Alberta
Malign Neglect: What Calgary’s Water-Main Break Reveals about the Failure of City Government
Alberta
Made in Alberta! Province makes it easier to support local products with Buy Local program

Show your Alberta side. Buy Local. |
When the going gets tough, Albertans stick together. That’s why Alberta’s government is launching a new campaign to benefit hard-working Albertans.
Global uncertainty is threatening the livelihoods of hard-working Alberta farmers, ranchers, processors and their families. The ‘Buy Local’ campaign, recently launched by Alberta’s government, encourages consumers to eat, drink and buy local to show our unified support for the province’s agriculture and food industry.
The government’s ‘Buy Local’ campaign encourages consumers to buy products from Alberta’s hard-working farmers, ranchers and food processors that produce safe, nutritious food for Albertans, Canadians and the world.
“It’s time to let these hard-working Albertans know we have their back. Now, more than ever, we need to shop local and buy made-in-Alberta products. The next time you are grocery shopping or go out for dinner or a drink with your friends or family, support local to demonstrate your Alberta pride. We are pleased tariffs don’t impact the ag industry right now and will keep advocating for our ag industry.”
Alberta’s government supports consumer choice. We are providing tools to help folks easily identify Alberta- and Canadian-made foods and products. Choosing local products keeps Albertans’ hard-earned dollars in our province. Whether it is farm-fresh vegetables, potatoes, honey, craft beer, frozen food or our world-renowned beef, Alberta has an abundance of fresh foods produced right on our doorstep.
Quick facts
- This summer, Albertans can support local at more than 150 farmers’ markets across the province and meet the folks who make, bake and grow our food.
- In March 2023, the Alberta government launched the ‘Made in Alberta’ voluntary food and beverage labelling program to support local agriculture and food sectors.
- Through direct connections with processors, the program has created the momentum to continue expanding consumer awareness about the ‘Made in Alberta’ label to help shoppers quickly identify foods and beverages produced in our province.
- Made in Alberta product catalogue website
Related information
Alberta
Province to expand services provided by Alberta Sheriffs: New policing option for municipalities

Expanding municipal police service options |
Proposed amendments would help ensure Alberta’s evolving public safety needs are met while also giving municipalities more options for local policing.
As first announced with the introduction of the Public Safety Statutes Amendment Act, 2024, Alberta’s government is considering creating a new independent agency police service to assume the police-like duties currently performed by Alberta Sheriffs. If passed, Bill 49 would lay additional groundwork for the new police service.
Proposed amendments to the Police Act recognize the unique challenges faced by different communities and seek to empower local governments to adopt strategies that effectively respond to their specific safety concerns, enhancing overall public safety across the province.
If passed, Bill 49 would specify that the new agency would be a Crown corporation with an independent board of directors to oversee its day-to-day operations. The new agency would be operationally independent from the government, consistent with all police services in Alberta. Unlike the Alberta Sheriffs, officers in the new police service would be directly employed by the police service rather than by the government.
“With this bill, we are taking the necessary steps to address the unique public safety concerns in communities across Alberta. As we work towards creating an independent agency police service, we are providing an essential component of Alberta’s police framework for years to come. Our aim is for the new agency is to ensure that Albertans are safe in their communities and receive the best possible service when they need it most.”
Additional amendments would allow municipalities to select the new agency as their local police service once it becomes fully operational and the necessary standards, capacity and frameworks are in place. Alberta’s government is committed to ensuring the new agency works collaboratively with all police services to meet the province’s evolving public safety needs and improve law enforcement response times, particularly in rural communities. While the RCMP would remain the official provincial police service, municipalities would have a new option for their local policing needs.
Once established, the agency would strengthen Alberta’s existing policing model and complement the province’s current police services, which include the RCMP, Indigenous police services and municipal police. It would help fill gaps and ensure law enforcement resources are deployed efficiently across the province.
Related information
-

 2025 Federal Election1 day ago
2025 Federal Election1 day agoRCMP Whistleblowers Accuse Members of Mark Carney’s Inner Circle of Security Breaches and Surveillance
-

