Health
Private Footage Reveals Leading Medical Org’s Efforts To ‘Normalize’ Gender Ideology
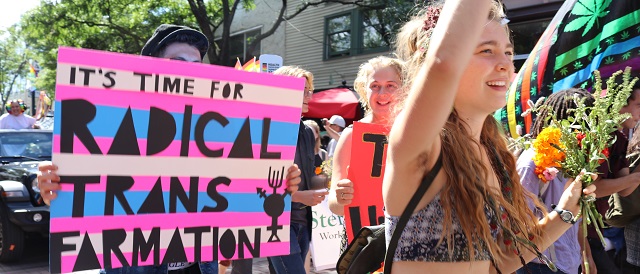
 From the Daily Caller News Foundation
From the Daily Caller News Foundation
By MEGAN BROCK AND KATE ANDERSON
I have developed a part of my brain that’s very fluid around with some of my folks asking them each week, what name are you going by? What pronouns are we using today? So it keeps us flexible to be doing this work.
This is the seventh article in the “WPATH Tapes” series on the World Professional Association for Transgender Health and the gender medical industry. Read the overview of our investigation here.
Members of the world’s most prominent transgender medical organization encouraged fellow doctors to push transgender ideology beyond the healthcare field into schools and their communities, according to internal recordings obtained by the Daily Caller News Foundation.
In September 2022, the World Professional Association of Transgender Health (WPATH) Global Education Institute (GEI) hosted an event that included a series of education sessions for certification in transgender medicine. The event coincided with the release of WPATH’s updated medical guidance, called the Standards of Care Version 8 (SOC 8), and provided additional insights on its clinical applications.
During the sessions WPATH members were encouraged to “normalize” preferred pronoun use as a way to “create societal change” and behave in a way that “affirms” their patients’ gender identity, such as by asking female patients if they have a penis.
Psychologist Ren Massey, the co-chair of WPATH GEI, said clinicians should be ready to act as advocates for “gender diversity” in school settings. Massey earned a Ph.D. in clinical psychology from University of South Florida and is not a physician.
“We want to have the skills to negotiate multiple roles,” Massey said. “Because I have both had to be the therapist and then go talk to the school and be an advocate, or do a talk to the whole community of a school. So, I’m in multiple hats that we get to navigate, if we are advocating and helping and supporting our trans and gender diverse folks we are working with.”
Massey did not respond to requests for comment, and neither did Massey’s psychology practice.
Transgender ideology includes the belief that a person’s sex can be different from their “gender identity,” which SOC 8 defines as “a person’s deeply felt, internal, intrinsic sense of their own gender.” It’s a rejection of long-established scientific understanding of biology that there are only two sexes based on the fact there are only two types of reproductive cells — sperm and ova.
The term “gender identity” was popularized in the 1960s by controversial sexologist John Money, who’s most high-profile experiment involved advising parents of a boy whose penis was damaged in a botched circumcision to cut the rest of it off and raise him as a girl. At age 15, the boy — who was raised as “Brenda” — discovered the truth and rejected further hormone treatments. He eventually committed suicide at age 38.
The very concept of “gender identity” creates the possibility of changing one’s sex — a biological impossibility — through medical interventions, therefore creating a demand for medical sex reassignment interventions.
SOC 8 recommends that gender dysphoric minors be given the opportunity to “change” their sex through medical interventions. The guidance has been used to inform government regulations, insurance policies, and recommendations by numerous medical organizations, increasing minors access to sex reassignment procedures.
‘We Will Facilitate Changes’
The call for clinicians to be involved in local schools was echoed by WPATH-affiliated psychologist Dr. Wallace Wong in a presentation titled “Foundations in Gender Affirming Mental Health Care in Childhood and Adolescence.” Wong explained how therapists can play a pivotal role in facilitating change by helping schools embrace transgenderism and explained that schools need to embrace the use of preferred pronouns.
“A lot of time we will facilitate changes. It’s not unusual that you will go to the school with the parents together and educate the school what to do,” said Wong. “A lot of the times, some school they say, ‘we don’t know what to do.’ You say, ‘that doesn’t fly, I will teach you how to do,’” Wong said.
Wong did not respond to requests for comment, and the Diversity and Emotional Wellness Centre, where Wong works, provided additional contact information but did not provide comment.
SOC 8 recommends that “health care professionals work with families, schools, and other relevant settings to promote acceptance of gender diverse expressions of behavior and identities of the adolescent.”
