Justice
Quebec teacher challenges Education Minister’s gender transition policy

From the Justice Centre for Constitutional Freedoms
The administrators notified the teacher that if she disclosed any information about the child’s in-school gender transition during that spring interview, the teacher would be fired immediately.
MONTREAL, QC: The Justice Centre for Constitutional Freedoms announces the launch of a constitutional challenge in Quebec’s Superior Court against the Ministry of Education. This action is brought on behalf of a teacher who refused to lie to the parents of a 14-year-old student seeking a female-to-male gender transition, as her school administration had ordered her to do.
Following directives in the Education Minister’s Guide and Procedures on trans and non-binary persons’ gender identity, the student’s Montreal high school created a set of procedures to make it illegal to inform parents (or guardians) when their child seeks a gender transition.
At the beginning of October 2023, school administrators advised teachers that they should designate the 14-year-old student with the masculine pronouns “he/him” in class. But when dealing with the student’s parents, teachers were ordered to use the student’s given name and feminine pronouns. They gave this order even though there was no evidence or suspicion of parental abuse.
The teacher informed the administration that while she agreed to observe the student’s pronoun preferences, the teacher objected to the requirement that she lie to parents about their child’s gender change, especially during an upcoming parent/teacher interview.
That interview did not occur. Instead, the school allowed the teacher to submit a written report to the student, copied to the parents, which avoided the use of pronouns. While granting this exception, the school made it clear that the teacher would be obligated to meet with the parents during a parent/teacher interview scheduled for the spring if the parents requested such interview. The administrators notified the teacher that if she disclosed any information about the child’s in-school gender transition during that spring interview, the teacher would be fired immediately.
At that point, the teacher, assisted by the Justice Centre, filed the constitutional challenge to nullify the Minister of Education’s Guide and Procedures because, notably, they “contravene parental rights protected by section 7 of the Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms…in defiance of the principles of fundamental justice and without sufficient justification in a free and democratic society.” The teacher also believes that the Guide and Procedures violate the teacher’s section 2 Charter right to freedom of conscience.
Having to lie to her pupil’s parents was the last straw for the plaintiff teacher. “I couldn’t live with myself if I did that,” the teacher stated. “I won’t look them in the eye and intentionally lie about the fact that we are enabling their child to undergo a significant psychosocial intervention without their knowledge.”
According to the teacher’s lawyer, Olivier Séguin, this would be the first time that a court action raised freedom of conscience without also raising freedom of religion. Section 2(a) of the Charter guarantees both freedom of conscience and religion.
“It’s true that the prohibition on lying is common to all religions, but my client’s conscientious objection is not religious in nature,” Mr. Séguin explains.
The teacher went on to say, “Transparent collaboration with parents is essential to my role as a teacher and critical for the long-term wellbeing of children. Lying to parents about how we are treating their children, or about what is going on with children at school, violates the principles of my vocation.”
While it is true that the law does not expressly mention how schools should handle cases like this one, Mr. Séguin says, the Guide’s authors appear to have issued a ministerial directive on the sly, through a “guidance” intended for schools, in which they make the law say things it simply does not say.
For example, in its section entitled “Legal framework” (page 8), the Guide cites section 60 of the Civil Code of Quebec, which states that a request for a name change may be made on the initiative of a minor aged 14 or over, but the Guide ignores section 62, located right next to it, which states that parents must be notified of the request for a change of name and that they are permitted to object.
The Guide’s authors also cite article 71 of the same Civil Code, which also says, like Section 60, a request for a change of gender may be made on the initiative of a minor aged 14 or over. But again, the authors of the Guide fail to note Article 73, which states that parents must be able to object to any such change.
Mr. Séguin does not consider Minister of Education Bernard Drainville responsible for the omissions. The Quebec newspaper Le Devoir had already pointed out that by opposing mixed-sex toilets in schools, he had placed himself in contradiction with “the recommendations of his own ministry,” i.e. the recommendations set out in the Guide.
In the same article, Le Devoir reported that the Guide was the result of collaboration between (1) the Ministry of Justice and (2) the Ministry of Family, (3) the Office Against Homophobia and Transphobia, (4) the Research Chair in Sexual Diversity and Gender Plurality, Université du Québec à Montréal, and (5) the National Table Against Homophobia & Transphobia in Education Networks.
Mr. Séguin says he doesn’t believe the omissions are unintended incompetence, stating, “The irregularities with which the Guide is riddled are both too obvious and too numerous to see anything other than a desire to mislead readers by falsely claiming to translate the letter of the law. I see it as a form of usurpation of power, a denial of democracy.”
As for his client’s position, he says, “Secrecy towards parents, which in practice amounts to lying to them, is a serious violation of the legal contract that binds the state and its citizens.”
Alberta
Red Deer Justice Centre Grand Opening: Building access to justice for Albertans

