Uncategorized
Thai, Saudi officials meet over case of young Saudi woman

BANGKOK — Thailand’s immigration police chief met Tuesday with officials from the Saudi Embassy in Bangkok, as Saudi Arabia tried to distance itself from accusations that it tried to block a young woman’s effort to flee her family and seek asylum abroad.
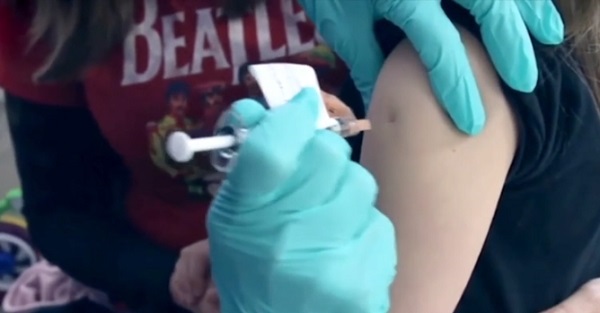
Rahaf Mohammed Alqunun arrived in Bangkok from Kuwait late Saturday after slipping away from her family, whom she accused of abusing her. The 18-year-old was stopped by officials in Thailand who confiscated her passport.
Her urgent pleas for help over Twitter from an airport hotel room garnered tens of thousands of followers and the attention of the U.N.’s refugee agency, the U.N. High Commissioner for Refugees. Public pressure prompted Thai officials to return her passport and let her temporarily stay in Thailand.
Alqunun alleged several times that Saudi officials were involved in seizing her passport. However, in repeated statements, including one issued Tuesday, the Saudi Embassy in Thailand has said it is only monitoring her situation.
The statement, which described Alqunun’s case as a “family affair,” said the kingdom did not demand her deportation to Saudi Arabia. The embassy — and Thai officials — earlier also said that Alqunun was stopped by Thai authorities in Bangkok because she did not have a return ticket, a hotel reservation or itinerary to show she was a tourist, which appeared to have raised a flag about the reasons for her trip.
Thailand’s immigration police chief, Maj. Gen. Surachate Hakparn, told reporters Tuesday that Saudi diplomats told him they are satisfied with how her case had been handled.
“The position of two countries on this matter is the same — that the priority is to provide her safety. We are both concerned for Miss Rahaf’s safety and well-being,” said Surachate. “The Saudi charge d’affaires said he is satisfied and expressed confidence on the work of Thai immigration, of the Thai government, and of the Foreign Ministry yesterday.”
Surachate said Alqunun’s father and brother were due to arrive soon in Bangkok, but that it was her decision whether to meet with them. On Twitter, she has expressed fear of such a meeting. The father had previously been expected Monday night.
A spokesman for the U.N. High Commissioner for Refugees at its Geneva headquarters, Babar Baloch, said Tuesday it’s premature to say what will happen next, but that it could take several days for the agency to look into Alqunun’s claims. He said it “too early to tell” if she will be granted asylum or refugee status.
Saudi Arabia’s human rights record has come under intense scrutiny since the killing of Saudi writer Jamal Khashoggi in October. Khashoggi, who wrote critically of Crown Prince Mohammed bin Salman in columns for The Washington Post, had been living in self-imposed exile before he was killed and dismembered inside the Saudi Consulate in Istanbul by Saudi agents.
The kingdom offered various shifting accounts around the circumstances of his death before eventually settling on the explanation that he died in a botched operation to forcibly bring him back to Saudi Arabia.
Some Saudi female runaways fleeing abuse by their families have been caught trying to seek asylum abroad in recent years. Saudi activists say the kingdom, through its embassies abroad, has at times put pressure on border patrol agents in foreign countries to deport the women back to Saudi Arabia.
In 2017, Dina Ali Lasloom triggered a firestorm online when she was stopped en route to Australia, where she planned to seek asylum. She was forced to return to Saudi Arabia and was not publicly heard from again, according to activists tracking her whereabouts.
Australia national broadcaster ABC reported that the country’s Home Affairs Department announced late Tuesday that it would consider Alqunun’s application for asylum if she was found to be a genuine refugee, and called on the Thai authorities and UNHCR to assess her claim as quickly as possible.
Human Rights Watch earlier called on the Australian government to allow Alqunun’s entry into that country, amid worries about her visa status.
The organization’s Australian director, Elaine Pearson, said she had seen electronic confirmation of her tourist visa, but that Alqunun could no longer access her visa page on Australia’s immigration
Though refugee status would mean a different form of visa would be needed, Pearson said Australia’s apparent cancellation of Alqunun’s tourist visa was a worrying sign.
Since Australia has expressed concern in the past about women’s rights in Saudi Arabia, it should “come forward and offer protection for this young woman,” Pearson said.
___
Marshallsea reported from Sydney. Associated Press writers Kaweewit Kaewjinda in Bangkok, Jamey Keaten in Geneva and Aya Batrawy in Dubai, United Arab Emirates, contributed to this report.
Tassanee Vejpongsa And Trevor Marshallsea, The Associated Press
Uncategorized
Mortgaging Canada’s energy future — the hidden costs of the Carney-Smith pipeline deal