“Using different pronouns for children is a step towards their social transition. It is now well established that social transition leads to the medicalization of their care,” Dr. Stanley Goldfarb of Do No Harm, a watchdog organization focused on keeping identity politics out of healthcare and medical schools, told the DCNF.
“It is inappropriate for anyone to advocate gender transition in gender dysphoric children unless they have had extensive psychological counseling and are part of some formal research protocol,” Goldfarb said. “This is the new policy in the United Kingdom and in multiple European countries.”
Without naming a specific doctor, Goldfarb said that “for a physician to speak to untrained personnel given the psychological difficulties that these children often experience along with their gender dysphoria, is bordering on malpractice.”
‘The Face Of The Enemy’
As European nations such as Norway, Sweden, Denmark, and the U.K. have restricted or halted the use of cross-sex hormones and puberty blockers in minors, WPATH has rallied against similar bans in the United States.
The WPATH GEI educational event dedicated an entire session to transgender legal and policy issues. Paula Neira, a biological man who identifies as a woman and is program director of LGBTQ Equity & Education at Johns Hopkins Medicine, gave a presentation titled “Legal Issues & Policy.” During the talk, Neira criticized legislative efforts aimed at stopping child sex changes and protecting women’s sports.
“Numerous states have either engaged in having litigation and legislation proposed or the government has taken actions that are targeting the LGBTQ+ community broadly, and then at least half of these bills are specifically targeting transgender people, particularly transgender youth. The way that these bills are being played out is, one is attempts to ban gender affirming care,” Neira said.
“In Alabama they’re trying to criminalize, by making it a felony, to provide gender-affirming care to transgender youth. The bill is called the “Alabama Child Compassion and Protection Act” so the height of cynicism and hypocrisy,” Neira said.
Neira ended the session by calling on WPATH members to band together and stand firm against “attacks” on the transgender community.
“Being defiant in the face of the enemy is not something that’s unfamiliar to me,” Neria said. “It’s going to take a lot of resolve. It’s going take a lot of resilience. It’s going take a lot of mutual support, to stand firm under these attacks. And that’s what we have to do. And we have to do it with a clear strategic eye. And that means banding together. It means being strategic in how we challenge policy, how we advocate and make persuasive arguments.”
“And together we’re gonna get back to making progress no matter how bleak it looks now, as long as we never give in. And we never surrender,” Neira told the audience, prompting applause.
Neira did not respond to requests for comment. Johns Hopkins Medicine, where Neira works, responded but did not provide comment.
‘Helps All Humans’
Throughout the 30 hours of WPATH GEI recordings reviewed by the DCNF, speakers cast a vision of moving gender ideology beyond sex change procedures and promoting it in other domains such as schools, communities and public policy.
Dr. Scott Leibowitz, a WPATH board member and SOC 8 co-author, said it “helps all humans” to promote the acceptance of transgender ideology in a diversity of settings.
“We recommend health care professionals who work with families. They should work with families, schools, and other relevant settings to promote acceptance of gender diverse expressions of behavior and identities of the adolescent,” Leibowitz said.
“Notice, we don’t say: ‘work with these settings to promote acceptance of transgender people,’” Leibowitz told the audience. “We actually think it’s broader than that because by helping promote acceptance of gender diversity as a whole, we believe that helps all humans, including trans people. It doesn’t reinforce the notion of boxes, which is what we’re trying to move away from.”
Leibowitz declined an interview request through a Nationwide Children’s Hospitals spokesperson.
WPATH’s commitment to social change is captured in its own guidelines.
“WPATH recognizes that health is not only dependent upon high-quality clinical care but also relies on social and political climates that ensure social tolerance, equality, and the full rights of citizenship,” the guidelines read. “Health is promoted through public policies and legal reforms that advance tolerance and equity for gender diversity and that eliminate prejudice, discrimination, and stigma. WPATH is committed to advocacy for these policy and legal changes.”
‘Creating Change By Using Different Language’
WPATH members were also encouraged to use preferred pronouns in healthcare practices, with Massey describing the use of preferred pronouns as a way to create social change.
“I would encourage you in your practices to have universal approaches to correct pronouns. So, training your staff so they’re aware and have good interaction skills. Maybe even have role plays with them,” Massey said.
“We are creating change by using different language,” said Massey.
Massey, who maintains an active psychology practice, said it’s “good clinical practice” to let clients dictate terminology used to describe their sex and gender.
