Health
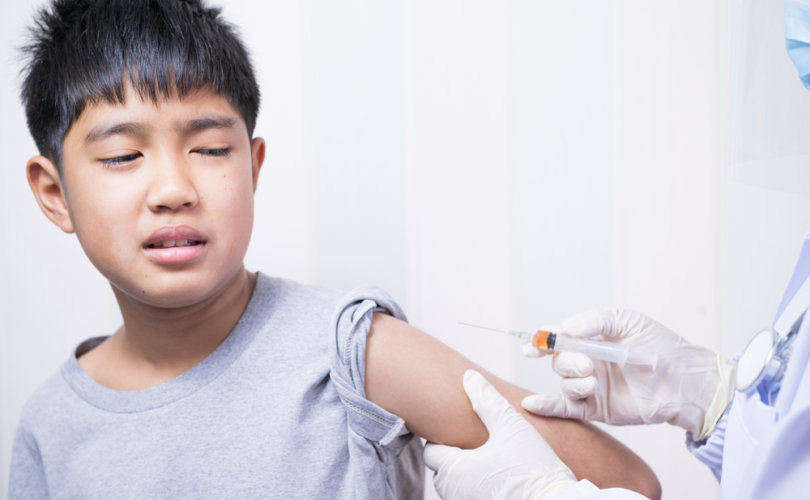
Dad says 5-year-old develops autism after being forced to get 18 vaccines in 1 day
From LifeSiteNews
By Michael Nevradakis Ph. D., The Defender
As part of a custody battle, a Tennessee judge ordered a family to vaccinate all three of their children, all of whom had never been vaccinated. Five-year-old Isaac immediately became ill and was eventually diagnosed with severe regressive autism.
In 2016, David Ihben moved his wife and three children from Chicago to Jamestown, in rural Tennessee, with high hopes for a new and calmer life.
But the dream turned into a nightmare for David and his children in December 2019, when divorce proceedings and a subsequent custody battle resulted in the forced vaccination of the children – and changed the family’s fortunes forever.
Ihben said his ex-wife decided “this wasn’t the life she wanted.” So they were attempting to develop a parenting plan in family court – when Tennessee judge Todd Burnett “pulled up the vaccine issue” after discovering the couple’s children were unvaccinated – and forced the parents to vaccinate their children.
Ihben’s two oldest children – daughter Hannah and son Joseph – were spared significant adverse events following their vaccination.
But his youngest son, Isaac, wasn’t so fortunate. After receiving 18 vaccines in one day, Isaac developed severe regressive autism. Today, he requires around-the-clock care.
The children’s mother soon abandoned the children, leaving Ihben to raise them as a single parent – even though he is still obliged to pay child support.
Ihben shared his story with Children’s Health Defense’s (CHD) Vax-Unvax bus. In a subsequent interview with The Defender, he detailed the challenges he faces in caring for Isaac and the harassment he endured from officials in his community. Ihben shared documentation with The Defender verifying his story.
‘How can a judge force medical care without a doctor’s input?’
Ihben told The Defender his entire family was unvaccinated. “I’ve never had any. My dad was drafted by the Army in 1961, and he didn’t get any either. We’ve never vaccinated,” he said. “Our children had to sign religious exemptions for school.”
During divorce proceedings though, his wife’s attorney used the vaccination issue to drive a wedge between the parents.
“When we went to court, I guess her attorney knew that [Burnett] was a pro-vaccine judge and that’s something that they could get me on,” Ihben said.
According to Ihben, Burnett told the couple that it was his “personal opinion that not vaccinating your children is child abuse.” He then told the couple that whichever parent would be willing to vaccinate the children that same day would leave the courthouse with custody.
“I said, ‘Your Honor, we have rights. It’s between the mom and their father,’” Ihben recalled. “Her attorney whispered to her, and she goes, ‘I’ll take them down and vaccinate them today.’”
“I was so surprised, because me and my ex-wife didn’t agree on much, but we did agree on that,” Ihben said, referring to their views on vaccination.
After the hearing, Ihben and his wife were granted joint custody of the children, with their mother as their primary guardian. Later that day, the children received their childhood vaccines – and Isaac immediately became sick.
“My daughter had previous allergies … so the doctor refused to give her all in one day. They split those … She didn’t have any side effects from what I can see,” Ihben said. “[Joseph] was in the ICU for a couple of days but seems to be okay. But [Isaac] spent 12 days in the ICU, eight days with a 106-degree fever.”
