espionage
In 2025 Critical Political Choices Will Define Canada’s Future: Clement
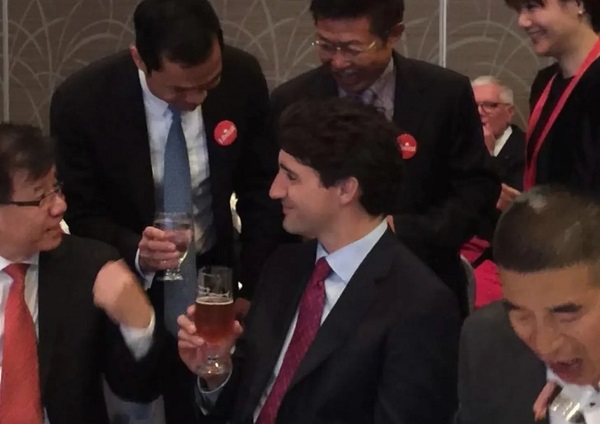

Justin Trudeau had a Liberal Party fundraiser in Vancouver with a number of Chinese Nationals that included individuals in United Front groups with official ties to Beijing, along with former Liberal multiculturalism minister and prominent party fundraiser Raymond Chan. Numerous donations into Trudeau’s personal Montreal election riding flowed after this Vancouver dinner.
Many Canadian politicians have forged unhealthy relationships with China; Ottawa must renew its most important partnership with the United States, former senior Mountie Garry Clement writes.
As Canada looks ahead to 2025, it stands at a crucial juncture, facing both unprecedented challenges and emerging opportunities. The nation’s evolving relationship with China, ongoing concerns about money laundering, the upcoming federal election, and its delicate position in U.S.-Canada relations present an intricate web of issues that will shape the country’s future. How Canada navigates these issues in the next year will determine not only its global standing but also its domestic harmony.
The China Challenge
Since the era of Pierre Elliott Trudeau, many Canadian politicians have forged what we now recognize as unhealthy relationships with China, enabling the country to interfere in our electoral process at all levels of government. This has provided an opportunity for Triads and Chinese Communist Party sympathizers to infiltrate Canadian society and Canadian politics.
In the past decade, Canada’s relationship with China has been strained, primarily due to geopolitical tensions and human rights concerns, but this has not resulted in any meaningful restrictions being placed on China by Canada. In 2025, this relationship will remain a balancing act—Canada must tread carefully between maintaining diplomatic and trade ties with a rising global power while aligning with Western allies who increasingly view China as a strategic adversary. Canadian politicians will also need to understand and accept that United Front Groups existing in Chinese diaspora communities across Canada have been shown to be allied with the Chinese government.
Canada’s foreign policy decisions will likely be influenced by developments in China’s global ambitions, particularly in areas such as the Belt and Road Initiative, the Taiwan issue, and its growing military presence in the South China Sea. The country’s relationship with China is at a crossroads, with growing calls for Canada to take a firmer stance on human rights issues, such as the treatment of Uyghurs in Xinjiang and Hong Kong’s autonomy. On the other hand, China remains a vital trading partner, especially in the context of Canada’s resource exports. Notwithstanding this, Canada will have a decision to make and hopefully it leans towards protecting Canada’s sovereignty.
Canada must also be prepared to reassess its foreign policy posture as the global balance of power continues to shift. The 2025 federal election could provide a pivotal moment in shaping public opinion on China and its place in Canada’s future.
We break international stories and this requires elite expertise, time and legal costs.
Money Laundering: An Ongoing Domestic and International Concern
Another pressing issue for Canada in 2025 is the continuing challenge of money laundering, particularly within its real estate and financial sectors. Internationally, Canada’s role in global financial markets means that it cannot afford to be complacent about illicit financial flows. Recent reports have highlighted how foreign actors, including from China, have used Canadian institutions to launder money and hide illicit funds.
The Cullen Commission highlighted that Canada has failed on so many fronts to ensure an effective and efficient legislative, enforcement, and prosecutorial regime existed for almost two decades, thereby making Canada an attractive venue for transnational organized crime groups. This has resulted in Canada having to prove that as a country we can combat money laundering if we want to shore up our failing international credibility. Failure to address these concerns will damage Canada’s reputation as a stable and transparent financial hub, while also complicating its relationships with other Western countries, including the United States. The government must intensify efforts to strengthen regulatory frameworks and enhance cross-border cooperation in financial crime prevention.
