Business
Enbridge to pay Bad River band $5.1M in Line 5 profits, move pipeline by 2026: judge

This June 29, 2018 photo shows tanks at the Enbridge Energy terminal in Superior, Wisc. A U.S. judge in that state has ordered the Calgary-based energy giant to pay an Indigenous band US$5.1 million and to remove the Line 5 pipeline from the band’s property within three years. THE CANADIAN PRESS/AP-Jim Mone
By James McCarten in Washington
Calgary-based Enbridge Inc. must pay an Indigenous band in Wisconsin more than US$5 million in Line 5 profits and relocate the controversial cross-border pipeline within the next three years, a U.S. judge says.
A rupture on territory that belongs to the Bad River Band of the Lake Superior Chippewa would constitute a clear public nuisance under federal law, district court Judge William Conley said in a decision late Friday.
But while the order affirms that Enbridge has been trespassing on Bad River land since 2013, when certain permits for the 70-year-old pipeline were allowed to lapse, it stops short of causing “economic havoc” with an immediate shutdown.
“The use of trespass on a few parcels to drive the effective closure of all of Line 5 has always been about a tail wagging a much larger dog,” Conley writes in his opinion.
In other words, there are “much larger public policy issues” surrounding cross-border pipelines like Line 5 that the band’s arguments, while valid, lack the power to overcome, he said.
Those issues “involve not only the sovereign rights of the band, but the rights of multiple states and international relations between the United States and Canada.”
Enbridge has already agreed to reroute the line, an essential energy conduit for much of the U.S. Midwest as well as Ontario and Quebec. But Conley wants that project completed more quickly than currently planned.
“Considering all the evidence, the court cannot countenance an infinite delay or even justify what would amount to a five-year forced easement with little realistic prospect of a reroute proceeding even then,” he wrote.
“The court will give Enbridge an additional three years to complete a reroute. If Enbridge fails to do so, the three years will at least give the public and other affected market players time to adjust to a permanent closure of Line 5.”
Enbridge’s lawyers continue to dispute the finding that the company is trespassing on Indigenous territory and intend to appeal the decision, and may also request a stay pending its outcome, said spokesperson Juli Kellner.
“Enbridge’s position has long been that a 1992 contract between Enbridge and the band provides legal permission for the line to remain in its current location,” Kellner said.
“Timely government permit approvals” would be necessary to complete the reroute within three years, while relocating the pipe currently on Bad River territory would take about a year, she added.
Any shutdown before then “would jeopardize the delivery of reliable and affordable energy to U.S. and Canadian families and businesses, disrupt local and regional economies, and violate the Transit Pipeline Treaty.”
Talks between the two countries have been ongoing for months under the terms of that treaty, a 1977 agreement that effectively prohibits either side from unilaterally closing off the flow of hydrocarbons.
In prior court documents, Enbridge has accused the band of being focused on a single outcome: the permanent closure of the pipeline on their territory “while refusing much less extreme alternative measures.”
The band argues that several weeks of spring flooding along the Bad River has washed away so much of the riverbank and supporting terrain that a breach is “imminent” and a shutdown order more than justified.
Enbridge insists the dangers are being overstated — and even if they were real, the company’s court-ordered contingency plan, which spells out the steps it would take, would be a far more rational solution.
Conley’s order Friday included tweaks to that plan to establish a more “conservative” threshold for the conditions that would trigger it, such as lower water levels and flow rates on the river.
“The court is particularly concerned that Enbridge’s plan does not account for inevitable delays that could occur due to weather conditions, supply and equipment problems and human error.”
Enbridge has also been rebuffed repeatedly in its efforts to perform remedial work on the site, which would include using sandbags and trees to fortify the riverbanks —decisions the band has defended as its sovereign right.
Heavy flooding that began in early April washed away significant portions of the riverbank where Line 5 intersects the Bad River, a meandering, 120-kilometre course that feeds Lake Superior and a complex network of ecologically delicate wetlands.
The band has been in court with Enbridge since 2019 in an effort to compel the pipeline’s owner and operator to reroute Line 5 around its traditional territory — something the company has already agreed to do.
But the flooding has turned a theoretical risk into a very real one, the band argued, and time is now of the essence.
Line 5 meets the river just past a location the court has come to know as the “meander,” where the riverbed snakes back and forth multiple times, separated from itself only by several metres of forest and the pipeline itself.
But it was clear both from Friday’s order and an in-person hearing last month, when Conley openly questioned the band’s motives, that he faults the band for rejecting Enbridge’s proposed plans to mitigate the danger.
“The band has refused to approve any of Enbridge’s remediation and prevention proposals, much less proposed even one project of its own to prevent or at least slow further erosion at the meander,” he wrote.
The neighbouring state of Michigan, led by Attorney General Dana Nessel, has been waging its own war against Line 5, fearing a leak in the Straits of Mackinac, the ecologically delicate waterway where the pipeline crosses the Great Lakes.
The economic arguments against shutting down the pipeline, which carries 540,000 barrels of oil and natural gas liquids daily across Wisconsin and Michigan to refineries in Sarnia, Ont., are by now well-known.
Line 5’s defenders, which include the federal government, say a shutdown would cause major economic disruption across the Prairies and the U.S. Midwest, where it provides feedstock to refineries in Michigan, Ohio and Pennsylvania.
It also supplies key refining facilities in Ontario and Quebec, and is vital to the production of jet fuel for major airports on both sides of the Canada-U.S. border, including Detroit Metropolitan and Pearson International in Toronto.
This report by The Canadian Press was first published June 17, 2023.
Business
Hudson’s Bay Bid Raises Red Flags Over Foreign Influence

