Energy
LATE TO THE PARTY: Liberal Resource Minister Minister Suddenly Discovers Canada Needs East-West Pipeline

From Energy Now
By Jim Warren
On Thursday, February 6 federal energy and natural resources Minister Jonathan Wilkinson told reporters about a brilliant idea he’d come up with. He said Canada should think about building an east-west oil pipeline. He claimed doing so could provide Ontario, Quebec and parts further east greater security of supply.
Furthermore, such a pipeline would eliminate the need to buy tanker loads of oil from places like Saudi Arabia and Nigeria. And what’s more it could provide us with the opportunity to export Canadian oil to countries other than the US.
Talk about being late to the party. It’s as though the Energy East project never made it onto the national agenda.
Wilkinson told reporters how a pipeline like Enbridge’s Line 5 is vulnerable to shut down by US authorities. Line 5 carries oil from the prairies through the northern US Midwest before delivering it to the refinery and petrochemicals facilities at Sarnia, Ontario.
This is not breaking news. The Liberals have been well aware of the threat for years. Michigan governor, Gretchen Whitmer waged a well-publicized multi-year campaign to have Line 5 shut down.
According to a CBC report, Wilkinson said, “successive Canadian governments never really gave it much thought that a lot of the energy the country needs to power its economy flows through the U.S.”
That’s a stretch. He apparently doesn’t consider the governments of Alberta and Saskatchewan to be Canadian governments. The real problem is Ottawa wasn’t listening when premiers Notley, Kenney, Smith, Wall and Moe explained the value of an all-Canadian Energy East pipeline. They also had plenty to say about the cancellation of Energy East in 2017 and the role Ottawa played by creating the regulatory approval quagmire that helped kill it.
No less puzzling is that Wilkinson imagines such a pipeline could ever be built under the BANANAs (build absolutely nothing, anywhere, near anything) regulatory barriers implemented by the Liberals which make it next to impossible for anyone to build a new pipeline. When Jason Kenney referred to Bill C-69 as The No More Pipelines Bill he wasn’t just whistling Dixie.
The only major export pipeline to be built in the wake of C-69, was the Trans Mountain expansion (TMX). And it was only completed because the owner, the Government of Canada, was prepared to incur the staggering costs of navigating its own pipeline approval regulations. A pipeline originally budgeted to cost $6.8 billion wound up costing an additional $54 billion. Sane investors simply aren’t prepared to accept that level of unreasonable cost and uncertainty.
A first step in getting new pipelines built would be eliminating Bill C-69 along with Bill C-48, the West coast tanker ban. Wilkinson didn’t touch on those points when telling reporters about his bold new idea.
One has to wonder, after11 years of anti-oil and anti-pipeline policy making, if Wilkinson really means what he’s saying. Has he truly experienced a road to Damascus level conversion due to the threat of US tariffs?
Another plausible explanation for Wilkinson’s call for the resurrection of Energy East is that he’s seen the polling numbers. An Angus Reid poll conducted earlier this month shows 79% of Canadians from across the country support new oil and gas pipelines to tidewater on the east and west coasts. The poll also shows 74% of Quebec respondents now support the idea of building new pipelines to tidewater.

If those numbers hold, Canada’s next government could possibly revisit Energy East. If they succeeded in getting the line built it would represent the most visionary nation building project since the building of the trans-continental railway.
No less surprising is, despite the rise in public support for pipelines, Quebec Premier Francois Legault says he won’t accept a new oil pipeline in his province. Legault is out of step with Quebec opinion on more issues than pipelines. The separatist Parti Quebecois is currently leading Legault’s Coalition Avenir Quebec by 10 points in party preference polls. This is not to say the PQ is any more pipeline friendly.
After11 years of Liberal anti-oil and anti-pipeline policy making, Wilkinson is finally on the right side of the Energy East idea. Some might say better late than never—better to change one’s mind than to continue being wrong. Others will say it is a flip flop of epic proportions and questionable sincerity. Skeptical pundits will question whether Wilkinson’s new found fondness for pipelines is any more credible than Mark Carney’s pledge to get rid of the carbon tax.
Wilkinson is a bright man, so it is possible he has believed Energy East was a good idea for some time. Too bad he didn’t tell us sooner. He waited too long to come clean to expect electoral redemption.
Canadian Energy Centre
First Nations in Manitoba pushing for LNG exports from Hudson’s Bay

