National
The elements of Marc Garneau – A special report from Paul Wells

|
|
He was trained to admit every error. Then he went into politics. A feature interview with the retiring MP for Notre-Dame-de-Grâce—Westmount
Introduction
When you resign your seat in the House of Commons, you get to keep your phone for 90 days. The deadlines for cleaning out your offices on Parliament Hill and in your riding are tighter but still civilized. Soon Marc Garneau will leave his constituency office on the third floor of a nondescript office building in Westmount, the affluent anglophone enclave west of downtown Montreal, for the last time. But there’s no rush, so he met me there on Monday.
Trying to get politicians to speak frankly while they’re still in office is not always rewarding, It gets easier quickly once they leave. So I thought a visit with Garneau was worth the drive to Montreal, even though he’s been cagey in his remarks to journalists since he announced his retirement on March 8. I’ll cut to the chase: His interview with me wasn’t the work of a rebel either. Garneau remains a gentleman and a Liberal. He offered only praise for Justin Trudeau. But on several issues — communications philosophy; the handling of the Freedom Convoy occupation of Ottawa; and the proper attitude toward one’s own fallibility — he drew occasional sharp distinctions between his attitude and the Trudeau government’s.
I took the scenic route to get to that stuff. Garneau was the first Canadian to fly in space. He was a national celebrity before Trudeau finished high school. And while that’s a historic distinction, Garneau shares with many more parliamentarians a long career outside politics that preceded, and informed, his career in elected office. Not all of that is the stuff of every conversation, but this one was valedictory in tone. I thought it best to start at the beginning.
This is an unusually long post on the Paul Wells newsletter. I figured I owed everyone a good feature read. I’m leaving the paywall off. You can help spread word about the writing I do by sharing this with a friend or with your networks.
I also want to remind readers that writing this newsletter is what I do for a living. When you decide to become a paid subscriber, you help support this work. You also make it possible for me to do things too few of my colleagues elsewhere are able to do — things like travelling, or paying a professional photographer properly to illustrate my work.
1. Water
I began by asking him about the year and a half he spent as a combat systems engineer on the HMCS Algonquin. When he arrived on board, it was the newest destroyer in the Canadian Navy.
“It was what I had dreamt of from the beginning of my life,” he said. “My first love was the Navy.” His father’s family was francophone Quebecers, soldiers from way back. His father fought in the infantry in WWII and was posted in Germany for two years as the Cold War settled in. “I crossed the ocean with my parents in 1956 coming back from Germany,” he said. “We came back on a ship that was on its last voyage, the Samaria, and I just fell in love with the ocean. A few years later, we went back to England on the Empress of Britain. Those confirmed for me that I wanted to be in the Navy.”
The Algonquin, a big boat with 280 crew, spent three months doing exercises as part of STANAVFORLANT, NATO’s multinational Standing Naval Force Atlantic, which would pretend the Soviet Union was up to various kinds of risky business and figure out ways to respond. Off Puerto Rico he led tests of the new Sea Sparrow missile system. Around Newfoundland’s outports, the Algonquin took the province’s lieutenant governor on an annual tour.
Young Garneau wasn’t particularly interested in moving up the ranks. “I’m an engineer. I didn’t want to be the ship captain. I wanted to be the engineer that kept the equipment going. That may not sound very exciting. But for me that was exciting, because it’s quite a job to keep all that equipment operational in case you had to go into conflict.”
2. Air
Advancement for its own sake held no appeal. But when he saw a nondescript ad from the National Research Council calling for applicants for Canada’s first astronaut corps, that sounded better than a promotion. “Wow. The idea of possibly going into space just blew me away. At the same time, I thought my chances [of being chosen] were pretty close to zero.”
In May of 1983 there were 4,200 applicants. Six months later, six remained. It became clear pretty soon the program wasn’t just looking for technical expertise but for — well, for heroes. Or at least for people who wouldn’t screw up the illusion.
