Fraser Institute
Health-care costs for typical Canadian family will reach almost $18,000 this year
From the Fraser Institute
By Nathaniel Li and Milagros Palacios and Nadeem Esmail
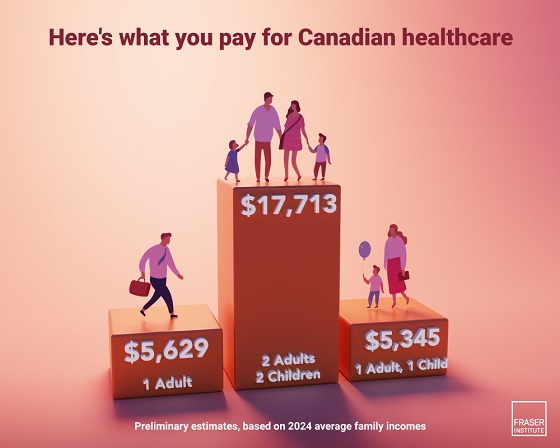
A typical Canadian family of four will pay an estimated $17,713 for public health-care insurance this year, finds a new study released today by the Fraser Institute, an independent, non-partisan Canadian public policy think-tank.
“Canadians pay a substantial amount of money for health care through a variety of taxes—even if we don’t pay directly for medical services,” said Nadeem Esmail, senior fellow at the Fraser Institute and co-author of The Price of Public Health Care Insurance, 2024.
Most Canadians are unaware of the true cost of health care because they never see a bill for medical services, may only be aware of partial costs collected via employer health taxes and contributions (in provinces that impose them), and because general government revenue—not a dedicated tax—funds Canada’s public health-care system.
The study estimates that a typical Canadian family consisting of two parents and two children with an average household income of $176,266 will pay $17,713 for public health care this year. Couples without dependent children will pay an estimated $16,528. Single Canadians will pay $5,629 for health care insurance, and single parents with one child will pay $5,345.
Since 1997, the first year for which data is available, the cost of healthcare for the average Canadian family has increased substantially, and has risen more quickly than its income. In fact, the cost of public health care insurance for the average Canadian family increased 2.2 times as fast as the cost of food, 1.6 times as fast as the cost of housing, and 1.7 times as fast as the average income.
“Understanding how much Canadians actually pay for health care, and how much that amount has increased over time, is an important first step for taxpayers to assess the value and performance of the health-care system, and whether it’s financially sustainable,” Esmail said.
- Canadians often misunderstand the true cost of our public health care system. This occurs partly because Canadians do not incur direct expenses for their use of health care, and partly because Canadians cannot readily determine the value of their contribution to public health care insurance.
- In 2024, preliminary estimates suggest the average payment for public health care insurance ranges from $4,908 to $17,713 for six common Canadian family types, depending on the type of family.
- Between 1997 and 2024, the cost of public health care insurance for the average Canadian family increased 2.2 times as fast as the cost of food, 1.7 times as fast as the average income, and 1.6 times as fast as the cost of shelter. It also increased much more rapidly than the cost of clothing, which has been falling in recent years.
- The 10 percent of Canadian families with the lowest incomes will pay an average of about $639 for public health care insurance in 2024. The 10 percent of Canadian families who earn an average income of $81,825 will pay an average of $7,758 for public health care insurance, and the families among the top 10 percent of income earners in Canada will pay $47,071.
Authors:
2025 Federal Election
Housing starts unchanged since 1970s, while Canadian population growth has more than tripled
From the Fraser Institute
By: Austin Thompson and Steven Globerman
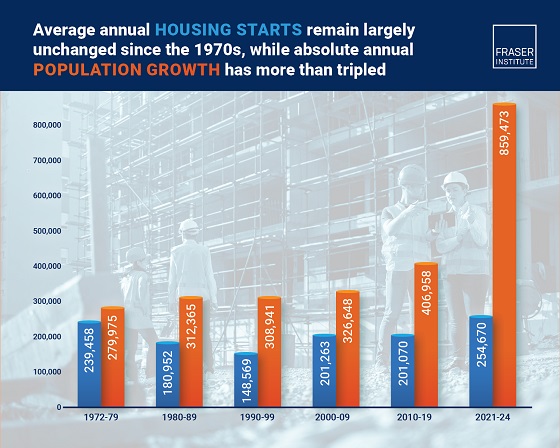
The annual number of new homes being built in Canada in recent years is virtually the same as it was in the 1970s, despite annual population growth
now being three times higher, finds a new study published today by the Fraser Institute, an independent, non-partisan Canadian public policy think tank.
“Despite unprecedented levels of immigration-driven population growth following the COVID-19 pandemic, Canada has failed to ramp up homebuilding sufficiently to meet housing demand,” said Steven Globerman, Fraser Institute senior fellow and co-author of The Crisis in Housing Affordability: Population Growth and Housing Starts 1972–2024.
Between 2021 and 2024, Canada’s population grew by an average of 859,473 people per year, while only 254,670 new housing units were started annually. From 1972 to 1979, a similar number of new housing units were built—239,458—despite the population only growing by 279,975 people a year.
As a result, more new residents are competing for each new home than in the past, which is driving up housing costs.
“The evidence is clear—population growth has been outpacing housing construction for decades, with predictable results,” Globerman said.
“Unless there is a substantial acceleration in homebuilding, a slowdown in population growth, or both, Canada’s housing affordability crisis is unlikely to improve.”
The Crisis in Housing Affordability: Population Growth and Housing Starts 1972–2024
- Canada experienced unprecedented population growth following the COVID-19 pandemic without a commensurately large increase in new homebuilding.
- The imbalance between population growth and new housing construction is reflected in a significant gap between housing demand and supply, which is driving up housing costs.
- Canada’s population grew by a record 1.23 million new residents in 2023 almost entirely due to immigration. That growth was more than double the pre-pandemic record set in 2019.
- Population growth slowed to 951,517 in 2024, still well above any year before 2023.
- Nationally, construction began on about 245,367 new housing units in 2024, down from a recent high of 271,198 starts in 2021—Canada’s annual number of housing starts peaked at 273,203 in 1976.
- Canada’s annual number of housing starts regularly exceeded 200,000 in past decades, when absolute population growth was much lower.
- In 2023, Canada added 5.1 new residents for every housing unit started, which was the highest ratio over the study’s timeframe and well above the average rate of 1.9 residents for every unit started observed over the study period (1972–2024).
- This ratio improved modestly in 2024, with 3.9 new residents added per housing start. However, the ratio remains far higher than at any point prior to the COVID-19 pandemic.
- These national trends are broadly mirrored across all 10 provinces, where annual population growth relative to housing starts is, to varying degrees, elevated when compared to long-run averages.
- Without an acceleration in homebuilding, a slowdown in population growth, or both, Canada’s housing affordability crisis will likely persist.
Austin Thompson
Education
Schools should focus on falling math and reading grades—not environmental activism

