Crime
RCMP Bust B.C. Fentanyl Superlab Linked to Mexico and Transnational Exports

In a remote mountainous area of British Columbia, federal police have dismantled the largest fentanyl laboratory ever discovered in Canada. This western province has become a critical front in the Five Eyes battle against the production and distribution of deadly synthetic narcotics trafficked globally by networks involving Chinese and Iranian state-sponsored mafias and Mexican cartels.
In a groundbreaking discovery, the RCMP located the superlab in Falkland—a village of 946 residents nestled in the rugged terrain between Calgary and Vancouver—using Phenyl-2-Propanone (P2P) to manufacture methamphetamine. This production method, primarily employed by Mexican cartels, stems from the precursors and scientific expertise Mexican cartels have gathered from elite Chinese criminals since the early 2000s, according to U.S. enforcement sources.
David Teboul, Commander of the RCMP Federal Policing program in the Pacific Region, underscored the significance: “Manufacturing methamphetamine using P2P had not been seen in Western Canada until now,” he said. “The P2P manufacturing method has been the primary method used by Mexican cartels to produce methamphetamine for years.”
Demonstrating the destructive power of the cartels involved, the RCMP seized a staggering cache of illicit substances and weapons. Officers confiscated 54 kilograms of fentanyl, massive amounts of precursor chemicals, 390 kilograms of methamphetamine, 35 kilograms of cocaine, 15 kilograms of MDMA, and 6 kilograms of cannabis. The superlab was described as the largest and most sophisticated of its kind, capable of producing multiple types of illicit drugs.
“To put things into context,” Teboul said, “the over 95 million potentially lethal doses of fentanyl that have been seized could have taken the lives of every Canadian at least twice over.”
A large portion of the product was destined for other countries.
During the investigation, RCMP officers learned of several large shipments of methamphetamine prepared for international export. They intercepted 310 kilograms of methamphetamine before it could leave Canada, preventing a significant quantity from reaching global markets—a critical point as Canada faces pressure from its allies over its role in the global fentanyl and methamphetamine trade.
Teboul noted that the RCMP collaborated with its Five Eyes enforcement partners—an intelligence alliance comprising Canada, the United States, the United Kingdom, Australia, and New Zealand. Although Teboul did not provide specific details, this cooperation underscores the international scope of the transnational investigation.
The first suspect, Gaganpreet Singh Randhawa, was identified and arrested during raids. He is currently in custody and faces multiple charges, including possession and export of controlled substances, possession of prohibited firearms and devices, and possession of explosive devices. More arrests are expected, Teboul said.
The scale of this criminal network echoes the power and violence fueling gang wars that have rocked British Columbia, putting innocent lives at risk during high-powered shootouts in Vancouver. Investigators seized a total of 89 firearms, including 45 handguns, 21 AR-15-style rifles, and submachine guns—many of which were loaded and ready for use. The searches also uncovered small explosive devices, vast amounts of ammunition, firearm silencers, high-capacity magazines, body armor, and $500,000 in cash.
British Columbia has been grappling with an influx of synthetic opioids like fentanyl, significantly exacerbating the opioid crisis across Canada. The province has witnessed a surge in overdose deaths, prompting law enforcement to intensify efforts against drug production and trafficking networks. Experts highlight weaknesses in Canadian laws and a lack of federal oversight at the Port of Vancouver, which have been exploited by transnational crime and money laundering organizations from China, Iran, and Mexico.
This significant bust comes at a time when Canada is under increased scrutiny from international allies over its role as a hub for the export of fentanyl and methamphetamine. The superlab takedown appears to align with serious concerns raised by lawmakers in Washington about how Canada and Mexico are being used by transnational crime organizations to distribute fentanyl worldwide.
A recent U.S. congressional report argues that the Chinese Communist Party’s (CCP) strategy relies less on overt military actions and more on covert tactics, including trafficking of fentanyl and leveraging money laundering, aimed at exploiting vulnerabilities across social, economic, and health domains.