From the Frontier Centre for Public Policy
A billionaire’s retail ambition might also serve Beijing’s global influence strategy. Canada must look beyond the storefront
When B.C. billionaire Weihong Liu publicly declared interest in acquiring Hudson’s Bay stores, it wasn’t just a retail story—it was a signal flare in an era where foreign investment increasingly doubles as geopolitical strategy.
The Hudson’s Bay Company, founded in 1670, remains an enduring symbol of Canadian heritage. While its commercial relevance has waned in recent years, its brand is deeply etched into the national identity. That’s precisely why any potential acquisition, particularly by an investor with strong ties to the People’s Republic of China (PRC), deserves thoughtful, measured scrutiny.
Liu, a prominent figure in Vancouver’s Chinese-Canadian business community, announced her interest in acquiring several Hudson’s Bay stores on Chinese social media platform Xiaohongshu (RedNote), expressing a desire to “make the Bay great again.” Though revitalizing a Canadian retail icon may seem commendable, the timing and context of this bid suggest a broader strategic positioning—one that aligns with the People’s Republic of China’s increasingly nuanced approach to economic diplomacy, especially in countries like Canada that sit at the crossroads of American and Chinese spheres of influence.
This fits a familiar pattern. In recent years, we’ve seen examples of Chinese corporate involvement in Canadian cultural and commercial institutions, such as Huawei’s past sponsorship of Hockey Night in Canada. Even as national security concerns were raised by allies and intelligence agencies, Huawei’s logo remained a visible presence during one of the country’s most cherished broadcasts. These engagements, though often framed as commercially justified, serve another purpose: to normalize Chinese brand and state-linked presence within the fabric of Canadian identity and daily life.
What we may be witnessing is part of a broader PRC strategy to deepen economic and cultural ties with Canada at a time when U.S.-China relations remain strained. As American tariffs on Canadian goods—particularly in aluminum, lumber and dairy—have tested cross-border loyalties, Beijing has positioned itself as an alternative economic partner. Investments into cultural and heritage-linked assets like Hudson’s Bay could be seen as a symbolic extension of this effort to draw Canada further into its orbit of influence, subtly decoupling the country from the gravitational pull of its traditional allies.
From my perspective, as a professional with experience in threat finance, economic subversion and political leveraging, this does not necessarily imply nefarious intent in each case. However, it does demand a conscious awareness of how soft power is exercised through commercial influence, particularly by state-aligned actors. As I continue my research in international business law, I see how investment vehicles, trade deals and brand acquisitions can function as instruments of foreign policy—tools for shaping narratives, building alliances and shifting influence over time.
Canada must neither overreact nor overlook these developments. Open markets and cultural exchange are vital to our prosperity and pluralism. But so too is the responsibility to preserve our sovereignty—not only in the physical sense, but in the cultural and institutional dimensions that shape our national identity.
Strategic investment review processes, cultural asset protections and greater transparency around foreign corporate ownership can help strike this balance. We should be cautious not to allow historically Canadian institutions to become conduits, however unintentionally, for geopolitical leverage.
In a world where power is increasingly exercised through influence rather than force, safeguarding our heritage means understanding who is buying—and why.
Scott McGregor is the managing partner and CEO of Close Hold Intelligence Consulting.
Bjorn Lomborg
Net zero’s cost-benefit ratio is crazy high

