Crime
Here’s How A Venezuelan Gang Was Able To Infiltrate The US And Wreak Havoc In Major Cities

From the Daily Caller News Foundation
A notorious Venezuelan gang is extending its tentacles into the U.S. on the back of the Biden-Harris administration’s border crisis, and experts say that immigration authorities have no way of identifying the criminal group’s members before they hit American soil.
The gang, known as Tren de Aragua, has made headlines in recent weeks with its criminal activities in multiple states, according to multiple reports. Yet, border authorities have virtually zero tools to detect Venezuelan migrants’ affiliations with the gang, as the U.S.’ diplomatic relationship with the beleaguered country is effectively on ice, experts told the Daily Caller News Foundation.
“We have next to no vetting for the Venezuelans who are entering the country, because we have no relationship with the government of Venezuela and that’s true of other migrant nationalities,” Jessica Vaughan, director of policy studies at the Center for Immigration Studies, told the DCNF. “We have no way of knowing whether they were in prison in Venezuela. We have no idea if they’ve been living in a third-world country for years before they tried to come to the United States. We’re essentially letting them in on their word.”
A hotel in El Paso, Texas, was shut down on Sept. 9 following an investigation into Tren de Aragua and other gangs’ use of the complex where alleged incidents of drug use and prostitution occurred, according to the El Paso Times. Additionally, the Dallas Police Department confirmed to the DCNF that there is an ongoing investigation into the gang’s activities in the area.
“We’re really not seeing Tren de Aragua operate in McAllen or Del Rio, or anything else like that,” Ammon Blair, former Customs and Border Patrol (CBP) agent and senior fellow at the Texas Public Policy Foundation, told the DCNF. “But they are operating in El Paso, because it’s a major city … there’s a large diaspora of Venezuelans there.”
In Aurora, Colorado, 10 Tren de Aragua members were identified by police on Sept. 11 as part of an investigation into a string of alleged criminal incidents at apartment complexes in the city, according to FOX 31. The alleged crimes include felony menacing, assault, motor vehicle theft and numerous shootings.
The property management company overseeing the complexes said the gang had effectively “taken over” the buildings, according to The Denver Post.
Tren de Aragua’s nefarious presence has even managed to draw the gaze of the Biden Treasury Department, which declared the gang a transnational criminal organization and announced sanctions in July, citing its involvement in human trafficking, drug trafficking and money laundering. Tren de Aragua started as a prison gang in the Venezuelan state of Aragua in 2013, taking over the Torocon prison and making it their base of operations, growing to around 5,000 members in 2023, according to Insight Crime.
Unlike other gangs, Tren de Aragua doesn’t have a defined set of tattoos that would make it easy for law enforcement to identify members, according to the El Paso Times. The gang’s main target is Venezuelan migrants, who they extort, smuggle and sex traffic to other countries, including the U.S., according to Insight Crime.
In order for CBP to get criminal records from Venezuelans, they would have to use Interpol data, as the U.S. doesn’t have a memorandum of agreement with Venezuela to exchange criminal records, Blair told the DCNF. Moreover, CBP often has to release the detainee before they can obtain criminal records from Interpol.
“Once Biden came into office and offered catch and release policies, temporary protected status, you name it, the Venezuelans started fleeing to the U.S. from all the other countries as well,” Blair told the DCNF. “So when we receive a lot of Venezuelans at the border, we’ll see that many Venezuelans have multiple identification cards from multiple countries, and so it’s very difficult to ascertain who they are.”
From fiscal year 2021 to 2023, CBP saw a 421% increase in Venezuelans encountered at the southern border, according to CBP data.
CBP told the DCNF that the agency has enhanced measures to screen for gangs, and any person deemed a threat is referred for prosecution or investigation as required. It also cited the Biden administration’s initiatives to curtail illegal immigration from the southern border, saying that the majority of southern border encounters in the last three fiscal years have resulted in a removal, return or expulsion.
“They’re now going to be in every diaspora of Venezuelans or Venezuelan communities inside the United States,” Blair added. “And now that we’ve imported over half a million Venezuelans since Biden’s been in office, they’re going to be in every one of those communities.”
Republican Texas Gov. Greg Abbott announced Monday he would designate Tren de Aragua a terrorist organization and bring the “full weight of the government” on the gang, according to The Texas Tribune. The gang has been active in the state since 2021, and more than 3,000 illegal immigrants from Venezuela have been arrested since then, according to Abbott.
“When it comes to migration from South America and Venezuela, I think that’s somewhere where they have a comparative advantage that they’ve taken advantage of,” Zack Smith, senior legal fellow at the Heritage Foundation told the DCNF. “And then I think also, in that same way, drug trafficking seems to be something that they’re able to tap into as well.”
In 2023, the Department of Homeland Security Investigations (HSI) partnered with Peru to create a “Transnational Crime Investigation Unit” to combat Tren de Aragua, according to Dialogo Americas. Peru is one of the many South American countries involved in the gang’s network for trafficking people and drugs.
“We’re not heavily scrutinizing anyone coming in,” Blair told the DCNF. “We’re not detaining them. We’re using alternatives to detention, so no one’s really being vetted.”
A U.S. Department of State spokesperson told the DCNF that the agency is working to contain the threat from the gang nationwide, citing efforts from the Biden administration to curtail illegal border crossings. The agency also said they partner with the Department of Homeland Security and the Department of Justice to disrupt the gang’s activity abroad and have improved their vetting tools.
The El Paso Police Department did not respond to the DCNF’s requests for comment.
Featured Image: Mani Albrecht U.S. Customs and Border Protection Office of Public Affairs Visual Communications Division
2025 Federal Election
Police Associations Endorse Conservatives. Poilievre Will Shut Down Tent Cities