 Autism2 days ago
Autism2 days agoAutism Rates Reach Unprecedented Highs: 1 in 12 Boys at Age 4 in California, 1 in 31 Nationally
-

 Health2 days ago
Health2 days agoTrump admin directs NIH to study ‘regret and detransition’ after chemical, surgical gender transitioning
-

 Also Interesting1 day ago
Also Interesting1 day agoBetFury Review: Is It the Best Crypto Casino?
-
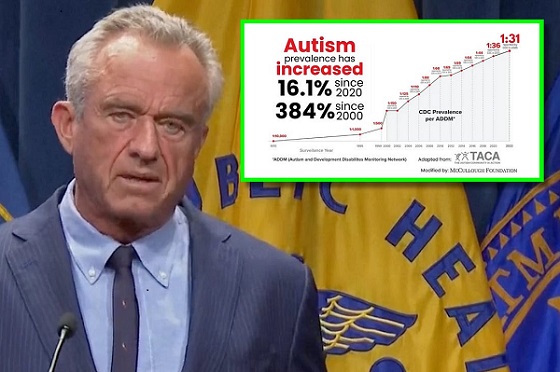
 Autism1 day ago
Autism1 day agoRFK Jr. Exposes a Chilling New Autism Reality
-
 COVID-191 day ago
COVID-191 day agoCanadian student denied religious exemption for COVID jab takes tech school to court
-

