Uncategorized
Lamar leads Grammy noms, where women make a comeback

NEW YORK — The music of “Black Panther,” with Kendrick Lamar in its starring role, officially owns the 2019 Grammy Awards, where women are heavily represented in the major four categories following a year where their presence was barely felt.
The Recording Academy announced Friday that Lamar is the top contender with eight nominations, including seven for his musical companion to the Marvel Studios juggernaut starring Chadwick Boseman and Michael B. Jordan. “Black Panther: The Album, Music From and Inspired By” is up for album of the year, a category where women make up five of the eight nominees. Cardi B, Kacey Musgraves, Janelle Monae, H.E.R. and Brandi Carlile also are up for the top prize, along with Drake and Post Malone.
The upcoming Grammys is the first where the academy extended its top four categories from five nominees to eight.
The “Panther” nomination would give Lamar a chance to win album of the year after losing three times. His most recent loss was in February when his critically acclaimed “DAMN” fell short to Bruno Mars’ “24K Magic,” though Lamar’s project would go on to win a Pulitzer Prize for music two months later, making him the first non-classical or jazz artist to win the prestigious
Lamar’s Top 10 hit, the SZA-assisted “All the Stars,” is nominated for both record and song of the year (a songwriter’s award). Five other songs scored nominations in both categories, including Lady Gaga and Bradley Cooper’s “Shallow” from “A Star Is Born”; Childish Gambino’s “This Is America”; Drake’s “God’s Plan”; Zedd, Maren Morris and Grey’s “The Middle”; and Carlile’s “The Joke.”
Ella Mai’s “Boo’d Up” and Shawn Mendes’ “In My Blood” earned song of the year nods, while Post Malone’s “Rockstar” and Cardi B’s “I Like It,” featuring Bad Bunny and J Balvin, round out the nominees for record of the year.
Following Lamar, Drake — the year’s most successful artist — earned seven nominations. Though nominated for album of the year, he was surprisingly shut out of best rap album, where his rival Pusha T earned a nomination.
Drake’s frequent collaborator, producer Boi-1Da, earned six nods, as did Carlile, who also scored nominations in the American Roots category.
Cardi B, Gaga, H.E.R., Morris, Gambino, producer Sounwave and engineer Mike Bozzi scored five nominations each.
The nominees for the 2019 Grammys mark a departure from this year’s show, where women were underrepresented in the top four categories. Of the eight best new artist nominees, six are women, including H.E.R., Chloe x Halle, Dua Lipa, Margo Price, Bebe Rexha and Jorja Smith. Rock band Greta Van Fleet and country singer Luke Combs also earned nominations.
Recording Academy CEO Neil Portnow was criticized earlier this year at the Grammys when he said women need to “step up” when asked about the lack of women in the top categories, which he later acknowledged was a “poor choice of words.” It forced the academy to launch a new task force focused on inclusion and diversity; Portnow also announced he would be leaving the academy in 2019.
“In any given year there could be more folks from one area or one gender or one genre or one ethnicity that are making recordings and being successful with them than in another year. So, in many ways we’re just a reflection of that,” Portnow said in an interview with The Associated Press. “This year clearly there were many women not only making music but making great music and making music that resonates with our peer voters in terms of excellence, and so that certainly is at the forefront.”
Another milestone for women is in the non-classical producer of the year category, where songwriting extraordinaire Linda Perry earned a nomination. She’s just the seventh woman ever nominated for prize and first since 2004.
“Linda represents what we hope becomes the norm, which is the elimination of gender bias in producing and engineering in our industry,” Portnow said.
Perry will compete with Pharrell Williams, Boi-1Da, Larry Klein and Kanye West, the only nomination he earned.
Taylor Swift, a two-time album of the year winner, also only earned one nomination — her “reputation” album is up best pop vocal album. Justin Timberlake, whose “Man of the Woods” albums flopped earlier this year, picked up a nod for “Say Something,” his collaboration with Chris Stapleton.
Beyonce and Jay-Z, billed as The Carters, as well Ariana Grande, didn’t earn any of the big nominations. The Carters earned two nods in the R&B category along with best music video, while Grande picked up two nods in pop.
Artists who were completely snubbed include Carrie Underwood, Sam Smith, Migos, Kane Brown, Nicki Minaj, XXXTentacion and Juice WRLD, whose “Lucid Dreams” was one of the year’s biggest hits.
Some acts scored their first nominations ever, including Florida Georgia Line, whose megahit “Meant to Be” with Rexha is up best country duo/group performance. Camila Cabello, Malone, Mendes, Dan + Shay and DJ Mustard are also first-time nominees.
Gaga, who earned acting and music Golden Globe nominations Thursday, picked up four Grammy nominations for “Shallow,” while “Joanne” is up for best pop solo performance. The soundtrack for “A Star Is Born” was released after Grammy eligibility, though “Shallow” was released in time and also earned Cooper two nominations.
Other famous faces outside of music to earn nominations include Tiffany Haddish and former U.S. president Jimmy Carter, both up for best spoken word album. Dave Chappelle, Chris Rock, Fred Armisen, Jim Gaffigan and Patton Oswalt are up for best comedy album.
Mac Miller, who died in September, earned a nomination for best rap album with “Swimming.” Chris Cornell, who died last year, is up for best rock performance with “When Bad Does Good.”
Demi Lovato, who relapsed after six years of sobriety and was hospitalized for an overdose in July, earned a nomination for best pop duo/group performance for “Fall In Line,” her duet with Christina Aguilera.
Those who earned four nominations are Musgraves, Malone, PJ Morton, Dave Cobb, Ludwig Goransson, Noah Shebib and SZA, who earned a Golden Globe nomination alongside Lamar for “All the Stars” on Thursday.
Lamar has won 12 Grammys throughout his career. Though seven of his eight nominations come from “Black Panther,” he also earned a nod for co-writing Jay Rock’s “Win,” up for best rap song.
The 2019 Grammys will hand out awards in its 84 categories live from the Staples Center in Los Angeles on Feb. 10, 2019.
_____
Online:
http://www.grammy.com
Mesfin Fekadu, The Associated Press
Uncategorized
Mortgaging Canada’s energy future — the hidden costs of the Carney-Smith pipeline deal