The new Red Deer Justice Centre will help Albertans resolve their legal matters faster.
Albertans deserve to have access to a fair, accessible and transparent justice system. Modernizing Alberta’s courthouse infrastructure will help make sure Alberta’s justice system runs efficiently and meets the needs of the province’s growing population.
Alberta’s government has invested $191 million to build the new Red Deer Justice Centre, increasing the number of courtrooms from eight to 12, allowing more cases to be heard at one time.
“Modern, accessible courthouses and streamlined services not only strengthen our justice
system – they build safer, stronger communities across the province. Investing in the new Red Deer Justice Centre is vital to helping our justice system operate more efficiently, and will give people in Red Deer and across central Alberta better access to justice.”

Government of Alberta and Judiciary representatives with special guests at the Red Deer Justice Centre plaque unveiling event April 22, 2025.
On March 3, all court services in Red Deer began operating out of the new justice centre. The new justice centre has 12 courtrooms fully built and equipped with video-conference equipment to allow witnesses to attend remotely if they cannot travel, and vulnerable witnesses to testify from outside the courtroom.
The new justice centre also has spaces for people taking alternative approaches to the traditional courtroom trial process, with the three new suites for judicial dispute resolution services, a specific suite for other dispute resolution services, such as family mediation and civil mediation, and a new Indigenous courtroom with dedicated venting for smudging purposes.
“We are very excited about this new courthouse for central Alberta. Investing in the places where people seek justice shows respect for the rights of all Albertans. The Red Deer Justice Centre fills a significant infrastructure need for this rapidly growing part of the province. It is also an important symbol of the rule of law, meaning that none of us are above the law, and there is an independent judiciary to decide disputes. This is essential for a healthy functioning democracy.”
“Public safety and access to justice go hand in hand. With this investment in the new Red Deer Justice Centre, Alberta’s government is ensuring that communities are safer, legal matters are resolved more efficiently and all Albertans get the support they need.”
“This state-of-the-art facility will serve the people of Red Deer and surrounding communities for generations. Our team at Infrastructure is incredibly proud of the work done to plan, design and build this project. I want to thank everyone, at all levels, who helped make this project a reality.”
Budget 2025 is meeting the challenge faced by Alberta with continued investments in education and health, lower taxes for families and a focus on the economy.

