Business
King’s coronation cost taxpayers $534,000 and counting

From the Canadian Taxpayers Federation
Author: Franco Terrazzano
Trudeau’s troupe spent $305,188 on accommodations at the Edwardian Pastoria Hotels Ltd., a high-end luxury hotel chain in London. They also spent $45,760 at the Great Scotland Yard Hotel and $15,881 at the Southampton Row Hotel.
Prime Minister Justin Trudeau and the Canadian delegation to King Charles III’s coronation racked up $534,675 in expenses during the three-day trip.
Final costs are expected to rise even higher as expenses are still being processed, according to access-to-information records obtained by the Canadian Taxpayers Federation.
“The King’s coronation is a big event, but that doesn’t mean taxpayers should be paying half-a-million dollars so more than 100 people can travel to England,” said Franco Terrazzano, CTF Federal Director. “It seems like this government goes out of its way to bring along as many people as possible and to stay in the fanciest hotels.”
Canada’s delegation was 102 people strong – including 87 travelling with Trudeau and 15 travelling with Governor General Mary Simon. That means the cost per traveller was $5,241 for the three-day trip.
Trudeau’s troupe spent $305,188 on accommodations at the Edwardian Pastoria Hotels Ltd., a high-end luxury hotel chain in London. They also spent $45,760 at the Great Scotland Yard Hotel and $15,881 at the Southampton Row Hotel.
Simon and her entourage spent $155,283 on rooms at the London & Regional hotel.
Bureaucrats bought $300 worth of wine and beer for the flights to London, then spent $555 at “Majestic Wine London” upon arrival, according to the records.
“Did taxpayers really need to pay for 102 people to travel to England, and did they each need to rack up an average bill of $5,000?” Terrazzano said. “And if bureaucrats want to delete a couple cold ones, they’re paid more than enough money to pick up the tab themselves.”
King Charles III acceded to the throne Sept. 8, 2022, following the death of Queen Elizabeth II. His coronation was held at Westminster Abbey May 6, 2023.
In addition to Trudeau and Simon, the Canadian delegation included various bureaucrats, several Indigenous leaders, a handful of youth leaders and astronauts Jennifer Sidey-Gibbons and Jeremy Hanson, among others.
Canada also sent a sizeable delegation to Queen Elizabeth II’s state funeral in September 2022, racking up nearly $400,000 in hotel costs alone.
Included among those costs was a $6,000-per-night luxury suite at the Corinthia Hotel, which came with a marble bathroom and “complimentary butler service.”
After bureaucrats refused to disclose who had stayed in the River Suite, the CTF filed an access-to-information request. In response, the government released the records, but redacted the name.
The CTF then launched a legal challenge to force the government to disclose who stayed in the suite.
Trudeau finally admitted he stayed in the $6,000 per-night luxury suite during President Joe Biden’s visit to Canada in March 2023.
Documents obtained by the Toronto Sun in February revealed that federal bureaucrats were worried about the cost of hotels for the King’s coronation in the aftermath of the earlier scandal over the $6,000-per-night luxury suite.
Writing to a bureaucrat at Global Affairs Canada, Davon Singh, Director of the Executive Office & Head of Visits at Canada’s High Commission in London, wondered if the size of the Canadian delegation should be reduced to save on costs.
“Should we look into reduced numbers or stick with the amount you’ve currently sent us?” Singh wrote.
“I think we should keep our current numbers,” read the response from the Visits Coordinator for Global Affairs Canada.
2025 Federal Election
Poilievre will cancel Mark Carney’s new Liberal packaging law and scrap the Liberal plastic ban!

From Conservative Party Communications
Conservative Leader Pierre Poilievre promised today that a new Conservative government will stop Mark Carney’s proposed Liberal food tax and scrap the existing Liberal plastic ban. Poilievre will:
- Stop proposed new labelling and packaging requirements that will raise the cost of fresh produce by as much as 34% and cost the average Canadian household an additional $400 each year.
- Scrap the Liberal plastics ban, including the ban on straws, grocery bags, food containers and cutlery, and other single-use plastics, letting consumers and businesses choose what works for them.
- Protect restaurants, grocers, and low-income Canadians from one-size-fits-all packaging rules that disproportionately affect those who can least afford it.
“After the Lost Liberal Decade, many Canadians can barely afford to put food on the table. And now Mark Carney and the Liberals want to make it even harder with a new food packaging law that will raise the price of food–again,” said Poilievre. “A new Conservative government will keep food prices down by scrapping the Liberal plastic ban and stopping Carney’s new Liberal food tax.”
After a decade of out-of-control spending and massive tax increases, families are spending $800 more on food this year than they did in 2024, and food banks had to handle a record two million visits in a single month. In Montreal, 44 percent of CEGEP students are experiencing some form of food insecurity, while places like Hawkesbury, Kingston, Toronto and Mississauga have all declared food insecurity emergencies.
And food prices are still rocketing upwards, surging by 3.2% over the last year, with no end in sight. In the last month alone, food inflation increased by 1.9 percentage points—the largest monthly jump in food prices in decades.
As if this wasn’t bad enough, Liberals have made life even more expensive and inconvenient for Canadians by banning plastics – including everything from straws to bags to food packaging. The current Liberal ban on single-use plastics will cost Canadians $1.3 billion dollars over the next decade.