“They wanted us to write essays about why we thought that we were particularly well suited. Did we realize that we would become public figures? And were we ready for that? And did we think it was important for Canada? Medical [exams] like you’d never had before. Every single thing checked, because you had to be 100% fit. Then they brought us in for the last week and and they subjected us to a whole bunch of things.
“We had to give presentations in front of the selection board. Any attempted humour was met with a stone-cold face. I remember coming out of it thinking, ‘I’ve totally bombed this.’ But they’d all been trained not to react to anything.
“Do you remember somebody called Keith Morrison?” I sure do. TV reporter and anchor, CTV to the CBC to NBC. He actually interviewed me once, when that was an odd thing to do, and I remember he was good at it. “Well, Keith was hired for the week. And he put us through our paces, sort of doing the interview thing. So that was another thing they wanted to know, if you’d be able to do that. They had us in social settings, like a cocktail kind of thing. [They wanted to see] whether you were relatively comfortable in the company of total strangers, that kind of thing. So it’s a pretty thorough week. And by the end of that, they said, ‘Look, stand by your telephone between five and seven on the third of December and you’ll get a call.’ We’re 20 at that point. ‘It’ll either be to say, sorry you didn’t make it, or, you made it.’ And I was fortunate to be one of the six chosen. They called about six o’clock. They didn’t beat around the bush. ‘Look, you made it. Congratulations. Keep it private and we’ll trot you out on the following Monday.’ Which they did.”
When you know what happened next in Garneau’s career, all this prodding and profiling and media scrutiny takes on a different meaning. He started to meet prime ministers.
Pierre Trudeau: “Man of powerful intellect. Everyone knows that. There are warmer people than Pierre Trudeau. But very cordial.”
Brian Mulroney: “Mulroney had just been elected. He wanted to meet Ronald Reagan right away… I was summoned, along with two of my crew members, Bob Crippen and Kathryn Sullivan. Which, by the way, is a total no-no. You do not take the next crew that’s going to fly in three weeks out of their bubble of training and getting ready. Except if it’s POTUS. Reagan thought it was good idea, so we were summoned. I spent time in the Oval Office with with Reagan, whom I liked right away, and Mulroney, whom I also liked right away…. I was even at the Shamrock Summit a couple of months later in Quebec City. I wasn’t quite so happy with what PMO told me to do, which is to come up through the floor on a thing that was raising me up with smoke and lighting on me, dressed in my flight suit, and having to say, ‘Take me to your leader,’ which the crowd liked. And I thought, ‘I’m making a fool of myself here.’”
On the first trip, Garneau was a payload specialist, which meant he had responsibility for a suite of Canadian scientific experiments and little else. But he had two audiences he wanted to please. NASA was the first. “I had to make a good impression so that, based on a sample of one, they’d say, ‘Okay, he did pretty well. Let’s keep inviting Canadians to fly.’ And quite a few Canadians have flown.”
Canadians were the second audience. “I wanted Canadians to be proud of me.”
Both audiences gave him the thumbs up. Today there’s a high school in Toronto named after him. In 1992 Garneau and Chris Hadfield reported for training to become mission specialists, with much broader responsibility for mission success. It took another year of training before Garneau was eligible for his second flight, in 1996. His third and final mission was at the end of 2000. There were Russians waiting at the International Space Station when the shuttle Endeavour delivered Garneau and the others. Relations with Russia were as warm as they’ve ever been. “It was more than cordial. Frankly our lives depended on one another.”
It was a longer acquaintance with higher stakes than most of us ever experience. “One of the things I loved the most about NASA was that if you fuck up” — he paused before using the salty word — “you confess. That is the culture there.”
Probably this does not need to be spelled out, but here goes anyway. This culture of honesty was not a simple preference. Shuttle crews rode a lake of liquid fuel and twin towers of solid fuel at speeds their own ancestors could not have imagined. If a bug slipped into the system it could kill them and set spaceflight back decades, as indeed it did, twice. Owning up to error was the primary method of keeping colleagues, and the dream of spaceflight, alive.