“I’ve had folks that within the same day or within the same week may shift from feeling masculine, feminine, both, neither,” Massey said.
“And so that’s a thing like I have developed a part of my brain that’s very fluid around with some of my folks asking them each week, what name are you going by? What pronouns are we using today? So it keeps us flexible to be doing this work. There is so much evolution and so much exciting work developing.”
SOC 8 recommends that healthcare professionals use the “language or terminology” preferred by the patient.
‘Normalize It’
Dr. Jennifer Slovis, the medical director of the Oakland Kaiser Permanente Gender Clinic, promoted the use of an electronic medical database that collects sexual orientation and gender identity information for all patients. On the form, healthcare providers were expected to indicate a patient’s preferred pronouns and gender identity, as well as take an “organ inventory” for the patient.
The organ inventory asks both men and women to indicate their reproductive organs on a list that includes the cervix, breasts, uterus, vagina, testes, prostate and penis. Clinicians were also asked to indicate which organs were present at birth, had been surgically constructed, or developed by hormones.
Slovis explained that to “normalize” the organ inventory, this data needs to be collected for all patients, including “cisgender” patients.
“Cisgender people too, we should be doing this for everybody. That’s the only way we’re going to normalize it, if we do it for everybody,” said Slovis.
Slovis did not respond to requests for comment, and neither did Kaiser Permanente, where Slovis works.
In a presentation titled “Foundations in Primary Care,” Dr. Erika Sullivan said organ inventories needed to be constantly taken because patients’ organs “change.”
“One of the things I always like to illustrate with this is that you don’t just ask this question once, right? Because this changes. And so sexual practices change, pronouns change, organs change,” said Sullivan.
“You kind of have to constantly take that inventory to find out like, what’s what, what’s where, what are we doing?” Sullivan said.
WPATH’s SOC 8 supports the use of organ inventories.
“In electronic health records, organ/anatomical inventories can be standardly used to inform appropriate clinical care, rather than relying solely on assigned sex at birth and/ or gender identity designations,” the guidelines read.
Sullivan also explained the importance of using preferred pronouns and not assuming a patient’s pronouns based on outward appearance.
“I should be asking this of everybody and introducing myself this way, ‘Hi, I’m Erica, I use she/her pronouns,’” Sullivan said. “Because I think if we are going by sort of presentation, we are taking so much bias and so much judgment into that space. It’s really important to just wipe that away. So asking everyone’s pronouns is important because really, ultimately, you have to question your assumptions.”
Sullivan did not respond to requests for comment, and neither did the University of Utah, where Sullivan works.
Goldfarb said doctors should focus on patient care, not promoting gender ideology.
“It is not the job of physicians to create a culture of gender ideology. The job of physicians is to care for ill people,” Goldfarb said. “The proper care for children with gender dysphoria is intensive psychological treatment. The idea that all this should be normalized represents pure ideology and is not based on hard science or valid clinical research.”
WPATH did not respond to multiple requests for comment.
Health
US podcaster Glenn Beck extends a lifeline to a Saskatchewan woman waiting for MAiD

From LifeSiteNews
Jolene Van Alstine was approved for euthanasia after tiring of waiting years for surgery in Canada
A Canadian woman is looking to die by state-sanctioned euthanasia because she has had to endure long wait times to get what she considers to be proper care for a rare parathyroid disease.
The woman is Jolene Van Alstine, whose condition, normocalcemic primary hyperparathyroidism (nPHPT), causes her to experience vomiting, nausea, and bone pain.
As noted in a recent CBC report, Van Alstine claims she is not able to get proper surgery to remove her parathyroid in her home province of Saskatchewan, as there are no surgeons in that province who can perform that type of surgery.
She has said her “friends have stopped visiting me” and she is “isolated” and living “alone lying on the couch for eight years, sick and curled up in a ball, pushing for the day to end.”
“I go to bed at six at night because I can’t stand to be awake anymore,” she said.
As a result of her frustrations with the healthcare system, Van Alstine applied for Canada’s Medical Assistance in Dying (MAiD). She was approved for the procedure on January 7, 2026.
Saskatchewan Health Minister Jeremy Cockrill met with Van Alstine last month to try to see if he could help her, but what they talked about remains confidential.
“The Government of Saskatchewan expresses its sincere sympathy for all patients who are suffering with a difficult health diagnosis,” the government said.
As reported by LifeSiteNews, over 23,000 Canadians have died while on wait lists for medical care as Prime Minister Mark Carney’s Liberal government is focused on euthanasia expansions.
