Uncategorized
Deported man is suspect in deadly California beatings
LOS ANGELES — A man who was deported from the United States six times was expected in court Wednesday to face charges after police say he killed three people and injured four in attacks targeting sleeping homeless men in California.
Investigators believe Ramon Escobar, 47, began attacking the men at random on Sept. 8, shortly after he arrived in California from Houston, where he’s considered a person of interest in the disappearance of his uncle and aunt.
Escobar, who was believed homeless himself, likely targeted victims to rob them, Los Angeles police Capt. William Hayes told reporters Tuesday.
Detectives have seized a wooden baseball bat and bolt cutters that they believe were used to bludgeon men as they lay sleeping on the beach or on the street in Los Angeles and suburban Santa Monica, police said. All but one of the men was homeless.
Escobar was arrested Monday and was expected to be charged with murder and attempted murder as early as Wednesday, followed by his arraignment.
It wasn’t immediately known whether Escobar had an attorney who could speak for him.
Escobar was being held without bail but U.S. Immigrations and Customs Enforcement officials have filed a detainer seeking to take him into custody if he is released, the agency said.
Escobar was first ordered removed from the country in 1988 and was deported to his native El Salvador six times between 1997 and 2011, ICE said in a statement Tuesday night.
He was released from ICE custody last year after successfully appealing his latest immigration case, ICE said. The agency didn’t indicate his current legal status.
However, Escobar has six felony convictions for burglary and illegal reentry, ICE said.
Escobar spent five years in prison for robbery starting in the mid-1990s, Hayes said. Records in Texas show Escobar has had arrests for vehicle burglary, trespassing, failure to stop, public intoxication and two assaults, most recently in November 2017. That case was described as a
Texas authorities also want to talk to Escobar about the disappearances late last month of 60-year-old Dina Escobar and her brother, 65-year-old Rogelio Escobar, Houston police said in a statement.
Dina Escobar’s burned van was found in Galveston, Texas, a few days after she went looking for her brother. She was last seen Aug. 28, two days after her brother vanished, the statement said.
Dina Escobar’s daughter, Ligia Salamanca, told KTRK-TV in Houston earlier Tuesday that her cousin, Ramon Escobar, had never come across as violent and wasn’t a source of trouble for the family.
“She loved him as she would a son,” Salamanca said of her mother’s devotion to Ramon Escobar.
Salamanca said he had been looking for work and needed a place to stay, so he was taken in by his uncle, who went missing days later.
Investigators believe Escobar was the man who used a baseball bat to bash the heads of three homeless men sleeping on downtown Los Angeles streets before dawn on Sept. 16, police said in a statement. Two died.
Escobar is believed to be the man captured on surveillance video ransacking the pockets and belongings of some downtown Los Angeles victims.
Two homeless men sleeping on the beach were bludgeoned in the head early on Sept. 8 and Sept. 10, leaving one in critical condition, officials said.
Another man who apparently was sleeping on the beach was found dead under the Santa Monica Pier on Sept. 20. Steven Ray Cruze Jr., 39, of San Gabriel, had been beaten to death.
Authorities at first described him as homeless, but family and friends said the father of two, who loved to fish at the pier, worked boats in
___
Follow Weber at https://twitter.com/WeberCM .
___
Associated Press journalists Robert Jablon and John Antczak in Los Angeles, David Warren in Dallas and researcher Jennifer Farrar in New York contributed to this report.
Christopher Weber, The Associated Press
Uncategorized
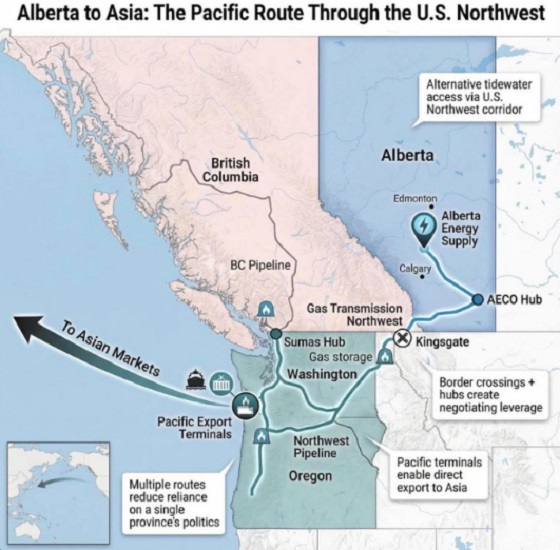
Mortgaging Canada’s energy future — the hidden costs of the Carney-Smith pipeline deal


