Addictions
London Police Chief warns parliament about “safer supply” diversion

London Police Chief Thai Truong testifies to House of Commons Standing Committee on November 26, 2024.
By Adam Zivo
“Vulnerable individuals are being targeted by criminals who exchange these prescriptions for fentanyl, exacerbating addiction and community harm,” said London Police Chief Thai Truong.
Thai Truong, the police chief of London, Ontario, testified in parliament last week that “safer supply” opioids are “obviously” being widely diverted to the black market, leading to greater profits for organized crime. His insights further illustrate that the safer supply diversion crisis is not disinformation, as many harm reduction advocates have speciously claimed.
Truong’s testimony was given to the House of Commons Standing Committee on Health, which is in the midst of an extended study into the opioid crisis. While the committee has heard from dozens of witnesses, Truong’s participation was particularly notable, as safer supply was first piloted in London in 2016 and the city has, since then, been a hotbed for opioid diversion.
“While the program is well intentioned, we are seeing concerning outcomes related to the diversion of safe supply medications… these diverted drugs are being resold within our community, trafficked to other jurisdictions, and even used as currency to obtain fentanyl, perpetuating the illegal drug trade,” he said in his opening speech. “Vulnerable individuals are being targeted by criminals who exchange these prescriptions for fentanyl, exacerbating addiction and community harm.”
He later clarified to committee members that these vulnerable individuals include women who are being pressured to obtain safer supply opioids for black market resale.
Safer supply programs are supposed to provide pharmaceutical-grade addictive drugs – mostly 8-mg tablets of hydromorphone, an opioid as potent as heroin – as an alternative to riskier street substances. The programs generally supply these drugs at no cost to recipients, with almost no supervised consumption, and have a strong preference for Dilaudid, a brand of hydromorphone that is manufactured by Purdue Pharma.
Addiction experts and police leaders across Canada have reported that safer supply patients regularly divert their hydromorphone to the black market. A recent study by Dr. Brian Conway, director of Vancouver’s Infectious Disease Centre, for example, showed that a quarter of his safer supply patients diverted all of their hydromorphone, and that another large, but unknown, percentage diverted at least some of their pills.
Truong’s parliamentary testimony, which mostly rehashed information he shared in a press conference last July, further corroborated these concerns.
He noted that in 2019, the city’s police force seized 847 hydromorphone pills, of which only 75 were 8-mg Dilaudids. Seizures increased after access to safer supply expanded in 2020, and, by 2023, exploded to over 30,000 pills (a roughly 3,500 per cent increase), of which roughly half were 8-mg Dilaudids. During this period, the number of annual overdose deaths in the city also increased from 73 to 123 (a 68 per cent increase), he said.
Relatedly, Truong noted that the price of hydromorphone in London – $2-5 a pill – is now much lower than in other parts of the province.
As an increasing number of police departments across Canada have publicly acknowledged that they are seeing skyrocketing hydromorphone seizures, some safer supply advocates have claimed, without evidence, that these pills were mostly stolen from pharmacies, and not diverted by safer supply patients. Truong’s parliamentary testimony dispelled this myth: “These increases cannot be attributed to pharmacy thefts, as London has had only one pharmacy robbery since 2019.”
The police chief declined to answer repeated questions about the efficacy of safer supply, or to opine on whether the experimental program should be replaced with alternative interventions with stronger evidence bases. “I’m not here to criticize the safe supply program, but to address the serious challenges associated with its diversion,” he said, noting his own lack of medical expertise.
The chief emphasized that, while more needs to be done to stop safer supply diversion, the addiction crisis is a “complex issue” that cannot be tackled solely through law enforcement. He advocated for a “holistic” approach that integrates prevention, harm reduction and treatment, and acknowledged the importance of London’s community health and social service partners.
Our content is always free. Subscribe to get BTN’s latest news and analysis,
or donate to our journalism fund.
In response to Truong’s testimony, NDP MP Gord Johns, an avid safer supply advocate, downplayed the importance of the diversion crisis by arguing that “people aren’t dying from a safer supply of drugs; they’re dying from fentanyl.”
While it is true that 81 per cent of overdose deaths in 2024 involved fentanyl, addiction physicians across Canada have repeatedly debunked Johns’ argument as misleading. The dangers of diverted hydromorphone is not that it directly kills users, but rather that it easily hooks individuals into addiction, leading many of them to graduate to deadly fentanyl use.
Johns previously faced criticism when, in a September health committee meeting, he seemingly used parliamentary maneuvers to reduce the speaking time of a grieving father, Greg Sword, whose daughter, Kamilah, died of drug-related causes after she and her friends got hooked on diverted hydromorphone.
There is currently no credible evidence that safer supply works. Most supporting studies simply interview safer supply patients and present their opinions as objective fact, despite significant issues with bias and reliability. Data presented in a 2024 study published in the British Medical Journal, which followed over 5,000 drug users in B.C., showed that safer supply led to no statistically significant mortality reductions once confounding factors were fully filtered out.
An impending update to Canada’s National Opioid Use Disorder Guideline, which was recently presented at a conference organized by the Canadian Society of Addiction Medicine, determined that the evidence base for safer supply is “essentially low-level.” Similarly, B.C’s top doctor acknowledged earlier this year that safer supply is “not fully evidence-based.”
This article was syndicated in The Bureau, an online media publication that investigates foreign interference, organized crime, and the drug trade.
Addictions
Manitoba Is Doubling Down On A Failed Drug Policy
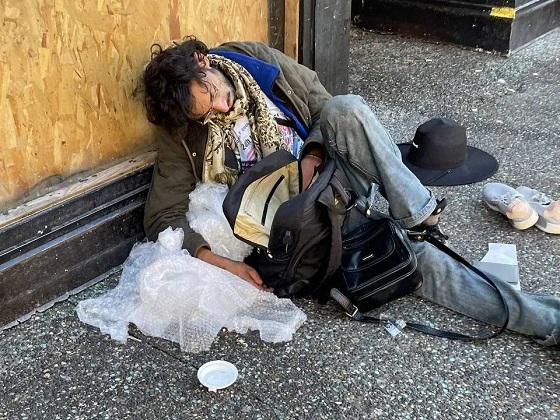