From the Canadian Energy Centre
By Will Gibson
NeeStaNan project would use port location selected by Canadian government more than 100 years ago
Building a port on Hudson’s Bay to ship natural resources harvested across Western Canada to the world has been a long-held dream of Canadian politicians, starting with Sir Wilfred Laurier.
Since 1931, a small deepwater port has operated at Churchill, Manitoba, primarily shipping grain but more recently expanding handling of critical minerals and fertilizers.
A group of 11 First Nations in Manitoba plans to build an additional industrial terminal nearby at Port Nelson to ship liquefied natural gas (LNG) to Europe and potash to Brazil.
Robyn Lore, a director with project backer NeeStaNan, which is Cree for “all of us,” said it makes more sense to ship Canadian LNG to Europe from an Arctic port than it does to send Canadian natural gas all the way to the U.S. Gulf Coast to be exported as LNG to the same place – which is happening today.
“There is absolutely a business case for sending our LNG directly to European markets rather than sending our natural gas down to the Gulf Coast and having them liquefy it and ship it over,” Lore said. “It’s in Canada’s interest to do this.”
Over 100 years ago, the Port Nelson location at the south end of Hudson’s Bay on the Nelson River was the first to be considered for a Canadian Arctic port.
In 1912, a Port Nelson project was selected to proceed rather than a port at Churchill, about 280 kilometres north.
The Port Nelson site was earmarked by federal government engineers as the most cost-effective location for a terminal to ship Canadian resources overseas.
Construction started but was marred by building challenges due to violent winter storms that beached supply ships and badly damaged the dredge used to deepen the waters around the port.
By 1918, the project was abandoned.
In the 1920s, Prime Minister William Lyon MacKenzie King chose Churchill as the new location for a port on Hudson’s Bay, where it was built and continues to operate today between late July and early November when it is not iced in.
Lore sees using modern technology at Port Nelson including dredging or extending a floating wharf to overcome the challenges that stopped the project from proceeding more than a century ago.
He said natural gas could travel to the terminal through a 1,000-kilometre spur line off TC Energy’s Canadian Mainline by using Manitoba Hydro’s existing right of way.
A second option proposes shipping natural gas through Pembina Pipeline’s Alliance system to Regina, where it could be liquefied and shipped by rail to Port Nelson.
The original rail bed to Port Nelson still exists, and about 150 kilometers of track would have to be laid to reach the proposed site, Lore said.
“Our vision is for a rail line that can handle 150-car trains with loads of 120 tonnes per car running at 80 kilometers per hour. That’s doable on the line from Amery to Port Nelson. It makes the economics work for shippers,” said Lore.
Port Nelson could be used around the year because saltwater ice is easier to break through using modern icebreakers than freshwater ice that impacts Churchill between November and May.
Lore, however, is quick to quell the notion NeeStaNan is competing against the existing port.
“We want our project to proceed on its merits and collaborate with other ports for greater efficiency,” he said.
“It makes sense for Manitoba, and it makes sense for Canada, even more than it did for Laurier more than 100 years ago.”
Energy
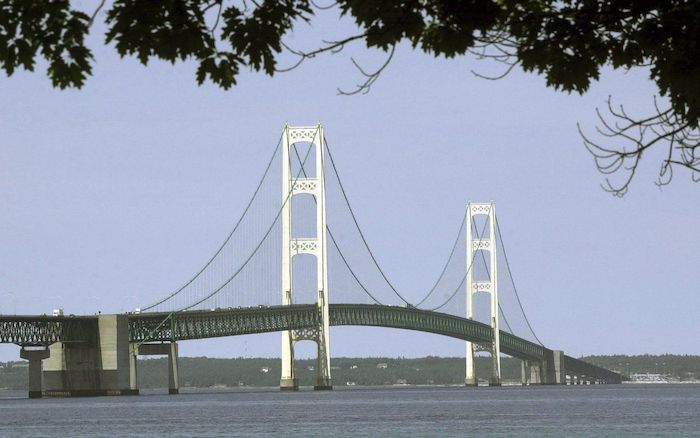
Straits of Mackinac Tunnel for Line 5 Pipeline to get “accelerated review”: US Army Corps of Engineers