“Fentanyl precursors are manufactured in China and shipped to Mexico and Canada. For precursors that arrive in Mexico, Chinese transnational mafias work with Mexican cartels to smuggle and distribute fentanyl in the United States on behalf of the CCP,” the report states. “The DEA confirmed Chinese transnational crime leaders hold government positions in the CCP and indicated that Chinese transnational crime organizations are dedicated to the CCP.”
“The public deserves to know about the CCP’s role in fentanyl production and how the Party is using fentanyl as a chemical weapon to kill Americans,” the report adds. It recommends that Washington publicly “blame the CCP as much as the DEA and its partners currently blame the Sinaloa Cartel” for fentanyl trafficking and urges the government to “educate international allies about CCP chemical warfare” and encourage them to condemn Chinese transnational crime.
According to congressional investigations, Beijing is actively incentivizing the export of fentanyl and methamphetamine worldwide. The report alleges that Chinese criminal organizations, including Triads led by individuals with official positions in the CCP, are working alongside Mexican cartels to generate profit to fund interference operations in America.
The Bureau is a reader-supported publication. To receive new posts and support my work, consider becoming a free or paid subscriber.
Business
China, Mexico, Canada Flagged in $1.4 Billion Fentanyl Trade by U.S. Financial Watchdog
 Sam Cooper
Sam Cooper
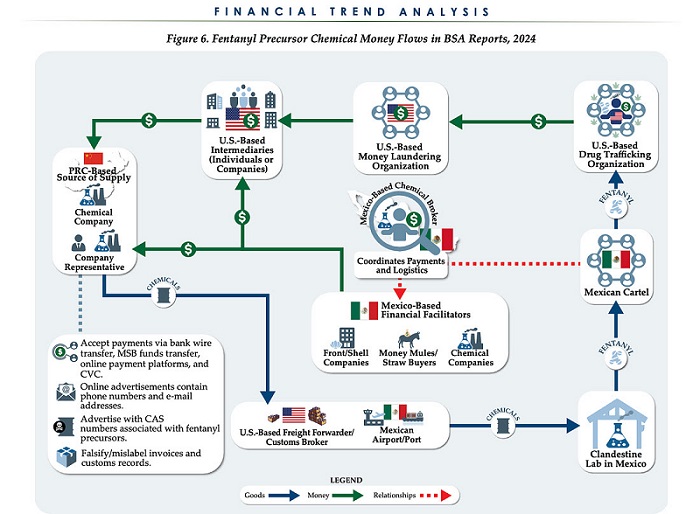
The U.S. Treasury’s Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN) has identified $1.4 billion in fentanyl-linked suspicious transactions, naming China, Mexico, Canada, and India as key foreign touchpoints in the global production and laundering network. The analysis, based on 1,246 Bank Secrecy Act filings submitted in 2024, tracks financial activity spanning chemical purchases, trafficking logistics, and international money laundering operations.
The data reveals that Mexico and the People’s Republic of China were the two most frequently named foreign jurisdictions in financial intelligence gathered by FinCEN. Most of the flagged transactions originated in U.S. cities, the report notes, due to the “domestic nature” of Bank Secrecy Act data collection. Among foreign jurisdictions, Mexico, China, Hong Kong, and Canada were cited most often in fentanyl-related financial activity.
The FinCEN report points to Mexico as the epicenter of illicit fentanyl production, with Mexican cartels importing precursor chemicals from China and laundering proceeds through complex financial routes involving U.S., Canadian, and Hong Kong-based actors.
The findings also align with testimony from U.S. and Canadian law enforcement veterans who have told The Bureau that Chinese state-linked actors sit atop a decentralized but industrialized global fentanyl economy—supplying precursors, pill presses, and financing tools that rely on trade-based money laundering and professional money brokers operating across North America.
“Filers also identified PRC-based subjects in reported money laundering activity, including suspected trade-based money laundering schemes that leveraged the Chinese export sector,” the report says.
