National
McDavid puts up three points as Edmonton Oilers double up Winnipeg Jets 4-2
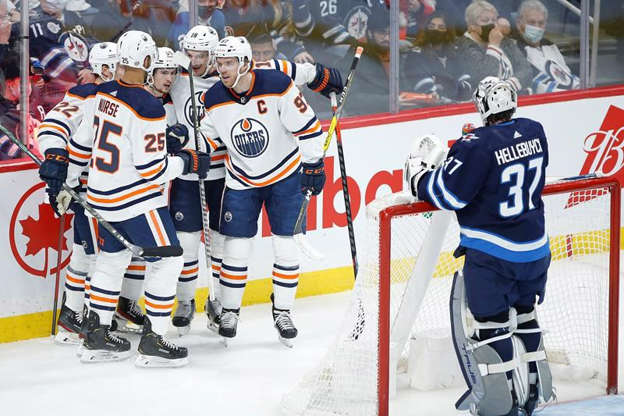
WINNIPEG — Connor McDavid is back atop the NHL scoring race after putting up a goal and two assists Saturday as the Edmonton Oilers beat the Winnipeg Jets 4-2, extending their win streak to five straight.
McDavid has 71 points (26 goals, 45 assists) on the season, two ahead of teammate Leon Draisatl, who picked up one assist against the Jets.
Zach Hyman, Kailer Yamamoto and Darnell Nurse also had goals for Edmonton (28-18-3) while Tyson Barrie contributed a pair of assists.
Winnipeg (22-19-8) scored a pair of third-period goals, with one coming short-handed from Adam Lowry and Kyle Connor adding another on a power play.
Mikko Koskinen stopped 22 shots for Edmonton, which has now tallied five straight wins under interim head coach Jay Woodcroft.
Connor Hellebuyck made 36 saves for Winnipeg, which is 5-3-1 after a six-game winless streak.
The Oilers showed the Jets how to work a power play in the first period.
Winnipeg had a five-on-three man advantage for 90 seconds, but didn’t get a shot on goal after a lot of passing back and forth.
Edmonton then got its first power play of the game and Hyman tipped in Barrie’s point shot through traffic at the 12:17 mark, 20 seconds into the advantage.
The Oilers are 15-0 when scoring first this season.
Edmonton outshot the Jets 15-5 in the opening period.
Winnipeg showed more life early in the second, putting two shots at Koskinen in the first minute. Paul Stastny flipped a close backhand toward the net, but the goalie quickly thrust out his pad for the save.
It was Koskinen’s first game playing since he went into COVID-19 protocol right after the NHL all-star break.
A couple of minutes later on the other side of the ice, Hellebuyck got his body in front of a close-in shot by Yamamoto.
Yamamoto stayed persistent and it paid off. He got his own rebound and recorded his 10th goal of the season at 7:46.
Draisaitl helped make it 3-0, sending a backhand pass across front of the net to McDavid, who fired the puck past Hellebuyck at 10:50.
McDavid’s latest point streak sits at six games, including three goals and eight helpers.
The Oilers had a 13-11 edge in shots on goal in the middle frame.
Koskinen stood tall in the third, stopping Jets defenceman Brenden Dillon on a short-handed breakaway midway through the period. Dillon was playing in his 700th career game.
Lowry then got a breakaway and put a shot under Koskinen’s pads at 10:45. Connor followed up with his 29th goal of the season, a one-timer at 14:38.
Blake Wheeler picked up an assist on Connors’ goal, giving him 12 points in his last four games, including three goals.
The Jets went on the power play with 2:05 left in the third when the Oilers were called for too many men on the ice, but couldn’t capitalize and Nurse scored on the empty net with three seconds remaining.
Winnipeg will embark on a four-game road trip beginning Monday afternoon in Calgary against the Flames. Edmonton is set to host the Minnesota Wild on Sunday night.
This report by The Canadian Press was first published Feb. 19, 2022.
Judy Owen, The Canadian Press
Business
Canada’s Illusion of Stability May Crumble in 2026 Amid Increasingly Dangerous Geopolitics