Much of the commentary on the Carney-Smith pipeline Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) has focused on the question of whether or not the proposed pipeline will ever get built.
That’s an important topic, and one that deserves to be examined — whether, as John Robson, of the indispensable Climate Discussion Nexus, predicted, “opposition from the government of British Columbia and aboriginal groups, and the skittishness of the oil industry about investing in a major project in Canada, will kill [the pipeline] dead.”
But I’m going to ask a different question: Would it even be worth building this pipeline on the terms Ottawa is forcing on Alberta? If you squint, the MOU might look like a victory on paper. Ottawa suspends the oil and gas emissions cap, proposes an exemption from the West Coast tanker ban, and lays the groundwork for the construction of one (though only one) million barrels per day pipeline to tidewater.
But in return, Alberta must agree to jack its industrial carbon tax up from $95 to $130 per tonne at a minimum, while committing to tens of billions in carbon capture, utilization, and storage (CCUS) spending, including the $16.5 billion Pathways Alliance megaproject.
Here’s the part none of the project’s boosters seem to want to mention: those concessions will make the production of Canadian hydrocarbon energy significantly more expensive.
As economist Jack Mintz has explained, the industrial carbon tax hike alone adds more than $5 USD per barrel of Canadian crude to marginal production costs — the costs that matter when companies decide whether to invest in new production. Layer on the CCUS requirements and you get another $1.20–$3 per barrel for mining projects and $3.60–$4.80 for steam-assisted operations.
While roughly 62% of the capital cost of carbon capture is to be covered by taxpayers — another problem with the agreement, I might add — the remainder is covered by the industry, and thus, eventually, consumers.
Total damage: somewhere between $6.40 and $10 US per barrel. Perhaps more.
“Ultimately,” the Fraser Institute explains, “this will widen the competitiveness gap between Alberta and many other jurisdictions, such as the United States,” that don’t hamstring their energy producers in this way. Producers in Texas and Oklahoma, not to mention Saudi Arabia, Venezuela, or Russia, aren’t paying a dime in equivalent carbon taxes or mandatory CCUS bills. They’re not so masochistic.
American refiners won’t pay a “low-carbon premium” for Canadian crude. They’ll just buy cheaper oil or ramp up their own production.
In short, a shiny new pipe is worthless if the extra cost makes barrels of our oil so expensive that no one will want them.
And that doesn’t even touch on the problem for the domestic market, where the higher production cost will be passed onto Canadian consumers in the form of higher gas and diesel prices, home heating costs, and an elevated cost of everyday goods, like groceries.
Either way, Canadians lose.
So, concludes Mintz, “The big problem for a new oil pipeline isn’t getting BC or First Nation acceptance. Rather, it’s smothering the industry’s competitiveness by layering on carbon pricing and decarbonization costs that most competing countries don’t charge.” Meanwhile, lurking underneath this whole discussion is the MOU’s ultimate Achilles’ heel: net-zero.
The MOU proudly declares that “Canada and Alberta remain committed to achieving Net-Zero greenhouse gas emissions by 2050.” As Vaclav Smil documented in a recent study of Net-Zero, global fossil-fuel use has risen 55% since the 1997 Kyoto agreement, despite trillions spent on subsidies and regulations. Fossil fuels still supply 82% of the world’s energy.
With these numbers in mind, the idea that Canada can unilaterally decarbonize its largest export industry in 25 years is delusional.
This deal doesn’t secure Canada’s energy future. It mortgages it. We are trading market access for self-inflicted costs that will shrink production, scare off capital, and cut into the profitability of any potential pipeline. Affordable energy, good jobs, and national prosperity shouldn’t require surrendering to net-zero fantasy.If Ottawa were serious about making Canada an energy superpower, it would scrap the anti-resource laws outright, kill the carbon taxes, and let our world-class oil and gas compete on merit. Instead, we’ve been handed a backroom MOU which, for the cost of one pipeline — if that! — guarantees higher costs today and smothers the industry that is the backbone of the Canadian economy.
This MOU isn’t salvation. It’s a prescription for Canadian decline.
Uncategorized
Cost of bureaucracy balloons 80 per cent in 10 years: Public Accounts

