Uncategorized
Migrant caravan re-forms in Mexico, members vow to reach US

CIUDAD HIDALGO, Mexico — Despite Mexican efforts to stop them at the border, about 2,000 Central American migrants swam or rafted across a river separating that country from Guatemala, re-formed their mass caravan in Mexico and vowed to resume their journey toward the United States.
The migrants, who said they gave up trying to enter Mexico legally because the asylum application process was too slow, gathered Saturday at a park in the border city of Ciudad Hidalgo. They voted by a show of hands to continue north en masse, then marched to the bridge crossing the Suchiate River and urged those still on it to come join them.
“We are going to reach the United States,” said Erasmo Duarte, a migrant from Danli, Honduras, despite warnings to turn back this week from U.S. President Donald Trump, who has sought to make the caravan and border security into a campaign issue before the U.S. midterm election in November.
The decision to re-form the migrant caravan capped a day in which Mexican authorities again refused mass entry to migrants on the bridge, instead accepting small groups for asylum processing and giving out 45-day visitor permits to some. Authorities handed out numbers for people to be processed in a strategy seen before at U.S. border posts when dealing with large numbers of migrants.
But many became impatient and circumventing the border gate, crossing the river on rafts, by swimming or by wading in full view of the hundreds of Mexican police manning the blockade on the bridge. Some paid locals the equivalent of $1.25 to ferry them across the muddy waters. They were not detained on reaching the Mexican bank.
“We couldn’t wait because we had already waited too long and they only told us lies,” said Duarte, who joined the caravan with his wife and children six days ago.
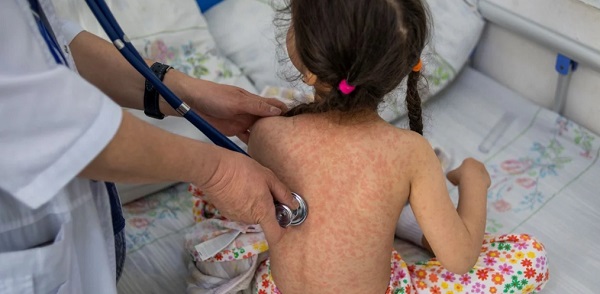
Sairy Bueso, a 24-year old Honduran mother of two, was another migrant who abandoned the bridge and crossed into Mexico via the river. She clutched her 2-year-old daughter Dayani, who had recently had a heart operation, as she got off a raft.
“The girl suffered greatly because of all the people crowded” on the bridge, Bueso said. “There are risks that we must take for the good of our children.”
Group leaders said the caravan, which will be smaller than the original one, would strike out Sunday morning for the city of Tapachula.
Where easily 3,000 people were on the bridge the previous day, the crowd had thinned out considerably by Saturday. In addition to those who crossed the river, immigration agents processed migrants in small groups and then bused them to an open-air, metal-roof fairground in Tapachula, where the Red Cross set up small blue tents on the concrete floor.
Each time a small side gate opened to allow people to pass for processing, there was a crush of bodies as migrants desperately pushed forward. Scarleth Cruz hoisted a crying, sweat-soaked baby girl above the crowd, crying out: “This girl is suffocating.”
Cruz, 20, said she was going to ask for political asylum because of threats and repression she faced back in Honduras from President Juan Orlando Hernandez’s governing party.
“Why would I want to go to the United States if I’m going to be persecuted” there as well, she said.
Mexico’s Interior Department said it had received 640 refugee requests by Hondurans at the border crossing. It released photos of migrants getting off buses at a shelter and receiving food and medical attention.
At least half a dozen migrants fainted in the crush.
Some tore open a fence on the Guatemala side of the bridge and threw two young children, perhaps age 6 or 7, and their mother into the muddy waters about 40 feet below. They were rafted to safety in on the Mexican bank.
Mexican workers handed food and bottled water to the migrants on the bridge. Through the bars, a doctor gave medical attention to a woman who feared her young son was running a fever.
Sustenance also came from Guatemalan locals — for Carlos Martinez, a 24-year-old from Santa Barbara, Honduras, the plate of chicken with rice was the first bite to eat he’d had all day.
“It is a blessing that they have given us food,” Martinez said. “It gives me courage to keep waiting, as long as I can.”
Migrants cited widespread poverty and gang violence in Honduras, one of the world’s deadliest nations by homicide rate, as their reasons for joining the caravan.
“One cannot live back there,” said Fidelina Vasquez, a grandmother
The caravan elicited a series of angry tweets and warnings from Trump early in the week, but Mexico’s handling of the migrants at it southern border seems to have satisfied him more recently.
“So as of this moment, I thank Mexico,” Trump said Friday at an event in Scottsdale, Arizona. “I hope they continue. But as of this moment, I thank Mexico. If that doesn’t work out, we’re calling up the military — not the Guard.”
“They’re not coming into this country,” Trump added.
“The Mexican Government is fully engaged in finding a solution that encourages safe, secure, and orderly migration,” State Department Spokeswoman Heather Nauert said Saturday, “and both the United States and Mexico continue to work with Central American governments to address the economic, security, and governance drivers of illegal immigration.”
After an emergency meeting in Guatemala, presidents Hernandez of Honduras and Jimmy Morales of Guatemala said an estimated 5,400 migrants had entered Guatemala since the caravan was announced a week ago, and about 2,000 Hondurans have returned voluntarily.
Morales said a Honduran migrant died in the town of Villa Nueva, 20 miles (30
Some Hondurans were weary of the journey and disappointed by the violence at the crossing, and just wanted to head home.
“We thought the caravan was passive but there were unruly people, I was disappointed,” said Gonzalo Martinez, a 37-year-old farmer, as he boarded a bus in Tecun Uman, Guatemala to take him back to Honduras.
___
Mark Stevenson reported from Ciudad Hidalgo, and Sonia Perez D. reported from Tecun Uman, Guatemala. Associated Press writers Sonny Figueroa in Guatemala City and Peter Orsi in Mexico City contributed to this report.
Mark Stevenson And Sonia Perez D., The Associated Press
Uncategorized
Poilievre on 2025 Election Interference – Carney sill hasn’t fired Liberal MP in Chinese election interference scandal