A point emphasized by Canadian and U.S. experts—including former U.S. State Department investigator Dr. David Asher—that professional Chinese money laundering networks operating in North America are significantly commanded by Chinese Communist Party–linked Triad bosses based in Ontario and British Columbia—is not explored in detail in this particular FinCEN report.¹
Chinese chemical manufacturers—primarily based in Guangdong, Zhejiang, and Hebei provinces—were repeatedly cited for selling fentanyl precursors via wire transfers and money service businesses. These sales were often facilitated through e-commerce platforms, suggesting that China’s global retail footprint conceals a lethal underground market—one that ultimately fuels a North American public health crisis. In many cases, the logistics were sophisticated: some Chinese companies even offered delivery guarantees and customs clearance for precursor shipments, raising red flags for enforcement officials.
While China’s industrial base dominates the global fentanyl supply chain, Mexican cartels are the next most prominent state-like actors in the ecosystem—but the report emphasizes that Canada and India are rising contributors.
“Subjects in other foreign countries—including Canada, the Dominican Republic, and India—highlight the presence of alternative suppliers of precursor chemicals and fentanyl,” the report says.
“Canada-based subjects were primarily identified by Bank Secrecy Act filers due to their suspected involvement in drug trafficking organizations allegedly sourcing fentanyl and other drugs from traditional drug source countries, such as Mexico,” it explains, adding that banking intelligence “identified activity indicative of Canada-based individuals and companies purchasing precursor chemicals and laboratory equipment that may be related to the synthesis of fentanyl in Canada. Canada-based subjects were primarily reported with addresses in the provinces of British Columbia and Ontario.”
FinCEN also flagged activity from Hong Kong-based shell companies—often subsidiaries or intermediaries for Chinese chemical exporters. These entities were used to obscure the PRC’s role in transactions and to move funds through U.S.-linked bank corridors.
Breaking down the fascinating and deadly world of Chinese underground banking used to move fentanyl profits from American cities back to producers, the report explains how Chinese nationals in North America are quietly enlisted to move large volumes of cash across borders—without ever triggering traditional wire transfers.
These networks, formally known as Chinese Money Laundering Organizations (CMLOs), operate within a global underground banking system that uses “mirror transfers.” In this system, a Chinese citizen with renminbi in China pays a local broker, while the U.S. dollar equivalent is handed over—often in cash—to a recipient in cities like Los Angeles or New York who may have no connection to the original Chinese depositor aside from their role in the laundering network. The renminbi, meanwhile, is used inside China to purchase goods such as electronics, which are then exported to Mexico and delivered to cartel-linked recipients.
FinCEN reports that US-based money couriers—often Chinese visa holders—were observed depositing large amounts of cash into bank accounts linked to everyday storefront businesses, including nail salons and restaurants. Some of the cash was then used to purchase cashier’s checks, a common method used to obscure the origin and destination of the funds. To banks, the activity might initially appear consistent with a legitimate business. However, modern AI-powered transaction monitoring systems are increasingly capable of flagging unusual patterns—such as small businesses conducting large or repetitive transfers that appear disproportionate to their stated operations.
On the Mexican side, nearly one-third of reports named subjects located in Sinaloa and Jalisco, regions long controlled by the Sinaloa Cartel and Cartel Jalisco Nueva Generación. Individuals in these states were often cited as recipients of wire transfers from U.S.-based senders suspected of repatriating drug proceeds. Others were flagged as originators of payments to Chinese chemical suppliers, raising alarms about front companies and brokers operating under false pretenses.
The report outlines multiple cases where Mexican chemical brokers used generic payment descriptions such as “goods” or “services” to mask wire transfers to China. Some of these transactions passed through U.S.-based intermediaries, including firms owned by Chinese nationals. These shell companies were often registered in unrelated sectors—like marketing, construction, or hardware—and exhibited red flags such as long dormancy followed by sudden spikes in large transactions.
