Uncategorized
U.S. voting system faces test on Election Day
ATLANTA — Federal and state officials have been working for nearly two years to shore up the nation’s election infrastructure from cyberattacks by Russians or others seeking to disrupt the voting process.
It turns out that many of the problems are closer to home.
Early voting leading up to Tuesday’s midterm election revealed a wide variety of concerns with voting and registration systems around the country — from machines that changed voter selections to registration forms tossed out because of clerical errors.
Election officials and voting rights groups fear that voter confidence in the results could be undermined if such problems become even more widespread on Election Day, as millions of Americans head to the polls to decide pivotal races for Congress and governor.
Already there is concern that last-minute court rulings on voter ID requirements, the handling of absentee ballots and other issues in a handful of states will sow confusion among voters and poll workers.
“We expect poll workers will be overwhelmed, just as voters are overwhelmed, and there will be lots of provisional ballots,” said Sara Henderson, head of Common Cause in Georgia, where voting-rights groups have been raising numerous concerns about election security and voter access.
The problems come amid a surge of interest, with registrations and early-voting turnout running well ahead of what is typically seen during a midterm election.
As Election Day voting began across the East Coast, there were scattered reports of long lines and some polling places not opening on time, which are not unusual problems in any election.
The election marks the first nationwide voting since Russia targeted state election systems in the 2016 presidential race. Federal, state and local officials have been working to make the nation’s myriad election systems more secure. They have beefed up their cybersecurity protections and improved communications and intelligence-sharing.
The U.S. Department of Homeland Security, FBI and other federal agencies have opened a command
“We want them to be as informed as possible,” said Matt Masterson, senior cybersecurity adviser with the Department of Homeland Security.
There have been no signs so far that Russia or any other foreign actor has tried to launch cyberattacks against voting systems in any state, according to federal authorities. There was also no indication that any systems have been compromised that would prevent voting, change vote counts, or disrupt the ability to tally votes, U.S. officials said.
But early voting and voter registration has been problematic in a number of states. Problems include faulty machines in Texas and North Carolina, inaccurate mailers in Missouri and Montana, and voter registration problems in Tennessee and Georgia.
In other states, including Kansas, Election Day polling places have been closed or consolidated, leading to worries that voters will be disenfranchised if they can’t find a way to get there and cast a ballot.
Questions about election integrity erupted in recent days in Georgia, where the governor’s race is among the most closely watched elections in the country.
Over the weekend, reports of security vulnerabilities within the state’s online voter registration portal prompted a flurry of accusations from the Secretary of State’s office, which is overseen by Republican gubernatorial candidate Brian Kemp. His office claimed without providing evidence that Democrats had tried to hack into the system. Democrats dismissed that as an effort to distract voters from a problem in a system Kemp oversees.
DHS officials have boasted that the 2018 midterms will be the most secure election in U.S. history, pointing to federal intrusion-detection sensors that will protect “90
But similar sensors used at the federal level have performed badly. According to a Sept. 14 letter from the Office of Management and Budget, those sensors had a 99
Nationally, some 6,500 poll watchers are being deployed by a coalition of civil rights and voting advocacy groups to assist people who encounter problems at the polls. That is more than double the number sent to polling places in 2016, while the number of federal election monitors has declined.
___
Long reported from Washington. AP writer Michael Balsamo contributed to this story.
___
Follow Christina Almeida Cassidy at https://twitter.com/AP_Christina and Colleen Long at http://twitter.com/ctlong1 .
___
For AP’s complete coverage of the U.S. midterm elections: http://apne.ws/APPolitics
Christina A. Cassidy And Colleen Long, The Associated Press
Uncategorized
Mortgaging Canada’s energy future — the hidden costs of the Carney-Smith pipeline deal


