Business
Five Government Programs That Musk’s Government Efficiency Agency Could Put On The Chopping Block

 From the Daily Caller News Foundation
From the Daily Caller News Foundation
Federally-funded progressive pet projects and wasteful spending alike could be on the way out if Elon Musk succeeds in his quest to improve the administrative state’s efficiency.
Right-of-center policy experts previously told the Daily Caller News Foundation that they hope Musk’s Department of Government Efficiency will improve federal data collection practices and cut wasteful expenditures. Musk took to X on Thursday to express his openness to reeling in federal spending on transgender research and diversity, equity and inclusion (DEI) programs.
In July, the United States of America’s debt surpassed $35 trillion for the first time in history, with the balance expected to exceed $36 trillion in the near future.
Over the past year, the DCNF has collected dozens of examples of wasteful or otherwise strange programs the Biden-Harris administration has pumped public funds into, feeding the deficit. Here are five examples of what could come under scrutiny from Musk’s efficiency agency.
1. Improper Payments
The Biden-Harris administration is on track to have paid out over $1 trillion in improper payments by the time President-elect Donald Trump takes office and the Department of Government Efficiency gets to work in January 2025. Federal guidelines define an improper payment as any disbursement “made by the government to the wrong person, in the wrong amount or for the wrong reason.”
Common examples of improper payments include erroneous payments made through the Medicaid and Medicare systems, misallocated COVID-19 aid, benefits paid to dead people and taxpayer funds lost to fraud. Large sums of improper payments are not a problem unique to the Biden-Harris administration. During Trump’s first administration, the government disclosed $814 billion in inflation-adjusted improper payments.
Not all improper payments are totally lost after being sent out. The Biden-Harris administration managed to recover about $51 billion of the $235.7 billion it erroneously disbursed in 2023.
Both parties have expressed concern about the magnitude of improper payments put out by the federal government, with a bipartisan group of legislators in the House pushing the Improper Payments Transparency Act, a bill introduced in May that would require the president’s budget request to identify common payment errors and formulate ways to address them.
2. Tax Dollars Funding LGBT Activism Abroad
Spokespeople for the State Department have previously told the DCNF that promoting LGBT inclusion in other countries is a “foreign policy priority” of the Biden-Harris administration, a statement supported by materials the agency publishes.
Under President Joe Biden, the State Department and The United States Agency for International Development (USAID) have spent millions working to fund transgender surgeries, bankroll LGBT activists and engage pro-transgender in social engineering abroad.
USAID, for instance, gave $2 million to Asociacion Lambda, a Guatemala-based organization, to both engage in pro-LGBT activism and to provide people with “gender-affirming care,” federal records show. Asociacion Lambda attempts to influence elections in Guatemala and meets with government officials to engage in advocacy.
The State Department, meanwhile, funded the production of a play in North Macedonia where God is portrayed as a bisexual that has constant sex with hermaphroditic angels and communists are painted in a positive light.
“Americans are far from agreeing on how to deal with race, sex, and ‘gender’ in schools and workplaces,” Heritage Foundation senior research fellow Simon Hankinson wrote in a 2022 report. “Even when U.S. national consensus is there, restraint is always necessary in attempting to convince other nations that one’s own values should be theirs. The U.S. must balance the likelihood of convincing potential allies with the likelihood of hostile reactions to perceived interference or ‘cultural colonialism.’”
Other programs the Biden-Harris administration approved to push homosexuality and transsexuality abroad included bankrolling the creation of 2,500 “LGBTQI+ allies” in India, using tax dollars to “foster a united and equal queer-feminist discourse in Albanian society,” staging a film festival in Portugal featuring incestual and pedophilic themes, funding gay pride events across the globe and deploying public funds to support the work of “queer” Muslim writers living in India.
3. ‘Indigenous Knowledge’ Grants
In November 2022, the Biden-Harris administration released a memo defining indigenous knowledge as “a body of observations, oral and written knowledge, innovations, practices, and beliefs developed by Tribes and Indigenous Peoples through interaction and experience with the environment” that “is applied to phenomena across biological, physical, social, cultural and spiritual systems.”