From the Frontier Centre for Public Policy
Manitoba is choosing to expand the same drug policy model that other provinces are abandoning, policies that normalize addiction while sidelining treatment, recovery, and public safety.
The New Democrat premier of British Columbia, David Eby, stood before reporters last spring and called his government’s decision to permit public drug use in certain spaces a failure.
The policy was part of the broader “harm reduction” strategy meant to address overdose deaths. Instead, it had stirred public anger, increased street disorder and had helped neither users nor the communities that host them. “We do not accept street disorder that makes communities feel unsafe,” Eby said. The province scrapped the plan.
In Alberta, the Conservative government began shutting down safer-supply prescribing due to concerns about drug diversion and misuse. The belief that more opioids can resolve the opioid crisis is losing credibility.
Ontario Progressive Conservatives are moving away from harm reduction by shutting down supervised consumption sites near schools and limiting safer-supply prescribing. Federal funding for programs is decreasing, and the province is shifting its focus to treatment models, even though not all sites are yet closed.
Yet amid these non-partisan reversals, Manitoba’s government has announced its intention to open a supervised drug-use site in Winnipeg. Premier Wab Kinew said, “We have too many Manitobans dying from overdose.” True. But it does not follow that repeating failed approaches will yield different results.
Reversing these failed policies is not a rejection of compassion. It is a recognition that good intentions do not produce good outcomes. Vancouver and Toronto have hosted supervised drug-use sites for years. The death toll keeps rising. Drug deaths in British Columbia topped 2,500 in 2023, even with the most expansive harm reduction infrastructure in the country. A peer-reviewed study published this year found that hospitalizations from opioid poisoning rose after B.C.’s safer-supply policy was implemented. Emergency department visits increased by more than three cases per 100,000 population, with no corresponding drop in fatal overdoses.
And the problem persists day to day. Paramedics in B.C. responded to nearly 4,000 overdose calls in July 2024 alone. The monthly call volume has exceeded 3,000 almost every month this year. These are signs of crisis management without a path to recovery.
There are consequences beyond public health. These policies change the character of neighbourhoods. Businesses suffer. Residents feel unsafe. And most tragically, the person using drugs is offered little more than a cot, a nurse and a quiet signal to continue. Real help, like treatment, housing and purpose, remains out of reach.
Somewhere along the way, bureaucracies stopped asking what recovery looks like. They have settled for managing human decline. They call it compassion. But it is really surrender, wrapped in medical language.
Harm reduction had its time. It made sense when it first emerged, during the AIDS crisis, when dirty needles spread HIV. Back then, the goal was to stop a deadly virus. Today, that purpose has been lost.
When policy drifts into ideology, reality becomes an afterthought. Underneath today’s approach is the belief that drug use is inevitable, that people cannot change, that liberty means letting others fade away quietly. These ideas do not reflect science. They do not reflect hope. They reflect despair. They reflect a politics that prioritizes the appearance of compassion over effectiveness.
What Manitoba needs is treatment access that meets the scale of the problem. That means detox beds, recovery homes and long-term care focused on restoring lives. These may not generate the desired headlines, but they work. They are demanding. They are slow. And they offer respect to the person behind the addiction.
There are no shortcuts. No policy will undo decades of pain overnight. But a policy that keeps people stuck using is not mercy. It is maintenance with no way out.
A government that believes in its people should not copy failure.
Marco Navarro-Genie is vice-president of research at the Frontier Centre for Public Policy and co-author, with Barry Cooper, of Canada’s COVID: The Story of a Pandemic Moral Panic (2023).
Addictions
The Death We Manage, the Life We Forget

