Crime
“Fake Chinese income” mortgages fuel Toronto Real Estate Bubble: Canadian Bank Leaks
Canadian Banking Money Laundering Investigation Reposted in Light of Ottawa’s Fentanyl Czar Pledge
In response to Ottawa’s pledge to tackle fentanyl-linked money laundering—including the appointment of a “fentanyl czar” and new intelligence-sharing initiatives with the United States—The Bureau is reposting this February 2024 investigation estimating tens of billions, potentially several hundred billion, laundered through Vancouver and Toronto real estate via underground banking networks tied to China and global narcotics trafficking, including fentanyl.
FINTRAC’s 2023 analysis of 48,000 transactions involving members of the Chinese diaspora exposed vast wire transfers from Hong Kong and Mainland China, funneled through “money mule” accounts linked to students, homemakers, and shell businesses—including law firms. These findings raised serious concerns about Canada’s banking oversight but led to no prosecutions in Canada. The study also revealed laundering patterns central to the U.S. Justice Department’s $3 billion TD Bank case, with international students from China working with Beijing’s United Front networks playing key roles in the TD Bank money laundering, according to U.S. investigator David Asher, a former Trump Administration official. The revelations underscore how the so-called “Vancouver Model”—once centered on laundering drug proceeds through British Columbia government casinos—evolved during the COVID-19 pandemic, embedding itself deeper into Canada’s banking and legal systems. These findings align with research from SFU urban planner Andy Yan, who has documented how foreign capital distorts Canada’s housing market, with mortgage approvals and home purchases far exceeding reported local incomes.
At the heart of this investigation is HSBC Canada whistleblower “D.M.,” who believes they uncovered at least $500 million in dubious Toronto-area mortgages backed by fabricated remote-work salaries from China. After raising the alarm internally, D.M. says HSBC Canada introduced only superficial reforms and pressured him to delete critical records—deepening his conviction that Canada’s financial oversight remains dangerously weak.
Former RCMP investigators Garry Clement and Cal Chrustie, who reviewed D.M.’s evidence, warn that systemic vulnerabilities persist. Chrustie—who has extensively documented Canada’s weak regulations enabling underground banking linked to organized crime in China, Iran, and Mexico—pointed to the 2012 U.S. Justice Department case where HSBC was fined $1.9 billion over $881 million in cartel-linked transactions involving Mexico’s Sinaloa cartel and Colombia’s Norte del Valle cartel.
As Andy Yan has emphasized, governments at all levels bear responsibility for enabling foreign capital to flood Canada’s housing market without adequate transparency. “When you have programs designed to domesticate foreign capital into local real estate, you see these income-to-home-price incongruities,” he said.
Ottawa’s new fentanyl czar is tasked with coordinating intelligence-sharing and enforcement actions with U.S. agencies to disrupt fentanyl trafficking and related money laundering. Trudeau’s government has also pledged to designate cartels as terrorist organizations, a move that could have sweeping consequences for Canadian banks by exposing them to heightened U.S. financial scrutiny and enforcement actions.
It remains to be seen what position Liberal Party leadership favourite Mark Carney—former Governor of the Bank of Canada (2008–2013) and the Bank of England (2013–2020), and a globally influential banker—will take on Canada’s ongoing struggles with financial crime and illicit capital flows. While the Bank of Canada does not oversee financial crime enforcement, Carney’s extensive experience in international financial regulation—gained through his roles involving oversight at global institutions such as the Bank for International Settlements and his active participation in forums on financial stability—suggests he could offer valuable insights into Canada’s banking vulnerabilities. This is particularly noteworthy as he emerges as a political contender and potential Prime Minister.
OTTAWA, Canada — The whistleblower, a Canadian business school graduate, was staggered by the suspicious home loans he discovered in 2022 when he joined a mortgage approval team in a small HSBC branch on the outskirts of Toronto.
He knew of suspicions surrounding Chinese capital in British Columbia real estate, but had never witnessed shady lending while working at an HSBC branch in Campbell River, a bucolic town on the coast of Vancouver Island.
When he arrived at HSBC’s bank in Aurora, an affluent suburb north of Toronto, he discovered explosive growth in home loans to Chinese diaspora buyers during the Covid-19 pandemic.
Chinese migrants living across Toronto were obtaining mortgages from HSBC while supposedly earning extravagant salaries from remote-work jobs in China. In one example, an Ontario casino worker that owned three homes also claimed to earn $345,000 in 2020 analyzing data remotely for a Beijing company.
Before joining HSBC Canada, the whistleblower had studied fake-income mortgage frauds for his Business Masters degree at Vancouver Island University. After arriving at Aurora in February 2022, while digging into the branch’s loan books and interrogating his colleagues, he made mind-blowing assessments.
Since 2015, the whistleblower concluded, more than 10 Toronto-area HSBC branches had issued at least $500-million in home loans to diaspora buyers claiming exaggerated incomes or non-existent jobs in China.
These foreign-income scams spiked during the pandemic, the whistleblower believed, because borrowers could somewhat plausibly claim to be working remotely in other countries while riding out Covid-19 in Canada.