The Federal Election: A Fork in the Road
As 2025 approaches, Canada’s political landscape is increasingly polarized. The upcoming federal election promises to be a defining moment for the nation, as Canadians grapple with issues such as climate change, economic recovery post-COVID, affordability, and national unity. Without a doubt, I would argue the silent majority has been awakened and recognizes the past eight years of adopting a strong left-leaning stance has destroyed our reputation, thereby making us an easy target for President-elect Trump’s jibes and eventual pressure policies. The federal government will need to address voter concerns over Canada’s long-term economic health, our failed federal enforcement activity, and our weakened military.
At the same time, the political environment is also becoming more contentious, with rising populism and discontent in some regions. The election could see significant shifts in power, with both the Liberal and Conservative parties positioning themselves to address key issues such as national security, healthcare, and environmental sustainability. The outcome of this election will set the tone for how Canada navigates both domestic and international relations in the years to come.
U.S.-Canada Relations: A Symbiotic but Complex Partnership
Canada’s relationship with the United States remains the cornerstone of its foreign policy. As the world’s largest trading partner, the U.S. is integral to Canada’s economy. However, relations between the two countries are often fraught with tensions, from trade disputes to environmental policies. In 2025, this partnership will be tested further, particularly as both nations contend with the challenges of climate change, security concerns, and evolving trade agreements.
The U.S. presidential election in 2024 has already caused profound impacts on Canada’s policy decisions and political culture. While Canada and the U.S. share many common interests, the complexities of these issues—ranging from pipeline disputes to defense policy—will require sophisticated diplomacy to ensure the continued strength of this vital partnership.
Canada will also need to navigate the increasing pressure from the U.S. to align with its foreign policy stance, particularly in relation to China, Russia, and international trade agreements. While maintaining sovereignty is critical, Canada must ensure its policies do not continue to erode relations with its largest neighbor and closest ally.
A Year of Critical Decisions
Canada in 2025 faces a year of unprecedented decisions, with geopolitical tensions, financial integrity, and political stability all in play. The global stage is shifting, and Canada’s role within this changing landscape will depend on how effectively it addresses both internal challenges and external pressures. As the nation prepares for an important election and responds to global geopolitical shifts, it will need strong, visionary leadership to steer it through uncertain waters. Whether it is rethinking its relationship with China, confronting the realities of money laundering, or strengthening ties with the U.S., Canada’s future will depend on its ability to navigate this complex and interconnected world.
Ultimately, 2025 presents Canada with an opportunity to reassert its values, chart a clear course in the face of global uncertainty, and ensure that it remains a respected and influential player on the world stage.
Garry Clement consults with corporations on anti-money laundering, contributed to the Canadian academic text Dirty Money, and wrote Undercover, In the Shady World of Organized Crime and the RCMP
The Bureau is a reader-supported publication. To receive new posts and support my work, consider becoming a free or paid subscriber.
2025 Federal Election
The Anhui Convergence: Chinese United Front Network Surfaces in Australian and Canadian Elections