 Marco Navarro-Génie
Marco Navarro-Génie
Our culture has lost the plot about what it means to live.
Reading that Manitoba is bringing supervised consumption to Winnipeg got me thinking.
Walk through just about any major Canadian city, and you will see them. Figures bent forward at seemingly impossible angles, swaying in the characteristic “fentanyl fold,” suspended between consciousness and oblivion. They resemble the zombies of fiction: bodies that move through space without agency, awareness, or connection to the world around them. We think of zombies as the walking dead. Health workers and bureaucrats reverse their overdoses, send them back to the street, and call it saving lives.
At the same time, Canada offers medical assistance in dying to a woman who cited chemical sensitivities and the inability to find housing. It has been offered to veterans who asked for support and were met instead with an option for death. We fight to prevent one form of death while facilitating another. The contradiction is not accidental. It reveals something about the people involved and the funding behind it. That’s our culture. Us. It appears to me that our culture no longer knows what life is.
Ask any politician or program bureaucrat, and you will hear them explain, in the dry language of bureaucracy, that the twin approach to what they call harm reduction and medical assistance in dying (MAiD) rests on the shared premise of what they believe to be compassion. They think they respect autonomy, prevent suffering, and keep people alive when possible. It sounds humane. It is, in practice, incoherent. Bear with me for a moment.
The medical establishment administers naloxone to reverse overdoses in people who spend as many as twenty hours a day unconscious. They live without meaningful relationships or memories, with little capacity for choice. The technocrats and politicians call that saving lives. They also provide assisted death to people whose suffering comes primarily from poverty, isolation, or lack of housing. There was a time when these factors could, at least in theory, be addressed so that the terminal decision did not need to be made. Now they are accepted as grounds for ending life.
But why is one preference final and the other treated as an error to correct? That question reflects the deeper disorientation.
We saw the same thing during COVID. Elderly people in care homes were left without touch, family, or comfort for days. They often died in solitude, their dementia accelerated by isolation. And those conditions were inflicted upon them in the name of saving their lives. The “system” measured success in preventing infections, not in preserving connections. Je me souviens. Or we should.
There is a pattern here. We have reduced the idea of saving lives to keeping bodies breathing, while ignoring what makes a life human: agency, meaning, development, and relationship. And in doing so, we begin to define life as mere biological persistence. But to define life by the capacity to breathe and perform basic functions is to place ourselves on the same footing as the non-human animals. It is to say, tacitly, that there is no fundamental distinction between a person and a creature. That, too, is a form of forgetting.
To be clear, the argument here is not that hopeless drug users should be administered MAiD. Instead, it is essential to recognize that the intellectual framework behind harm reduction and MAiD must be taken seriously, as it rests on some rationally defensible claims. In an age where most arguments are emotive and unexamined, the mildly logical has become strangely compelling.
It begins with the idea of autonomy. We cannot force others to live by our values. Every person must decide what makes life worth living. To insist otherwise is paternalism.
Then comes pragmatic compassion. People will use drugs whether we approve or not. People will find their lives unbearable, whether we acknowledge it or not. We can support them or moralize while they die.
There is also an emphasis on subjective experience. No one knows another’s pain. If someone says their suffering is intolerable, we are in no position to deny it, they say. If a user would rather face opioids than withdrawal and despair, are we entitled to interfere?
Finally, the comparison to medical ethics: we do not withhold insulin from diabetics who continue to eat poorly. We do not deny cancer treatment to smokers. Medicine responds to suffering, even when the patient has contributed to their condition. Harm reduction, they argue, simply applies that principle to addiction.