Now Mark Carney wants to make it worse by adding complicated and costly new food packaging rules that will drive up the price of food even more–in effect, a new Liberal food tax. Plastic food packaging makes up 1/3 of all plastic packaging in Canada. The proposed Liberal food tax will cost the average Canadian household an additional $400 each year, waste half a million tonnes of food, decrease access to imported fruit and produce, and increase food inflation. The Chemistry Industry Association of Canada has also warned that this tax will put up to 60,000 Canadians out of work.
“The Liberals’ ideological crusade against convenience has already driven up food prices and the last thing Canadians need is Mark Carney’s new food tax added directly to your grocery bill,” said Poilievre. “The choice for Canadians is clear, a fourth Liberal term that will make food even more expensive or a new Conservative government that will axe the food tax and bring back straws, grocery bags and other items, to make life more affordable and convenient for Canadians – For a Change.”
Business
Ted Cruz, Jim Jordan Ramp Up Pressure On Google Parent Company To Deal With ‘Censorship’

From the Daily Caller News Foundation
By Andi Shae Napier
Republican Texas Sen. Ted Cruz and Republican Ohio Rep. Jim Jordan are turning their attention to Google over concerns that the tech giant is censoring users and infringing on Americans’ free speech rights.
Google’s parent company Alphabet, which also owns YouTube, appears to be the GOP’s next Big Tech target. Lawmakers seem to be turning their attention to Alphabet after Mark Zuckerberg’s Meta ended its controversial fact-checking program in favor of a Community Notes system similar to the one used by Elon Musk’s X.
Cruz recently informed reporters of his and fellow senators’ plans to protect free speech.
Dear Readers:
As a nonprofit, we are dependent on the generosity of our readers.
Please consider making a small donation of any amount here. Thank you!
“Stopping online censorship is a major priority for the Commerce Committee,” Cruz said, as reported by Politico. “And we are going to utilize every point of leverage we have to protect free speech online.”
Following his meeting with Alphabet CEO Sundar Pichai last month, Cruz told the outlet, “Big Tech censorship was the single most important topic.”
Jordan, Chairman of the House Judiciary Committee, sent subpoenas to Alphabet and other tech giants such as Rumble, TikTok and Apple in February regarding “compliance with foreign censorship laws, regulations, judicial orders, or other government-initiated efforts” with the intent to discover how foreign governments, or the Biden administration, have limited Americans’ access to free speech.
“Throughout the previous Congress, the Committee expressed concern over YouTube’s censorship of conservatives and political speech,” Jordan wrote in a letter to Pichai in March. “To develop effective legislation, such as the possible enactment of new statutory limits on the executive branch’s ability to work with Big Tech to restrict the circulation of content and deplatform users, the Committee must first understand how and to what extent the executive branch coerced and colluded with companies and other intermediaries to censor speech.”
Jordan subpoenaed tech CEOs in 2023 as well, including Satya Nadella of Microsoft, Tim Cook of Apple and Pichai, among others.
Despite the recent action against the tech giant, the battle stretches back to President Donald Trump’s first administration. Cruz began his investigation of Google in 2019 when he questioned Karan Bhatia, the company’s Vice President for Government Affairs & Public Policy at the time, in a Senate Judiciary Committee hearing. Cruz brought forth a presentation suggesting tech companies, including Google, were straying from free speech and leaning towards censorship.
Even during Congress’ recess, pressure on Google continues to mount as a federal court ruled Thursday that Google’s ad-tech unit violates U.S. antitrust laws and creates an illegal monopoly. This marks the second antitrust ruling against the tech giant as a different court ruled in 2024 that Google abused its dominance of the online search market.
-
 Business1 day ago
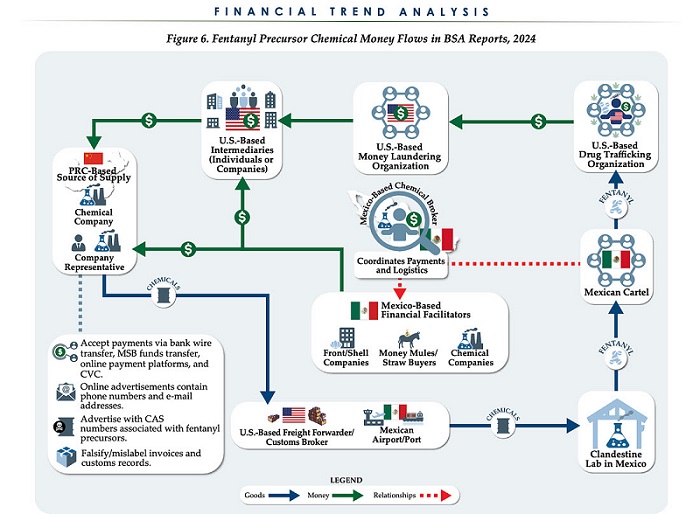
Business1 day agoChina, Mexico, Canada Flagged in $1.4 Billion Fentanyl Trade by U.S. Financial Watchdog
-

 2025 Federal Election2 days ago
2025 Federal Election2 days agoTucker Carlson Interviews Maxime Bernier: Trump’s Tariffs, Mass Immigration, and the Oncoming Canadian Revolution
-

 espionage1 day ago
espionage1 day agoEx-NYPD Cop Jailed in Beijing’s Transnational Repatriation Plot, Canada Remains Soft Target
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoDOGE Is Ending The ‘Eternal Life’ Of Government
-

 2025 Federal Election2 days ago
2025 Federal Election2 days agoCanada drops retaliatory tariffs on automakers, pauses other tariffs
-

 2025 Federal Election1 day ago
2025 Federal Election1 day agoBREAKING from THE BUREAU: Pro-Beijing Group That Pushed Erin O’Toole’s Exit Warns Chinese Canadians to “Vote Carefully”
-
 Daily Caller1 day ago
Daily Caller1 day agoDOJ Releases Dossier Of Deported Maryland Man’s Alleged MS-13 Gang Ties
-

 Daily Caller1 day ago
Daily Caller1 day agoTrump Executive Orders ensure ‘Beautiful Clean’ Affordable Coal will continue to bolster US energy grid