Revealing Beijing’s Transnational Influence Strategy
From Markham to Sydney: Tracing the CCP’s Overseas Influence Web
In the waning days of two federal election campaigns on opposite sides of the world, striking patterns of Chinese Communist Party election influence and political networking are surfacing—all tied to an increasingly scrutinized Chinese diaspora group with roots in the province of Anhui.
In Australia, Liberal candidate Scott Yung opened a business gala co-hosted by the Anhui Association of Sydney, a group officially designated by Beijing as an “overseas Chinese liaison station,” as reported by James King of 7NEWS. King identifies the Anhui group as part of a global network directed by Beijing’s United Front Work Department, an influence arm of the Chinese state that aims to shape foreign societies through elite capture and soft power.
King’s reporting is reigniting global concern over Chinese foreign interference, of the type previously exposed by The Bureau in Canada, which revealed that several Liberal Party of Canada officials, deeply involved in fundraising and election campaigning in the Greater Toronto Area, also serve as directors of an Anhui-based United Front “friendship” group with ties to a notorious underground casino operation.
That same group shares overlapping members and leadership with the Jiangsu Commerce Council of Canada (JCCC), a United Front-affiliated organization that controversially met with Liberal leadership candidate Mark Carney in January.
In the 7NEWS report, Yung is shown speaking—as a representative of Opposition Leader Peter Dutton—at a charity fundraiser co-hosted by the Anhui Association, a group previously celebrated by Beijing for supporting China’s territorial claims over Taiwan. According to King, the Anhui Association of Sydney was one of 14 overseas Chinese organizations designated in 2016 by the Anhui Foreign Affairs Office to serve as a liaison station advancing Beijing’s international strategy. Government documents show the group received AUD $200,000 annually, with instructions to “integrate overseas Chinese resources” into Anhui’s economic and social development.
Yung’s appearance on behalf of Liberal leader Dutton at an event ultimately backed by Beijing echoed mounting concerns surrounding Labor Prime Minister Anthony Albanese, his opponent in Australia’s May election.
Just weeks earlier, The Australian revealed that Albanese had dined with the vice-president of a United Front group at a Labor fundraiser—prompting sharp criticism from Liberal campaign spokesperson James Paterson, the Shadow Minister for Home Affairs. Paterson said Albanese had “all sorts of serious questions” to answer, warning that “Xi Jinping has described the United Front Work Department as the Party’s magic weapon,” according to 7NEWS.
The news organization emphasized that it “does not suggest that the Anhui Association of Sydney, its former chairman, or any of its associates have committed foreign interference or otherwise acted illegally,” noting that it is legal in Australia to act on behalf of a foreign government—so long as those actions are not covert, deceptive, or threatening.
But King’s investigation underscores a broader concern—echoed in reporting from Canada and New Zealand—that Chinese diaspora organizations, operating through the CCP’s United Front system, are being strategically leveraged by Beijing’s intelligence and foreign policy arms to fund major political parties across liberal democracies, influence parliamentary policy in line with CCP objectives, and shape leadership pipelines, including the placement of favored candidates and bureaucrats into sensitive government roles.
This strategy finds a near-identical expression in Canada, where intelligence officials in Toronto have long monitored a related organization: the Hefei Friendship Association, which maintains structural ties—via Anhui province United Front entities—to the Sydney group. Founded prior to 2012 by alleged underground casino operator Wei Wei, the Hefei group is based in Markham, Ontario, and plays a central role in an ongoing CSIS investigation into foreign interference.