Much of the commentary on the Carney-Smith pipeline Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) has focused on the question of whether or not the proposed pipeline will ever get built.
That’s an important topic, and one that deserves to be examined — whether, as John Robson, of the indispensable Climate Discussion Nexus, predicted, “opposition from the government of British Columbia and aboriginal groups, and the skittishness of the oil industry about investing in a major project in Canada, will kill [the pipeline] dead.”
But I’m going to ask a different question: Would it even be worth building this pipeline on the terms Ottawa is forcing on Alberta? If you squint, the MOU might look like a victory on paper. Ottawa suspends the oil and gas emissions cap, proposes an exemption from the West Coast tanker ban, and lays the groundwork for the construction of one (though only one) million barrels per day pipeline to tidewater.
But in return, Alberta must agree to jack its industrial carbon tax up from $95 to $130 per tonne at a minimum, while committing to tens of billions in carbon capture, utilization, and storage (CCUS) spending, including the $16.5 billion Pathways Alliance megaproject.
Here’s the part none of the project’s boosters seem to want to mention: those concessions will make the production of Canadian hydrocarbon energy significantly more expensive.
As economist Jack Mintz has explained, the industrial carbon tax hike alone adds more than $5 USD per barrel of Canadian crude to marginal production costs — the costs that matter when companies decide whether to invest in new production. Layer on the CCUS requirements and you get another $1.20–$3 per barrel for mining projects and $3.60–$4.80 for steam-assisted operations.
While roughly 62% of the capital cost of carbon capture is to be covered by taxpayers — another problem with the agreement, I might add — the remainder is covered by the industry, and thus, eventually, consumers.
Total damage: somewhere between $6.40 and $10 US per barrel. Perhaps more.
“Ultimately,” the Fraser Institute explains, “this will widen the competitiveness gap between Alberta and many other jurisdictions, such as the United States,” that don’t hamstring their energy producers in this way. Producers in Texas and Oklahoma, not to mention Saudi Arabia, Venezuela, or Russia, aren’t paying a dime in equivalent carbon taxes or mandatory CCUS bills. They’re not so masochistic.
American refiners won’t pay a “low-carbon premium” for Canadian crude. They’ll just buy cheaper oil or ramp up their own production.
In short, a shiny new pipe is worthless if the extra cost makes barrels of our oil so expensive that no one will want them.
And that doesn’t even touch on the problem for the domestic market, where the higher production cost will be passed onto Canadian consumers in the form of higher gas and diesel prices, home heating costs, and an elevated cost of everyday goods, like groceries.
Either way, Canadians lose.
So, concludes Mintz, “The big problem for a new oil pipeline isn’t getting BC or First Nation acceptance. Rather, it’s smothering the industry’s competitiveness by layering on carbon pricing and decarbonization costs that most competing countries don’t charge.” Meanwhile, lurking underneath this whole discussion is the MOU’s ultimate Achilles’ heel: net-zero.
The MOU proudly declares that “Canada and Alberta remain committed to achieving Net-Zero greenhouse gas emissions by 2050.” As Vaclav Smil documented in a recent study of Net-Zero, global fossil-fuel use has risen 55% since the 1997 Kyoto agreement, despite trillions spent on subsidies and regulations. Fossil fuels still supply 82% of the world’s energy.
With these numbers in mind, the idea that Canada can unilaterally decarbonize its largest export industry in 25 years is delusional.
This deal doesn’t secure Canada’s energy future. It mortgages it. We are trading market access for self-inflicted costs that will shrink production, scare off capital, and cut into the profitability of any potential pipeline. Affordable energy, good jobs, and national prosperity shouldn’t require surrendering to net-zero fantasy.If Ottawa were serious about making Canada an energy superpower, it would scrap the anti-resource laws outright, kill the carbon taxes, and let our world-class oil and gas compete on merit. Instead, we’ve been handed a backroom MOU which, for the cost of one pipeline — if that! — guarantees higher costs today and smothers the industry that is the backbone of the Canadian economy.
This MOU isn’t salvation. It’s a prescription for Canadian decline.
Uncategorized
Cost of bureaucracy balloons 80 per cent in 10 years: Public Accounts