From the Fraser Institute
The best academic estimates show that over the century, policies to achieve net zero would cost every person on Earth the equivalent of more than CAD $4,000 every year. Of course, most people in poor countries cannot afford anywhere near this. If the cost falls solely on the rich world, the price-tag adds up to almost $30,000 (CAD) per person, per year, over the century.
Canada has made a legal commitment to achieve “net zero” carbon emissions by 2050. Back in 2015, then-Prime Minister Trudeau promised that climate action will “create jobs and economic growth” and the federal government insists it will create a “strong economy.” The truth is that the net zero policy generates vast costs and very little benefit—and Canada would be better off changing direction.
Achieving net zero carbon emissions is far more daunting than politicians have ever admitted. Canada is nowhere near on track. Annual Canadian CO₂ emissions have increased 20 per cent since 1990. In the time that Trudeau was prime minister, fossil fuel energy supply actually increased over 11 per cent. Similarly, the share of fossil fuels in Canada’s total energy supply (not just electricity) increased from 75 per cent in 2015 to 77 per cent in 2023.
Over the same period, the switch from coal to gas, and a tiny 0.4 percentage point increase in the energy from solar and wind, has reduced annual CO₂ emissions by less than three per cent. On that trend, getting to zero won’t take 25 years as the Liberal government promised, but more than 160 years. One study shows that the government’s current plan which won’t even reach net-zero will cost Canada a quarter of a million jobs, seven per cent lower GDP and wages on average $8,000 lower.
Globally, achieving net-zero will be even harder. Remember, Canada makes up about 1.5 per cent of global CO₂ emissions, and while Canada is already rich with plenty of energy, the world’s poor want much more energy.
In order to achieve global net-zero by 2050, by 2030 we would already need to achieve the equivalent of removing the combined emissions of China and the United States — every year. This is in the realm of science fiction.
The painful Covid lockdowns of 2020 only reduced global emissions by about six per cent. To achieve net zero, the UN points out that we would need to have doubled those reductions in 2021, tripled them in 2022, quadrupled them in 2023, and so on. This year they would need to be sextupled, and by 2030 increased 11-fold. So far, the world hasn’t even managed to start reducing global carbon emissions, which last year hit a new record.
Data from both the International Energy Agency and the US Energy Information Administration give added cause for skepticism. Both organizations foresee the world getting more energy from renewables: an increase from today’s 16 per cent to between one-quarter to one-third of all primary energy by 2050. But that is far from a transition. On an optimistically linear trend, this means we’re a century or two away from achieving 100 percent renewables.
Politicians like to blithely suggest the shift away from fossil fuels isn’t unprecedented, because in the past we transitioned from wood to coal, from coal to oil, and from oil to gas. The truth is, humanity hasn’t made a real energy transition even once. Coal didn’t replace wood but mostly added to global energy, just like oil and gas have added further additional energy. As in the past, solar and wind are now mostly adding to our global energy output, rather than replacing fossil fuels.
Indeed, it’s worth remembering that even after two centuries, humanity’s transition away from wood is not over. More than two billion mostly poor people still depend on wood for cooking and heating, and it still provides about 5 per cent of global energy.
Like Canada, the world remains fossil fuel-based, as it delivers more than four-fifths of energy. Over the last half century, our dependence has declined only slightly from 87 per cent to 82 per cent, but in absolute terms we have increased our fossil fuel use by more than 150 per cent. On the trajectory since 1971, we will reach zero fossil fuel use some nine centuries from now, and even the fastest period of recent decline from 2014 would see us taking over three centuries.
Global warming will create more problems than benefits, so achieving net-zero would see real benefits. Over the century, the average person would experience benefits worth $700 (CAD) each year.
But net zero policies will be much more expensive. The best academic estimates show that over the century, policies to achieve net zero would cost every person on Earth the equivalent of more than CAD $4,000 every year. Of course, most people in poor countries cannot afford anywhere near this. If the cost falls solely on the rich world, the price-tag adds up to almost $30,000 (CAD) per person, per year, over the century.
Every year over the 21st century, costs would vastly outweigh benefits, and global costs would exceed benefits by over CAD 32 trillion each year.
We would see much higher transport costs, higher electricity costs, higher heating and cooling costs and — as businesses would also have to pay for all this — drastic increases in the price of food and all other necessities. Just one example: net-zero targets would likely increase gas costs some two-to-four times even by 2030, costing consumers up to $US52.6 trillion. All that makes it a policy that just doesn’t make sense—for Canada and for the world.
-