Documents and sources reviewed by The Bureau confirm that the Hefei Friendship Association shares leadership with the Jiangsu Commerce Council of Canada (JCCC), a group openly tied to provincial-level United Front Work Department officials in Jiangsu, the province adjacent to Anhui. In earlier reporting on the Markham illegal casino network—widely referred to as the 5 Decourcy case—The Bureau cited an investigator with direct knowledge of what intelligence sources describe as a botched national security probe. The inquiry focused on Canadian politicians attending the casino alongside Chinese community leaders affiliated with Beijing’s overseas influence operations.
One legal source close to the file summarized the issue bluntly: “The national security and intelligence apparatus of this country is ineffective and broken. I’m in disbelief at the lack of ethics and enforcement around government officials.”
According to national security sources, the 5 Decourcy mansion-casino is viewed as just one visible node in a transnational system stretching from Toronto to Vancouver—a system that includes organized crime networks, unregistered lobbying, and foreign-aligned political financing. A CSIS source confirmed that the operation—which allegedly entertained politicians—fits Beijing’s model of leveraging transnational organized crime to advance political goals abroad. That model, they noted, closely mirrors warnings from Australia’s ASIO, which has linked similar figures in the real estate sector to major donations to all three of Australia’s major political parties, including those led by Dutton and Albanese.
Further investigation by The Bureau reveals deeper overlap between the Anhui United Front networks and the Jiangsu group that met with Mark Carney in January. Among the co-directors of the Anhui United Front group—pictured in meetings and named in documents alongside Wei Wei—is a prominent Markham-area Liberal riding official, involved in fundraising for Justin Trudeau. That same individual holds a leadership role with the JCCC, which met with Carney in a meeting that was initially denied, then downplayed.
Images reviewed by The Bureau show Wei Wei seated beside a Liberal Party politician and community organizer at a private association gathering, while another Liberal official with ties to the JCCC stands behind them. A second photo, taken inside Wei Wei’s residence, shows additional Liberal figures affiliated with Anhui- and Jiangsu-linked United Front community groups.
Documents obtained by King show that the Anhui Association of Sydney was tasked to “strive to closely integrate overseas Chinese affairs with the province’s economic and social development,” according to the director of the Anhui Foreign Affairs and Overseas Chinese Affairs Office. The Bureau has reviewed similar language in Canadian documents signed by JCCC leaders, including the Hefei Friendship Association director tied to Wei Wei—reinforcing that both the Canadian and Australian networks appear to operate under direct, formal tasking from provincial CCP entities.
As these revelations now resurface in the middle of Canada’s federal election campaign, they echo with findings in New Zealand. The 2018 political implosion involving MP Jami-Lee Ross offered a cautionary tale of how foreign-aligned networks can entangle party finances, diaspora outreach, and internal leadership struggles.
Ross, once a rising star in New Zealand’s National Party, secretly recorded party leader Simon Bridges discussing a controversial $100,000 donation, which Ross alleged was tied to Chinese business interests. The scandal shattered National’s leadership and exposed vulnerabilities in its campaign finance ecosystem. In an interview with Stuff, Ross described how his relationships with Chinese community leaders, while partly grounded in legitimate social engagement, also became channels for Beijing’s political aims.
“These [Chinese] associations, which bring together the expat Chinese community, they probably do have a good social function in many regards,” Ross said. “But there’s a wider agenda. And the wider agenda is influencing political parties. And by influencing political parties, you end up influencing the government of the day. What average New Zealander out there can get the leadership of a political party to go to their home for dinner? What average person out there could just click their fingers and command 10 MPs to come to their event? Most people can’t. Money buys their influence.”
2025 Federal Election
CHINESE ELECTION THREAT WARNING: Conservative Candidate Joe Tay Paused Public Campaign