Much of the commentary on the Carney-Smith pipeline Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) has focused on the question of whether or not the proposed pipeline will ever get built.
That’s an important topic, and one that deserves to be examined — whether, as John Robson, of the indispensable Climate Discussion Nexus, predicted, “opposition from the government of British Columbia and aboriginal groups, and the skittishness of the oil industry about investing in a major project in Canada, will kill [the pipeline] dead.”
But I’m going to ask a different question: Would it even be worth building this pipeline on the terms Ottawa is forcing on Alberta? If you squint, the MOU might look like a victory on paper. Ottawa suspends the oil and gas emissions cap, proposes an exemption from the West Coast tanker ban, and lays the groundwork for the construction of one (though only one) million barrels per day pipeline to tidewater.
But in return, Alberta must agree to jack its industrial carbon tax up from $95 to $130 per tonne at a minimum, while committing to tens of billions in carbon capture, utilization, and storage (CCUS) spending, including the $16.5 billion Pathways Alliance megaproject.
Here’s the part none of the project’s boosters seem to want to mention: those concessions will make the production of Canadian hydrocarbon energy significantly more expensive.
As economist Jack Mintz has explained, the industrial carbon tax hike alone adds more than $5 USD per barrel of Canadian crude to marginal production costs — the costs that matter when companies decide whether to invest in new production. Layer on the CCUS requirements and you get another $1.20–$3 per barrel for mining projects and $3.60–$4.80 for steam-assisted operations.
While roughly 62% of the capital cost of carbon capture is to be covered by taxpayers — another problem with the agreement, I might add — the remainder is covered by the industry, and thus, eventually, consumers.
Total damage: somewhere between $6.40 and $10 US per barrel. Perhaps more.
“Ultimately,” the Fraser Institute explains, “this will widen the competitiveness gap between Alberta and many other jurisdictions, such as the United States,” that don’t hamstring their energy producers in this way. Producers in Texas and Oklahoma, not to mention Saudi Arabia, Venezuela, or Russia, aren’t paying a dime in equivalent carbon taxes or mandatory CCUS bills. They’re not so masochistic.
American refiners won’t pay a “low-carbon premium” for Canadian crude. They’ll just buy cheaper oil or ramp up their own production.
In short, a shiny new pipe is worthless if the extra cost makes barrels of our oil so expensive that no one will want them.
And that doesn’t even touch on the problem for the domestic market, where the higher production cost will be passed onto Canadian consumers in the form of higher gas and diesel prices, home heating costs, and an elevated cost of everyday goods, like groceries.
Either way, Canadians lose.
So, concludes Mintz, “The big problem for a new oil pipeline isn’t getting BC or First Nation acceptance. Rather, it’s smothering the industry’s competitiveness by layering on carbon pricing and decarbonization costs that most competing countries don’t charge.” Meanwhile, lurking underneath this whole discussion is the MOU’s ultimate Achilles’ heel: net-zero.
The MOU proudly declares that “Canada and Alberta remain committed to achieving Net-Zero greenhouse gas emissions by 2050.” As Vaclav Smil documented in a recent study of Net-Zero, global fossil-fuel use has risen 55% since the 1997 Kyoto agreement, despite trillions spent on subsidies and regulations. Fossil fuels still supply 82% of the world’s energy.
With these numbers in mind, the idea that Canada can unilaterally decarbonize its largest export industry in 25 years is delusional.
This deal doesn’t secure Canada’s energy future. It mortgages it. We are trading market access for self-inflicted costs that will shrink production, scare off capital, and cut into the profitability of any potential pipeline. Affordable energy, good jobs, and national prosperity shouldn’t require surrendering to net-zero fantasy.If Ottawa were serious about making Canada an energy superpower, it would scrap the anti-resource laws outright, kill the carbon taxes, and let our world-class oil and gas compete on merit. Instead, we’ve been handed a backroom MOU which, for the cost of one pipeline — if that! — guarantees higher costs today and smothers the industry that is the backbone of the Canadian economy.
This MOU isn’t salvation. It’s a prescription for Canadian decline.
Uncategorized
Cost of bureaucracy balloons 80 per cent in 10 years: Public Accounts