 2025 Federal Election1 day ago
2025 Federal Election1 day agoBureau Exclusive: Chinese Election Interference Network Tied to Senate Breach Investigation
-
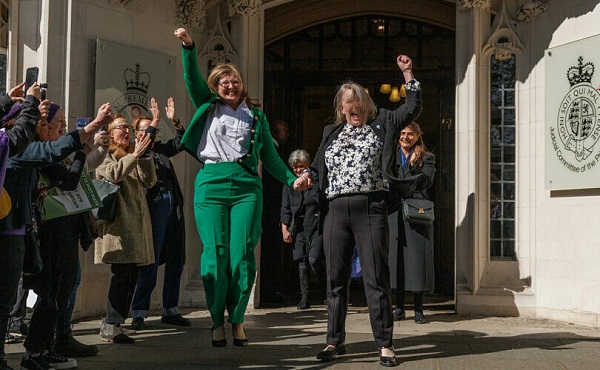 International1 day ago
International1 day agoUK Supreme Court rules ‘woman’ means biological female
 Mission failure: The rupture of Calgary’s high-pressure water main on June 5 flooded 16th Avenue and threatened the city’s water supply; repairs were halted for a day after two workers were injured, an excess of caution that led to anger and frustration over the city’s basic competence. (Sources of photos: (top)
Mission failure: The rupture of Calgary’s high-pressure water main on June 5 flooded 16th Avenue and threatened the city’s water supply; repairs were halted for a day after two workers were injured, an excess of caution that led to anger and frustration over the city’s basic competence. (Sources of photos: (top)  Built in 1975, the Bearspaw South feeder main draws from the Bearspaw Water Treatment Facility on the Bow River (bottom) and supplies 60 percent of Calgary’s drinking water. (Sources of photos: (top)
Built in 1975, the Bearspaw South feeder main draws from the Bearspaw Water Treatment Facility on the Bow River (bottom) and supplies 60 percent of Calgary’s drinking water. (Sources of photos: (top)  A story full of holes: City officials said the water main had been inspected and tested regularly, and that no leaks had been found; experts pointed out a catastrophic breakage of the line’s multi-layered structure would not likely begin with small leaks – and it emerged the line had not actually been drained and inspected since 2007. (Sources: (left photo)
A story full of holes: City officials said the water main had been inspected and tested regularly, and that no leaks had been found; experts pointed out a catastrophic breakage of the line’s multi-layered structure would not likely begin with small leaks – and it emerged the line had not actually been drained and inspected since 2007. (Sources: (left photo)  Pointing fingers: Calgary mayor Jyoti Gondek blamed Alberta’s UCP government for denying Calgary the money for maintenance and repairs; however, Calgary had never asked for such funding, and in any case received $224 million this year to allocate as it pleased. (Source of screenshot:
Pointing fingers: Calgary mayor Jyoti Gondek blamed Alberta’s UCP government for denying Calgary the money for maintenance and repairs; however, Calgary had never asked for such funding, and in any case received $224 million this year to allocate as it pleased. (Source of screenshot:  Core failures: As in many Western cities, Calgary’s leadership refuses to focus on the basic responsibilities of municipal government, like fixing potholes, clearing snow or ensuring public transit is safe and effective; it prefers building bike lanes people don’t use and planning the next multi-billion-dollar transit line. (Sources of photos (clockwise starting top left):
Core failures: As in many Western cities, Calgary’s leadership refuses to focus on the basic responsibilities of municipal government, like fixing potholes, clearing snow or ensuring public transit is safe and effective; it prefers building bike lanes people don’t use and planning the next multi-billion-dollar transit line. (Sources of photos (clockwise starting top left):  Crisis of competence: Experienced technical specialists, managers and tradesman have been leaving or getting purged from organizations that prioritize conformity to progressive causes like ESG and wokism over the nuts and bolts of keeping systems running. At bottom, engineer James Buker, a retired city waterworks employee. (Source of bottom photo:
Crisis of competence: Experienced technical specialists, managers and tradesman have been leaving or getting purged from organizations that prioritize conformity to progressive causes like ESG and wokism over the nuts and bolts of keeping systems running. At bottom, engineer James Buker, a retired city waterworks employee. (Source of bottom photo:  Hectoring and lecturing: When the state of emergency was declared, local media focussed increasingly citizens’ compliance with water restrictions; the mayor lectured Calgarians on the need to “dig in and do a little bit more”. Shown at bottom, people filling their water jugs at the city’s emergency supply trailer. (Sources of photos: (top)
Hectoring and lecturing: When the state of emergency was declared, local media focussed increasingly citizens’ compliance with water restrictions; the mayor lectured Calgarians on the need to “dig in and do a little bit more”. Shown at bottom, people filling their water jugs at the city’s emergency supply trailer. (Sources of photos: (top)  Water, water everywhere: The clampdown was based on a fear the city would not have enough water to fight a single major fire, this in a city posting daily water surpluses of 100 million litres, with two rivers (including the Bow River shown at top), two large reservoirs (including the Glenmore Reservoir shown at bottom) and multiple small water bodies to draw from.
Water, water everywhere: The clampdown was based on a fear the city would not have enough water to fight a single major fire, this in a city posting daily water surpluses of 100 million litres, with two rivers (including the Bow River shown at top), two large reservoirs (including the Glenmore Reservoir shown at bottom) and multiple small water bodies to draw from. They don’t make ‘em like they used to: The water main break forced the city to rely on the 92-year-old Glenmore Water Treatment Plant (right), built on the north side of the Glenmore Reservoir (left), an engineering marvel of its era.
They don’t make ‘em like they used to: The water main break forced the city to rely on the 92-year-old Glenmore Water Treatment Plant (right), built on the north side of the Glenmore Reservoir (left), an engineering marvel of its era. “Logic clearly dictates that the needs of the many outweigh the needs of the few,” said Star Trek’s Mr. Spock (left); the same progressives who used to nod in agreement to that line seemed more worried about two injured workers than the mission to repair infrastructure critical to 1.6 million Calgarians. Shown at right, a Japanese kamikaze pilot in a damaged single-engine bomber over the U.S. Aircraft Carrier USS Essex, off the Philippine Islands, November 1944. (Source of right photo:
“Logic clearly dictates that the needs of the many outweigh the needs of the few,” said Star Trek’s Mr. Spock (left); the same progressives who used to nod in agreement to that line seemed more worried about two injured workers than the mission to repair infrastructure critical to 1.6 million Calgarians. Shown at right, a Japanese kamikaze pilot in a damaged single-engine bomber over the U.S. Aircraft Carrier USS Essex, off the Philippine Islands, November 1944. (Source of right photo: 