Much of the commentary on the Carney-Smith pipeline Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) has focused on the question of whether or not the proposed pipeline will ever get built.
That’s an important topic, and one that deserves to be examined — whether, as John Robson, of the indispensable Climate Discussion Nexus, predicted, “opposition from the government of British Columbia and aboriginal groups, and the skittishness of the oil industry about investing in a major project in Canada, will kill [the pipeline] dead.”
But I’m going to ask a different question: Would it even be worth building this pipeline on the terms Ottawa is forcing on Alberta? If you squint, the MOU might look like a victory on paper. Ottawa suspends the oil and gas emissions cap, proposes an exemption from the West Coast tanker ban, and lays the groundwork for the construction of one (though only one) million barrels per day pipeline to tidewater.
But in return, Alberta must agree to jack its industrial carbon tax up from $95 to $130 per tonne at a minimum, while committing to tens of billions in carbon capture, utilization, and storage (CCUS) spending, including the $16.5 billion Pathways Alliance megaproject.
Here’s the part none of the project’s boosters seem to want to mention: those concessions will make the production of Canadian hydrocarbon energy significantly more expensive.
As economist Jack Mintz has explained, the industrial carbon tax hike alone adds more than $5 USD per barrel of Canadian crude to marginal production costs — the costs that matter when companies decide whether to invest in new production. Layer on the CCUS requirements and you get another $1.20–$3 per barrel for mining projects and $3.60–$4.80 for steam-assisted operations.
While roughly 62% of the capital cost of carbon capture is to be covered by taxpayers — another problem with the agreement, I might add — the remainder is covered by the industry, and thus, eventually, consumers.
Total damage: somewhere between $6.40 and $10 US per barrel. Perhaps more.
“Ultimately,” the Fraser Institute explains, “this will widen the competitiveness gap between Alberta and many other jurisdictions, such as the United States,” that don’t hamstring their energy producers in this way. Producers in Texas and Oklahoma, not to mention Saudi Arabia, Venezuela, or Russia, aren’t paying a dime in equivalent carbon taxes or mandatory CCUS bills. They’re not so masochistic.
American refiners won’t pay a “low-carbon premium” for Canadian crude. They’ll just buy cheaper oil or ramp up their own production.
In short, a shiny new pipe is worthless if the extra cost makes barrels of our oil so expensive that no one will want them.
And that doesn’t even touch on the problem for the domestic market, where the higher production cost will be passed onto Canadian consumers in the form of higher gas and diesel prices, home heating costs, and an elevated cost of everyday goods, like groceries.
Either way, Canadians lose.
So, concludes Mintz, “The big problem for a new oil pipeline isn’t getting BC or First Nation acceptance. Rather, it’s smothering the industry’s competitiveness by layering on carbon pricing and decarbonization costs that most competing countries don’t charge.” Meanwhile, lurking underneath this whole discussion is the MOU’s ultimate Achilles’ heel: net-zero.
The MOU proudly declares that “Canada and Alberta remain committed to achieving Net-Zero greenhouse gas emissions by 2050.” As Vaclav Smil documented in a recent study of Net-Zero, global fossil-fuel use has risen 55% since the 1997 Kyoto agreement, despite trillions spent on subsidies and regulations. Fossil fuels still supply 82% of the world’s energy.
With these numbers in mind, the idea that Canada can unilaterally decarbonize its largest export industry in 25 years is delusional.
This deal doesn’t secure Canada’s energy future. It mortgages it. We are trading market access for self-inflicted costs that will shrink production, scare off capital, and cut into the profitability of any potential pipeline. Affordable energy, good jobs, and national prosperity shouldn’t require surrendering to net-zero fantasy.If Ottawa were serious about making Canada an energy superpower, it would scrap the anti-resource laws outright, kill the carbon taxes, and let our world-class oil and gas compete on merit. Instead, we’ve been handed a backroom MOU which, for the cost of one pipeline — if that! — guarantees higher costs today and smothers the industry that is the backbone of the Canadian economy.
This MOU isn’t salvation. It’s a prescription for Canadian decline.
Uncategorized
Cost of bureaucracy balloons 80 per cent in 10 years: Public Accounts

