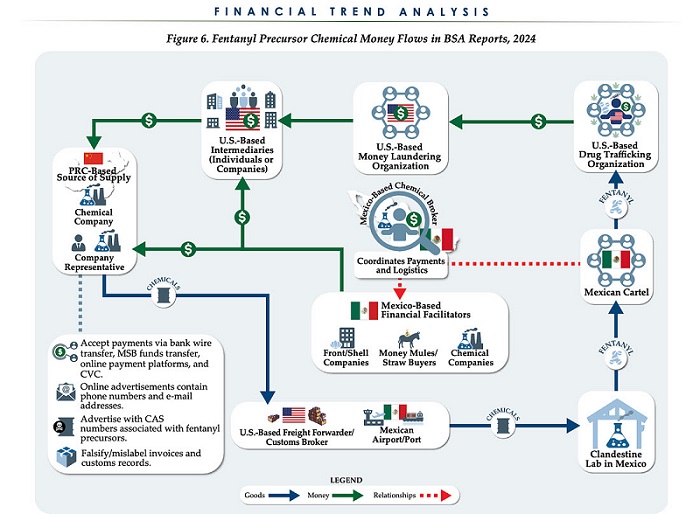
 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoChina, Mexico, Canada Flagged in $1.4 Billion Fentanyl Trade by U.S. Financial Watchdog
-

 2025 Federal Election2 days ago
2025 Federal Election2 days agoTucker Carlson Interviews Maxime Bernier: Trump’s Tariffs, Mass Immigration, and the Oncoming Canadian Revolution
-

 espionage2 days ago
espionage2 days agoEx-NYPD Cop Jailed in Beijing’s Transnational Repatriation Plot, Canada Remains Soft Target
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoDOGE Is Ending The ‘Eternal Life’ Of Government
-

 2025 Federal Election2 days ago
2025 Federal Election2 days agoBREAKING from THE BUREAU: Pro-Beijing Group That Pushed Erin O’Toole’s Exit Warns Chinese Canadians to “Vote Carefully”
-

 2025 Federal Election2 days ago
2025 Federal Election2 days agoCanada drops retaliatory tariffs on automakers, pauses other tariffs
-
 Daily Caller1 day ago
Daily Caller1 day agoDOJ Releases Dossier Of Deported Maryland Man’s Alleged MS-13 Gang Ties
-

 Daily Caller1 day ago
Daily Caller1 day agoTrump Executive Orders ensure ‘Beautiful Clean’ Affordable Coal will continue to bolster US energy grid