While a small bank of Aurora’s size was expected to issue about $23-million in residential loans every year, this branch had shovelled out $88-million in mortgages in 2020, according to the whistleblower, and over $50-million in 2021.
The whistleblower, whomThe Bureau is calling D.M., immigrated to Canada as an international student from India, making him a minority among mostly Chinese-Canadian co-workers at the Aurora branch.
As D.M. probed his colleagues, his belief gained conviction, that HSBC Canada and other Canadian banks including CIBC had systemic problems with highly questionable mortgages issued to diaspora buyers with unverified sources of wealth in China.
Losing sleep, in April 2022, D.M. sent an audacious email to senior bank executives: “I am going to reveal potential mortgage fraud at HSBC Bank Canada and possibly some employees benefited from the fraud, financially pocketing thousands of dollars, which I call the proceeds of crime.”
D.M.’s explosive four-page complaint triggered an internal investigation that led to some reforms at HSBC Canada according to internal emails obtained by The Bureau.
But more than a year later, D.M. was so dissatisfied with the bank’s response that he risked sharing his story and numerous internal documents for an unprecedented journalistic investigation into Canada’s housing affordability crisis.
“I found out a huge mortgage fraud showing borrowers with exaggerated income from one specific country, China, pretending to be working remotely,” D.M. informed The Bureau in June 2023. “I believe the housing prices in Toronto are linked to this, because this is about income verification in banks, which is supposed to moderate demand.”
The Bureau asked HSBC Canada to review emailed information for this story and provide an appropriate manager for an interview regarding D.M. ‘s records and allegations.
“I won’t have anyone to speak with you directly,” Sharon Wilks, Head of Communications, responded. “But for context: As a global bank, HSBC is at the forefront of efforts to identify, prevent and deter financial crime … We will not do business with individuals or entities we believe are engaged in illicit conduct.”
Wilks added that HSBC Canada “can and do regularly exit relationships with clients whose activities we deem too risky.”
The Bureau’s seven-month investigation into D.M.’s allegations suggests HSBC Canada and other Canadian banks could have issued many billions of dollars in questionable mortgages to Chinese diaspora buyers, and a significant cause of Canada’s real estate bubble is hundreds of billions in illicit fund transfers from China into Canada, and bank lending that amplifies its impacts, especially in Toronto and Vancouver home prices.
“There are thousands of these cases, large scale,” D.M. said in an interview. “Hardworking Canadians are denied mortgages and these Chinese residents forge documents and get mortgages approved, heating up the already hot Ontario real estate markets.”
“These people don’t have steady jobs or income in Canada,” he alleged, “but what they are doing is scams to launder money, and get mortgages using fake documents.”
The Bureau’s investigation included asking seven prominent Canadian experts to assess some of D.M.’s documents, allegations and conclusions.
This investigation suggests D.M. ‘s calculation is plausible, that the Aurora branch and other Toronto-area HSBC branches have issued at least $500-million in questionable Chinese income loans since 2015.
But D.M’s findings could also change the public’s understanding of housing affordability in Toronto and Vancouver, a politically explosive issue expected to frame Canada’s upcoming federal election.
This is because, according to the academics and criminologists that reviewed D.M.’s documents with The Bureau, his evidence fits into FINTRAC’s much broader examinations of suspicious real estate and banking transactions.
In 2023, the anti-money laundering watchdog published a ground-breaking study into 48,000 Chinese diaspora banking transactions.
FINTRAC found that during the Covid-19 pandemic, because Canadian casinos were closed, Chinese underground banking schemes evolved, flooding electronic fund transfers from Hong Kong into Canadian bank accounts that served like corridors for murky real estate transactions.
The Bureau’s analysis also finds that what D.M. discovered in Toronto banks, finally sheds light on mysterious capital flows discovered by a prominent Canadian academic in 2015, in a study of Vancouver land titles and mortgages.
That examination of $525-million worth of real estate purchases in a six-month period found 66 percent of buyers in several affluent neighbourhoods were recent Chinese diaspora migrants, and most mortgages went to buyers with little or no income in Canada.
Similarly, what D.M. found in his probe of pandemic-era loans could be called the evolving “Toronto Method” of an underground banking system discovered first in Vancouver, and found to be laundering a stunning $1.2-billion in cash from Mainland China through British Columbia government casinos in 2014.
This system of shadowy transfers was dubbed the “Vancouver Model” by an Australian professor, and brings together transnational organized crime, affluent Chinese nationals seeking to export their wealth abroad, and Canadian casinos, banks and real estate, in transactions that evade policing because the pivotal cash exchanges are done off the books by professional money launderers serving the global Chinese diaspora.
According to FINTRAC’s 2023 study of 48,000 pandemic-era transactions, this evolving Vancouver Model network “simultaneously facilitates money laundering and the circumvention of Chinese currency controls”
“As a result of the temporary closures of Canadian casinos due to the COVID-19 pandemic, professional money launderers began to diversify their money laundering methods,” FINTRAC’s study says.
“During this time, FINTRAC observed a rise in money laundering typologies involving transferring large sums of funds to Canada from foreign money services businesses, often located in China, notably Hong Kong, and the laundering of the funds primarily through the real estate, securities, automotive and legal professions.”