From the Fraser Institute
In 2019 Toronto District School Board (TDSB) trustees passed a “climate emergency” resolution and promised to develop a climate action plan. Not only does the TDSB now have an entire department in their central office focused on this goal, but it also publishes an annual climate action report.
Imagine you were to ask a random group of Canadian parents to describe the primary mission of schools. Most parents would say something along the lines of ensuring that all students learn basic academic skills such as reading, writing and mathematics.
Fewer parents are likely to say that schools should focus on reducing their environmental footprints, push students to engage in environmental activism, or lobby for Canada to meet the 2016 Paris Agreement’s emission-reduction targets.
And yet, plenty of school boards across Canada are doing exactly that. For example, the Seven Oaks School Division in Winnipeg is currently conducting a comprehensive audit of its environmental footprint and intends to develop a climate action plan to reduce its footprint. Not only does Seven Oaks have a senior administrator assigned to this responsibility, but each of its 28 schools has a designated climate action leader.
Other school boards have gone even further. In 2019 Toronto District School Board (TDSB) trustees passed a “climate emergency” resolution and promised to develop a climate action plan. Not only does the TDSB now have an entire department in their central office focused on this goal, but it also publishes an annual climate action report. The most recent report is 58 pages long and covers everything from promoting electric school buses to encouraging schools to gain EcoSchools certification.
Not to be outdone, the Vancouver School District (VSD) recently published its Environmental Sustainability Plan, which highlights the many green initiatives in its schools. This plan states that the VSD should be the “greenest, most sustainable school district in North America.”
Some trustees want to go even further. Earlier this year, the British Columbia School Trustees Association released its Climate Action Working Group report that calls on all B.C. school districts to “prioritize climate change mitigation and adopt sustainable, impactful strategies.” It also says that taking climate action must be a “core part” of school board governance in every one of these districts.
Apparently, many trustees and school board administrators think that engaging in climate action is more important than providing students with a solid academic education. This is an unfortunate example of misplaced priorities.
There’s an old saying that when everything is a priority, nothing is a priority. Organizations have finite resources and can only do a limited number of things. When schools focus on carbon footprint audits, climate action plans and EcoSchools certification, they invariably spend less time on the nuts and bolts of academic instruction.
This might be less of a concern if the academic basics were already understood by students. But they aren’t. According to the most recent data from the Programme for International Student Assessment (PISA), the math skills of Ontario students declined by the equivalent of nearly two grade levels over the last 20 years while reading skills went down by about half a grade level. The downward trajectory was even sharper in B.C., with a more than two grade level decline in math skills and a full grade level decline in reading skills.
If any school board wants to declare an emergency, it should declare an academic emergency and then take concrete steps to rectify it. The core mandate of school boards must be the education of their students.
For starters, school boards should promote instructional methods that improve student academic achievement. This includes using phonics to teach reading, requiring all students to memorize basic math facts such as the times table, and encouraging teachers to immerse students in a knowledge-rich learning environment.
School boards should also crack down on student violence and enforce strict behaviour codes. Instead of kicking police officers out of schools for ideological reasons, school boards should establish productive partnerships with the police. No significant learning will take place in a school where students and teachers are unsafe.
Obviously, there’s nothing wrong with school boards ensuring that their buildings are energy efficient or teachers encouraging students to take care of the environment. The problem arises when trustees, administrators and teachers lose sight of their primary mission. In the end, schools should focus on academics, not environmental activism.
-