Within the United States, California, Florida, and New York were most commonly identified in fentanyl-related financial filings. These locations serve as key hubs for distribution and as collection points for laundering proceeds. Cash deposits and peer-to-peer payment platforms were the most cited methods for fentanyl-linked transactions, appearing in 54 percent and 51 percent of filings, respectively.
A significant number of flagged transactions included slang terms and emojis—such as “blues,” “ills,” or blue dots—in memo fields. Structured cash deposits were commonly made across multiple branches or ATMs, often linked to otherwise legitimate businesses such as restaurants, salons, and trucking firms.
FinCEN also tracked a growing number of trade-based laundering schemes, in which proceeds from fentanyl sales were used to buy electronics and vaping devices. In one case, U.S.-based companies owned by Chinese nationals made outbound payments to Chinese manufacturers, using funds pooled from retail accounts and shell companies. These goods were then shipped to Mexico, closing the laundering loop.
Another key laundering method involved cryptocurrency. Nearly 10 percent of all fentanyl-related reports involved virtual currency, with Bitcoin the most commonly cited, followed by Ethereum and Litecoin. FinCEN flagged twenty darknet marketplaces as suspected hubs for fentanyl distribution and cited failures by some digital asset platforms to catch red-flag activity.
Overall, FinCEN warns that fentanyl-linked funds continue to enter the U.S. financial system through loosely regulated or poorly monitored channels, even as law enforcement ramps up enforcement. The Drug Enforcement Administration reported seizures of over 55 million counterfeit fentanyl pills in 2024 alone.
The broader pattern is unmistakable: precursor chemicals flow from China, manufacturing occurs in Mexico, Canada plays an increasing role in chemical acquisition and potential synthesis, and drugs and proceeds flood into the United States, supported by global financial tools and trade structures. The same infrastructure that enables lawful commerce is being manipulated to sustain the deadliest synthetic drug crisis in modern history.
The Bureau is a reader-supported publication.
To receive new posts and support my work, consider becoming a free or paid subscriber.
Invite your friends and earn rewards
Business
Closing information gaps to strengthen Canada’s border security and track fentanyl
By Sean Parker, Dawn Jutla, and Peter Copeland for Inside Policy
To promote better results, we lay out a collaborative approach
Despite exaggerated claims about how much fentanyl is trafficked across the border from Canada to the United States, the reality is that our detection, search, and seizure capacity is extremely limited.
We’re dealing with a “known unknown”: a risk we’re aware of, but don’t yet have the capacity to understand its extent.
What’s more, it may be that the flow of precursor chemicals—ingredients used in the production of fentanyl—is where much of the concern lies. Until we enhance our tracking, search, and seizure capacity, much will remain speculative.
As border security is further scrutinized, and the extent of fentanyl production and trafficking gets brought into sharper focus, the role of the federal government’s Precursor Chemical Risk Management Unit (PCRMU)—announced recently by Health Canada—will become apparent.
Ottawa recently took action to enhance the capabilities of the PCRMU. It says the new unit will “provide better insights into precursor chemicals, distribution channels, and enhanced monitoring and surveillance to enable timely law enforcement action.” The big question is, how will the PCRMU track the precursor drugs entering into Canada that are used to produce fentanyl?
Key players in the import-export ecosystem do not have the right regulatory framework and responsibilities to track and share information, detect suspect activities, and be incentivized to act on it. That’s one of the reasons why we know so little about how much fentanyl is produced and trafficked.
Without proper collaboration with industry, law enforcement, and financial institutions, these tracking efforts are doomed to fail. To promote better results, we lay out a collaborative approach that distributes responsibilities and retools incentives. These measures would enhance information collection capabilities, incentivize system actors to compliance, and better equip law enforcement and border security services for the safety of Canadians.
Trade-off bottleneck: addressing the costs of enhanced screening
To date, it’s been challenging to increase our ability to detect, search, and seize illegal goods trafficked through ports and border crossings. This is due to trade-offs between heightened manual search and seizure efforts at ports of entry, and the economic impacts of these efforts.