These wire transfers from China were routed into bank accounts of “multiple, unrelated individuals in Canada,” that served as “money mules” in byzantine networks involving Canada-based real estate developers, real estate agents, mortgage brokers and banks.
These Chinese diaspora bank account owners often claimed they were students, homemakers, office managers, or unemployed, FINTRAC reported.
They sometimes used their accounts to send bank drafts to others in Canada for home purchases, or served as “straw buyers” for offshore investors.
“Mortgage payments are sourced from incoming funds from China,” FINTRAC’s alert said.
FINTRAC’s study doesn’t say that Canadian banks knowingly issued fake-income mortgages to Chinese diaspora buyers in Toronto.
But in an interview, D.M. said banking staff are trained to guard against fraud, and the loan application packages he reviewed in Aurora beggared belief.
“The bank found out that one lady works in a casino part-time but got a $1.4 million mortgage showing over $300,000 annual income,” he said. “Plus she takes money as benefits from the government, for her two kids.”
In other examples, an HSBC mortgage client claimed to earn $700,000 annually for remote work in China, while simultaneously living in Canada and paying off a $10,000 student loan.
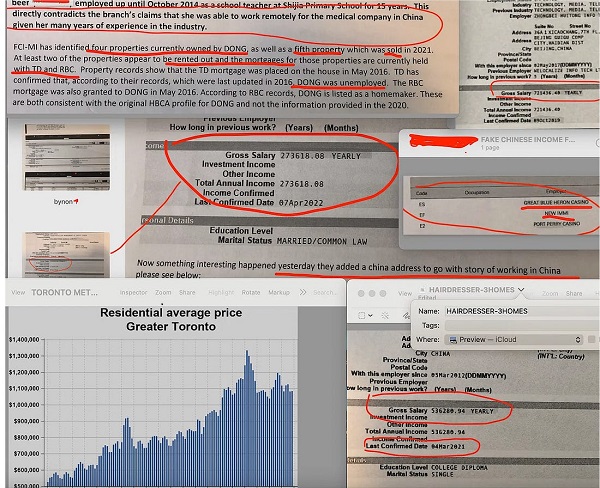
Another woman who owned homes in Aurora, Markham and Scarborough, worked part-time as a hairdresser while also claiming to earn $536,280 at a “Business Manager” job in Guangzhou.
“Canadian workers have been put out of the real estate market by people working as a hairdresser that own a couple homes,” D.M. said in an interview.
“How is that fair?”
The most shocking case reviewed by The Bureau, shows that one woman that owns at least four Toronto properties opened her HSBC Aurora bank account in 2013, claiming to be a “Homemaker with no annual income.”
But her Toronto account soon received incredible amounts of wire transfers from HSBC China accounts, and paid out “high value cheques” to third parties for real estate purchases.
This case suggests “Toronto Method” shadow banking described in FINTRAC’s 2023 study has been seeping into Toronto real estate for about a decade.
And yet in 2020, this same woman applied for another HSBC Canada mortgage, claiming to earn $763,000 remotely from her job in China.
This evidence from the HSBC whistleblower complements the seminal investigations of Simon Fraser University academic Andy Yan, who examined sales from August 2014 to February 2015 in several communities on Vancouver’s westside. The average home price in Yan’s study was $3-million.
Looking back at his Vancouver findings in comparison to D.M.’s Toronto banking documents, Yan told The Bureau “I think this helps affirm some of my early work that I did, almost nine years ago.”
“This goes to the core of our banking system,” he said, “and how are we verifying identities and how are we verifying incomes.”
In Yan’s controversial study the vast majority of mortgages went to buyers listing their occupation as home-maker, followed by students, and managers. HSBC and CIBC were the dominant lenders.
Unlike the HSBC whistleblower, Yan had no access to internal banking data regarding the purported origin of funds behind these mortgages taken by Chinese diaspora buyers.
But in an interview, Yan said what he found most interesting back in 2015, was suspicions that Chinese migrants were often buying homes with bulk cash, weren’t accurate. The truth was more complex and seems to be clarified by D.M.’s mortgage findings in Toronto.
“It’s about that global flow of capital, and how it’s multiplied by Canada’s mortgage and lending system,” Yan said. “Because you have to remember, one of the biggest conclusions about my study was that it wasn’t bags of cash that were being used to purchase Vancouver homes outright. They were loans being used. So now, I’m thinking, this is where my study connects up to what you have discovered in Toronto.”
“The interesting story here,” Yan added, “is what happens in Toronto real estate may not repeat Vancouver, but it perhaps rhymes.”
Probably the most famous Chinese property owner from Yan’s 2015 study areas is Huawei executive Meng Wanzhou. In 2009 her family bought a home in Vancouver’s Dunbar neighborhood for $2.73 million, land titles show. In 1998, ten years before Vancouver Model transactions started to surge in Vancouver real estate, the home was sold for $370,000. The home is now valued at almost $6-million.
Ashleigh Rhea Gonzales, a former RCMP data scientist who recently published a criminology thesis finding Chinese diaspora underground banking causes significantly more money laundering into Canada’s real estate than previously estimated, said that D.M.’s findings resemble her own Vancouver Model research.