A new Euthanasia Prevention Coalition report revealed that Canada has euthanized 90,000 people since 2016, the year it was legalized.
Americans offering Jolene surgery help now say they have made contact with her
Van Alstine’s story has gone viral on the social media platform X, catching the attention of well-known American personalities, some who have claimed they can help her.
“If there is any surgeon in America who can do this, I’ll pay for this patient to come down here for treatment,” Glenn Beck wrote Tuesday on X.
“THIS is the reality of ‘compassionate’ progressive healthcare. Canada must END this insanity and Americans can NEVER let it spread here.”
According to Beck in a subsequent X post, he has had “surgeons who emailed us standing by to help her.”
“We are in contact with Jolene and her husband! Please continue to pray for her health,” he wrote on X.
“Will update more soon.”
As reported by LifeSiteNews recently, a Conservative MP’s private member’s bill that, if passed, would ban euthanasia for people with mental illness received the full support of the Euthanasia Prevention Coalition.
Lobby groups have pushed for MAiD to be expanded to minors.
Desiring to expand the procedure to even more Canadians, former Prime Minister Justin Trudeau’s government sought to expand from just the chronically and terminally ill to those suffering solely from mental illness. The current Liberal government appears to want to continue with the MAiD regime.
However, in February, after pushback from pro-life, medical, and mental health groups as well as most of Canada’s provinces, the federal government delayed the mental illness expansion until 2027.
Health
The Data That Doesn’t Exist

ACIP voted to un-recommend the Hep B birth dose, but here’s the problem: they still can’t weigh the other side of the ledger
Sunday, something happened that has never happened in the history of American public health: ACIP voted 8-3 to un-recommend the universal birth dose of hepatitis B for babies born to mothers who test negative for the virus. After 34 years of jabbing every American newborn within hours of taking their first breath—regardless of whether their mother had hepatitis B—the committee finally acknowledged what 25 European countries figured out decades ago: it doesn’t make sense.
But watching this vote unfold, I couldn’t help but notice the absurdity of the debate itself. Committee members who opposed the change kept saying variations of the same thing: “We’ve heard ‘do no harm’ as a moral imperative. We are doing harm by changing this wording.” Another said “no rational science has been presented” to support the change.
How to End the Autism Epidemic is a reader-supported publication.
To receive new posts and support my work, consider becoming a free or paid subscriber.
And therein lies the fundamental problem with ACIP—and with the entire vaccine regulatory apparatus in America. They literally cannot weigh risk versus benefit because they only have data on one side of the scale.
The Missing Side of the Ledger
When ACIP debates adding or removing a vaccine from the schedule, they can produce endless data on disease incidence. They can show you charts demonstrating how hepatitis B cases in infants dropped from thousands to single digits after 1991. They can model projected infections if vaccination rates decline. They have this data at their fingertips because tracking infectious disease is something our public health apparatus actually does.
But ask them to produce equivalent data on vaccine injury, and you’ll get silence. Not “the data shows injuries are rare.” Not “here’s our comprehensive tracking of adverse events.” Just… nothing. A void where information should be.
This is not an accident. This is by design.
The safety trials for Engerix-B and Recombivax HB—the two hepatitis B vaccines given to American newborns—monitored adverse events for four to five days after injection. That’s it. If your baby developed seizures on day six, or regressed into autism over the following months, or developed autoimmune disease in the following year—none of that would appear in the pre-licensure safety data.
And the post-market surveillance? VAERS is a voluntary reporting system that the CDC itself acknowledges captures only a tiny fraction of adverse events. A Harvard-funded study found it captures perhaps 1% of actual vaccine injuries. Vaccine court has paid out over $5 billion in claims while simultaneously being structured to make filing nearly impossible for average families.
So when Dr. Cody Meissner voted against removing the Hep B birth dose and said he saw “clear evidence of the benefits” but “not the harms,” he was accidentally revealing the entire rotten structure. Of course he doesn’t see the harms. Nobody is systematically looking for them.
The Invisibility of Vaccine Injury
Here’s what most people don’t understand about vaccine injury: it’s nothing like a gunshot wound.
If you shoot someone, the cause is obvious. There’s a bullet, a wound, blood, a clear mechanism of action visible to any observer. Even a medical examiner who’s never seen the victim before can determine cause of death.
