Uncategorized
Trump team turns over written answers to Mueller’s questions

WASHINGTON — President Donald Trump has provided the special counsel with written answers to questions about his knowledge of Russian interference in the 2016 election, his lawyers said Tuesday, avoiding at least for now a potentially risky sit-down with prosecutors. It’s the first time he has directly
The step is a milestone in the negotiations between Trump’s attorneys and special counsel Robert Mueller’s team over whether and when the president might sit for an interview.
The compromise outcome, nearly a year in the making, offers some benefit to both sides. Trump at least temporarily averts the threat of an in-person interview, which his lawyers have long resisted, while Mueller secures on-the-record statements whose accuracy the president will be expected to stand by for the duration of the investigation.
The responses may also help stave off a potential subpoena fight over Trump’s testimony if Mueller deems them satisfactory. They represent the first time the president is known to have described to investigators his knowledge of key moments under scrutiny by prosecutors.
But investigators may still press for more information.
Mueller’s team months ago presented Trump’s legal team with dozens of questions they wanted to ask the president related to whether his campaign
Mueller left open the possibility that he would follow up with additional questions on obstruction, though Trump’s lawyers — who had long resisted any face-to-face interview — have been especially adamant that the Constitution shields him from having to answer any questions about actions he took as president.
Trump attorney Jay Sekulow offered no details on the current Q&A, saying merely that “the written questions submitted by the special counsel’s office … dealt with issues regarding the Russia-related topics of the inquiry. The president responded in writing.” He said the legal team would not release copies of the questions and answers or discuss any correspondence it has had with the special counsel’s office.
Another of Trump’s lawyers, Rudy Giuliani, said the lawyers continue to believe that “much of what has been asked raised serious
“It is time to bring this inquiry to a conclusion,” Giuliani said.
The president told reporters last week that he had prepared the responses himself.
Trump said in a Fox News interview that aired Sunday that he was unlikely to answer questions about obstruction, saying, “I think we’ve wasted enough time on this witch hunt and the answer is, probably, we’re finished.”
Trump joins a list of recent presidents who have submitted to questioning as part of a criminal investigation.
In 2004, President George W. Bush was interviewed by special counsel Patrick Fitzgerald’s office during an investigation into the leaked identity of a covert CIA officer. In 1998, President Bill Clinton testified before a federal grand jury in independent counsel Ken Starr’s Whitewater investigation.
“It’s very extraordinary if this were a regular case, but it’s not every day that you have an investigation that touches upon the White House,” Solomon Wisenberg, a Washington lawyer who was part of Starr’s team and conducted the grand jury questioning of Clinton, said of a prosecutor accepting written answers.
Mueller could theoretically still try to subpoena the president if he feels the answers are not satisfactory.
But Justice Department leaders, including acting Attorney General Matthew Whitaker — who now oversees the investigation and has spoken pejoratively of it in the past — would have to sign off on such a move, and it’s far from clear that they would. It’s also not clear that Mueller’s team would prevail if a subpoena fight reached the Supreme Court.
“Mueller certainly could have forced the issue and issued a subpoena, but I think he wants to present a record of having bent over backwards to be fair,” Wisenberg said.
The Supreme Court has never directly ruled on whether a president can be subpoenaed to testify in a criminal case. Clinton was subpoenaed to appear before the Whitewater grand jury, but investigators withdrew the subpoena after he agreed to appear voluntarily.
Other cases involving Presidents Richard Nixon and Clinton have presented similar issues for the justices that could be instructive now.
In 1974, for instance, the court ruled that Nixon could be ordered to turn over subpoenaed recordings, a decision that hastened his resignation. The court in 1997 said Clinton could be questioned under oath in a sexual harassment lawsuit brought by Paula Jones.
___
Follow Eric Tucker on Twitter at http://www.twitter.com/etuckerAP
Eric Tucker, The Associated Press
Uncategorized
Trump Admin Establishing Council To Make Buildings Beautiful Again


From the Daily Caller News Foundation
By Jason Hopkins
The Trump administration is creating a first-of-its-kind task force aimed at ushering in a new “Golden Age” of beautiful infrastructure across the U.S.
The Department of Transportation (DOT) will announce the establishment of the Beautifying Transportation Infrastructure Council (BTIC) on Thursday, the Daily Caller News Foundation exclusively learned. The BTIC seeks to advise Transportation Secretary Sean Duffy on design and policy ideas for key infrastructure projects, including highways, bridges and transit hubs.
“What happened to our country’s proud tradition of building great, big, beautiful things?” Duffy said in a statement shared with the DCNF. “It’s time the design for America’s latest infrastructure projects reflects our nation’s strength, pride, and promise.”
“We’re engaging the best and brightest minds in architectural design and engineering to make beautiful structures that move you and bring about a new Golden Age of Transportation,” Duffy continued.
Mini scoop – here is the DOT’s rollout of its Beautifying Transportation Infrastructure Council, which will be tasked with making our buildings beautiful again. pic.twitter.com/
9iV2xSxdJM — Jason Hopkins (@jasonhopkinsdc) October 23, 2025
The DOT is encouraging nominations of the country’s best architects, urban planners, artists and others to serve on the council, according to the department. While ensuring that efficiency and safety remain a top priority, the BTIC will provide guidance on projects that “enhance” public areas and develop aesthetic performance metrics.
The new council aligns with an executive order signed by President Donald Trump in August 2025 regarding infrastructure. The “Making Federal Architecture Beautiful Again” order calls for federal public buildings in the country to “respect regional architectural heritage” and aims to prevent federal construction projects from using modernist and brutalist architecture styles, instead returning to a classical style.
“The Founders, in line with great societies before them, attached great importance to Federal civic architecture,” Trump’s order stated. “They wanted America’s public buildings to inspire the American people and encourage civic virtue.”
“President George Washington and Secretary of State Thomas Jefferson consciously modeled the most important buildings in Washington, D.C., on the classical architecture of ancient Athens and Rome,” the order continued. “Because of their proven ability to meet these requirements, classical and traditional architecture are preferred modes of architectural design.”
The DOT invested millions in major infrastructure projects since Trump’s return to the White House. Duffy announced in August a $43 million transformation initiative of the New York Penn Station in New York City and in September unveiledmajor progress in the rehabilitation and modernization of Washington Union Station in Washington, D.C.
The BTIC will comprise up to 11 members who will serve two-year terms, with the chance to be reappointed, according to the DOT. The task force will meet biannually. The deadline for nominations will end Nov. 21.
Uncategorized
New report warns WHO health rules erode Canada’s democracy and Charter rights