This year also reaffirmed Canada’s habit of strategic hesitation. Despite overwhelming evidence and allied action, the federal government continued to delay meaningful steps against hostile foreign actors operating within our borders.
As 2026 starts with high-consequence geopolitical events in Venezuela and Iran, Canada continues to present itself to the world as stable, prosperous, and benign. Yet the defining lesson of this past year is that our perceived strength is increasingly an illusion — a façade sustained by political denial, regulatory weakness, and the monetization of risk.
Across multiple fronts — land ownership, real estate, immigration, organized crime, and national security — the same pattern has repeated itself. Warnings were issued. Evidence accumulated. And Ottawa largely chose inaction.
The result is a country drifting further into vulnerability while congratulating itself on tolerance and openness.
Canada’s economy remains dangerously reliant on sectors that are poorly regulated and easily exploited: real estate, land, natural resources, and mass immigration. Throughout the year, investigative reporting and law enforcement intelligence continued to show how foreign capital — often opaque, sometimes criminal — flows freely into these systems with little resistance.
From farmland acquisitions on Prince Edward Island and the Prairies, to urban real estate markets untethered from domestic incomes, Canada has treated ownership and sovereignty as inconveniences rather than safeguards. Weak beneficial ownership registries and limited enforcement ensure that we often do not know who truly controls critical assets — and, worse, seem uninterested in finding out.
This is not economic growth. It is asset stripping disguised as prosperity.
The most brutal manifestation of these blind spots remains fentanyl. In 2025, Canada further cemented its reputation as a preferred destination for laundering synthetic drug profits. Chinese triads, Mexican cartels, and domestic gangs continue to exploit casinos, shell companies, and real estate — not because they are clever, but because Canada is permissive.
Each overdose death is more than a public health failure. It is a financial crime, a national security issue, and a policy indictment. While peer nations have hardened their anti–money laundering regimes, Canada remains slow, fragmented, and politically cautious — a combination that organized crime understands perfectly.
This year also reaffirmed Canada’s habit of strategic hesitation. Despite overwhelming evidence and allied action, the federal government continued to delay meaningful steps against hostile foreign actors operating within our borders.
Some critics charge that Mark Carney’s Liberals are already seeking to water down the long-delayed foreign agent registry, with fines of as little as $50 for non-compliance, while the government has estimated almost 1,800 entities would be expected to register, with 50 additions every year, if this future law were adhered to.
The failure to decisively confront Iranian regime proxies, foreign influence operations, and transnational criminal networks reflects a broader unwillingness to accept that Canada is no longer insulated by geography or reputation.
Our allies increasingly see Canada not as a leader, but as a weak link.
Perhaps nowhere was short-term thinking more evident than in immigration and education policy. Foreign students have become a financial lifeline for institutions, yet oversight remains inadequate. Education visas increasingly function as labour permits in all but name, feeding industries already plagued by regulatory gaps.
Public safety consequences — including in commercial trucking — are no longer theoretical. Nor are concerns about transnational criminal exploitation of these pathways. Yet the federal response continues to prioritize revenue and labour supply over integrity and enforcement.
These are not isolated failures. They are symptoms of a governing philosophy that treats risk as politically inconvenient and accountability as optional. Critics are dismissed as alarmist. Warnings are reframed as xenophobic. And systemic problems are deferred until they become crises.
Canada has been entrusted with extraordinary abundance — land, resources, institutions, and social cohesion. Over the past year, it has become clearer than ever that we are squandering that inheritance.
A nation can only live on reputation for so long. The erosion visible in 2025 will accelerate unless decisive reforms follow: real transparency in ownership, enforceable anti–money laundering laws, a serious national security posture, and immigration systems rooted in integrity rather than expedience.
Canada does not need to abandon openness. It needs to pair openness with vigilance.
The year behind us should be remembered as a warning. Whether the year ahead becomes a correction — or a collapse — will depend on whether leaders finally choose stewardship over denial.
As former Conservative immigration minister Jason Kenney and Conservative Senate leader Leo Housakos have noted, as reported in The Bureau’s analysis of the information war emerging from the Trump administration’s indictment alleging a Maduro narco-state conspiracy, the events in Venezuela are global in nature, and connect directly to Canadian vulnerabilities to transnational money laundering and lax immigration controls that are strategically leveraged by hostile regimes from Beijing to Tehran and Moscow.
And according to Housakos, due to actions emanating from Central and South American authoritarian regimes, including Venezuela, and ultimately instigated by enemies from Beijing, Tehran and Moscow, the upshot is that Western democracies are now facing hybrid warfare threats unprecedented since the Second World War.
In other words, through the tools of transnational drug mafias, political corruption, disinformation, terror and protest, human trafficking, and weaponized migration, Xi, Putin, and the Iranian clerics are attempting to destabilize our societies, softening our defenses before kinetic warfare, or defeating us from within without firing a shot.
Without urgent and decisive leadership in Canada, and the moral clarity and just force that has been in such lack, the continuity of our nation’s great promise is increasingly in doubt.
The Bureau is a reader-supported publication.
To receive new posts and support my work, consider becoming a free or paid subscriber.
Frontier Centre for Public Policy
Canada’s NDP doesn’t deserve official party status