“This whistleblower’s allegations of widespread mortgage fraud at HSBC Canada align with some of the first-hand accounts from staff of some Canadian financial institutions that I have come across in my research on money laundering in British Columbia,” Gonzales said.
Gonzales, who worked for RCMP’s anti-gang unit in British Columbia until 2023, says she found reports of mortgage fraud accelerated “during the uptick in the Canadian housing bubble after the Vancouver 2010 Olympics,” and continued to surge from 2015 to 2018.
With all this considered, and comparing data sources in this story with previous evidence confirmed in British Columbia’s Cullen Commission, The Bureau estimates that from 2014 to 2023, well over $200-Billion in Vancouver Model and Toronto Method funds could have poured through underground diaspora networks and Canadian financial institutions into Toronto and Vancouver’s real estate.
A federal official not authorized to comment publicly also examined D.M.’s banking leaks for The Bureau, and called this information “explosive.”
The official said money laundering is increasing in Canada, and D.M.’s belief that Chinese-income mortgage fraud has boosted home prices in Toronto is likely true, but also should apply for Vancouver and Montreal real estate prices. The official noted that other nations require tax agencies to verify incomes for mortgages, which isn’t the case in Canada.
“It matters for our next generation because of the impact on the housing market,” the official said.
Queen’s University professor Christian Leuprecht – editor of Dirty Money, a new academic text that probes how Ottawa’s weak regulation has “turned the Canadian federation into a destination of choice for global financial crime” – also reviewed some of D.M. ‘s leaks.
“It’s not a new problem, but you’re taking it to the next level,” Leuprecht said.
“Why does this matter? Because organized crime isn’t just laundering their ill-gotten gains, like any good business person, when they buy real estate, they generate a down payment, then get a mortgage for the rest. Why buy one property when you can buy four?”
“Do you know how many mortgage frauds we have in our books?”
The Bureau’s review of HSBC Canada emails and D.M.’s text messages, shows he came to believe numerous employees at the Aurora branch had direct knowledge of faked Chinese income mortgages, and a veteran manager with oversight of more than 10 Greater Toronto branches knew about broad and questionable mortgage lending for Chinese diaspora clients.
Months after D.M. blew the whistle internally he exchanged texts with another employee, identifying colleagues that they believed had knowledge of diaspora mortgage scams.
The texts suggest D.M. believed HSBC Canada and other Canadian banks continued to hold vast amounts of suspicious foreign income mortgages, which could cause systemic loan quality risks if Toronto’s real estate prices decline.
“Do you know how many mortgage frauds we have in our books,” D.M. texted to his colleague. “It’s insane.”
“She told me,” the colleague replied, referring to an HSBC branch manager.
“She was like, if you do come, you gotta be prepared for the mortgage payout.”
“These people showed fake income and got mortgage,” D.M. continued. “Now interest rate is high, they can’t cope.”
“Other branches did the same thing too,” his co-worker replied. “I heard there’s a lot.”
“Absolutely,” D.M. texted. “All branches engaged in it.”
“This is like the unspoken secret,” his co-worker concluded. “I’m pretty sure other banks have it too. My Aunt have no income and got a mortgage for 700k. They just need a Covenanter from China.”
Generally, in mortgage contracts a covenanter takes responsibility for the loan if the primary borrower defaults.
Internal records reviewed by The Bureau confirm that on April 18, 2022, D.M. sent a lengthy complaint email to senior HSBC Canada executives, informing them of allegations he’d learned from his colleagues.
In it, he alleges that an Aurora manager had informed him of a complaint letter posted to the branch, that accused mortgage brokers and branch employees of colluding in scam mortgages emanating from Mainland China fraud networks.
Pointing to specific examples, D.M. claimed that another branch colleague had admitted processing numerous loan applications without meeting his clients, because a branch manager delivered her subordinates foreign income client applications so “they did not have to get sales themselves.”
“Surprisingly all these clients he would get will have foreign income most of the time very inflated like 400k or 670k a year,” D.M. wrote. “To me that’s suspicious, but he never questioned the branch manager because in Asian culture it’s disrespectful to question elders.”
D.M. also informs his bosses that one Aurora bank manager opened up to him, saying she believed allegations of mortgage fraud collusion involving some branch staff.
“She said yes, she knows specially in Mainland China there is a team who would even answer emails and phone calls verifying [Chinese income] but it’s a sophisticated and well organised scam,” D.M. ‘s email to HSBC Canada managers says.
His complaint explains that he continued to press an Aurora bank manager on her knowledge of fraud allegations.
“When I asked for such a serious issue if she raised a HSBC confidential [complaint] or not she evaded my question,” D.M. wrote. “Now we all love numbers, but I don’t think the bank will like these kinds of numbers achieved through this way.”
Describing why he contacted HSBC Canada executives directly, the whistleblower’s complaint says he felt confused and isolated, but D.M. decided “local leadership if not participated, at least turned a blind eye,” to Chinese fake-income scams, forcing D.M. to “bring up a serious issue against people of superior positions.”
“I could not have stayed silent, in fact I could not sleep well thinking about it,” his April 2022 complaint says. “It reminds me to some extent what happened with the Home Capital Group.”