From Conservative Party Communications
“Yes. He must be disqualified. I find it incredible that Mark Carney would allow someone to run for his party that called for a Canadian citizen to be handed over to a foreign government on a bounty, a foreign government that would almost certainly execute that Canadian citizen.
“Think about that for a second. We have a Liberal MP saying that a Canadian citizen should be handed over to a foreign dictatorship to get a bounty so that that citizen could be murdered. And Mark Carney says he should stay on as a candidate. What does that say about whether Mark Carney would protect Canadians?
“Mark Carney is deeply conflicted. Just in November, he went to Beijing and secured a quarter-billion-dollar loan for his company from a state-owned Chinese bank. He’s deeply compromised, and he will never stand up for Canada against any foreign regime. It is another reason why Mr. Carney must show us all his assets, all the money he owes, all the money that his companies owe to foreign hostile regimes. And this story might not be entirely the story of the bounty, and a Liberal MP calling for a Canadian to be handed over for execution to a foreign government might not be something that the everyday Canadian can relate to because it’s so outrageous. But I ask you this, if Mark Carney would allow his Liberal MP to make a comment like this, when would he ever protect Canada or Canadians against foreign hostility?
“He has never put Canada first, and that’s why we cannot have a fourth Liberal term. After the Lost Liberal Decade, our country is a playground for foreign interference. Our economy is weaker than ever before. Our people more divided. We need a change to put Canada first with a new government that will stand up for the security and economy of our citizens and take back control of our destiny. Let’s bring it home.”
Uncategorized
Canada Needs A Real Plan To Compete Globally