These arguments produced tangible benefits, they argue. Needle exchanges reduced HIV transmission. Naloxone kits prevented deaths. Safe injection sites meant fewer people dying alone. MAiD brought relief to those in agony. These were not trivial outcomes. I am aware.
Yet when we look more closely, the very logic that underlies these policies also exposes their fatal limitations.
Addiction undermines choice. It hijacks the brain’s ability to reason, compare, and choose. A person deep in addiction is not selecting between alternatives like someone choosing coffee or tea. The structure of choice, the human will, itself is broken. The addiction decides before the person does. St Augustine knew this. Dostoyevsky knew it too.
And for the empirically minded, the research supports this. In British Columbia, where the “safe supply” model was pioneered, some addiction physicians now say the policy is failing. Worse, it may be creating new opioid dependencies in people who were not previously addicted. A study earlier this year found that opioid‑related hospitalizations increased by about 33 percent, compared with pre‑policy rates. With the later addition of a drug-possession decriminalization policy, hospitalizations rose even more (overall, a 58 percent increase compared to before SOS’s implementation). The study concluded that neither safer supply nor decriminalization was associated with a statistically significant reduction in overdose deaths. This is not freedom. It is a new form of bondage, meticulously paved by official compassion.
Despair disguises itself as autonomy, especially in a spiritually unmoored culture that no longer knows how to cope with suffering. A person requesting assisted death because of chronic, untreatable pain may appear lucid and composed, but lucidity is not the same as wisdom. One can reason clearly from false premises. If life is reduced to the absence of pain and the preservation of comfort, then the presence of suffering will seem like failure, and death will appear rational. But that is not a genuine choice because it is based on a misapprehension of what life is. All life entails pain. Some of it is redemptive. Some of it is endured. But it does not follow that the presence of suffering justifies the conclusion of life.
Someone turning to drugs because of homelessness, abandonment, or despair is often in an even deeper eclipse of the will. Here, there is not even the appearance of deliberation, only the reach for numbness in the absence of meaning. What looks like a decision is the residue of collapse. We are not witnessing two forms of autonomy, one clearer than the other. We are witnessing the breakdown of autonomy in various forms, and pretending that it is freedom.
Biological survival is not life. When we maintain someone in a state of near-constant unconsciousness, with no relationships, no capacity for flourishing, we are not preserving life. We are preserving a body. The person may already be gone. To define life as nothing more than breathing and performing bodily functions is to deny what makes us human. It reduces us to the level of non-human creatures, sentient, perhaps, but without reason, memory, moral reflection, or the possibility of transcendence. It tacitly advances the view that there is no essential difference between a person and a critter, so long as both breathe and respond to some stimuli.
Governments do these things to keep ballooning overdosing deaths down, preferring to maintain drugs users among the undead instead. That reminds me of how the Mexican government hardly moves a finger to find the disappeared, 100,000 strong of lately. For as long ss they’re disappeared, they choose not to count them as homicides, and they feel justified in ignoring the causes of all the killing around them.
Some choices are nefarious. Some choices deserve challenge. Not all autonomous acts are equal. The decision to continue living with pain, or to fight addiction, requires agency. The decision to surrender to despair may signal the absence of it. To say all choices are equal is to empty the word autonomy of meaning.
This reflects a dangerously thin view of the human person that permeates our present. What we now call “harm” is only death or physical pain. What we call good is whatever someone prefers. But people are more than collections of wants.