“The whole thing is wrong on so many grounds,” D.M. continued.
“Now I know one more reason why Canadians and permanent residents are not getting into the housing market. It’s not only HSBC such things are happening across other Canadian banks as well.”
In the Home Capital case, the Ontario Securities Commission fined the prominent Ontario-based subprime mortgage lender in 2017, alleging Home Capital failed to disclose several of its mortgage brokerages had major problems with faked-income mortgages.
D.M. concluded his four-page complaint to senior executives, writing: “I recommend all mortgage deals of this branch in the last 3 years at least if not longer with Foreign income be probed.”
“Bank statements can be verified directly with the foreign banks or use a reputable third party to verify,” he suggested. “When we find someone with Fake ID or trying to impersonate someone we call the cops. But these people, both staff nor clients who did fraud were reported.”
Hours later on April 18, 2022, an HSBC Canada executive emailed back: “I am going to refer this to our Fraud and Risk teams and they will investigate your concerns.”
“The Implications are Broader”
The next day D.M. continued to hound HSBC Canada managers with emails to support his allegations, spotlighting the absurdity of massive Chinese remote incomes claimed by diaspora buyers.
He pointed to one woman with a $1.6-million HSBC Canada mortgage.
“The client claims to be in Canada but [is] a office supervisor in China. [In the] age of remote working in which country [does] a office supervisor makes 400k please tell me,” D.M. wrote.
“[W]hen I asked the co-worker she said her job is not to use the brain or be a police, when I asked do you think she makes that kind of money and how is she doing her job being in Canada to be an office supervisor in China[?]”
Pointing to another document, D.M. warned his managers about Ms. Chen, who claimed to make $721,000 annually as “project manager” for a Beijing telecommunications company, to secure a $1.89 million mortgage.
Again on May 4, 2022, D.M. emailed executives, suggesting internal records for an Aurora client named Ms. Lin had been altered soon after D.M. blew the whistle on fake Chinese income loans.
His email, which included Ms. Lin’s client profile, warned: “Something interesting happened yesterday, they added a China address to go with [the] story of working in China, please see below.”
The Aurora branch banking records disclosed to The Bureau show that Ms. Lin owns three homes in the blocks surrounding Pacific Mall in Markham.
“The client was onboarded on 24th March with Canada address only and Canadian tax residency,” D.M.’ s email continued.
“She claims to be working in China and have foreign income, so the story she is stuck in Canada due to Covid is very interesting. Suddenly yesterday she decided her address in China. Someone saw the discrepancies and the branch team decided to change it.”
“To me that’s a red flag done to align with the story portrayed.”
Next, D.M. exposed Ms. Lin’s foreign income claim.
“She works for Food processing company, a logistics officer making 273k a year,” he wrote. “I don’t know which logistics officer can work when physically in a different company and also who makes 273k working as a logistics officer.”
Citing another internal banking record, D.M.’s email pointed to Ms. Lin’s $273,000 income and said “it’s interesting how they did the verification.”
The email continues to explain that branch records showed Ms. Lin and her husband had a joint mortgage with a balance of $497,000 at CIBC.
But suddenly during Covid-19, Ms. Lin applied for a new mortgage for $1.2 million with HSBC Canada.
“When I see such things I can’t stay quiet,” D.M.’s May 2022 email says. “[I] was assuming with the new rules things will stop, [but] declining the mortgage or retraining the staff is like treating the symptoms.”
He added that many suspicious Chinese income loans had been “flagged by our Fraud Team already.”
The whistleblower’s scathing assessment ends with the observation that D.M. didn’t believe “someone woke up and decided to scam the bank, but [worked with] a sophisticated network of agents who are training people what to say and answer.”
“The implications are broader and as a responsible bank and citizen we have to,” request investigations from the Canadian Revenue Agency or Ontario Provincial Police, D.M. asserted.
The Bureau asked Gonzales, the former RCMP data scientist, to review some of D.M.’s documents and conclusions.
“From what I have reviewed, D.M.’s findings align with what appear to have been commonplace practices by some groups of staff complicit from the front line, middle office, and back office and sanctioned by management,” Gonzales wrote, adding “whether knowingly or not depends on the individual work cultures.”
The Bureau also asked Stephen Punwasi to review D.M. ‘s leaked banking documentation.
Punwasi is a financial expert who founded Better Dwelling, a real estate analysis website with a large following of young professionals trying to understand why they’re excluded from home ownership in Canadian cities.
He also provided analysis for British Columbia’s 2018 report into Vancouver Model money laundering in casinos, real estate and luxury vehicles.
What Punwasi explained to the report’s author, former RCMP executive Peter German, is that even though Vancouver Model money launderers don’t comprise a majority of buyers in Vancouver, their willingness to overbid on home sales causes ripples that sends prices skyrocketing, especially during times when political turmoil inside China triggers increased capital flight.
“In 2015 and 2016 Ontario saw this flood of money from China, just like British Columbia, and it was not just to do with immigration, it was due to President Xi’s political crack down on corruption,” Punwasi said. “I think we’ve seen that capital flight in Ontario and B.C. in two big cycles, also including 2020 and 2021.”