From 2021 to 2023, the Biden-Harris administration approved more than $831.8 million in grants that encouraged the use of indigenous knowledge in service of achieving the Biden administration’s goals.
The Department of Commerce, for instance, earmarked $575 million in June 2023, asking third parties to utilize indigenous knowledge to help mitigate the impact of weather events caused by climate change. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, meanwhile, made an estimated $18.75 million available in August 2023 for grantees to apply “Indigenous knowledge methods,” alongside other approaches, as part of a program intended to test experimental methods of reducing drug overdose.
The 2022 Biden-Harris administration memo ordered agencies to “recognize and, as appropriate, apply Indigenous Knowledge in decision making, research, and [their] policies.” Agencies were also instructed to consult with Indian spiritual leaders and not to assume that indigenous knowledge is incorrect when “Western” science contradicts it, with the memo calling science a tool of oppression.
“When I start hearing things about how there’s this other dimension where, you know, the animals interact with humans at a different level of reality, that’s just not a thing,” City University professor and biologist Massimo Pigliucci told the Washington Free Beacon, in reference to their reporting on the subject. “You can believe that and you have the right to believe it but it’s not empirical evidence.”
4. DEI at the VA and Beyond
As hundreds of thousands of veterans were stuck on benefit waitlists, Biden’s Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) took at least a dozen actions aimed at expanding DEI within the agency.
The VA had 378,000 claims from veterans that had been pending for at least 125 days at the end of 2023, according to the agency. In September 2021, shortly after Biden took office, the VA had just 210,854 claims that had been backlogged for the same length of time.
While the number of disabled veterans waiting on support grew, the Biden-Harris VA was focused on doing things like establishing an Inclusion, Diversity, Equity and Access Council, working on making its contractors more racially diverse and engaging in marketing campaigns aimed at reaching out to the “LGBTQ+” community and female veterans.
The VA is far from the only federal department that leaned into DEI in recent years as the various branches of the federal government collectively spend millions per year on diversity trainings. The Department of Health and Human Services alone spends tens of million per year on DEI programs and staff. Roughly a third of the funds disbursed by the National Science Foundation promoted DEI, according to a recent Senate Commerce Committee report.
5. Inventing Gay Landmarks
America’s national parks faced an estimated $23.3 billion maintenance backlog at the end of the 2023 fiscal year, according to a July report from the Congressional Research Service. While public parks languished, the National Park Service (NPS) diverted public funds to its “Underrepresented Communities Grant Program,” which is designed to diversify America’s historical landmarks to better include racial and sexual minorities.
During Biden’s tenure in office, NPS paid an array of government agencies and nonprofits to seek out “historic” LGBT locations to be placed on the National Register of Historic Places. When NPS approves a landmark to be added to the National Register of Historic Places, its owner becomes entitled to special tax breaks, with many state and local governments offering special grant programs for such locations.
NPS, for example, paid out $75,000 to Washington State’s Department of Archaeology and Historic Preservation for it to identify an “outstanding representation of queer history” and nominate it to be listed on the National Register of Historic Places. The service has spent $7.5 million on its Underrepresented Communities Grant Program since 2014, with Congress apportioning $1.25 million for the 2024 iteration of the program.
America’s national parks are billions of dollars behind on maintenance related to roads, buildings, water systems and campgrounds, according to the congressional report.
