Alberta
Alberta Environment Minister Schulz preparing for impending drought
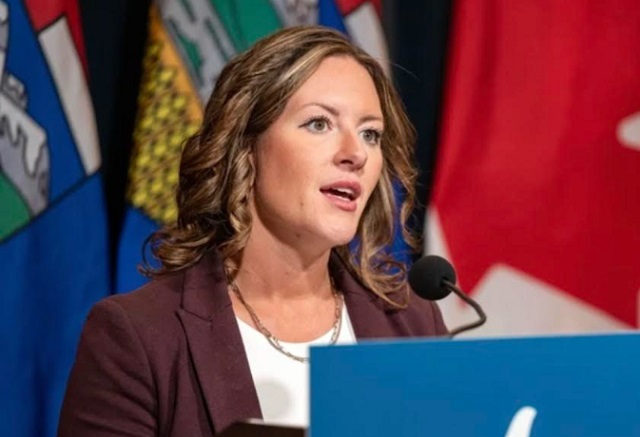

Taking action on drought in Alberta
“Alberta has five stages in its water management plan. Ranging from Stage 1, which is a minor drought to Stage 5, which is a province-wide emergency. We are currently in Stage 4.”
Water is one of Alberta’s most precious resources. We all use it, consume it, and rely on it.
Most of the water that Albertans use to drink, grow crops, run our businesses and sustain our environment comes from rain and melting snow. The last three years have brought droughts and water shortages in various parts of our province, including most of Southern Alberta this summer.
The world is also experiencing El Niño, a global phenomenon occurring for the first time in seven years. It’s causing less snow and rain, along with higher temperatures, around the world this winter. Recent forecasts indicate that there is a 62 percent chance that the unusually warm and dry conditions that we have experienced could continue until June 2024.
Alberta has five stages in its water management plan. Ranging from Stage 1, which is a minor drought to Stage 5, which is a province-wide emergency. We are currently in Stage 4.
Our government is now preparing for the possibility of a serious drought next year. The good news is
that Alberta is up to the challenge. This province has navigated droughts before and has a long, proud
history of coming together during tough times.
Officials in the department of Environment and Protected Areas have stood up a Drought Command Team and work is underway to finalize a Drought Emergency Plan.
Meetings have been held with communities, farmers, businesses and others to prepare. Many have
already taken action to implement conservation measures and adapt to reduced water levels. Our
government has announced up to $165 million in federal-provincial drought relief for livestock
producers. And, this summer and fall, Calgary, Medicine Hat and other communities adopted voluntary and mandatory restrictions on water use to help Alberta’s stressed river basins.
I commend the collective actions taken so far by so many people throughout Alberta.
Over the coming months, we will be carefully monitoring snowpack, rainfall, river levels and actual water use to develop our early warning capacity. We will use this information and scientific modelling to assess the risk of drought next year. We have launched alberta.ca/drought to keep all Albertans updated as we take these steps.
Together with our partners, we are doing everything we can to be fully prepared for whatever next year brings. An advisory panel of experts to help provide advice will be formed in the months ahead. And we are preparing for the future, looking at what long-term infrastructure is needed to help manage water supplies for future generations.
We cannot make it rain or snow, but all of us have a role to play. Conserving water can help your
community, as well as Albertans downstream from you. In the coming months, we will all have to pull
together to secure our province’s water supply. It is a challenge that I am confident Albertans will meet.
Rebecca Schulz, Minister of Environment and Protected Areas
Alberta
Red Deer Justice Centre Grand Opening: Building access to justice for Albertans
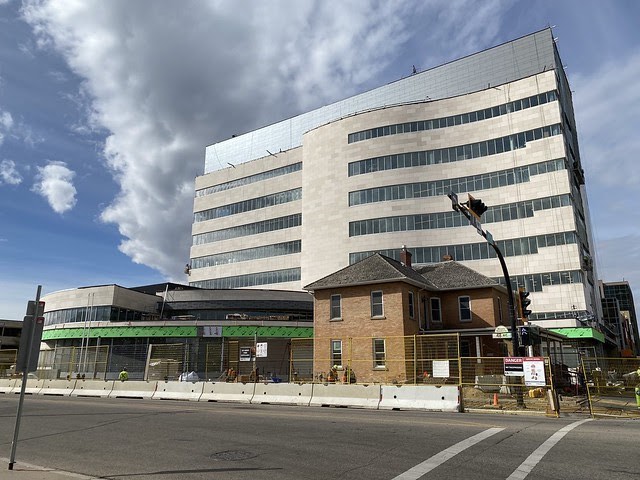

The new Red Deer Justice Centre will help Albertans resolve their legal matters faster.
Albertans deserve to have access to a fair, accessible and transparent justice system. Modernizing Alberta’s courthouse infrastructure will help make sure Alberta’s justice system runs efficiently and meets the needs of the province’s growing population.
Alberta’s government has invested $191 million to build the new Red Deer Justice Centre, increasing the number of courtrooms from eight to 12, allowing more cases to be heard at one time.
“Modern, accessible courthouses and streamlined services not only strengthen our justice
system – they build safer, stronger communities across the province. Investing in the new Red Deer Justice Centre is vital to helping our justice system operate more efficiently, and will give people in Red Deer and across central Alberta better access to justice.”