“I did hundreds of simulations. I was the first non-American CAPCOM ever. CAPCOM’s the guy who talks to the crew in orbit for Mission Control. And we did hundreds of simulations. I covered 17 missions, just as CAPCOM. And after every simulation, where the crew, perhaps, had not picked up the problem and had not reacted properly to it, we’d do a post mortem.
“And that culture of honesty and openness, which you absolutely need in the space business — you can’t have people making excuses or trying to hide things — that’s what I love the most. And I wish it existed in all facets of life, including the one I ended up in.”
3. Earth
Garneau first ran for Parliament in 2006, just west of Montreal Island, and lost, in the first of three elections when losing was most of what Liberals did. He was interested in Outremont in a 2007 by-election. So was Justin Trudeau. Stéphane Dion was the leader, though, and he thought a political scientist was just the ticket. Dion’s designated nominee, Jocelyn Coulon, did not fare well.
In 2008 Garneau inherited the Liberal nomination, essentially a Wonka golden ticket, in Westmount, as solid a Liberal fortress as any in Canada. Only a catastrophe could lose Westmount for the Liberal. In 2011 it almost happened — Garneau beat the New Democrat by only 642 votes in the party’s worst national defeat in since Confederation. Soon Peter C. Newman had a book out proclaiming the Liberals were history.
“There’s something intimate about being only 33 [MPs in the Liberal caucus], Garneau recalled. “We got to know each other in a kind of a relationship that you don’t get when you’re 150 or 160. So I really enjoyed the collegiality of having that small, small group. Although of course I was hoping it wouldn’t last too long.”
In 2013, Garneau, who hadn’t been interested in commanding a ship, decided to try his chances with a political party. He ran for the Liberal leadership. He had competition.
“I personally believe that I had good policy that I put in the shop window. What I didn’t have — what I still don’t have — is charisma. I’m not interested in charisma, by the way. I’ve lived my life very well without charisma. And I’m not saying the electorate chooses on a superficial basis. But there was something about Justin Trudeau that was incredibly appealing to people.”
Garneau bowed to the inevitable and dropped out of the race. Eighteen months later he was co-chair of the Liberal Party’s “International Affairs Council of Advisors,” with a threefold mission: Figure out the party’s foreign policy; teach foreign policy to a leader with extremely limited experience in the field; and be seen showing interest in foreign policy. The group met regularly. “Trudeau only came occasionally to meet everybody and to sort of stir stir things up and have a really good discussion,” Garneau said.
4. Fire
As co-chair (with Andrew Leslie) of Trudeau’s Council of Advisors, Garneau figured he had a good chance to become foreign minister. He got Transport.
“You know, I’ve lived 17 years of my life abroad. And I love foreign policy. I wasn’t expecting Transport. And it turned out to be a job I loved. Although at first I thought, ‘Why’d he put me in transport?’
“When I got the call that, you know, ‘The Prime Minister wants to meet you,’ I thought — This is after the vetting process, ‘Are there any skeletons in your closet?’ — I thought, ‘What’s he going to put me in?’ I thought, Defence because of my background. I was in the regular forces. Or I thought, then, maybe Industry, because I was the president of the Canadian Space Agency and I worked for the Minister of Industry, Science and Technology at the time. And maybe even Foreign Affairs, because he’d had me in this job for the past two years. I wasn’t expecting Transport.” Garneau chuckled at the incongruity of it. “But now, after a little while, I saw the logic of it. I was in the Navy, ships, so I know the marine environment. I know the air environment. And so there is a certain logic to it. And it’s a job that I came to love.” He held the post for five and a half years. Only David Collenette and Lionel Chevrier lasted longer.
The new governing caucus had five times as many MPs as the Liberal caucus it replaced. “It was a heady experience,” Garneau said. “And there was a certain amount of chaos, which is understandable because it takes a couple of years to learn the basics of your job.”
It must have been a management challenge for the Prime Minister’s Office, I ventured. To have a finance minister, health minister, justice minister, defence minister who’d never been Members of Parliament before, let alone cabinet ministers. How did the PMO handle that? “It was a little bit like when you see kindergarten children all tied up with ropes, going down the street.”