 International2 days ago
International2 days agoPope Francis has died aged 88
-
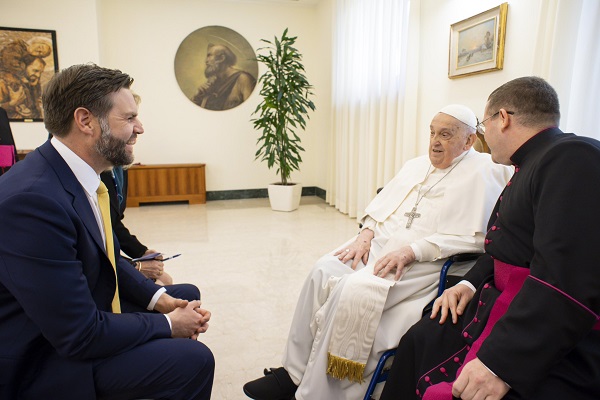

 International2 days ago
International2 days agoJD Vance was one of the last people to meet Pope Francis
-

 2025 Federal Election1 day ago
2025 Federal Election1 day agoOttawa Confirms China interfering with 2025 federal election: Beijing Seeks to Block Joe Tay’s Election
-

 2025 Federal Election1 day ago
2025 Federal Election1 day agoHow Canada’s Mainstream Media Lost the Public Trust
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoCanada Urgently Needs A Watchdog For Government Waste
-
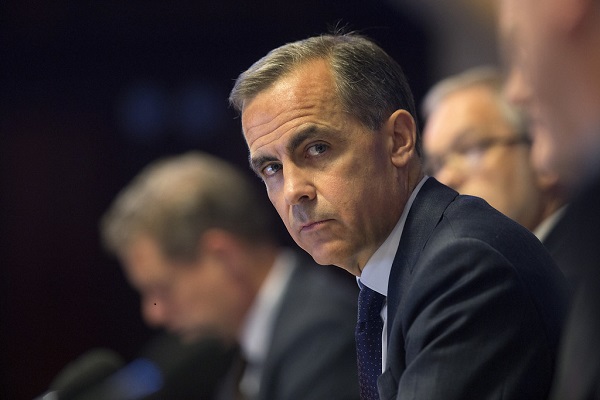

 2025 Federal Election16 hours ago
2025 Federal Election16 hours agoBREAKING: THE FEDERAL BRIEF THAT SHOULD SINK CARNEY
-
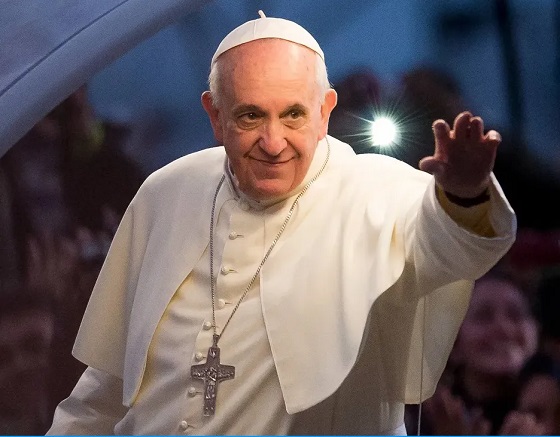

 International2 days ago
International2 days agoPope Francis Dies on Day after Easter
-
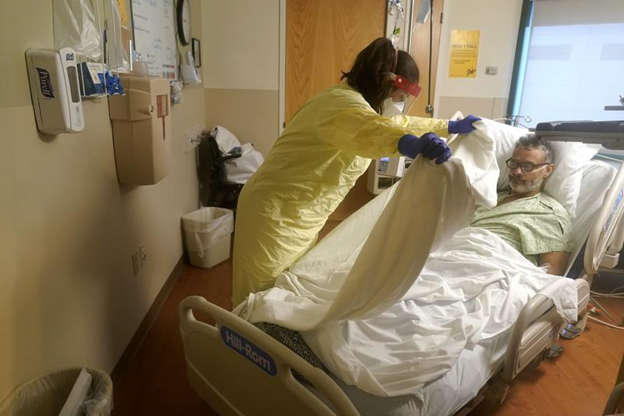

 COVID-191 day ago
COVID-191 day agoNearly Half of “COVID-19 Deaths” Were Not Due to COVID-19 – Scientific Reports Journal