Government of Alberta and Judiciary representatives with special guests at the Red Deer Justice Centre plaque unveiling event April 22, 2025.
On March 3, all court services in Red Deer began operating out of the new justice centre. The new justice centre has 12 courtrooms fully built and equipped with video-conference equipment to allow witnesses to attend remotely if they cannot travel, and vulnerable witnesses to testify from outside the courtroom.
The new justice centre also has spaces for people taking alternative approaches to the traditional courtroom trial process, with the three new suites for judicial dispute resolution services, a specific suite for other dispute resolution services, such as family mediation and civil mediation, and a new Indigenous courtroom with dedicated venting for smudging purposes.
“We are very excited about this new courthouse for central Alberta. Investing in the places where people seek justice shows respect for the rights of all Albertans. The Red Deer Justice Centre fills a significant infrastructure need for this rapidly growing part of the province. It is also an important symbol of the rule of law, meaning that none of us are above the law, and there is an independent judiciary to decide disputes. This is essential for a healthy functioning democracy.”
“Public safety and access to justice go hand in hand. With this investment in the new Red Deer Justice Centre, Alberta’s government is ensuring that communities are safer, legal matters are resolved more efficiently and all Albertans get the support they need.”
“This state-of-the-art facility will serve the people of Red Deer and surrounding communities for generations. Our team at Infrastructure is incredibly proud of the work done to plan, design and build this project. I want to thank everyone, at all levels, who helped make this project a reality.”
Budget 2025 is meeting the challenge faced by Alberta with continued investments in education and health, lower taxes for families and a focus on the economy.

Quick facts
- The new Red Deer Justice Centre is 312,000 sq ft (29,000 m2). (The old courthouse is 98,780 sq ft (9,177 m2)).
- The approved project funding for the Red Deer Justice Centre is about $191 million.
Alberta
Made in Alberta! Province makes it easier to support local products with Buy Local program

Show your Alberta side. Buy Local. |
When the going gets tough, Albertans stick together. That’s why Alberta’s government is launching a new campaign to benefit hard-working Albertans.
Global uncertainty is threatening the livelihoods of hard-working Alberta farmers, ranchers, processors and their families. The ‘Buy Local’ campaign, recently launched by Alberta’s government, encourages consumers to eat, drink and buy local to show our unified support for the province’s agriculture and food industry.
The government’s ‘Buy Local’ campaign encourages consumers to buy products from Alberta’s hard-working farmers, ranchers and food processors that produce safe, nutritious food for Albertans, Canadians and the world.
“It’s time to let these hard-working Albertans know we have their back. Now, more than ever, we need to shop local and buy made-in-Alberta products. The next time you are grocery shopping or go out for dinner or a drink with your friends or family, support local to demonstrate your Alberta pride. We are pleased tariffs don’t impact the ag industry right now and will keep advocating for our ag industry.”
Alberta’s government supports consumer choice. We are providing tools to help folks easily identify Alberta- and Canadian-made foods and products. Choosing local products keeps Albertans’ hard-earned dollars in our province. Whether it is farm-fresh vegetables, potatoes, honey, craft beer, frozen food or our world-renowned beef, Alberta has an abundance of fresh foods produced right on our doorstep.
Quick facts
- This summer, Albertans can support local at more than 150 farmers’ markets across the province and meet the folks who make, bake and grow our food.
- In March 2023, the Alberta government launched the ‘Made in Alberta’ voluntary food and beverage labelling program to support local agriculture and food sectors.
- Through direct connections with processors, the program has created the momentum to continue expanding consumer awareness about the ‘Made in Alberta’ label to help shoppers quickly identify foods and beverages produced in our province.
- Made in Alberta product catalogue website
Related information
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoIs Government Inflation Reporting Accurate?
-

 2025 Federal Election2 days ago
2025 Federal Election2 days agoCarney’s Hidden Climate Finance Agenda
-

 2025 Federal Election2 days ago
2025 Federal Election2 days agoStudy links B.C.’s drug policies to more overdoses, but researchers urge caution
-

 2025 Federal Election2 days ago
2025 Federal Election2 days agoWhen it comes to pipelines, Carney’s words flow both ways
-

 2025 Federal Election1 day ago
2025 Federal Election1 day agoPolls say Canadians will give Trump what he wants, a Carney victory.
-

 2025 Federal Election1 day ago
2025 Federal Election1 day agoPoilievre’s Conservatives promise to repeal policy allowing male criminals in female jails
-

 2025 Federal Election1 day ago
2025 Federal Election1 day agoTrump Has Driven Canadians Crazy. This Is How Crazy.
-

 2025 Federal Election1 day ago
2025 Federal Election1 day agoCarney Liberals pledge to follow ‘gender-based goals analysis’ in all government policy