In 2024, the Canada Border Services Agency (CBSA) admitted over 93 million travelers. Meanwhile, 5.3 million trucks transported commercial goods into Canada, around 3.6 million shipments arrived via air cargo, nearly 2 million containers were processed at Canadian ports, roughly 1.9 million rail cars carried goods into the country, and about 145.7 million courier shipments crossed the border. The CBSA employs a risk-based approach to border security, utilizing intelligence, behavioral analysis, and random selection to identify individuals or shipments that may warrant additional scrutiny. This triaging process aims to balance effective enforcement with the facilitation of legitimate travel and trade.
Exact percentages of travelers subjected to secondary inspections are not publicly disclosed, but it’s understood that only a small fraction undergo such scrutiny. We don’t learn about the prevalence of these issues through our border screening measures, but in crime reporting data—after it’s too late to avert.
It’s key to have an approach that minimizes time and personnel resources deployed at points of entry. To be effective without being economically disruptive, policymakers, law enforcement, and border security need to strengthen requirements for information gathering, live tracking, and sharing. Legislative and regulatory change to require additional information of buyers and sellers—along with stringent penalties to enforce non-compliance—is a low-cost, logistically efficient way of distributing responsibility for this complex and multifaceted issue. A key concept explored in this paper is strengthening governance controls (“controls”) over fentanyl supply chains through new processes and data digitization, which could aid the PCRMU in their strategic objectives.
Enhanced supply chain controls are needed
When it comes to detailed supply chain knowledge of fentanyl precursor chemicals moving in and out of Canada, regulator knowledge is limited.
That’s why regulatory reform is the backbone of change. It’s necessary to ensure that strategic objectives are met by all accountable stakeholders to protect the supply chain and identify issues. To rectify the issues, solutions can be taken by the PCRMU to obtain and govern a modern fentanyl traceability system/platform (“platform”) that would provide live transparency to regulators.
A fresh set of supply chain controls, integrated into a platform as shown in Fig. 1, could significantly aid the PCRMU in identifying suspicious activities and prioritizing investigations.

Our described system has two distinctive streams: one which leverages a combination of physical controls such as package tampering and altered documentation against a second stream that looks at payment counterparties. Customs agencies, transporters, receivers, and financial institutions would have a hand in ensuring that controls in the platform are working. The platform includes several embedded controls to enhance supply chain oversight. It uses commercially available Vision AI to assess packaging and blockchain cryptography to verify shipment documentation integrity. Shipment weight and quantity are tracked from source to destination to detect diversion, while a four-eyes verification process ensures independent reconciliation by the seller, customs, and receiver. Additionally, payment details are linked to shipments to uncover suspicious financial activity and support investigations by financial institutions and regulators like FINTRAC and FINCEN.
A modern platform securely distributes responsibility in a way that’s cost effective and efficient so as not to overburden any one actor. It also ensures that companies of all sizes can participate, and protects them from exploitation by criminals and reputational damage.
In addition to these technological enhancements and more robust system controls, better collaboration between the key players in the fentanyl supply chain is needed, along with policy changes to incentivize each key fentanyl supply chain stakeholder to adopt the new controls.
Canadian financial institutions: a chance for further scrutiny
Financial institutions (FIs) are usually the first point of contact when a payment is being made by a purchaser to a supplier for precursor chemicals that could be used in the production of fentanyl. It is crucial that they enhance their screening and security processes.
Chemicals may be purchased by wires or via import letters of credit. The latter is the more likely of the two instruments to be used because this ensures that the terms and conditions in the letter of credit are met with proof of shipment prior to payment being released. Payments via wire require less transparency.
Where a buyer pays for precursor chemicals with a wire, it should result in further scrutiny by the financial institution. Requests for supporting documentation including terms and conditions, along with proof of shipment and receipt, should be provided. Under new regulatory policy, buyers would be required to place such supporting documentation on the shared platform.