We should have learned this by now. In Alberta, safer supply prescribing was effectively banned in 2022. Officials cited diversion and lack of measurable improvement. We are forcing some people into treatment because we recognize the impairment of judgement in addiction.
In British Columbia, public drug use was quietly re-criminalized after communities rebelled. This was an admission of policy failure. “Keeping people safe is our highest priority,” Premier David Eby said. Yet safe supply remains. In 2023, the province recorded more than 2,500 overdose deaths. Paramedics continue to respond to thousands of overdose calls each month. This is not success. It is a managed collapse.
Meanwhile, Manitoba is preparing to open its own supervised drug-use site. Premier Wab Kinew said, “We have too many Manitobans dying from overdose… so this is one tool we can use.” That may be so. However, it is a tool that others are beginning to set aside. It is a largely discredited tool. Sadly, in the self-professed age of “Reconciliation” with Aboriginal Canadians, Aboricompassionadians are disproportionately affected by these discredited policies.
The Manitoba example illustrates the broader problem, despite damning evidence. Instead of asking what helps people live, we ask whether they gave consent. We do not ask whether they were capable of it. We ask whether they avoided death. We do not ask whether they found purpose.
We are not asking what might lead someone out of addiction. We are not asking what they need to flourish. We ask only what we can do to prevent them from dying in the short term. And when that becomes impossible, technocracy offers them death in a more organized form, cleanly approved by government. That’s compasson.
The deeper problem is not policy incoherence. It is the cultural despair that skates on the thin ice of meaninglessness. These policies make sense only in a culture that has already decided life is not worth too much. What matters is state endorsement and how it’s done .
It is more cost-effective to distribute naloxone than to construct long-term recovery homes. It is easier to train nurses to supervise injection than to provide months of residential treatment. It is far simpler to legalize euthanasia for the poor and the suffering than to work on solutions that lift them out of both. But is it right?
This is not compassion. It is surrender.
A humane policy would aim to restore agency, not validate its absence. It would seek out what helps people grow in wisdom and self-command, not what leaves them comfortably sedated. It would measure success not in lives prolonged into darker dependency but in persons recovered. In lives better lived.
This vision is harder. It costs time. It requires greater effort. It requires care and what some Christians call love of neighbour. It may require saying no when someone asks for help that could lead to ruin. But anything less is not mercy. It is a slow walk toward death while we leave the “system” to pretend there is no choice.
We did have a choice. We chose shallow comfort over deep obligation. We chose to manage symptoms rather than confront the deeper conditions of our age: loneliness, meaninglessness, despair. And now we live among the results: more, not fewer, people swaying in silence, already gone walking dead.
We might ask what we’ve forgotten about suffering, about responsibility, about what life is. Lives are at stake. True. But when our understanding of life is misdirected, so will be the policies the state gives us.
We are grateful that you’re reading Haultain Research.
For the full experience, and to help us bring you more quality research and commentary,
-

 COVID-192 days ago
COVID-192 days agoUniversity of Colorado will pay $10 million to staff, students for trying to force them to take COVID shots
-

 Bruce Dowbiggin2 days ago
Bruce Dowbiggin2 days agoIntegration Or Indignation: Whose Strategy Worked Best Against Trump?
-

 espionage2 days ago
espionage2 days agoWestern Campuses Help Build China’s Digital Dragnet With U.S. Tax Funds, Study Warns
-

 Bruce Dowbiggin2 days ago
Bruce Dowbiggin2 days agoWayne Gretzky’s Terrible, Awful Week.. And Soccer/ Football.
-

 Agriculture2 days ago
Agriculture2 days agoCanada’s air quality among the best in the world
-

 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoCanada invests $34 million in Chinese drones now considered to be ‘high security risks’
-

 Great Reset1 day ago
Great Reset1 day agoSurgery Denied. Death Approved.
-
 Health2 days ago
Health2 days agoCDC Vaccine Panel Votes to End Universal Hep B Vaccine for Newborns