The cost of the bureaucracy increased by $6 billion last year, according to newly released numbers in Public Accounts disclosures. The Canadian Taxpayers Federation is calling on Prime Minister Mark Carney to immediately shrink the bureaucracy.
“The Public Accounts show the cost of the federal bureaucracy is out of control,” said Franco Terrazzano, CTF Federal Director. “Tinkering around the edges won’t cut it, Carney needs to take urgent action to shrink the bloated federal bureaucracy.”
The federal bureaucracy cost taxpayers $71.4 billion in 2024-25, according to the Public Accounts. The cost of the federal bureaucracy increased by $6 billion, or more than nine per cent, over the last year.
The federal bureaucracy cost taxpayers $39.6 billion in 2015-16, according to the Public Accounts. That means the cost of the federal bureaucracy increased 80 per cent over the last 10 years. The government added 99,000 extra bureaucrats between 2015-16 and 2024-25.
Half of Canadians say federal services have gotten worse since 2016, despite the massive increase in the federal bureaucracy, according to a Leger poll.
Not only has the size of the bureaucracy increased, the cost of consultants, contractors and outsourcing has increased as well. The government spent $23.1 billion on “professional and special services” last year, according to the Public Accounts. That’s an 11 per cent increase over the previous year. The government’s spending on professional and special services more than doubled since 2015-16.
“Taxpayers should not be paying way more for in-house government bureaucrats and way more for outside help,” Terrazzano said. “Mere promises to find minor savings in the federal bureaucracy won’t fix Canada’s finances.
“Taxpayers need Carney to take urgent action and significantly cut the number of bureaucrats now.”
Table: Cost of bureaucracy and professional and special services, Public Accounts
| Year | Bureaucracy | Professional and special services |
|
$71,369,677,000 |
$23,145,218,000 |
|
|
$65,326,643,000 |
$20,771,477,000 |
|
|
$56,467,851,000 |
$18,591,373,000 |
|
|
$60,676,243,000 |
$17,511,078,000 |
|
|
$52,984,272,000 |
$14,720,455,000 |
|
|
$46,349,166,000 |
$13,334,341,000 |
|
|
$46,131,628,000 |
$12,940,395,000 |
|
|
$45,262,821,000 |
$12,950,619,000 |
|
|
$38,909,594,000 |
$11,910,257,000 |
|
|
$39,616,656,000 |
$11,082,974,000 |
-

 Haultain Research2 days ago
Haultain Research2 days agoSweden Fixed What Canada Won’t Even Name
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoWhat Do Loyalty Rewards Programs Cost Us?
-

 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoLand use will be British Columbia’s biggest issue in 2026
-

 International15 hours ago
International15 hours agoChina Stages Massive Live-Fire Encirclement Drill Around Taiwan as Washington and Japan Fortify
-

 Digital ID14 hours ago
Digital ID14 hours agoThe Global Push for Government Mandated Digital IDs And Why You Should Worry
-

 Business12 hours ago
Business12 hours agoFeds pull the plug on small business grants to Minnesota after massive fraud reports
-

 Energy1 day ago
Energy1 day agoWhy Japan wants Western Canadian LNG
-

 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoMainstream media missing in action as YouTuber blows lid off massive taxpayer fraud