The Justice Centre for Constitutional Freedoms has released a new report titled Canada’s Surrender of Sovereignty: New WHO health regulations undermine Canadian democracy and Charter freedoms. Authored by Nigel Hannaford, a veteran journalist and researcher, the report warns that Canada’s acceptance of the World Health Organization’s (WHO) revised International Health Regulations (IHR) represents a serious erosion of national independence and democratic accountability.
The IHR amendments, which took effect on September 19, 2025, authorize the WHO Director-General to declare global “health emergencies” that could require Canada to follow directives from bureaucrats in Geneva, bypassing the House of Commons and the will of Canadian voters.
The WHO regards these regulations as “binding,” despite having no ability or legal authority to impose such regulations. Even so, Canada is opting to accept the regulations as binding.
By accepting the WHO’s revised IHR, the report explains, Canada has relinquished its own control over future health crises and instead has agreed to let the WHO determine when a “pandemic emergency” exists and what Canada must do to respond to it, after which Canada must report back to the WHO.
In fact, under these International Health Regulations, the WHO could demand countries like Canada impose stringent freedom-violating health policies, such as lockdowns, vaccine mandates, or travel restrictions without debate, evidence review, or public accountability, the report explains.
Once the WHO declares a “Pandemic Emergency,” member states are obligated to implement such emergency measures “without delay” for a minimum of three months.
Importantly, following these WHO directives would undermine government accountability as politicians may hide behind international “commitments” to justify their actions as “simply following international rules,” the report warns.
Canada should instead withdraw from the revised IHR, following the example of countries like Germany, Austria, Italy, Czech Republic, and the United States. The report recommends continued international cooperation without surrendering control over domestic health policies.
Constitutional lawyer Allison Pejovic said, “[b]y treating WHO edicts as binding, the federal government has effectively placed Canadian sovereignty on loan to an unelected international body.”
“Such directives, if enforced, would likely violate Canadians’ Charter rights and freedoms,” she added.
Mr. Hannaford agreed, saying, “Canada’s health policies must be made in Canada. No free and democratic nation should outsource its emergency powers to unelected bureaucrats in Geneva.”
The Justice Centre urges Canadians to contact their Members of Parliament and demand they support withdrawing from the revised IHR to restore Canadian sovereignty and reject blind compliance with WHO directives.
-

 Censorship Industrial Complex1 day ago
Censorship Industrial Complex1 day agoEU’s “Democracy Shield” Centralizes Control Over Online Speech
-
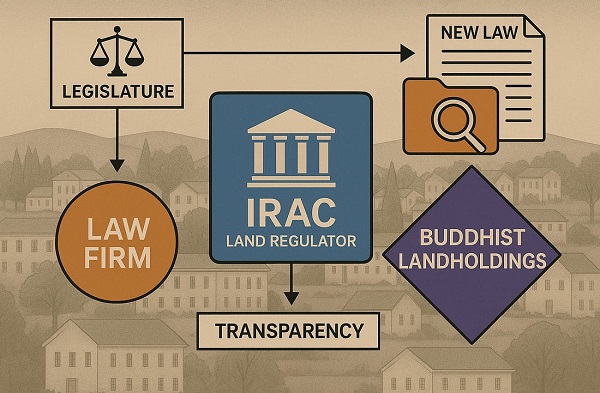
 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoP.E.I. Moves to Open IRAC Files, Forcing Land Regulator to Publish Reports After The Bureau’s Investigation
-
 COVID-192 days ago
COVID-192 days agoMajor new studies link COVID shots to kidney disease, respiratory problems
-

 Addictions19 hours ago
Addictions19 hours agoCanadian gov’t not stopping drug injection sites from being set up near schools, daycares
-

 International1 day ago
International1 day agoIs America drifting toward civil war? Joe Rogan thinks so
-

 Business19 hours ago
Business19 hours agoParliamentary Budget Officer begs Carney to cut back on spending
-

 International1 day ago
International1 day agoBondi and Patel deliver explosive “Clinton Corruption Files” to Congress
-

 International1 day ago
International1 day agoState Department designates European Antifa groups foreign terror organizations