From Conservative Party Communications
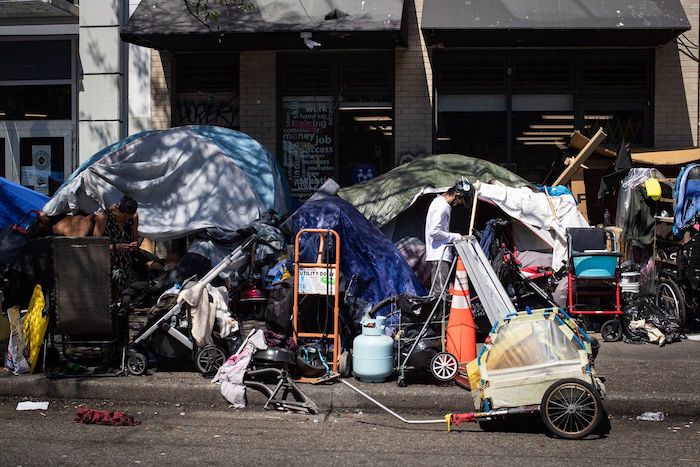
Under the Lost Liberal decade, homelessness has surged by 20% since 2018 and chronic homelessness has spiked 38%. In cities like Nanaimo, Victoria and London, the number of people living in tents and makeshift shelters has exploded. In Toronto alone, there were 82 encampments in early 2023—now there are over 200, with an estimated 1,400 in Ontario.
Yesterday, Conservative Leader Pierre Poilievre received the endorsement of the Toronto Police Association, the largest single association of its kind in Canada, representing approximately 8,000 civilian and uniformed members.
This follows the endorsement by the police associations of Durham, Peel, Barrie, and Sault Ste. Marie of the Conservative plan to stop the crime and keep Canadians safe, after the Liberal government’s easy bail and soft-on-crime policies unleashed a wave of violent crime.
“These men and women put their lives on the line every day to keep our streets safe,” Poilievre said. “Our Conservative team is honoured to have their support and will back them up with laws to help them protect all Canadians.”
Poilievre also announced that a new Conservative government will ensure that police have the legal power to remove dangerous encampments to end the homelessness and the mental health and addiction crisis that has trapped thousands in dangerous tent cities and make life unsafe for law-abiding Canadians who live near them.
“Parks where children played are now littered with needles. Small businesses are boarded up and whole blocks of storefronts are shuttered because their owners can’t afford to deal with constant break-ins and vandalism,” Pierre Poilievre said. “Public spaces belong to everyone, but law-abiding citizens, especially families and seniors, are being pushed out to accommodate chaos and violence.”
Canadian cities have a mixed record of dealing with encampments in public places, with some not acting because they don’t believe they have the legal authority to remove the camps. Conservatives will work with provinces and ensure law enforcement has the clear legal tools they need to remove encampments and give Canadians back the safe streets and public spaces they deserve.
A Poilievre-led government will do this by reversing the Liberals’ radical pro-drug policies and by:
- Amending the Criminal Code to give police the tools to charge individuals when they endanger public safety or discourage the public from using, moving through, or otherwise accessing public spaces by setting up temporary structures, including tents.
- Clarifying in law that police can dismantle illegal encampments and ensure individuals living in them who need help are connected with housing, addiction treatment, and mental health services.
- Giving judges the power to order people charged for illegally occupying public spaces with a temporary structure and simple possession of illegal drugs to mandatory drug treatment.
- Returning to a housing first approach to homelessness, ensuring people get off the streets into a stable place to live with the support they need to rebuild their lives.
Under the Lost Liberal decade, homelessness has surged by 20% since 2018 and chronic homelessness has spiked 38%. In cities like Nanaimo, Victoria and London, the number of people living in tents and makeshift shelters has exploded. In Toronto alone, there were 82 encampments in early 2023—now there are over 200, with an estimated 1,400 in Ontario.
These encampments are a direct result of radical Liberal policies such as drug decriminalization and unsafe supply. They are extremely dangerous for the people trapped in them, who endure overdoses, assaults, including sexual assaults, human trafficking, and even homicide, as well as the community around them.
Under the Poilievre plan, tent cities will no longer be an option—but recovery will be. Conservatives will give law enforcement the tools they need to help clean up our streets, deal with chronic offenders, and provide truly compassionate recovery and treatment where it is needed.