Vaccine injury doesn’t work that way. When aluminum nanoparticles from a vaccine cross the blood-brain barrier via macrophages, when they lodge in brain tissue and trigger chronic neuroinflammation, when a child slowly regresses over weeks or months—there’s no bullet. There’s no smoking gun. There’s just a before and an after, and a desperate parent trying to explain to doctors that something changed.
This invisibility is the vaccine program’s greatest protection. Because the injury mechanism is complex and delayed, because it doesn’t leave an obvious wound, because it requires actually looking to find—and because no one in authority is looking—the injuries simply don’t exist in the official record.
I watched my own son Jamie regress after his vaccines. A healthy, developing toddler who lost his words, stopped making eye contact, and retreated into a world we couldn’t reach. My wife and I know what happened. Thousands of other parents know the same thing happened to their children. But because this type of injury doesn’t show up on a simple blood test, because there’s no autopsy finding that says “vaccine-induced encephalopathy,” ACIP members can sit in a room and say with straight faces that they don’t see evidence of harm.
They’re not lying. They literally can’t see it. Because no one is measuring it.
The Chicken Pox Conundrum
Here’s an example that illustrates the insanity of our current approach.
The varicella (chicken pox) vaccine was added to the schedule in 1995. It definitely reduces chicken pox cases. The data is clear on that front. Mission accomplished, right?
But what about the other side of the ledger?
Emerging research suggests that wild chicken pox infection provides some protective effect against brain cancers—particularly glioma, the most common type of primary brain tumor. Multiple studies have found that people who had chicken pox as children have significantly lower rates of brain cancer later in life. The hypothesis is that the immune response to wild varicella provides lasting immunological benefits that extend far beyond preventing itchy spots.
Meanwhile, the vaccine itself has been associated with increased rates of autoimmune conditions. Studies have linked varicella vaccination to higher rates of herpes zoster (shingles) outbreaks in younger age groups, to autoimmune disorders, to various adverse events that weren’t captured in the original short-term safety trials.
So what’s the true risk-benefit of the chicken pox vaccine? Does preventing a week of itchy discomfort in childhood justify potentially increased rates of brain cancer and autoimmune disease later in life?
ACIP can’t answer this question. They literally don’t have the data. They can show you chicken pox cases going down. They cannot show you a comprehensive analysis of long-term neurological and immunological outcomes in vaccinated versus unvaccinated populations, because that study has never been done.
And so they keep recommending the vaccine based on the only data they have—the disease prevention data—while remaining willfully blind to consequences they’ve never bothered to measure.
The ACIP Paradox
Sunday’s vote was historic, but it also revealed the fundamental paradox of vaccine regulation in America.
The committee members who voted to remove the universal Hep B birth dose recommendation did so largely based on comparative evidence from Europe, parental concerns, and the basic logic that vaccinating a 12-hour-old baby for a sexually transmitted disease their mother doesn’t have makes no medical sense. They were right to do so.
But the committee members who voted against the change weren’t wrong either, from their perspective. They looked at the only data they have—disease prevention data—and concluded that removing the recommendation could lead to more hepatitis B cases. And within their limited framework, they’re correct.
The problem is the framework itself.
True risk-benefit analysis requires data on both risks AND benefits. ACIP has comprehensive data on benefits (disease prevention) and virtually no data on risks (vaccine injury). So every decision they make is fundamentally flawed from the start.
When Dr. Joseph Hibbeln complained that “no rational science has been presented” to support changing the recommendations, he was inadvertently indicting the entire system. Of course no comprehensive vaccine injury data was presented—such data doesn’t exist because no one has been willing to collect it.
This is like asking someone to make an informed financial decision while only showing them potential profits and hiding all possible losses. Of course the decision will be skewed. Of course you’ll end up with a bloated portfolio of high-risk investments that look great on paper.
The Real Reform
If RFK Jr. and the new HHS leadership want to actually fix the vaccine program, they need to understand that removing individual vaccines or making them “optional” is just rearranging deck chairs on the Titanic.
The real reform is creating the data infrastructure that should have existed from the beginning.
We need a comprehensive, long-term, vaccinated-versus-unvaccinated health outcomes study. Not a five-day safety trial. A multi-decade tracking of neurological, immunological, and developmental outcomes across populations with varying vaccination status. Florida just eliminated all vaccine mandates—that state alone could provide the data we need within ten years if someone had the courage to actually collect it.
We need a vaccine injury surveillance system that actually captures adverse events. Not a voluntary reporting system that misses 99% of injuries. An active surveillance system with trained clinicians looking for the kinds of delayed, complex injuries that vaccines actually cause.