 2025 Federal Election2 days ago
2025 Federal Election2 days agoASK YOURSELF! – Can Canada Endure, or Afford the Economic Stagnation of Carney’s Costly Climate Vision?
-

 Alberta2 days ago
Alberta2 days agoProvince to expand services provided by Alberta Sheriffs: New policing option for municipalities
-

 Alberta2 days ago
Alberta2 days agoMade in Alberta! Province makes it easier to support local products with Buy Local program
-

 2025 Federal Election2 days ago
2025 Federal Election2 days agoCSIS Warned Beijing Would Brand Conservatives as Trumpian. Now Carney’s Campaign Is Doing It.
-

 2025 Federal Election2 days ago
2025 Federal Election2 days agoInside Buttongate: How the Liberal Swamp Tried to Smear the Conservative Movement — and Got Exposed
-

 Bruce Dowbiggin1 day ago
Bruce Dowbiggin1 day agoIs HNIC Ready For The Winnipeg Jets To Be Canada’s Heroes?
-

 Dr. Robert Malone1 day ago
Dr. Robert Malone1 day agoThe West Texas Measles Outbreak as a Societal and Political Mirror
-
 COVID-191 day ago
COVID-191 day agoCOVID virus, vaccines are driving explosion in cancer, billionaire scientist tells Tucker Carlson