“Instead of getting people the help they need, the Liberals abandoned our communities to chaos,” Poilievre said. “Leaving people trapped by their addictions to live outdoors through Canadian winters, sick, malnourished, cold, wet and vulnerable is the furthest thing from compassionate.”
A Conservative government will also overhaul the Liberals’ dangerous pro-drug policies that have led to over 50,000 overdose deaths over the Lost Liberal Decade. Instead of flooding our streets with taxpayer-funded hard drugs, we will invest in recovery to break the cycle of despair and offer real hope.
Conservatives will allow judges to sentence offenders to mandatory treatment for addiction, and we will fund 50,000 addiction treatment spaces, ensuring that those struggling with substance use get the support they need to recover—because real compassion means helping people get better, not enabling their suffering.
In addition to these measures, Poilievre has a plan to end the soft-on-crime approach of the Lost Liberal Decade, end the chaos, and restore order and safety across Canada:
- Three-Strikes-and-You’re-Out Law: Individuals convicted of three serious offences will face a minimum prison term of 10 years and up to a life sentence, with no eligibility for bail, probation, parole, or house arrest.
- Mandatory Life Sentences: Life imprisonment for those convicted of five or more counts of human trafficking, importing or exporting ten or more illegal firearms, or trafficking fentanyl.
- Repeal of Bill C-75: Ending the Liberals’ catch-and-release policies to restore jail, not bail, for repeat violent offenders.
- New Offense for Intimate Partner Assault: Creation of a specific offense for assault of an intimate partner, with the strictest bail conditions for those accused, and ensuring that murder of an intimate partner, one’s own child, or a partner’s child is treated as first-degree murder.
- Consecutive Sentences for Repeat Violent Offenders: So there will no longer be sentencing discounts for multiple murderers.
Canadians can’t afford a fourth Liberal term of rising crime and chaos in our streets. We need a new Conservative government that will end the chaos, restore order on our streets and bring our loved ones home drug-free.
Business
China, Mexico, Canada Flagged in $1.4 Billion Fentanyl Trade by U.S. Financial Watchdog
 Sam Cooper
Sam Cooper
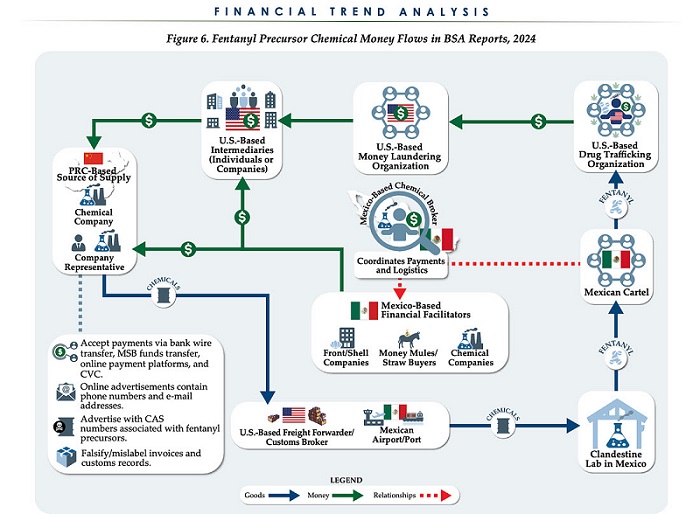
The U.S. Treasury’s Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN) has identified $1.4 billion in fentanyl-linked suspicious transactions, naming China, Mexico, Canada, and India as key foreign touchpoints in the global production and laundering network. The analysis, based on 1,246 Bank Secrecy Act filings submitted in 2024, tracks financial activity spanning chemical purchases, trafficking logistics, and international money laundering operations.
The data reveals that Mexico and the People’s Republic of China were the two most frequently named foreign jurisdictions in financial intelligence gathered by FinCEN. Most of the flagged transactions originated in U.S. cities, the report notes, due to the “domestic nature” of Bank Secrecy Act data collection. Among foreign jurisdictions, Mexico, China, Hong Kong, and Canada were cited most often in fentanyl-related financial activity.
The FinCEN report points to Mexico as the epicenter of illicit fentanyl production, with Mexican cartels importing precursor chemicals from China and laundering proceeds through complex financial routes involving U.S., Canadian, and Hong Kong-based actors.
The findings also align with testimony from U.S. and Canadian law enforcement veterans who have told The Bureau that Chinese state-linked actors sit atop a decentralized but industrialized global fentanyl economy—supplying precursors, pill presses, and financing tools that rely on trade-based money laundering and professional money brokers operating across North America.
“Filers also identified PRC-based subjects in reported money laundering activity, including suspected trade-based money laundering schemes that leveraged the Chinese export sector,” the report says.