Isaac, who was 5 years old at the time, was “just a normal happy kid,” Ihben said.
Today, Isaac has severe regressive autism. Ihben told The Defender:
“He doesn’t talk. He wears a diaper. He eats out of a baby bottle 20-30 times a day, he has speech therapy and will require 24-hour care and supervision for the rest of his life.
“I haven’t had a full night’s sleep in four years. He has to be changed every two hours, or he will have an accident. If you have a child with regressive autism or know someone, you will understand what our days are like.”
Ihben didn’t learn about Isaac’s injuries right away, because the court initially slapped him with a six-month restraining order. When the six months were up, he finally made plans to pick up his children for “two-hour supervised visitation” at a local McDonald’s.
“My youngest comes walking out and I’m like, ‘What’s going on?’” He said his oldest children then told him about what happened to Isaac. “My children told me everything that’s going on. Basically, nobody’s given me information. I had to go off what 10- and 11-year-olds were telling me,” Ihben said.
Ihben tried to find out what happened to Isaac – but encountered more obstacles at Cookeville Regional Medical Center, his local hospital. “The judge had sealed the hospital records. I still cannot get them,” he said.
It wasn’t until he enrolled his daughter in high school that, while obtaining her records from the local health department, he had a chance to view Isaac’s records. That’s when he saw that Isaac had received 18 vaccines in one day.
“How can a judge force medical care without a doctor’s input?” Ihben asked. “I don’t think judges should be dictating medical treatment from the bench.”
According to Ihben, doctors at Vanderbilt University in Nashville said Isaac’s injuries “are a direct result from forced vaccination,” with one doctor telling Ihben that “she’s seen only one other kid that acts like Isaac does.”
Required to continue paying child support, despite mother’s disappearance
Soon after seeing his children for the first time after the custody battle, another surprise was in store for Ihben and his family: Ihben’s ex-wife called to say she and the children had been evicted.
After he kept the children for a week, their mother “got a free house, everything furnished and paid,” and the children were returned to her.
“Then she got evicted from there” in May 2020, Ihben said. He again picked up the children – but that was the last they saw of their mother. According to Ihben, after her second eviction, she left town without a trace.
“We haven’t heard from her or seen her,” Ihben said. “It’ll be five years in May.”
Ihben still pays child support to the state, even though he alone takes care of the children. He said the child support money, which remains uncollected, goes to a state fund – and, if it remains unclaimed, will be confiscated by the state when the children reach adulthood.
Ihben said that though he has gone to court to request full custody of his children or a reduction of his child support payments, he has faced a catch-22 situation.
“The judge said, I can’t do anything unless you get her here in front of me,” Ihben said. “I was like, ‘I’ve served her. Nobody knows where she is.’”
Ihben said he believes the children’s mother didn’t realize Isaac was going to be hurt so badly, and “she just can’t face it.” He added, “I just don’t understand, if she’s been gone almost five years, why she still has full custody, why I still have to pay child support.”
Tennessee laws, local officials pose challenges for raising Isaac
Ihben described the day-to-day realities of caring for Isaac, who will turn 11 next month and just started the fifth grade in a special education program. He said:
“Our lives have changed forever. I can’t have a regular job. I pick up stuff here and there … I have an alarm that goes off every two hours to change Isaac. He eats in the middle of the night … We live out in the country. There’s no bus, so I take him to school back and forth.
“He doesn’t talk, so you don’t know if he’s sick, if he’s upset, if he’s hungry, if he’s cold, if he has a stomach ache … I’ve got a mental list, and I just check it off and hopefully I hit the one that calms him and provides what he needs.”
State rules also pose obstacles. “You’re not allowed to have home healthcare for a disabled child unless you have no other children in the home under 18,” Ihben said.
Ihben noted that Tennessee ranks among the states with the lowest level of funding for autistic children, adding that autistic children are frequently mistreated.
“Our local school district has restraint chairs for autistic children. They are allowed to put Isaac in a chair, to pepper spray him, to tase him. Police departments have no training for dealing with autistic children,” Ihben said.
Ihben said state, county and town officials have attempted to intimidate him and his family.
According to Ihben, the Tennessee Bureau of Investigation (TBI) showed up at his home on Dec. 5, 2023. “Somebody starts beating on the door … there’s a truck at the end of the road, a truck at the end of the other road and two trucks in the driveway. They had assault weapons.”
Ihben said the officers claimed that a social worker wanted to speak with him, but that he refused to open his door for them. He submitted a Freedom of Information Act request to the state to find out why his home was raided, but was told there are “no records of anything.”