Did the control ever chafe? “I had some times where I felt one way and and I felt that the centre did not necessarily agree with it. Yeah. That comes from the dynamic. If you’ve got your mandate letter, and you interpret that mandate letter the way you feel it must be implemented — you know, the vast majority of the time, no problem. But there was the odd occasion. You’ll forgive me if I don’t go into details on it. But I was very conscious of the fact [that] you have a chief of staff, your chief of staff is a key person for you. But that chief of staff reports to you, but also must report to the chief of staff of the Prime Minister. I made an indirect reference to it in my parting speech, that I sometimes made their life difficult because I might have wanted to go one way whilst the center didn’t necessarily want to go that way.”
We had been talking for more than an hour. I asked Garneau about the Freedom Convoy of January and February 2022, which has been on my mind. Specifically, I asked Garneau about his Liberal caucus colleague Joël Lightbound, who held an astonishing news conference in the second week of the Ottawa siege to say the Liberals’ COVID policy “stigmatizes and divides people.”
“I definitely took very much note of it,” he said of Lightbound’s surgical sortie. “Some of what he said is true. There were people on the Hill that were not extremists. They were just there because they felt that their rights were being not respected.” He faced his share of verbal abuse as he made his way to and from the Hill, but even still —
He paused. “I’ll be very candid. I don’t think we handled it as well as we could have.”
In what sense? “I think there was a sense that, ‘We’re not going to talk to you people. You’re just a bunch of troublemakers.’ I had always been brought up to not avoid dealing with difficult issues. This was an incredibly difficult issue.” Another pause. “So that’s just my personal comment.”
The other thing I wanted to ask him about was the tremendous controversy he and two other back-bench Liberals have stirred up over the interaction between Quebec’s newly beefed-up language law and Bill C-13, which proposes amendments to the federal Official Languages Act. This has put Garneau and his colleagues squarely on the side of Montreal’s anglophone population against a majority of Quebec’s elected politicians. And it’s brought Garneau in for some unaccustomed criticism. Barely two weeks before he resigned, he was complaining about the rough ride from Quebec commentators on Twitter.

12:40 PM ∙ Feb 18, 2023
Garneau’s comments on this were long, and would constitute inside baseball for most readers outside Quebec, but he didn’t like seeing Quebec’s language laws incorporated by reference into a federal bill. “I have very rarely disagreed with my party, but I disagreed with them on that.” It got worse for Garneau when he read 88 amendments introduced by the Bloc Québécois, five of which said that in case of a conflict between federal and provincial legislation, Quebec’s should predominate. Those amendments were eventually rejected, but by then Garneau was already on the record with his concerns. “I’m always ready to face criticism, but it got personal. And I think that’s sad.”
The controversy has been a much bigger deal inside Quebec than outside, but Garneau insisted it’s not why he’s leaving politics.
The reason I’m leaving is because I made that promise to my wife, and to my family. I actually told him after the 2019 election that that was my last election. I had been reappointed to Transport. And I thought, ‘Okay, this is a lovely way to finish.’
“Then in January of 2021, to my great surprise, the Prime Minister [shuffled Garneau.] I think it was motivated by the fact that Navdeep Bains pulled out. The Prime Minister, I personally think that he said, ‘Okay, I want François-Philippe to take over from that. And there’s a bit of musical chairs and I ended up in foreign affairs.
“But seven months later, an election was announced. And I felt, in all good conscience, that after seven months in that portfolio — to now say, ‘Sorry, I’m leaving,’ when I had been the fourth appointed in under six years, it just wouldn’t have been right.
“Now, if the prime minister had told me, ‘Mark, after this election, you won’t be in the cabinet,’ I wouldn’t have run. But he didn’t tell me that.
“I ran hoping to go back into that job. Because Lord knows there were things that I wanted to do. With respect to Afghanistan, China, the Indo-Pacific strategy, I’d been working all that stuff. But the bottom line was that he said, ‘You’re not in cabinet anymore.’