The cost of the bureaucracy increased by $6 billion last year, according to newly released numbers in Public Accounts disclosures. The Canadian Taxpayers Federation is calling on Prime Minister Mark Carney to immediately shrink the bureaucracy.
“The Public Accounts show the cost of the federal bureaucracy is out of control,” said Franco Terrazzano, CTF Federal Director. “Tinkering around the edges won’t cut it, Carney needs to take urgent action to shrink the bloated federal bureaucracy.”
The federal bureaucracy cost taxpayers $71.4 billion in 2024-25, according to the Public Accounts. The cost of the federal bureaucracy increased by $6 billion, or more than nine per cent, over the last year.
The federal bureaucracy cost taxpayers $39.6 billion in 2015-16, according to the Public Accounts. That means the cost of the federal bureaucracy increased 80 per cent over the last 10 years. The government added 99,000 extra bureaucrats between 2015-16 and 2024-25.
Half of Canadians say federal services have gotten worse since 2016, despite the massive increase in the federal bureaucracy, according to a Leger poll.
Not only has the size of the bureaucracy increased, the cost of consultants, contractors and outsourcing has increased as well. The government spent $23.1 billion on “professional and special services” last year, according to the Public Accounts. That’s an 11 per cent increase over the previous year. The government’s spending on professional and special services more than doubled since 2015-16.
“Taxpayers should not be paying way more for in-house government bureaucrats and way more for outside help,” Terrazzano said. “Mere promises to find minor savings in the federal bureaucracy won’t fix Canada’s finances.
“Taxpayers need Carney to take urgent action and significantly cut the number of bureaucrats now.”
Table: Cost of bureaucracy and professional and special services, Public Accounts
| Year | Bureaucracy | Professional and special services |
|
$71,369,677,000 |
$23,145,218,000 |
|
|
$65,326,643,000 |
$20,771,477,000 |
|
|
$56,467,851,000 |
$18,591,373,000 |
|
|
$60,676,243,000 |
$17,511,078,000 |
|
|
$52,984,272,000 |
$14,720,455,000 |
|
|
$46,349,166,000 |
$13,334,341,000 |
|
|
$46,131,628,000 |
$12,940,395,000 |
|
|
$45,262,821,000 |
$12,950,619,000 |
|
|
$38,909,594,000 |
$11,910,257,000 |
|
|
$39,616,656,000 |
$11,082,974,000 |
-

 International2 days ago
International2 days agoGeorgia county admits illegally certifying 315k ballots in 2020 presidential election
-

 Alberta2 days ago
Alberta2 days agoA Christmas wish list for health-care reform
-

 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoSome Of The Wackiest Things Featured In Rand Paul’s New Report Alleging $1,639,135,969,608 In Gov’t Waste
-

 Energy1 day ago
Energy1 day ago‘The electric story is over’
-

 Agriculture2 days ago
Agriculture2 days agoThe Climate Argument Against Livestock Doesn’t Add Up
-

 International20 hours ago
International20 hours ago$2.6 million raised for man who wrestled shotgun from Bondi Beach terrorist
-
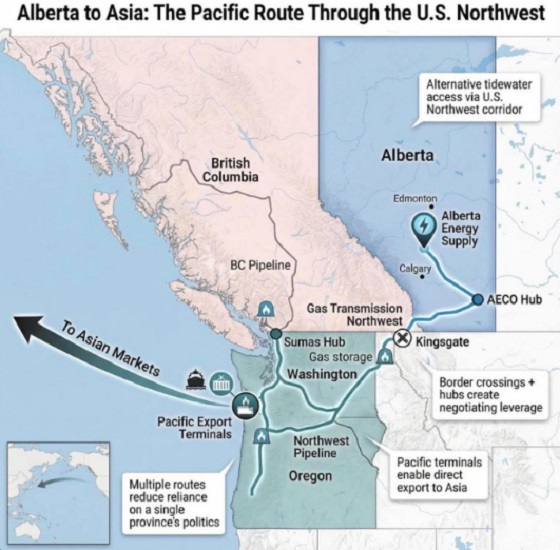
 Alberta2 days ago
Alberta2 days agoWhat are the odds of a pipeline through the American Pacific Northwest
-

 International2 days ago
International2 days agoCommunist China arrests hundreds of Christians just days before Christmas