A point emphasized by Canadian and U.S. experts—including former U.S. State Department investigator Dr. David Asher—that professional Chinese money laundering networks operating in North America are significantly commanded by Chinese Communist Party–linked Triad bosses based in Ontario and British Columbia—is not explored in detail in this particular FinCEN report.¹
Chinese chemical manufacturers—primarily based in Guangdong, Zhejiang, and Hebei provinces—were repeatedly cited for selling fentanyl precursors via wire transfers and money service businesses. These sales were often facilitated through e-commerce platforms, suggesting that China’s global retail footprint conceals a lethal underground market—one that ultimately fuels a North American public health crisis. In many cases, the logistics were sophisticated: some Chinese companies even offered delivery guarantees and customs clearance for precursor shipments, raising red flags for enforcement officials.
While China’s industrial base dominates the global fentanyl supply chain, Mexican cartels are the next most prominent state-like actors in the ecosystem—but the report emphasizes that Canada and India are rising contributors.
“Subjects in other foreign countries—including Canada, the Dominican Republic, and India—highlight the presence of alternative suppliers of precursor chemicals and fentanyl,” the report says.
“Canada-based subjects were primarily identified by Bank Secrecy Act filers due to their suspected involvement in drug trafficking organizations allegedly sourcing fentanyl and other drugs from traditional drug source countries, such as Mexico,” it explains, adding that banking intelligence “identified activity indicative of Canada-based individuals and companies purchasing precursor chemicals and laboratory equipment that may be related to the synthesis of fentanyl in Canada. Canada-based subjects were primarily reported with addresses in the provinces of British Columbia and Ontario.”
FinCEN also flagged activity from Hong Kong-based shell companies—often subsidiaries or intermediaries for Chinese chemical exporters. These entities were used to obscure the PRC’s role in transactions and to move funds through U.S.-linked bank corridors.
Breaking down the fascinating and deadly world of Chinese underground banking used to move fentanyl profits from American cities back to producers, the report explains how Chinese nationals in North America are quietly enlisted to move large volumes of cash across borders—without ever triggering traditional wire transfers.
These networks, formally known as Chinese Money Laundering Organizations (CMLOs), operate within a global underground banking system that uses “mirror transfers.” In this system, a Chinese citizen with renminbi in China pays a local broker, while the U.S. dollar equivalent is handed over—often in cash—to a recipient in cities like Los Angeles or New York who may have no connection to the original Chinese depositor aside from their role in the laundering network. The renminbi, meanwhile, is used inside China to purchase goods such as electronics, which are then exported to Mexico and delivered to cartel-linked recipients.
FinCEN reports that US-based money couriers—often Chinese visa holders—were observed depositing large amounts of cash into bank accounts linked to everyday storefront businesses, including nail salons and restaurants. Some of the cash was then used to purchase cashier’s checks, a common method used to obscure the origin and destination of the funds. To banks, the activity might initially appear consistent with a legitimate business. However, modern AI-powered transaction monitoring systems are increasingly capable of flagging unusual patterns—such as small businesses conducting large or repetitive transfers that appear disproportionate to their stated operations.
On the Mexican side, nearly one-third of reports named subjects located in Sinaloa and Jalisco, regions long controlled by the Sinaloa Cartel and Cartel Jalisco Nueva Generación. Individuals in these states were often cited as recipients of wire transfers from U.S.-based senders suspected of repatriating drug proceeds. Others were flagged as originators of payments to Chinese chemical suppliers, raising alarms about front companies and brokers operating under false pretenses.