The Bureau asked Punwasi if the banking records disclosed by D.M. help to explain Toronto’s real estate price surges.
“Absolutely,” he said, pointing to the case of Ms. Lin (who claimed a $273,000 remote-work income in China) and her three homes surrounding Markham’s Pacific Mall.
Property buyers that aren’t shopping for shelter, but for capital flight or money laundering vehicles, are what Punwasi terms the “marginal buyer.”
“The marginal buyer is like an exuberant buyer on crack, so if they are motivated to move as much money as possible,” he said, “the larger the mortgage they can get, it helps them to overpay for homes, and that can cause the price to launch.”
“So if you see a townhome in Toronto going for $2-million, you don’t know if it is mortgage money laundering or someone buying a place to live. You just have to compete with the going price.”
Punwasi says housing prices are a powerful political issue that will shape the next federal election.
But at the same time, young generations are confused by competing explanations on the causes of Canada’s housing affordability crisis, Punwasi believes, whether its lack of housing supply due to restrictive zoning bylaws, or increased demand due to recent immigration surges, or other factors that make Canada’s housing bubble an outlier in the Western world.
“There are so many conflicting narratives right now that people find it hard to believe the scale of impact that money laundering can have on Toronto real estate prices,” Punwasi said. “But no one has thought it through, that having criminals run our renting stock is a liability.”
Punwasi also believes that Prime Minister Justin Trudeau’s government has decreased scrutiny of money laundering in recent years.
He points to new data uncovered in a ministerial inquiry from Conservative MP Adam Chambers, who is a proponent of tougher money laundering laws, which found sharp declines in Canadian Revenue Agency audits of FINTRAC leads.
“The systemic corruption in housing has been snowballing,” Punwasi said, “to where it’s turned into, maybe the banks don’t need to check where the incomes are coming from, and now whole generations can’t find stable shelter.”
“Delete, delete, delete”
HSBC Canada emails reviewed by The Bureau show that while the bank appears to have responded to some of D.M. ‘s recommendations in 2022, troubling mortgage applications and problems with existing Chinese income loans continued.
A January 2023 email to an Aurora branch manager from HSBC Canada’s office in Montreal pointed to a client named Ms. B., who worked at an Ontario government casino, and owned homes across Toronto, in Richmond Hill, Newmarket and East York.
Documents show she obtained an HSBC Canada mortgage for $1.26 million in 2016, and that HSBC Canada staff “confirmed” in July 2021 that she was earning $345,000 with a remote work job in Beijing.
Despite her incredible claimed income, documents show, Ms. B. was having trouble paying at least one of her three mortgages.
An email from a “Senior Loss Mitigation” employee in Montreal to an Aurora branch employee says: “client is going through a tough time … her income is limited … I know she collect rent and she use it to pay her second mortgage. Please review the situation with the client to see if there is any special agreement available to her.”
But Aurora’s branch wrote back to the Montreal branch: “What we have told her is … if she really can’t pay, then she just have to put her house for sale … but she doesn’t want to do that.”
In an interview D.M. told The Bureau this case was typical.
“What they are doing is AirBnBing these properties,” he said. “But they can’t manage with higher interest rates.”
He said during mortgage application interviews at the Aurora branch he would often look across his desk and ask questions without letting clients know he was looking at their income claims from purported Chinese companies on his computer screen.
“Most of these people don’t even know what type of company is in their job profile,” he said.
And documents reviewed by The Bureau show that mortgage applications consistent with Fintrac’s 2023 Chinese money laundering report continued in Aurora.
In May 2023, D.M. emailed a senior HSBC Financial Crime Compliance investigator, writing “Just came across two profiles of clients and I have strong evidence these mortgages were also obtained with fake docs and fraudulently.”
When the investigator responded “I will take a look,” D.M. replied: “One had a CDA student loan of 10k and making 700k in China. Makes no sense, there are many other anomalies.”
In interviews, D.M. told The Bureau he waited “patiently for a year” after reporting his Chinese-income mortgage concerns to HSBC Canada managers, before concluding the bank’s response was insufficient.
“This has been going on for seven years and no one spoke up,” he said. “In my first meeting last year, they asked me a lot of questions, like why didn’t you use the normal channels? But I had no faith in the normal channels.”
“Many bank staff were obviously involved,” D.M. alleged. “It was not one or two employees turning the blind eye but the entire system, someone verifying those fake offer letters and pay stubs, or their bank statements from China.”
D.M. said his concerns also included HSBC Canada’s proposed sale to RBC, which was announced in 2022, about six months after D.M. ‘s April 2022 internal complaint. The sale was approved in December 2023 by Canada’s deputy Prime Minister Chrystia Freeland.
Christian Leuprecht, among other experts interviewed for this story, agreed that D.M.’s allegations of widespread Chinese-income frauds at HSBC Canada could raise questions about whether Freeland, Canada’s finance minister, had knowledge of mortgage lending investigations inside HSBC when she approved the sale.
Freeland directed RBC to “establish a new Global Banking Hub in Vancouver,” and “maintain Mandarin and Cantonese banking services at HSBC branch locations,” a Department of Finance statement says.