“And so, at this point, I felt it would be really not acceptable for me to say, ‘Okay, thank you for electing me three weeks ago, I’m leaving.’ So I felt I needed to put in some time. To my great personal satisfaction, I was given two things that I really enjoyed. One was to be chair of the Indigenous and Northern Affairs Committee, which I think has an important role with respect to reconciliation. And the other one was kind of unexpected… medical assistance in dying, where I was co-chair with a senator on this special mixed committee.”
That committee presented its final report in February. Garneau resigned three weeks later. He was already in the history books before he ever ran for office. Would he run now, in the atmosphere of today’s politics, if he were just starting out? Is there still room in politics for an engineer who just wants to make things work better? These are eternal questions, and I had already asked Garneau enough questions for one day.
2025 Federal Election
Inside the Convoy Verdict with Trish Wood

From Trish Wood is Critical
Peaceful convoy — violent voters. They convicted the wrong people.
TAMARA LICH, CHRIS BARBER AND THE OTHER TRUCKERS INSPIRED THIS: POLICE AND PROTESTORS HUGGING AND SINGING OH CANADA. THE TRUDEAU GOVERNMENT WAS ALREADY SMEARING THEM AS DANGEROUS.
In April of 2025, one day after the conviction of Lich and Barber for leading a protest with no violence, our politicians and media finally got what they wanted — division, and citizens absolutely hating each other. Watch these videos if you can, over and over again until it sinks in. View the one above and then the one below and decide who is harming the country.
Two middle-aged women had an “elbows up” fisticuffs yesterday near the waiting-to see-Mark-Carney line before an event. As you might figure, I was not surprised and knew violence was coming — not from a terror group and not from truckers. They pit us against each other with the full collaboration of paid-for media. We are broken, brainwashed and angry. We do not understand why our friends, neighbours and family vehemently support ideas that we know will harm the country.
They think we are monsters. And so it goes. Watch and compare to the scene above. And think about who was convicted this week.
Click image to see video
Our ideas can’t be discussed civilly and we must remain in our silos so as not to pose a threat to the elites — the way the Freedom Convoy did. This was Tamara and Chris’ mistake. They brought people together.
Liberals, and I would hazard all contemporary pols are not working to actually make our lives better. They seem to have their own agenda — even Trump whom I had some hope for.
Our lives get worse. They enrich themselves spending money overseas for wars we the people don’t want. And it seems they all walk away from “public service” with mucho brass in pocket.
The video of the fighting women shows the bread and circuses is now us. This ancient Roman idiom is defined as:
Bread and circuses” refers to pacifying people with food and entertainment to prevent them from taking action on civic duties.
During COVID-19, until January of 2022, they thought they had this modus operandi all locked-down. Canadians were compliant and some were even enjoying their marathons of garbage Netflix shows and soggy Door Dash deliveries. We were staying home, staying safe, getting fat and dependant on the government. Except the men and women who worked hard to keep the country running — like truckers. And those of us with a fully operative bullshit detector — you know, actual journalists.
There were many suicides, overdoses and other tragedies. Some of us allowed a sick parent to die alone. Our spiritual health declined and we closed off the part of our brain that safeguards our need for fellowship.
And then the Convoy happened and pulled back the curtain to reveal The Great and Mighty Oz manipulating the whole damn thing.
Yes, the Convoy’s presence in Ottawa was dangerous to the elites but not for the reasons they say. Of course it was disruptive for the citizens. Isn’t that what protests are supposed to be? But many forget that they were indirectly saving lives. I know it because people have told me.
The reason the Convoy had to be dramatically taken down and then punished for three years is because they reminded us – that we could push back and we were not alone. But when tyranny comes, united opposition must be crushed.
In the courtroom on Thursday, Justice Perkins-McVey went out of her way to speak highly of Tamara’s non-stop admonitions to the convoy that they stay peaceful, cooperate with police and put love at the top of their agenda. It was in almost every communication Tamara made to a big, burly group of mostly men who listened and then, even during the police violence were nearly Gandhi-like in their resistance. You can see it in the videos.