The report outlines multiple cases where Mexican chemical brokers used generic payment descriptions such as “goods” or “services” to mask wire transfers to China. Some of these transactions passed through U.S.-based intermediaries, including firms owned by Chinese nationals. These shell companies were often registered in unrelated sectors—like marketing, construction, or hardware—and exhibited red flags such as long dormancy followed by sudden spikes in large transactions.
Within the United States, California, Florida, and New York were most commonly identified in fentanyl-related financial filings. These locations serve as key hubs for distribution and as collection points for laundering proceeds. Cash deposits and peer-to-peer payment platforms were the most cited methods for fentanyl-linked transactions, appearing in 54 percent and 51 percent of filings, respectively.
A significant number of flagged transactions included slang terms and emojis—such as “blues,” “ills,” or blue dots—in memo fields. Structured cash deposits were commonly made across multiple branches or ATMs, often linked to otherwise legitimate businesses such as restaurants, salons, and trucking firms.
FinCEN also tracked a growing number of trade-based laundering schemes, in which proceeds from fentanyl sales were used to buy electronics and vaping devices. In one case, U.S.-based companies owned by Chinese nationals made outbound payments to Chinese manufacturers, using funds pooled from retail accounts and shell companies. These goods were then shipped to Mexico, closing the laundering loop.
Another key laundering method involved cryptocurrency. Nearly 10 percent of all fentanyl-related reports involved virtual currency, with Bitcoin the most commonly cited, followed by Ethereum and Litecoin. FinCEN flagged twenty darknet marketplaces as suspected hubs for fentanyl distribution and cited failures by some digital asset platforms to catch red-flag activity.
Overall, FinCEN warns that fentanyl-linked funds continue to enter the U.S. financial system through loosely regulated or poorly monitored channels, even as law enforcement ramps up enforcement. The Drug Enforcement Administration reported seizures of over 55 million counterfeit fentanyl pills in 2024 alone.
The broader pattern is unmistakable: precursor chemicals flow from China, manufacturing occurs in Mexico, Canada plays an increasing role in chemical acquisition and potential synthesis, and drugs and proceeds flood into the United States, supported by global financial tools and trade structures. The same infrastructure that enables lawful commerce is being manipulated to sustain the deadliest synthetic drug crisis in modern history.
The Bureau is a reader-supported publication.
To receive new posts and support my work, consider becoming a free or paid subscriber.
Invite your friends and earn rewards
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoIs Government Inflation Reporting Accurate?
-

 2025 Federal Election2 days ago
2025 Federal Election2 days agoCarney’s Hidden Climate Finance Agenda
-

 2025 Federal Election2 days ago
2025 Federal Election2 days agoWhen it comes to pipelines, Carney’s words flow both ways
-

 2025 Federal Election2 days ago
2025 Federal Election2 days agoStudy links B.C.’s drug policies to more overdoses, but researchers urge caution
-

 2025 Federal Election2 days ago
2025 Federal Election2 days agoPolls say Canadians will give Trump what he wants, a Carney victory.
-

 2025 Federal Election1 day ago
2025 Federal Election1 day agoCarney Liberals pledge to follow ‘gender-based goals analysis’ in all government policy
-

 2025 Federal Election1 day ago
2025 Federal Election1 day agoPoilievre’s Conservatives promise to repeal policy allowing male criminals in female jails
-

 2025 Federal Election1 day ago
2025 Federal Election1 day agoTrump Has Driven Canadians Crazy. This Is How Crazy.