Business
China, Mexico, Canada Flagged in $1.4 Billion Fentanyl Trade by U.S. Financial Watchdog
 Sam Cooper
Sam Cooper
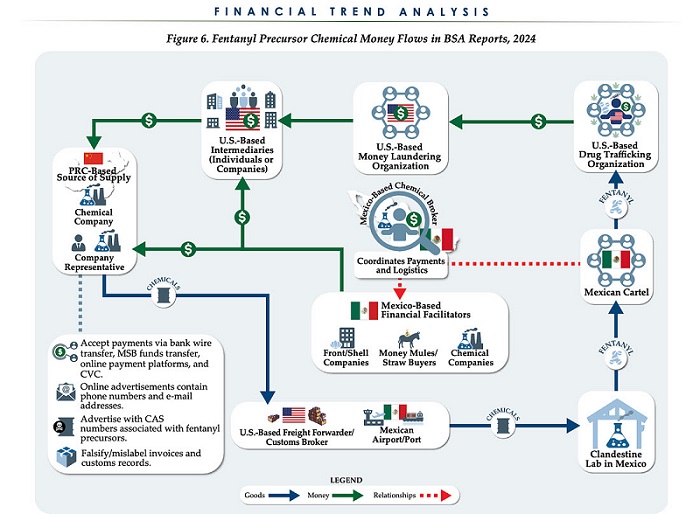
The U.S. Treasury’s Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN) has identified $1.4 billion in fentanyl-linked suspicious transactions, naming China, Mexico, Canada, and India as key foreign touchpoints in the global production and laundering network. The analysis, based on 1,246 Bank Secrecy Act filings submitted in 2024, tracks financial activity spanning chemical purchases, trafficking logistics, and international money laundering operations.
The data reveals that Mexico and the People’s Republic of China were the two most frequently named foreign jurisdictions in financial intelligence gathered by FinCEN. Most of the flagged transactions originated in U.S. cities, the report notes, due to the “domestic nature” of Bank Secrecy Act data collection. Among foreign jurisdictions, Mexico, China, Hong Kong, and Canada were cited most often in fentanyl-related financial activity.
The FinCEN report points to Mexico as the epicenter of illicit fentanyl production, with Mexican cartels importing precursor chemicals from China and laundering proceeds through complex financial routes involving U.S., Canadian, and Hong Kong-based actors.
The findings also align with testimony from U.S. and Canadian law enforcement veterans who have told The Bureau that Chinese state-linked actors sit atop a decentralized but industrialized global fentanyl economy—supplying precursors, pill presses, and financing tools that rely on trade-based money laundering and professional money brokers operating across North America.
“Filers also identified PRC-based subjects in reported money laundering activity, including suspected trade-based money laundering schemes that leveraged the Chinese export sector,” the report says.
A point emphasized by Canadian and U.S. experts—including former U.S. State Department investigator Dr. David Asher—that professional Chinese money laundering networks operating in North America are significantly commanded by Chinese Communist Party–linked Triad bosses based in Ontario and British Columbia—is not explored in detail in this particular FinCEN report.¹
Chinese chemical manufacturers—primarily based in Guangdong, Zhejiang, and Hebei provinces—were repeatedly cited for selling fentanyl precursors via wire transfers and money service businesses. These sales were often facilitated through e-commerce platforms, suggesting that China’s global retail footprint conceals a lethal underground market—one that ultimately fuels a North American public health crisis. In many cases, the logistics were sophisticated: some Chinese companies even offered delivery guarantees and customs clearance for precursor shipments, raising red flags for enforcement officials.
While China’s industrial base dominates the global fentanyl supply chain, Mexican cartels are the next most prominent state-like actors in the ecosystem—but the report emphasizes that Canada and India are rising contributors.
“Subjects in other foreign countries—including Canada, the Dominican Republic, and India—highlight the presence of alternative suppliers of precursor chemicals and fentanyl,” the report says.
“Canada-based subjects were primarily identified by Bank Secrecy Act filers due to their suspected involvement in drug trafficking organizations allegedly sourcing fentanyl and other drugs from traditional drug source countries, such as Mexico,” it explains, adding that banking intelligence “identified activity indicative of Canada-based individuals and companies purchasing precursor chemicals and laboratory equipment that may be related to the synthesis of fentanyl in Canada. Canada-based subjects were primarily reported with addresses in the provinces of British Columbia and Ontario.”
FinCEN also flagged activity from Hong Kong-based shell companies—often subsidiaries or intermediaries for Chinese chemical exporters. These entities were used to obscure the PRC’s role in transactions and to move funds through U.S.-linked bank corridors.