The less transparent a payment channel is in relation to the supply chain, the more concerning it should be from a risk point of view. Certain payment channels may be leveraged to further mask illicit activity throughout the supply chain. At the onset of the relationship the seller and buyers would link payment information on the platform (payment channel, recipient name, recipient’s bank, date, and payment amount) to each precursor or fentanyl shipment. The supplier, in turn, should record match payment information (payment channel, supplier name, supplier’s bank, date, and payment amount).
Linking payment to physical shipment would enable data analytics to detect irregularities. An irregularity is flagged when the amounts and/or volume of payments far exceed the value of the received goods or vice versa. The system would be able to understand which fentanyl supply chains tend to use a particular set of FIs. This makes it possible to conduct real-time mapping of companies, their fentanyl and precursor shipments and receipts, and the payment institutions they use. With this bigger picture, FIs and law enforcement could connect the dots faster.
Live traceability reporting
Today, suppliers of fentanyl precursors are subject to the Pre-Export Notification Online (PEN Online) database. This database enables governments to monitor international trade in precursor chemicals by sending and receiving pre-export notifications. The system helps prevent the diversion of chemicals used in the illicit manufacture of drugs by allowing authorities to verify the legitimacy of shipments before they occur.
To further strengthen oversight, the platform utilizes immutability technologies—such as blockchain or secure immutable databases—which can be employed to encrypt all shipping documents and securely share them. This presents an auditable form of chain-of-custody and makes any alterations apparent. Customs and buyers would have the capability to verify the authenticity of the originating documents in a way that doesn’t compromise business confidentiality. With the use of these technologies, law enforcement can narrow down their investigations.
An information gap currently exists as the receivers of the shipments don’t share their receipts information with PEN. To strengthen governance on fentanyl supply chains, regulatory policy and legislative changes are needed. The private sector should be mandated to report received quantities of fentanyl or its precursors, as well as suspicious receiving destinations. This could be accomplished on the platform which would embed the receiving process, a reconciliation process of the transaction, the secure upload and sharing of documents, and would be minimally disruptive to business processes.
Additionally, geo-location technology embedded in mobile devices and/or shipments would provide real-time location-based tracking of custody transactions. These geo-controls would ensure accountability across the fentanyl supply chain, in particular where shipments veer off or stop too long on regular shipping routes. Canadian transporters of fentanyl and its precursor chemicals should play an important role in detecting illicit diversion/activities.
Digital labelling
Licensed fentanyl manufacturers could add new unique digital labels to their shipments to get expedited clearance. For example, immutable digital labelling platforms enable tamper-proof digital labels for legitimate fentanyl shipments. This would give pharmacies, doctors, and regulators transparency into the fentanyl’s:
- Chemical composition and concentrations (determining legitimate vs. adulterated versions of the drug)
- Manufacturing facility ID, batch ID, and regulatory compliance status
- Intended buyer authentication (such as licensed pharmaceutical firms or distributors)
Immutable digital labelling platforms offer secure role-based access control. They can display customized data views according to time of day, language, and location. Digital labels could enable international border agencies and law enforcement to receive usable data, allowing legal shipments through faster while triggering closer shipment examinations for those without of a digital label.
International and domestic transporter controls
Transporters act as intermediaries in the supply chain. Their operations could be monitored through a regulatory policy that mandates their participation in the platform for fentanyl and precursor shipments. The platform would support a mobile app interface for participants on-the-move, as well as a web portal and application programming interfaces (APIs) for large-size supply chain participants. Secure scanning of packaging at multiple checkpoints, combined with real-time tracking, would provide an additional layer of protection against fraud, truckers taking bribes, and unauthorized alterations to shipments and documents.