The TBI raid took a toll on him. “I had a heart attack that night,” he said. “I couldn’t breathe.” He said the incident still affects him today. “I’m sure I have PTSD from it. I’m still under treatment,” Ihben said.
In June 2023, Ihben said he went to his county commission meeting to tell them about what happened to his family. The county commissioner, Jimmy Johnson, left him a voicemail warning him not to hold any rally or protest.
“The commissioner called the sheriff,” Ihben said, but ultimately “they backed off.”
In another incident, Ihben said he was banned from his local Walmart store after a store manager called the police because Isaac “was causing a disturbance.” This obliged Ihben to shop at another Walmart, an hour away from his home.
Ihben said it’s also difficult to find a lawyer to represent him and his family. “No attorney is willing to take on the judge.”
Local officials ‘tried to scare us’ into not doing Vax-Unvax bus interview
Ihben credited CHD and its Tennessee Chapter for helping him and his family. “We wouldn’t be here without CHD helping us out,” Ihben said. “The Tennessee Chapter has helped us out a lot.”
Ihben said he recently saw “Vaxxed 3” with members of the state’s CHD chapter. “What we have to live through every day is horrible, but it could be worse,” Ihben said, citing stories in the film of children who died post-vaccination.
According to Ihben, his efforts to promote CHD initiatives in his community, such as the visit of the Vax-Unvax bus earlier this year, have also been met with intimidation.
“We put a little flyer together [for the Vax-Unvax bus] and we started passing it out,” Ihben said. But on Feb. 1, the day of his bus interview, Ihben said his wife’s attorney, her husband – who is the attorney for the local school board – and Burnett, who mobilized the TBI, “tried to scare us into not doing the bus interview.”
Getting the word out, spreading the message is ‘the only weapon we have’
Isaac has recently shown some improvement, according to Ihben. “He’s doing better slowly … He’s in a lot of therapy. He’s starting to write some numbers and letters on his own. Teachers think he’s reading, but he’s still never said a word.”
Ihben said this has been a learning experience for his oldest children, who will “have to take care of Isaac every day” after his death. “That’s a lifetime commitment.”
Another silver lining, according to Ihben, is that Isaac’s story has become a learning experience for his family and many members of his local community.
“This hasn’t just got me learning. My kids are learning. Hannah and Joseph are learning about their government and their food and their environment. They’re teaching their friends about this.”
For Ihben, getting the word out and spreading the message is “the only weapon we have.” He said, “It’s powerful that my kids’ friends come up and say ‘we’re sorry for what happened to you, we’ve seen the [Vax-Unvax] interview.’”
Ihben said he hopes the message will help other children avoid Isaac’s fate. “I hope Isaac will be the last,” he said.
This article was originally published by The Defender – Children’s Health Defense’s News & Views Website under Creative Commons license CC BY-NC-ND 4.0. Please consider subscribing to The Defender or donating to Children’s Health Defense.
2025 Federal Election
Study links B.C.’s drug policies to more overdoses, but researchers urge caution

By Alexandra Keeler
A study links B.C.’s safer supply and decriminalization to more opioid hospitalizations, but experts note its limitations
A new study says B.C.’s safer supply and decriminalization policies may have failed to reduce overdoses. Furthermore, the very policies designed to help drug users may have actually increased hospitalizations.
“Neither the safer opioid supply policy nor the decriminalization of drug possession appeared to mitigate the opioid crisis, and both were associated with an increase in opioid overdose hospitalizations,” the study says.
The study has sparked debate, with some pointing to it as proof that B.C.’s drug policies failed. Others have questioned the study’s methodology and conclusions.
“The question we want to know the answer to [but cannot] is how many opioid hospitalizations would have occurred had the policy not have been implemented,” said Michael Wallace, a biostatistician and associate professor at the University of Waterloo.
“We can never come up with truly definitive conclusions in cases such as this, no matter what data we have, short of being able to magically duplicate B.C.”
Jumping to conclusions
B.C.’s controversial safer supply policies provide drug users with prescription opioids as an alternative to toxic street drugs. Its decriminalization policy permitted drug users to possess otherwise illegal substances for personal use.
The peer-reviewed study was led by health economist Hai Nguyen and conducted by researchers from Memorial University in Newfoundland, the University of Manitoba and Weill Cornell Medicine, a medical school in New York City. It was published in the medical journal JAMA Health Forum on March 21.