Breaking down the fascinating and deadly world of Chinese underground banking used to move fentanyl profits from American cities back to producers, the report explains how Chinese nationals in North America are quietly enlisted to move large volumes of cash across borders—without ever triggering traditional wire transfers.
These networks, formally known as Chinese Money Laundering Organizations (CMLOs), operate within a global underground banking system that uses “mirror transfers.” In this system, a Chinese citizen with renminbi in China pays a local broker, while the U.S. dollar equivalent is handed over—often in cash—to a recipient in cities like Los Angeles or New York who may have no connection to the original Chinese depositor aside from their role in the laundering network. The renminbi, meanwhile, is used inside China to purchase goods such as electronics, which are then exported to Mexico and delivered to cartel-linked recipients.
FinCEN reports that US-based money couriers—often Chinese visa holders—were observed depositing large amounts of cash into bank accounts linked to everyday storefront businesses, including nail salons and restaurants. Some of the cash was then used to purchase cashier’s checks, a common method used to obscure the origin and destination of the funds. To banks, the activity might initially appear consistent with a legitimate business. However, modern AI-powered transaction monitoring systems are increasingly capable of flagging unusual patterns—such as small businesses conducting large or repetitive transfers that appear disproportionate to their stated operations.
On the Mexican side, nearly one-third of reports named subjects located in Sinaloa and Jalisco, regions long controlled by the Sinaloa Cartel and Cartel Jalisco Nueva Generación. Individuals in these states were often cited as recipients of wire transfers from U.S.-based senders suspected of repatriating drug proceeds. Others were flagged as originators of payments to Chinese chemical suppliers, raising alarms about front companies and brokers operating under false pretenses.
The report outlines multiple cases where Mexican chemical brokers used generic payment descriptions such as “goods” or “services” to mask wire transfers to China. Some of these transactions passed through U.S.-based intermediaries, including firms owned by Chinese nationals. These shell companies were often registered in unrelated sectors—like marketing, construction, or hardware—and exhibited red flags such as long dormancy followed by sudden spikes in large transactions.
Within the United States, California, Florida, and New York were most commonly identified in fentanyl-related financial filings. These locations serve as key hubs for distribution and as collection points for laundering proceeds. Cash deposits and peer-to-peer payment platforms were the most cited methods for fentanyl-linked transactions, appearing in 54 percent and 51 percent of filings, respectively.
A significant number of flagged transactions included slang terms and emojis—such as “blues,” “ills,” or blue dots—in memo fields. Structured cash deposits were commonly made across multiple branches or ATMs, often linked to otherwise legitimate businesses such as restaurants, salons, and trucking firms.
FinCEN also tracked a growing number of trade-based laundering schemes, in which proceeds from fentanyl sales were used to buy electronics and vaping devices. In one case, U.S.-based companies owned by Chinese nationals made outbound payments to Chinese manufacturers, using funds pooled from retail accounts and shell companies. These goods were then shipped to Mexico, closing the laundering loop.
Another key laundering method involved cryptocurrency. Nearly 10 percent of all fentanyl-related reports involved virtual currency, with Bitcoin the most commonly cited, followed by Ethereum and Litecoin. FinCEN flagged twenty darknet marketplaces as suspected hubs for fentanyl distribution and cited failures by some digital asset platforms to catch red-flag activity.
Overall, FinCEN warns that fentanyl-linked funds continue to enter the U.S. financial system through loosely regulated or poorly monitored channels, even as law enforcement ramps up enforcement. The Drug Enforcement Administration reported seizures of over 55 million counterfeit fentanyl pills in 2024 alone.
The broader pattern is unmistakable: precursor chemicals flow from China, manufacturing occurs in Mexico, Canada plays an increasing role in chemical acquisition and potential synthesis, and drugs and proceeds flood into the United States, supported by global financial tools and trade structures. The same infrastructure that enables lawful commerce is being manipulated to sustain the deadliest synthetic drug crisis in modern history.
The Bureau is a reader-supported publication.
To receive new posts and support my work, consider becoming a free or paid subscriber.