Regulators and law enforcement participation
Technology-based fentanyl controls for suppliers, buyers, and transporters may be reinforced by international customs and law enforcement collaboration on the platform. Both CBSA and law enforcement could log in and view alerts about suspicious activities issued from the FIs, transporters, or receivers. The reporting would allow government personnel to view a breakdown of fentanyl importers, the number of import permit applications, and the amount of fentanyl and its precursors flowing into the country. Responsible regulatory agencies—such as the CBSA and PCRMU—could leverage the reporting to identify hot spots.
The platform would use machine learning to support CBSA personnel in processing an incoming fentanyl or precursor shipment. Machine learning refers to AI algorithms and systems that improve their knowledge with experience. For example, an AI assistant on the traceability system could use machine learning to predict and communicate which import shipments arriving at the border should be passed. It can base these suggestions on criteria like volume, price, origin of raw materials, and origin of material at import point. It can also leverage data from other sources such as buyers, sellers, and banks to make predictions. As an outcome, the shipment may be recommended to pass, flagged as suspicious, or deemed to require an investigation by CBSA.
It’s necessary to keep up to date on new precursor chemicals as the drug is reformulated. Here, Health Canada can play a role, using its new labs and tests—expected as part of the recently announced Canadian Drug Analysis Centre—to provide chemical analysis of seized fentanyl. This would inform which additional chemical supply chains should be tracked in the PCRMU’s collaborative platform, and all stakeholders would widen their scope of review.
These new tools would complement existing cross-border initiatives, including joint U.S.-Canada and U.S.-Mexico crackdowns on illicit drug labs, as well as sovereign efforts. They have the potential to play a vital role in addressing fentanyl trafficking.
A robust, multi-pronged strategy—integrating existing safeguards with a new PCRMU traceability platform—could significantly disrupt the illegal production and distribution of fentanyl. By tracking critical supply chain events and authenticating shipment data, the platform would equip law enforcement and border agencies in Canada, the U.S., and Mexico with timely, actionable intelligence. The human toll demands urgency: from 2017 to 2022, the U.S. averaged 80,000 opioid-related deaths annually, while Canada saw roughly 5,500 per year from 2016 to 2024. In just the first nine months of 2024, Canadian emergency services responded to 28,813 opioid-related overdoses.
Combating this crisis requires more than enforcement. It demands enforceable transparency. Strengthened governance—powered by advanced traceability technology and coordinated public-private collaboration—is essential. This paper outlines key digital controls that can be implemented by global suppliers, Canadian buyers, transporters, customs, and financial institutions. With federal leadership, Canada can spearhead the adoption of proven, homegrown technologies to secure fentanyl supply chains and save lives.
Sean Parker is a compliance leader with well over a decade of experience in financial crime compliance, and a contributor to the Macdonald-Laurier Institute.
Dawn Jutla is the CEO of Peer Ledger, the maker of a traceability platform that embeds new control processes on supply chains, and a professor at the Sobey School of Business.
Peter Copeland is deputy director of domestic policy at the Macdonald-Laurier Institute.
-

 International1 day ago
International1 day agoPope Francis has died aged 88
-

 International1 day ago
International1 day agoPope Francis Dies on Day after Easter
-

 International1 day ago
International1 day agoJD Vance was one of the last people to meet Pope Francis
-

 2025 Federal Election16 hours ago
2025 Federal Election16 hours agoOttawa Confirms China interfering with 2025 federal election: Beijing Seeks to Block Joe Tay’s Election
-

 2025 Federal Election16 hours ago
2025 Federal Election16 hours agoReal Homes vs. Modular Shoeboxes: The Housing Battle Between Poilievre and Carney
-

 COVID-1916 hours ago
COVID-1916 hours agoNearly Half of “COVID-19 Deaths” Were Not Due to COVID-19 – Scientific Reports Journal
-

 2025 Federal Election16 hours ago
2025 Federal Election16 hours agoHow Canada’s Mainstream Media Lost the Public Trust
-

 2025 Federal Election16 hours ago
2025 Federal Election16 hours agoPOLL: Canadians want spending cuts