From the Frontier Centre for Public Policy
By Jay Goldberg
Losing seats has consequences. Bending the rules after the fact isn’t one of them
Are the present rules in Canada’s Parliament grotesquely unfair? The New Democratic Party wants Canadians to think so.
The NDP suffered a crushing blow in April’s federal election, losing more than two-thirds of its seats and official party status to boot.
Ever since, the party’s leaders have been trying to convince Prime Minister Mark Carney to bend the rules and allow the party to regain what is called official party status.
As of today, a party in the House of Commons needs at least 12 seats to qualify as an official party. The NDP’s interim leader, Don Davies, wants to see Carney lower the threshold so the NDP’s seven-member caucus can qualify.
“If he wants this Parliament to work and he wants to do anything progressive, he’s going to have to reach out to New Democrats,” said Davies. “It’s up to the Liberals.”
“Reaching out” means more than just a phone call. For Davies, it means granting the NDP official party status, which comes with millions of dollars of operational funding, paid for by taxpayers, as well as the right to participate as a party in Question Period and sit on parliamentary committees.
Changing the rules simply because the NDP failed to connect with voters last spring would be an insult to Canadian taxpayers.
But Davies’ plea does raise some questions. Why is the number 12? Why not 10, or 20 for that matter? And is the 12-seat threshold high by national standards?
The Westminster system of government, which Canada adheres to, is clear about many things. For example, in order to form a majority government, a party needs to hold at least 50 per cent plus one of the seats in the legislative chamber.
But in Canada, the threshold to qualify for official party status is all over the map. In the House of Commons, it is 12. In the Senate, it is nine. And in provincial legislatures across the country, it ranges from one seat in Prince Edward Island to two in British Columbia to five in New Brunswick and 10 per cent of the total seats in Ontario.
The federal NDP may have a point that the 12-seat threshold at the federal level is an arbitrary number. But does it fall outside the national range? Is it at the upper end of the spectrum, and thus perhaps genuinely unfair?
At the lowest end of the range among Canada’s provinces is British Columbia. In that province, a party needs to hold just two of 93 seats in the legislature, or 2.15 per cent, to gain official party status. At the upper end of the range is New Brunswick. In that province, a party needs to hold five of 49 seats, or 10.2 per cent, to gain official party status.
At the federal level, the NDP holds just two per cent of the seats in the House of Commons.
That means that even if British Columbia’s rules, the most liberal in the country, were applied at the federal level, the NDP would not qualify for official party status.
In other words, not only would today’s federal NDP fail to qualify for official party status in British Columbia, but it would also fail to qualify for official party status in province after province across the country.
Relatively speaking, the current House of Commons rules, which require a party to hold 12 seats, or 3.5 per cent of the total seats in the chamber, to gain official party status, are at the liberal end of the spectrum.
So the NDP’s argument does not stand up to the facts. Across the country, based on the size of its caucus, the NDP would not qualify as an official party. The present rules in the House of Commons are well within the normal bounds of rules in legislatures from coast to coast.
Canadian taxpayers should not be on the hook just because the NDP did not receive more support at the polls.
Jay Goldberg is a fellow with the Frontier Centre for Public Policy.
-

 Frontier Centre for Public Policy1 day ago
Frontier Centre for Public Policy1 day agoIs Canada still worth the sacrifice for immigrants?
-

 Bruce Dowbiggin1 day ago
Bruce Dowbiggin1 day agoThe Olympic Shutout: No Quebec Players Invited For Canada
-

 International1 day ago
International1 day agoNetwork of Nonprofits with Marxist and CCP Ties, and Elected Socialists Race to Counter Washington’s Narrative of the Maduro Raid
-

 Canadian Energy Centre1 day ago
Canadian Energy Centre1 day agoFive reasons why 2026 could mark a turning point for major export expansions
-

 Alberta1 day ago
Alberta1 day agoTrump’s Venezuela Geopolitical Earthquake Shakes up Canada’s Plans as a “Net Zero” Energy Superpower
-

 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoPolicy uncertainty continues to damage Canada’s mining potential
-

 Environment1 day ago
Environment1 day agoLeft-wing terrorists sabotage German power plant, causing massive power outage
-

 Energy1 day ago
Energy1 day agoTrump’s Venezuela Move: A $17 Trillion Reset of Global Geopolitics and a Pivotal Shift in US Energy Strategy