The cost of the bureaucracy increased by $6 billion last year, according to newly released numbers in Public Accounts disclosures. The Canadian Taxpayers Federation is calling on Prime Minister Mark Carney to immediately shrink the bureaucracy.
“The Public Accounts show the cost of the federal bureaucracy is out of control,” said Franco Terrazzano, CTF Federal Director. “Tinkering around the edges won’t cut it, Carney needs to take urgent action to shrink the bloated federal bureaucracy.”
The federal bureaucracy cost taxpayers $71.4 billion in 2024-25, according to the Public Accounts. The cost of the federal bureaucracy increased by $6 billion, or more than nine per cent, over the last year.
The federal bureaucracy cost taxpayers $39.6 billion in 2015-16, according to the Public Accounts. That means the cost of the federal bureaucracy increased 80 per cent over the last 10 years. The government added 99,000 extra bureaucrats between 2015-16 and 2024-25.
Half of Canadians say federal services have gotten worse since 2016, despite the massive increase in the federal bureaucracy, according to a Leger poll.
Not only has the size of the bureaucracy increased, the cost of consultants, contractors and outsourcing has increased as well. The government spent $23.1 billion on “professional and special services” last year, according to the Public Accounts. That’s an 11 per cent increase over the previous year. The government’s spending on professional and special services more than doubled since 2015-16.
“Taxpayers should not be paying way more for in-house government bureaucrats and way more for outside help,” Terrazzano said. “Mere promises to find minor savings in the federal bureaucracy won’t fix Canada’s finances.
“Taxpayers need Carney to take urgent action and significantly cut the number of bureaucrats now.”
Table: Cost of bureaucracy and professional and special services, Public Accounts
| Year | Bureaucracy | Professional and special services |
|
$71,369,677,000 |
$23,145,218,000 |
|
|
$65,326,643,000 |
$20,771,477,000 |
|
|
$56,467,851,000 |
$18,591,373,000 |
|
|
$60,676,243,000 |
$17,511,078,000 |
|
|
$52,984,272,000 |
$14,720,455,000 |
|
|
$46,349,166,000 |
$13,334,341,000 |
|
|
$46,131,628,000 |
$12,940,395,000 |
|
|
$45,262,821,000 |
$12,950,619,000 |
|
|
$38,909,594,000 |
$11,910,257,000 |
|
|
$39,616,656,000 |
$11,082,974,000 |
-

 International2 days ago
International2 days agoGeorgia county admits illegally certifying 315k ballots in 2020 presidential election
-

 Alberta1 day ago
Alberta1 day agoA Christmas wish list for health-care reform
-

 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoSome Of The Wackiest Things Featured In Rand Paul’s New Report Alleging $1,639,135,969,608 In Gov’t Waste
-

 Energy1 day ago
Energy1 day ago‘The electric story is over’
-
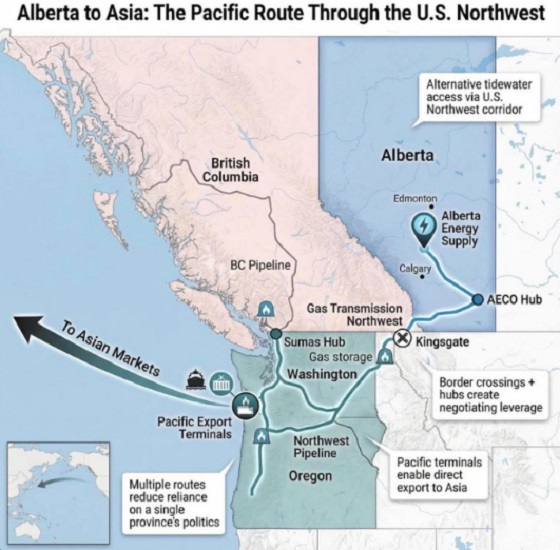
 Alberta2 days ago
Alberta2 days agoWhat are the odds of a pipeline through the American Pacific Northwest
-

 International2 days ago
International2 days agoCommunist China arrests hundreds of Christians just days before Christmas
-

 Alberta2 days ago
Alberta2 days agoCalgary’s new city council votes to ban foreign flags at government buildings
-

 Alberta19 hours ago
Alberta19 hours agoOttawa-Alberta agreement may produce oligopoly in the oilsands