We need accountability for manufacturers. The 1986 National Childhood Vaccine Injury Act removed all liability from vaccine makers—and predictably, the vaccine schedule exploded afterward while safety research stagnated. Why would any company invest in safety when they can’t be sued for injuries?
Without this data, every ACIP meeting will be the same performance we watched this week: members confidently citing disease prevention data while admitting they can’t see evidence of harm—not because harm doesn’t exist, but because no one is looking for it.
What Comes Next
Sunday’s vote was a crack in the wall. For the first time, an American regulatory body acknowledged that perhaps vaccinating every newborn within hours of birth for a disease primarily transmitted through sex and IV drug use doesn’t make sense when the mother has already tested negative.
But the forces of institutional inertia are already mobilizing. The American Academy of Pediatrics is “disappointed.” The American Medical Association is calling for the CDC to reject the recommendation. The pharmaceutical industry—which collects over $225 million annually from Hep B birth doses alone—will fight to restore the universal recommendation.
They will cite the same data they always cite: disease prevention data. Cases prevented. Infections avoided. Lives saved—theoretically.
They will not cite vaccine injury data, because that data doesn’t exist in any comprehensive form. They will not present long-term health outcomes in vaccinated versus unvaccinated children, because those studies have been actively avoided for decades. They will not acknowledge the thousands of families who have watched their children regress after vaccination, because those injuries aren’t captured in any official database.
And this is why ACIP will always be hamstrung. Until we build the data infrastructure to actually measure vaccine injury—to put real numbers on the other side of the ledger—every vaccine decision will be based on incomplete information. Every “risk-benefit analysis” will be a fraud, because we’re only measuring half the equation.
The hepatitis B birth dose vote was a small victory. But the larger battle—for actual science, for complete data, for true informed consent—that battle is just beginning.
And until we win it, ACIP will continue making decisions in the dark, confidently citing evidence of benefits while remaining deliberately blind to the harms they’ve never bothered to measure.
About the author
J.B. Handley is the proud father of a child with Autism. He spent his career in the private equity industry and received his undergraduate degree with honors from Stanford University. His first book, How to End the Autism Epidemic, was published in September 2018. The book has sold more than 75,000 copies, was an NPD Bookscan and Publisher’s Weekly Bestseller, broke the Top 40 on Amazon, and has more than 1,000 Five-star reviews. Mr. Handley and his nonspeaking son are also the authors of Underestimated: An Autism Miracle and co-produced the film SPELLERS, available now on YouTube.
How to End the Autism Epidemic is a reader-supported publication.
To receive new posts and support my work, consider becoming a free or paid subscriber.
-

 Alberta1 day ago
Alberta1 day agoThe Recall Trap: 21 Alberta MLA’s face recall petitions
-
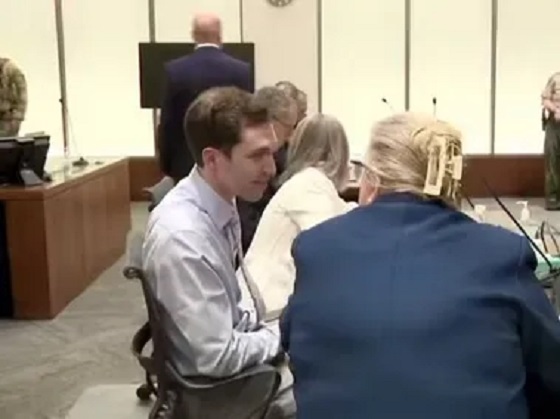

 International1 day ago
International1 day agoTyler Robinson shows no remorse in first court appearance for Kirk assassination
-

 Energy1 day ago
Energy1 day agoCanada’s future prosperity runs through the northwest coast
-

 illegal immigration1 day ago
illegal immigration1 day agoUS Notes 2.5 million illegals out and counting
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoHigh-speed rail between Toronto and Quebec City a costly boondoggle for Canadian taxpayers
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoThe world is no longer buying a transition to “something else” without defining what that is
-

 2025 Federal Election2 days ago
2025 Federal Election2 days agoToo Close for Comfort: Carney Floor Crosser Comes From a Riding Tainted by PRC Interference
-

 Daily Caller19 hours ago
Daily Caller19 hours ago‘There Will Be Very Serious Retaliation’: Two American Servicemen, Interpreter Killed In Syrian Attack