From the Frontier Centre for Public Policy
Ottawa’s ideological policies have left Canada vulnerable. Strategic action is needed now
As Canada navigates an increasingly complex geopolitical landscape, the next federal government must move beyond reflexive anti—Americanism regardless of its political leanings. Instead, Canada should prioritize national interests while avoiding unnecessary conflict and subservience.
The notion that Canada can stand alone is as misguided as the idea that it is only an economic appendage of the United States. Both perspectives have influenced policy in Ottawa at different times, leading to mistakes.
Rather than engaging in futile name-calling or trade disputes, Canada must take strategic steps to reinforce its autonomy. This approach requires a pragmatic view rooted in Realpolitik—recognizing global realities, mitigating risks, governing for the whole country, and seizing opportunities while abandoning failed ideologies.
However, if Washington continues to pursue protectionist measures, Canada must find effective ways to counteract the weakened position Ottawa has placed the country in over the past decade.
One key strategy is diversifying trade relationships, notably by expanding economic ties with emerging markets such as India and Southeast Asia. This will require repairing Canada’s strained relationship with India and regaining political respect in China.
Unlike past Liberal trade missions, which often prioritized ideological talking points over substance, Canada must negotiate deals that protect domestic industries rather than turning summits into platforms for moral posturing.
A more effective approach would be strengthening partnerships with countries that value Canadian resources instead of vilifying them under misguided environmental policies. Expand LNG exports to Europe and Asia and leverage Canada’s critical minerals sector to establish reciprocal supply chains with non-Western economies, reducing economic reliance on the U.S.
Decades of complacency have left Canada vulnerable to American influence over its resource sector. Foreign-funded environmental groups have weakened domestic energy production, handing U.S. industries a strategic advantage. Ottawa must counter this by ensuring Canadian energy is developed at home rather than allowing suppressed domestic production to benefit foreign competitors.
Likewise, a robust industrial policy—prioritizing mining, manufacturing, and agricultural resilience—could reduce dependence on U.S. and Chinese imports. This does not mean adopting European-style subsidies but rather eliminating excessive regulations that make Canadian businesses uncompetitive, including costly domestic carbon tariffs.
Another key vulnerability is Canada’s growing military dependence on the U.S. through NORAD and NATO. While alliances are essential, decades of underfunding and neglect have turned the Canadian Armed Forces into little more than a symbolic force. Canada must learn self-reliance and commit to serious investment in defence.
Increasing defence spending—not to meet NATO targets but to build deterrence—is essential. Ottawa must reform its outdated procurement processes and develop a domestic defence manufacturing base, reducing reliance on foreign arms deals.
Canada’s vast Arctic is also at risk. Without continued investment in northern sovereignty, Ottawa may find itself locked out of its own backyard by more assertive global powers.
For too long, Canada has relied on an economic model that prioritizes federal redistribution over wealth creation and productivity. A competitive tax regime—one that attracts investment instead of punishing success—is essential.
A capital gains tax hike might satisfy activists in Toronto, but it does little to attract investments and encourage economic growth. Likewise, Ottawa must abandon ideological green policies that threaten agri-food production, whether by overregulating farmers or ranchers. At the same time, it must address inefficiencies in supply management once and for all. Canada must be able to feed a growing world without unnecessary bureaucratic obstacles.
Ottawa must also create an environment where businesses can innovate and grow without excessive regulatory burdens. This includes eliminating interprovincial trade barriers that stifle commerce.
Similarly, Canada’s tech sector, long hindered by predatory regulations, should be freed from excessive government interference. Instead of suffocating innovation with compliance mandates, Ottawa should focus on deregulation while implementing stronger security measures for foreign tech firms operating in Canada.
Perhaps Ottawa’s greatest mistake is its knee-jerk reactions to American policies, made without a coherent long-term strategy. Performative trade disputes with Washington and symbolic grandstanding in multilateral organizations do little to advance Canada’s interests.
Instead of reacting emotionally, Canada must take proactive steps to secure its economic, resource, and defence future. That is the role of a responsible government.
History’s best strategists understood that one should never fight an opponent’s war but instead dictate the terms of engagement. Canada’s future does not depend on reacting to Washington’s policies—these are calculated strategies, not whims. Instead, Canada’s success will be determined by its ability to act in the interests of citizens in all regions of the country, and seeing the world as it is rather than how ideological narratives wish it to be.
Marco Navarro-Génie is the vice president of research at the Frontier Centre for Public Policy. With Barry Cooper, he is co-author of Canada’s COVID: The Story of a Pandemic Moral Panic (2023).
-

 Alberta2 days ago
Alberta2 days agoMedical regulator stops short of revoking license of Alberta doctor skeptic of COVID vaccine
-

 MacDonald Laurier Institute2 days ago
MacDonald Laurier Institute2 days agoRushing to death in Canada’s MAiD regime
-

 2025 Federal Election1 day ago
2025 Federal Election1 day agoHarper Endorses Poilievre at Historic Edmonton Rally: “This Crisis Was Made in Canada”
-

 Energy2 days ago
Energy2 days agoEnergy group urges Trump administration to restock oil reserves
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoTrump eyes end of capital gains tax in 2025
-

 Bruce Dowbiggin2 days ago
Bruce Dowbiggin2 days agoBettman Gives Rogers Keys To The Empire. Nothing Will Change
-

 2025 Federal Election2 days ago
2025 Federal Election2 days agoPoilievre Will Bring in ‘One and Done’ Resource Approvals, and Ten Specific Projects Including LNG Canada Phase II
-
 conflict1 day ago
conflict1 day agoZelensky Alleges Chinese Nationals Fighting for Russia, Calls for Global Response