Quick facts
- The new Red Deer Justice Centre is 312,000 sq ft (29,000 m2). (The old courthouse is 98,780 sq ft (9,177 m2)).
- The approved project funding for the Red Deer Justice Centre is about $191 million.
International
UK Supreme Court rules ‘woman’ means biological female
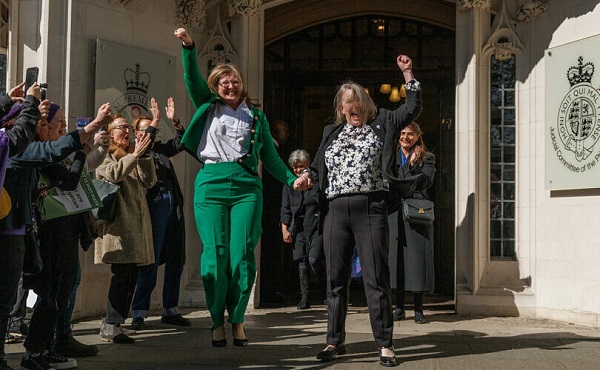
Susan Smith (L) and Marion Calder, directors of ‘For Women Scotland’ cheer as they leave the Supreme Court on April 16, 2025, in London, England after winning their appeal in defense of biological reality
From LifeSiteNews
By Michael Haynes, Snr. Vatican Correspondent
The ruling, in which the court rejected transgender legal status, comes as a victory for campaigners who have urged the recognition of biological reality and common sense in the law.
The U.K. Supreme Court has issued a ruling stating that “woman” in law refers to a biological female, and that transgender “women” are not female in the eyes of the law.
In a unanimous verdict, the Supreme Court of the United Kingdom ruled today that legally transgender “women” are not women, since a woman is legally defined by “biological sex.”
Published April 16, the Supreme Court’s 88-page verdict was handed down on the case of Women Scotland Ltd (Appellant) v. The Scottish Ministers (Respondent). The ruling marks the end of a battle of many years between the Scottish government and women’s right campaigners who sought to oppose the government’s promotion of transgender ideology.
In 2018, the Scottish government issued a decision to allow the definition of “woman” to include men who assume their gender to be female, opening the door to allowing so-called “transgender” individuals to identify as women.
This guidance was challenged by women’s rights campaigners, arguing that a woman should be defined in line with biological sex, and in 2022 the Scottish government was forced to change its definition after the court found that such a move was outside the government’s “legislative competence.”
Given this, the government issued new guidance which sought to cover both aspects: saying that biological women are women, but also that men with a “gender recognition certificate” (GRC) are also considered women. A GRC is given to people who identify as the opposite sex and who have had medical or surgical interventions in an attempt to “reassign” their gender.
Women Scotland Ltd appealed this new guidance. At first it was rejected by inner courts, but upon their taking the matter to the Supreme Court in March last year, the nation’s highest judicial body took up the case.
Today, with the ruling issued against transgender ideology, women’s campaigners are welcoming the news as a win for women’s safety.
“A thing of beauty,” praised Lois McLatchie Miller from the Alliance Defending Freedom legal group.
“They looked at the whole argument, not just who goes in what bathroom and trans women. This is going to change organizations, employers, service providers,” Maya Forstater, chief executive of Sex Matters, told the Telegraph. “Everyone is going to have to pay attention to this, this is from the highest court in the land. It’s saying sex in the Equality Act is biological sex. Self ID is dead.”
“Victory,” commented Charlie Bently-Astor, a prominent campaigner for biological reality against the transgender movement, after she nearly underwent surgical transition herself at a younger age.
“After 15 years of insanity, the U.K. Supreme Court has ruled that men who say they are ‘trans women’ are not women,” wrote leader of the Christian political movement David Kurten.
Leader of the Conservative Party – the opposition to the current Labour government – Kemi Badenoch welcomed the court’s ruling, writing that “saying ‘trans women are women’ was never true in fact and now isn’t true in law, either.”
Others lamented the fact that the debate even was taking place, let alone having gone to the Supreme Court.
“What a parody we live in,” commented Reform Party candidate Joseph Robertson.
Rupert Lowe MP – who has risen to new prominence in recent weeks for his outspoken condemnation of the immigration and rape gang crisis – wrote, “Absolute madness that we’re even debating what a woman is – it’s a biological fact. No amount of woke howling will ever change that.”
However, the Supreme Court did not wish to get pulled into siding with certain arguments, with Lord Hodge of the tribunal stating that “we counsel against reading this judgment as a triumph of one or more groups in our society at the expense of another. It is not.”
The debate has taken center stage in the U.K. in recent years, not least for the role played by the current Labour Prime Minister Keir Starmer. Starmer himself has become notorious throughout the nation for his contradictions and inability to answer the question of what a woman is, having flip-flopped on saying that a woman can have a penis, due to his support for the transgender movement.
At the time of going to press, neither Starmer nor his deputy Angela Rayner issued a statement about the Supreme Court ruling. There has been no statement issued from the Scottish government either, nor from the office of the first minister.
Transgender activists have expectedly condemned the ruling as “a disgusting attack on trans rights.” One leading transgender campaigner individual told Sky News, “I am gutted to see the judgement from the Supreme Court which ends 20 years of understanding that transgender people with a GRC are able to be, for all intents and purposes, legally recognized as our true genders.”
-

 2025 Federal Election2 days ago
2025 Federal Election2 days agoPolls say Canadians will give Trump what he wants, a Carney victory.
-

 2025 Federal Election2 days ago
2025 Federal Election2 days agoThe Anhui Convergence: Chinese United Front Network Surfaces in Australian and Canadian Elections
-

 2025 Federal Election1 day ago
2025 Federal Election1 day agoPoilievre Campaigning To Build A Canadian Economic Fortress
-

 Automotive1 day ago
Automotive1 day agoCanadians’ Interest in Buying an EV Falls for Third Year in a Row
-

 2025 Federal Election2 days ago
2025 Federal Election2 days agoTrump Has Driven Canadians Crazy. This Is How Crazy.
-

 2025 Federal Election2 days ago
2025 Federal Election2 days agoCarney Liberals pledge to follow ‘gender-based goals analysis’ in all government policy
-

 2025 Federal Election2 days ago
2025 Federal Election2 days agoPoilievre’s Conservatives promise to repeal policy allowing male criminals in female jails
-

 conflict2 days ago
conflict2 days agoTrump tells Zelensky: Accept peace or risk ‘losing the whole country’