From the Daily Caller News Foundation
By Audrey Streb
The Army Corps of Engineers on Tuesday announced an accelerated review of a Michigan pipeline tunnel under the Straits of Mackinac following President Donald Trump’s declaration of a “national energy emergency” on day one of his second term.
Enbridge’s Line 5 oil pipeline is among 600 projects to receive an emergency designation following Trump’s January executive order declaring a national energy emergency and expediting reviews of pending energy projects. The action instructed the Army Corps to use emergency authority under the Clean Water Act to speed up pipeline construction.
“An energy supply situation which would result in an unacceptable hazard to life, a significant loss of property, or an immediate, unforeseen, and significant economic hardship,” if not acted upon quickly, the public notice reads.

U.S. President Donald Trump holds up a signed executive order as (L-R) U.S. Treasury Secretary Scott Bessent, Secretary of Commerce Howard Lutnick and Interior Secretary Doug Burgum look on in the Oval Office of the White House on April 09, 2025 in Washington, DC. (Photo by Anna Moneymaker/Getty Images)
“Line 5 is critical energy infrastructure,” Calgary-based Enbridge wrote to the DCNF. The company noted that it submitted its permit applications to state and federal regulators five years ago and described the project as “designed to make a safe pipeline safer while also ensuring the continued safe, secure, and affordable delivery of essential energy to the Great Lakes region.”
Army Corps’ Detroit District did not respond to the DCNF’s request for a copy of the notice or for comment.
The pipeline has been active since 1953 and extends for 645 miles across the state of Michigan, according to the Department of Environment, Great Lakes, and Energy website. Line 5 supplies 65% of the propane needs in Michigan’s Upper Peninsula and 55% of the state’s overall propane demand, according to Enbridge.
The project has faced legal trouble and permitting delays that have hindered its expansion. Michigan Democratic Gov. Gretchen Whitmer in 2019 used a legal opinion by Attorney General Dana Nessel to argue that the law that created the authority to approve the project “because its provisions go beyond the scope of what was disclosed in its title.”
The State of Michigan greenlit the project in 2021 and the Michigan Public Service Commission approved placing the new pipeline segment in 2023.
Trump has championed an American energy production revival, stating throughout his 2024 campaign that he wanted to “drill, baby, drill,” in reference to oil drilling on U.S. soil.
-

 2025 Federal Election2 days ago
2025 Federal Election2 days agoRCMP Whistleblowers Accuse Members of Mark Carney’s Inner Circle of Security Breaches and Surveillance
-

 Also Interesting2 days ago
Also Interesting2 days agoBetFury Review: Is It the Best Crypto Casino?
-
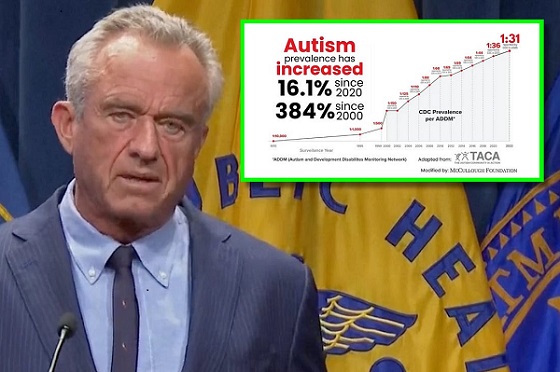
 Autism2 days ago
Autism2 days agoRFK Jr. Exposes a Chilling New Autism Reality
-
 COVID-191 day ago
COVID-191 day agoCanadian student denied religious exemption for COVID jab takes tech school to court
-

 2025 Federal Election2 days ago
2025 Federal Election2 days agoBureau Exclusive: Chinese Election Interference Network Tied to Senate Breach Investigation
-
 International1 day ago
International1 day agoUK Supreme Court rules ‘woman’ means biological female
-

 2025 Federal Election1 day ago
2025 Federal Election1 day agoNeil Young + Carney / Freedom Bros
-

 Health1 day ago
Health1 day agoWHO member states agree on draft of ‘pandemic treaty’ that could be adopted in May