The cost of the bureaucracy increased by $6 billion last year, according to newly released numbers in Public Accounts disclosures. The Canadian Taxpayers Federation is calling on Prime Minister Mark Carney to immediately shrink the bureaucracy.
“The Public Accounts show the cost of the federal bureaucracy is out of control,” said Franco Terrazzano, CTF Federal Director. “Tinkering around the edges won’t cut it, Carney needs to take urgent action to shrink the bloated federal bureaucracy.”
The federal bureaucracy cost taxpayers $71.4 billion in 2024-25, according to the Public Accounts. The cost of the federal bureaucracy increased by $6 billion, or more than nine per cent, over the last year.
The federal bureaucracy cost taxpayers $39.6 billion in 2015-16, according to the Public Accounts. That means the cost of the federal bureaucracy increased 80 per cent over the last 10 years. The government added 99,000 extra bureaucrats between 2015-16 and 2024-25.
Half of Canadians say federal services have gotten worse since 2016, despite the massive increase in the federal bureaucracy, according to a Leger poll.
Not only has the size of the bureaucracy increased, the cost of consultants, contractors and outsourcing has increased as well. The government spent $23.1 billion on “professional and special services” last year, according to the Public Accounts. That’s an 11 per cent increase over the previous year. The government’s spending on professional and special services more than doubled since 2015-16.
“Taxpayers should not be paying way more for in-house government bureaucrats and way more for outside help,” Terrazzano said. “Mere promises to find minor savings in the federal bureaucracy won’t fix Canada’s finances.
“Taxpayers need Carney to take urgent action and significantly cut the number of bureaucrats now.”
Table: Cost of bureaucracy and professional and special services, Public Accounts
| Year | Bureaucracy | Professional and special services |
|
$71,369,677,000 |
$23,145,218,000 |
|
|
$65,326,643,000 |
$20,771,477,000 |
|
|
$56,467,851,000 |
$18,591,373,000 |
|
|
$60,676,243,000 |
$17,511,078,000 |
|
|
$52,984,272,000 |
$14,720,455,000 |
|
|
$46,349,166,000 |
$13,334,341,000 |
|
|
$46,131,628,000 |
$12,940,395,000 |
|
|
$45,262,821,000 |
$12,950,619,000 |
|
|
$38,909,594,000 |
$11,910,257,000 |
|
|
$39,616,656,000 |
$11,082,974,000 |
-

 Censorship Industrial Complex5 hours ago
Censorship Industrial Complex5 hours agoUS Under Secretary of State Slams UK and EU Over Online Speech Regulation, Announces Release of Files on Past Censorship Efforts
-

 Business8 hours ago
Business8 hours ago“Magnitude cannot be overstated”: Minnesota aid scam may reach $9 billion
-

 Alberta1 day ago
Alberta1 day agoAlberta project would be “the biggest carbon capture and storage project in the world”
-

 Energy1 day ago
Energy1 day agoNew Poll Shows Ontarians See Oil & Gas as Key to Jobs, Economy, and Trade
-

 Fraser Institute2 days ago
Fraser Institute2 days agoCarney government sowing seeds for corruption in Ottawa
-

 Daily Caller22 hours ago
Daily Caller22 hours agoIs Ukraine Peace Deal Doomed Before Zelenskyy And Trump Even Meet At Mar-A-Lago?
-

 Alberta2 days ago
Alberta2 days agoAlberta Next Panel calls for less Ottawa—and it could pay off
-

 Energy2 days ago
Energy2 days agoWhile Western Nations Cling to Energy Transition, Pragmatic Nations Produce Energy and Wealth