Invite your friends and earn rewards
2025 Federal Election
Canada drops retaliatory tariffs on automakers, pauses other tariffs

 MxM News
MxM News
Quick Hit:
Canada has announced it will roll back retaliatory tariffs on automakers and pause several other tariff measures aimed at the United States. The move, unveiled by Finance Minister François-Philippe Champagne, is designed to give Canadian manufacturers breathing room to adjust their supply chains and reduce reliance on American imports.
Key Details:
- Canada will suspend 25% tariffs on U.S. vehicles for automakers that maintain production, employment, and investment in Canada.
- A broader six-month pause on tariffs for other U.S. imports is intended to help Canadian sectors transition to domestic sourcing.
- A new loan facility will support large Canadian companies that were financially stable before the tariffs but are now struggling.
Diving Deeper:
Ottawa is shifting its approach to the escalating trade war with Washington, softening its economic blows in a calculated effort to stabilize domestic manufacturing. On Tuesday, Finance Minister François-Philippe Champagne outlined a new set of trade policies that provide conditional relief from retaliatory tariffs that have been in place since March. Automakers, the hardest-hit sector, will now be eligible to import U.S. vehicles duty-free—provided they continue to meet criteria that include ongoing production and investment in Canada.
“From day one, the government has reacted with strength and determination to the unjust tariffs imposed by the United States on Canadian goods,” Champagne stated. “We’re giving Canadian companies and entities more time to adjust their supply chains and become less dependent on U.S. suppliers.”
The tariff battle, which escalated in April with Canada slapping a 25% tax on U.S.-imported vehicles, had caused severe anxiety within Canada’s auto industry. John D’Agnolo, president of Unifor Local 200, which represents Ford employees in Windsor, warned the BBC the situation “has created havoc” and could trigger a recession.
Speculation about a possible Honda factory relocation to the U.S. only added to the unrest. But Ontario Premier Doug Ford and federal officials were quick to tamp down the rumors. Honda Canada affirmed its commitment to Canadian operations, saying its Alliston facility “will operate at full capacity for the foreseeable future.”
Prime Minister Mark Carney reinforced the message that the relief isn’t unconditional. “Our counter-tariffs won’t apply if they (automakers) continue to produce, continue to employ, continue to invest in Canada,” he said during a campaign event. “If they don’t, they will get 25% tariffs on what they are importing into Canada.”
Beyond the auto sector, Champagne introduced a six-month tariff reprieve on other U.S. imports, granting time for industries to explore domestic alternatives. He also rolled out a “Large Enterprise Tariff Loan Facility” to support big businesses that were financially sound prior to the tariff regime but have since been strained.
While Canada has shown willingness to ease its retaliatory measures, there’s no indication yet that the U.S. under President Donald Trump will reciprocate. Nevertheless, Ottawa signaled its openness to further steps to protect Canadian businesses and workers, noting that “additional measures will be brought forward, as needed.”
-

 2025 Federal Election2 days ago
2025 Federal Election2 days agoRCMP Whistleblowers Accuse Members of Mark Carney’s Inner Circle of Security Breaches and Surveillance
-

 Also Interesting2 days ago
Also Interesting2 days agoBetFury Review: Is It the Best Crypto Casino?
-
 Autism2 days ago
Autism2 days agoRFK Jr. Exposes a Chilling New Autism Reality
-
 COVID-192 days ago
COVID-192 days agoCanadian student denied religious exemption for COVID jab takes tech school to court
-

 2025 Federal Election2 days ago
2025 Federal Election2 days agoBureau Exclusive: Chinese Election Interference Network Tied to Senate Breach Investigation
-
 International2 days ago
International2 days agoUK Supreme Court rules ‘woman’ means biological female
-

 2025 Federal Election2 days ago
2025 Federal Election2 days agoNeil Young + Carney / Freedom Bros
-

 Health2 days ago
Health2 days agoWHO member states agree on draft of ‘pandemic treaty’ that could be adopted in May