John Lennon would have been proud and in fact Imagine was played for the protestors who at one point sang along. But according to Judge Perkins-McVey, Lich’s commitment to keeping the peace will work only as mitigation during sentencing in a couple of weeks. She was found guilty of mischief in a definition so broad it includes everyone no matter what they actually did. I still can’t believe it.
The other revelation, I’m being sarcastic here, is that Chris Barber swears when he is talking to other truckers. I was uneasy that Perkins-McVey read out word-for-word an expletive-filled rant by an exhausted and frustrated Barber in which she herself repeated his words in the courtroom, F-bomb for F-bomb, making him sound like a crude, aggressive person. Which he is not. I could see he was embarrassed as his words were never meant for consumption in a setting like that.
It wasn’t necessary and to me, it felt like a swerve to appease the Crown. I have never heard Chris speak that way in front of civilians, even myself and I have been known to F-bomb in front of him on occasion – a kind of tacit permission that he has never accepted. In the heart of Ottawa, a city beset by gentility, it became clear in Courtroom Five that the subtext might be interpreted as — the crudeness of these working class protestors was an assault on the city’s good name and manners.
For all they did in Ottawa and for the country, Barber was reduced in that courtroom to an angry man who couldn’t control his potty-mouth. Talk about prejudicial. Maybe she was giving the defence a gift for the appeal. I hated it on a visceral level. This was not the kindly, thoughtful judge I had been observing through the course of the trial. How could she not know the affect she was having? Perhaps she did.
Ready for more?
Carbon Tax
The book the carbon taxers don’t want you to read

By Franco Terrazzano
Prime Minister Mark Carney wrote a 500-page book praising carbon taxes.
Well, I just wrote a book smashing through the government’s carbon tax propaganda.
It tells the inside story of the fight against the carbon tax. And it’s THE book the carbon taxers don’t want you to read.
My book is called Axing the Tax: The Rise and Fall of Canada’s Carbon Tax.
Axing the Tax: The Rise and Fall of Canada’s Carbon Tax
Every now and then, the underdog wins one.
And it looks like that’s happening in the fight against the carbon tax.
It’s not over yet, but support for the carbon tax is crumbling. Some politicians vow to scrap it. Others hide behind vague plans to repackage it. But virtually everyone recognizes support for the current carbon tax has collapsed.
It wasn’t always this way.
For about a decade now, powerful politicians, government bureaucrats, academics, media elites and even big business have been pushing carbon taxes on the people.
But most of the time, politicians never asked the people if they supported carbon taxes. In other words, carbon taxes, and the resulting higher gas prices and heating bills, were forced on us.
We were told it was good for us. We were told carbon taxes were inevitable. We were told politicians couldn’t win elections without carbon taxes, even though the politicians that imposed them didn’t openly run on them. We were told that we needed to pay carbon taxes if we wanted to leave a healthy environment for our kids and grandkids. We were told we needed to pay carbon taxes if we wanted to be respected in the international community.
In this decade-long fight, it would have been understandable if the people had given up and given in to these claims. It would have been easier to accept what the elites wanted and just pay the damn bill. But against all odds, ordinary Canadians didn’t give up.
Canadians knew you could care about the environment and oppose carbon taxes. Canadians saw what they were paying at the gas station and on their heating bills, and they knew they were worse off, regardless of how many politicians, bureaucrats, journalists and academics tried to convince them otherwise. Canadians didn’t need advanced degrees in economics, climate science or politics to understand they were being sold a false bill of goods.
Making it more expensive for a mom in Port Hope to get to work, or grandparents in Toronto to pay their heating bill, or a student in Coquitlam to afford food won’t reduce emissions in China, Russia, India or the United States. It just leaves these Canadians, and many like them, with less money to afford everything else.
Ordinary Canadians understood carbon taxes amount to little more than a way for governments to take more money from us and dictate how we should live our lives. Ordinary Canadians also saw through the unfairness of the carbon tax.