Ultimately, D.M. says he chose to share his story with Canadian citizens partly because he felt pressured to erase evidence from his whistleblower complaint emails.
A June 2023 email from the bank’s personnel department says “we hereby demand that you immediately and permanently delete any and all HSBC information on any personal email accounts.”
Crime
The Uncomfortable Demographics of Islamist Bloodshed—and Why “Islamophobia” Deflection Increases the Threat


Addressing realities directly is the only path toward protecting communities, confronting extremism, and preventing further loss of life, Canadian national security expert argues.
After attacks by Islamic extremists, a familiar pattern follows. Debate erupts. Commentary and interviews flood the media. Op-eds, narratives, talking points, and competing interpretations proliferate in the immediate aftermath of bloodshed. The brief interval since the Bondi beach attack is no exception.
Many of these responses condemn the violence and call for solidarity between Muslims and non-Muslims, as well as for broader societal unity. Their core message is commendable, and I support it: extremist violence is horrific, societies must stand united, and communities most commonly targeted by Islamic extremists—Jews, Christians, non-Muslim minorities, and moderate Muslims—deserve to live in safety and be protected.
Yet many of these info-space engagements miss the mark or cater to a narrow audience of wonks. A recurring concern is that, at some point, many of these engagements suggest, infer, or outright insinuate that non-Muslims, or predominantly non-Muslim societies, are somehow expected or obligated to interpret these attacks through an Islamic or Muslim-impact lens. This framing is frequently reinforced by a familiar “not a true Muslim” narrative regarding the perpetrators, alongside warnings about the risks of Islamophobia.
These misaligned expectations collide with a number of uncomfortable but unavoidable truths. Extremist groups such as ISIS, Al-Qaeda, Hamas, Hezbollah, and decentralized attackers with no formal affiliations have repeatedly and explicitly justified their violence through interpretations of Islamic texts and Islamic history. While most Muslims reject these interpretations, it remains equally true that large, dynamic groups of Muslims worldwide do not—and that these groups are well prepared to, and regularly do, use violence to advance their version of Islam.
Islamic extremist movements do not, and did not, emerge in a vacuum. They draw from the broader Islamic context. This fact is observable, persistent, and cannot be wished or washed away, no matter how hard some may try or many may wish otherwise.
Given this reality, it follows that for most non-Muslims—many of whom do not have detailed knowledge of Islam, its internal theological debates, historical divisions, or political evolution—and for a considerable number of Muslims as well, Islamic extremist violence is perceived as connected to Islam as it manifests globally. This perception persists regardless of nuance, disclaimers, or internal distinctions within the faith and among its followers.
THE COST OF DENIAL AND DEFLECTION
Denying or deflecting from these observable connections prevents society from addressing the central issues following an Islamic extremist attack in a Western country: the fatalities and injuries, how the violence is perceived and experienced by surviving victims, how it is experienced and understood by the majority non-Muslim population, how it is interpreted by non-Muslim governments responsible for public safety, and how it is received by allied nations. Worse, refusing to confront these difficult truths—or branding legitimate concerns as Islamophobia—creates a vacuum, one readily filled by extremist voices and adversarial actors eager to poison and pollute the discussion.
Following such attacks, in addition to thinking first of the direct victims, I sympathize with my Muslim family, friends, colleagues, moderate Muslims worldwide, and Muslim victims of Islamic extremism, particularly given that anti-Muslim bigotry is a real problem they face. For Muslim victims of Islamic extremism, that bigotry constitutes a second blow they must endure. Personal sympathy, however, does not translate into an obligation to center Muslim communal concerns when they were not the targets of the attack. Nor does it impose a public obligation or override how societies can, do, or should process and respond to violence directed at them by Islamic extremists.
As it applies to the general public in Western nations, the principle is simple: there should be no expectation that non-Muslims consider Islam, inter-Islamic identity conflicts, internal theological disputes, or the broader impact on the global Muslim community, when responding to attacks carried out by Islamic extremists. That is, unless Muslims were the victims, in which case some consideration is appropriate.
Quite bluntly, non-Muslims are not required to do so and are entitled to reject and push back against any suggestion that they must or should. Pointedly, they are not Muslims, a fact far too many now seem to overlook.
The arguments presented here will be uncomfortable for many and will likely provoke polarizing discussion. Nonetheless, they articulate an important, human-centered position regarding how Islamic extremist attacks in Western nations are commonly interpreted and understood by non-Muslim majority populations.
Non-Muslims are free to give no consideration to Muslim interests at any time, particularly following an Islamic extremist attack against non-Muslims in a non-Muslim country. The sole exception is that governments retain an obligation to ensure the safety and protection of their Muslim citizens, who face real and heightened threats during these periods. This does not suggest that non-Muslims cannot consider Muslim community members; it simply affirms that they are under no obligation to do so.
The impulse for Muslims to distance moderate Muslims and Islam from extremist attacks—such as the targeting of Jews in Australia or foiled Christmas market plots in Poland and Germany—is understandable.
Muslims do so to protect their own interests, the interests of fellow Muslims, and the reputation of Islam itself. Yet this impulse frequently collapses into the “No True Scotsman” fallacy, pointing to peaceful Muslims as the baseline while asserting that the attackers were not “true Muslims.”