 Sam Cooper
Sam Cooper
Now, with six days until Canada’s pivotal vote—in an election likely to be decided across key Toronto battleground ridings—it appears that Tay’s ability to reach voters in person has also been downgraded.
Joseph Tay, the Conservative candidate identified by federal authorities as the target of aggressive Chinese election interference operations, paused in-person campaigning yesterday following advice from federal police, The Bureau has learned.
Two sources with awareness of the matter said the move came after the SITE Task Force—Canada’s election-threat monitor—confirmed that Tay is the subject of a highly coordinated transnational repression operation tied to the People’s Republic of China. The campaign seeks not only to discredit Tay, but to suppress the ability of Chinese Canadian voters to access his campaign messages online, via cyber operations conducted by Beijing’s internet authorities.
Now, with six days until Canada’s pivotal vote—in an election likely to be decided across key Toronto battleground ridings—it appears that Tay’s ability to reach voters in person has also been downgraded.
Tay, a journalist and pro-democracy advocate born in Hong Kong, is running for the Conservative Party in the Don Valley North riding. Federal intelligence sources have confirmed that his political activities have made him a top target for Beijing-linked online attacks and digital suppression efforts in the lead-up to next week’s federal election.
Tay’s need to suspend door-knocking yesterday in Don Valley North echoes concerns raised in a neighbouring riding during the 2021 federal campaign—where The Bureau previously uncovered allegations of Chinese government intimidation and targeting of voters and a Conservative incumbent. According to senior Conservative sources, Chinese agents attempted to intimidate voters and monitor the door-to-door campaign of then-incumbent MP Bob Saroya in Markham–Unionville.
Paul Chiang, a former police officer who unseated Saroya in 2021, stepped down as a candidate earlier this month after the RCMP confirmed it was reviewing remarks he made to Chinese-language media in January. During that event, Chiang reportedly said the election of Tay—a Canadian citizen wanted under Hong Kong’s National Security Law—to Parliament would cause “great controversy” for Canada. He then suggested, in a remark reported by a Chinese-language newspaper, that Tay could be turned over to the Toronto Chinese Consulate to claim the $180,000 bounty on his head. Chiang apologized after the comments were reported, claiming his remarks had been made in jest.
In a briefing yesterday, SITE disclosed that Tay has been the victim of similarly threatening online messaging.
One Facebook post circulated widely in Chinese-language forums declared: “Wanted for national security reasons, Joe Tay looks to run for a seat in the Canadian Parliament; a successful bid would be a disaster. Is Canada about to become a fugitive’s paradise?”
Tay, a former Hong Kong broadcaster whose independent reporting from Canada has drawn retaliation from Beijing, rejected Chiang’s apology in March, calling the remarks “the tradecraft of the Chinese Communist Party.” He added: “They are not just aimed at me; they are intended to send a chilling signal to the entire community to force compliance with Beijing’s political goals.” His concerns were echoed by NGOs and human rights organizations, which condemned Chiang’s comments as an endorsement of transnational repression.
In light of the RCMP’s reported advice to Tay this week, the challenges faced by Conservative candidates attempting to meet Chinese Canadian voters in Greater Toronto appear to reflect a broader and troubling pattern.
According to multiple senior figures from Erin O’Toole’s 2021 Conservative campaign—who spoke on condition of anonymity—O’Toole’s team was briefed by Canadian intelligence officials that Chinese government actors were surveilling then-incumbent MP Bob Saroya during the campaign. One source recalled, “There were Chinese officials following Bob Saroya around,” adding that “CSIS literally said repeatedly that this was ‘coordinated and alarming.’”
When asked to comment, O’Toole—who stepped down as leader following the Conservative’s 2021 loss—acknowledged awareness of voter intimidation reports but declined to confirm whether CSIS had briefed his team directly on the matter.
“Our candidate Bob Saroya was a hardworking MP who won against the Liberal wave in 2015,” O’Toole wrote in a statement. “He won in 2019 as well, but thousands of votes from the Chinese Canadian community stayed home in 2021. We heard reports of intimidation of voters. We also know the Consul General from China took particular interest in the riding and made strange comments to Mr. Saroya ahead of the election. It was always in the top three of the eight or nine ridings that I believe were flipped due to foreign interference.”
SITE’s new findings on Tay’s campaign in Don Valley North reinforce those long-standing concerns. “This is not about a single post going viral,” SITE warned. “It is a series of deliberate and persistent activity across multiple platforms—a coordinated attempt to distort visibility, suppress legitimate discourse, and shape the information environment for Chinese-speaking voters in Canada.”
The Task Force said the most recent wave of coordinated online activity occurred in late March, when a Facebook post appeared denigrating Tay’s candidacy. “Posts like this one appeared en masse on March 24 and 25 and appear to be timed for the Conservative Party’s announcement that Tay would run in Don Valley North,” SITE stated in briefing materials.
The Bureau is a reader-supported publication.
To receive new posts and support my work, consider becoming a free or paid subscriber.
Invite your friends and earn rewards
-

 Alberta2 days ago
Alberta2 days agoGovernments in Alberta should spur homebuilding amid population explosion
-

 Alberta2 days ago
Alberta2 days agoLow oil prices could have big consequences for Alberta’s finances
-

 International2 days ago
International2 days agoHistory in the making? Trump, Zelensky hold meeting about Ukraine war in Vatican ahead of Francis’ funeral
-
 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoIt Took Trump To Get Canada Serious About Free Trade With Itself
-

 2025 Federal Election2 days ago
2025 Federal Election2 days agoCarney’s budget is worse than Trudeau’s
-

 C2C Journal1 day ago
C2C Journal1 day ago“Freedom of Expression Should Win Every Time”: In Conversation with Freedom Convoy Trial Lawyer Lawrence Greenspon
-

 Opinion1 day ago
Opinion1 day agoCanadians Must Turn Out in Historic Numbers—Following Taiwan’s Example to Defeat PRC Election Interference
-

 2025 Federal Election19 hours ago
2025 Federal Election19 hours agoColumnist warns Carney Liberals will consider a home equity tax on primary residences