Many of the elites pushing the carbon tax—the media, politicians, taxpayer-funded professors, laptop activists and corporate lobbyists—were well off and wouldn’t feel the brunt of carbon taxes. After all, living in a downtown condo and clamouring for higher carbon taxes doesn’t require much gas, diesel or propane.
But running a business, working in a shop, getting kids to soccer and growing food on the farm does. These are the Canadians the political class forgot about when pushing carbon taxes. These are the Canadians who never gave up. These are the Canadians who took time out of their busy lives to sign petitions, organize and attend rallies, share posts on social media, email politicians and hand out bumper stickers.
Because of these Canadians, the carbon tax could soon be swept onto the ash heap of history. I wrote this book for two reasons.
The first is because these ordinary Canadians deserve it. They worked really hard for a really long time against the odds. When all the power brokers in government told them, “Do what we say—or pay,” they didn’t give up. They deserve to know the time and effort they spent fighting the carbon tax mattered. They deserve all the credit.
Thank you for everything you did.
The second reason I wrote this book is so people know the real story of the carbon tax. The carbon tax was bad from the start and we fought it from the start. By reading this book, you will get the real story about the carbon tax, a story you won’t find anywhere else.
This book is important because if the federal Liberals’ carbon tax is killed, the carbon taxers will try to lay blame for their defeat on Prime Minister Justin Trudeau. They will try to say that carbon taxes are a good idea, but Trudeau bungled the policy or wasn’t a good enough salesman. They will try to revive the carbon tax and once again make you pay more for gas, groceries, and home heating.
Just like with any failed five-year plan, there is a lingering whiff among the laptop class and the taxpayer-funded desk rulers that this was all a communication problem, that the ideal carbon tax hasn’t been tried yet. I can smell it outside my office building in Ottawa, where I write these words. We can’t let those embers smoulder and start a fire again.
This book shows why the carbon tax is and always will be bad policy for ordinary Canadians.
Franco’s note: You can pre-order a copy of my new book, Axing the Tax: The Rise and Fall of Canada’s Carbon Tax, here: https://www.amazon.ca/Axing-
-

 2025 Federal Election8 hours ago
2025 Federal Election8 hours agoPoilievre To Create ‘Canada First’ National Energy Corridor
-

 Automotive2 days ago
Automotive2 days agoAuto giant shuts down foreign plants as Trump moves to protect U.S. industry
-

 Energy1 day ago
Energy1 day agoTrump Takes More Action To Get Government Out Of LNG’s Way
-

 2025 Federal Election22 hours ago
2025 Federal Election22 hours agoMainstream Media Election Coverage: If the Election Was a NHL Game, the Ice Would be Constantly Tilted Up and to the Left
-
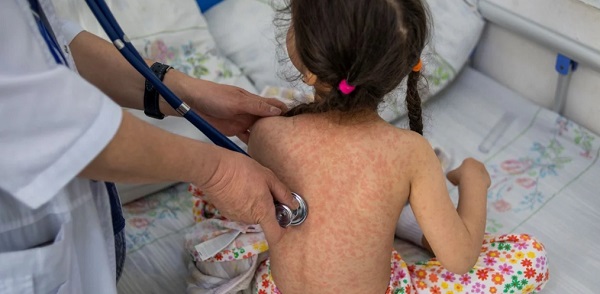
 Health1 day ago
Health1 day agoSelective reporting on measles outbreaks is a globalist smear campaign against Trump administration.
-

 COVID-192 days ago
COVID-192 days agoTrump’s new NIH head fires top Fauci allies and COVID shot promoters, including Fauci’s wife
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days ago‘Time To Make The Patient Better’: JD Vance Says ‘Big Transition’ Coming To American Economic Policy
-

 COVID-194 hours ago
COVID-194 hours agoMaxime Bernier slams Freedom Convoy leaders’ guilty verdict, calls Canada’s justice system ‘corrupt’