Such claims oversimplify the reality of Islam as it manifests globally and fail to address the legitimate political and social consequences that follow Islamic extremist attacks in predominantly non-Muslim Western societies. These deflections frequently produce unintended effects, such as strengthening anti-Muslim extremist sentiments and movements and undermining efforts to diminish them.
The central issue for public discourse after an Islamic extremist attack is not debating whether the perpetrators were “true” or “false” Muslims, nor assessing downstream impacts on Muslim communities—unless they were the targets.
It is a societal effort to understand why radical ideologies continue to emerge from varying—yet often overlapping—interpretations of Islam, how political struggles within the Muslim world contribute to these ideologies, and how non-Muslim-majority Western countries can realistically and effectively confront and mitigate threats related to Islamic extremism before the next attack occurs and more non-Muslim and Muslim lives are lost.
Addressing these realities directly is the only path toward protecting communities, confronting extremism, and preventing further loss of life.
Ian Bradbury, a global security specialist with over 25 years experience, transitioned from Defence and NatSec roles to found Terra Nova Strategic Management (2009) and 1NAEF (2014). A TEDx, UN, NATO, and Parliament speaker, he focuses on terrorism, hybrid warfare, conflict aid, stability operations, and geo-strategy.
The Bureau is a reader-supported publication.
To receive new posts and support my work, consider becoming a free or paid subscriber.
Crime
Brown University shooter dead of apparent self-inflicted gunshot wound

From The Center Square
By
Rhode Island officials said the suspected gunman in the Brown University mass shooting has been found dead of an apparent self-inflicted gunshot wound, more than 50 miles away in a storage facility in southern New Hampshire.
The shooter was identified as Claudio Manuel Neves-Valente, a 48-year-old Brown student and Portuguese national. Neves-Valente was found dead with a satchel containing two firearms inside in the storage facility, authorities said.
“He took his own life tonight,” Providence police chief Oscar Perez said at a press conference, noting that local, state and federal law officials spent days poring over video evidence, license plate data and hundreds of investigative tips in pursuit of the suspect.
Perez credited cooperation between federal state and local law enforcement officials, as well as the Providence community, which he said provided the video evidence needed to help authorities crack the case.
“The community stepped up,” he said. “It was all about groundwork, public assistance, interviews with individuals, and good old fashioned policing.”
Rhode Island Attorney General Peter Neronha said the “person of interest” identified by private videos contacted authorities on Wednesday and provided information that led to his whereabouts.
“He blew the case right open, blew it open,” Neronha said. “That person led us to the car, which led us to the name, which led us to the photograph of that individual.”
“And that’s how these cases sometimes go,” he said. “You can feel like you’re not making a lot of progress. You can feel like you’re chasing leaves and they don’t work out. But the team keeps going.”
The discovery of the suspect’s body caps an intense six-day manhunt spanning several New England states, which put communities from Providence to southern New Hampshire on edge.
“We got him,” FBI special agent in charge for Boston Ted Docks said at Thursday night’s briefing. “Even though the suspect was found dead tonight our work is not done. There are many questions that need to be answered.”
He said the FBI deployed around 500 agents to assist local authorities in the investigation, in addition to offering a $50,000 reward. He says that officials are still looking into the suspect’s motive.
Two students were killed and nine others were injured in the Brown University shooting Saturday, which happened when an undetected gunman entered the Barus and Holley building on campus, where students were taking exams before the holiday break. Providence authorities briefly detained a person in the shooting earlier in the week, but then released them.
Investigators said they are also examining the possibility that the Brown case is connected to the killing of a Massachusetts Institute of Technology professor in his hometown.
An unidentified gunman shot MIT professor Nuno Loureiro multiple times inside his home in Brookline, about 50 miles north of Providence, according to authorities. He died at a local hospital on Tuesday.
Leah Foley, U.S. attorney for Massachusetts, was expected to hold a news briefing late Thursday night to discuss the connection with the MIT shooting.
-

 armed forces2 days ago
armed forces2 days agoOttawa’s Newly Released Defence Plan Crosses a Dangerous Line
-

 espionage2 days ago
espionage2 days agoCarney Floor Crossing Raises Counterintelligence Questions aimed at China, Former Senior Mountie Argues
-

 Health1 day ago
Health1 day agoAll 12 Vaccinated vs. Unvaccinated Studies Found the Same Thing: Unvaccinated Children Are Far Healthier
-

 Energy2 days ago
Energy2 days ago75 per cent of Canadians support the construction of new pipelines to the East Coast and British Columbia
-

 Opinion1 day ago
Opinion1 day agoPope Leo XIV’s Christmas night homily
-

 armed forces1 day ago
armed forces1 day agoRemembering Afghanistan and the sacrifices of our military families
-

 Fraser Institute19 hours ago
Fraser Institute19 hours agoCarney government sowing seeds for corruption in Ottawa
-

 Fraser Institute1 day ago
Fraser Institute1 day agoHow to talk about housing at the holiday dinner table