The researchers used a statistical method to create a “synthetic” comparison group, since there is no ideal control group. The researchers then compared B.C. to other provinces to assess the impact of certain drug policies.
Examining data from 2016 to 2023, the study links B.C.’s safer supply policies to a 33 per cent rise in opioid hospitalizations.
The study says the province’s decriminalization policies further drove up hospitalizations by 58 per cent.
“Neither the safer supply policy nor the subsequent decriminalization of drug possession appeared to alleviate the opioid crisis,” the study concludes. “Instead, both were associated with an increase in opioid overdose hospitalizations.”
The B.C. government rolled back decriminalization in April 2024 in response to widespread concerns over public drug use. This February, the province also officially acknowledged that diversion of safer supply drugs does occur.
The study did not conclusively determine whether the increase in hospital visits was due to diverted safer supply opioids, the toxic illicit supply, or other factors.
“There was insufficient evidence to conclusively attribute an increase in opioid overdose deaths to these policy changes,” the study says.
Nguyen’s team had published an earlier, 2024 study in JAMA Internal Medicine that also linked safer supply to increased hospitalizations. However, it failed to control for key confounders such as employment rates and naloxone access. Their 2025 study better accounts for these variables using the synthetic comparison group method.
The study’s authors did not respond to Canadian Affairs’ requests for comment.
Subscribe for free to get BTN’s latest news and analysis – or donate to our investigative journalism fund.
Correlation vs. causation
Chris Perlman, a health data and addiction expert at the University of Waterloo, says more studies are needed.
He believes the findings are weak, as they show correlation but not causation.
“The study provides a small signal that the rates of hospitalization have changed, but I wouldn’t conclude that it can be solely attributed to the safer supply and decrim[inalization] policy decisions,” said Perlman.
He also noted the rise in hospitalizations doesn’t necessarily mean more overdoses. Rather, more people may be reaching hospitals in time for treatment.
“Given that the [overdose] rate may have gone down, I wonder if we’re simply seeing an effect where more persons survive an overdose and actually receive treatment in hospital where they would have died in the pre-policy time period,” he said.
The Nguyen study acknowledges this possibility.
“The observed increase in opioid hospitalizations, without a corresponding increase in opioid deaths, may reflect greater willingness to seek medical assistance because decriminalization could reduce the stigma associated with drug use,” it says.
“However, it is also possible that reduced stigma and removal of criminal penalties facilitated the diversion of safer opioids, contributing to increased hospitalizations.”
Karen Urbanoski, an associate professor in the Public Health and Social Policy department at the University of Victoria, is more critical.
“The [study’s] findings do not warrant the conclusion that these policies are causally associated with increased hospitalization or overdose,” said Urbanoski, who also holds the Canada Research Chair in Substance Use, Addictions and Health Services.
Her team published a study in November 2023 that measured safer supply’s impact on mortality and acute care visits. It found safer supply opioids did reduce overdose deaths.
Critics, however, raised concerns that her study misrepresented its underlying data and showed no statistically significant reduction in deaths after accounting for confounding factors.
The Nguyen study differs from Urbanoski’s. While Urbanoski’s team focused on individual-level outcomes, the Nguyen study analyzed broader, population-level effects, including diversion.
Wallace, the biostatistician, agrees more individual-level data could strengthen analysis, but does not believe it undermines the study’s conclusions. Wallace thinks the researchers did their best with the available data they had.
“We do not have a ‘copy’ of B.C. where the policies weren’t implemented to compare with,” said Wallace.
B.C.’s overdose rate of 775 per 100,000 is well above the national average of 533.
Elenore Sturko, a Conservative MLA for Surrey-Cloverdale, has been a vocal critic of B.C.’s decriminalization and safer supply policies.
“If the government doesn’t want to believe this study, well then I invite them to do a similar study,” she told reporters on March 27.
“Show us the evidence that they have failed to show us since 2020,” she added, referring to the year B.C. implemented safer supply.
This article was produced through the Breaking Needles Fellowship Program, which provided a grant to Canadian Affairs, a digital media outlet, to fund journalism exploring addiction and crime in Canada. Articles produced through the Fellowship are co-published by Break The Needle and Canadian Affairs.
Our content is always free – but if you want to help us commission more high-quality journalism,
consider getting a voluntary paid subscription.
Addictions
Addiction experts demand witnessed dosing guidelines after pharmacy scam exposed

By Alexandra Keeler
The move follows explosive revelations that more than 60 B.C. pharmacies were allegedly participating in a scheme to overbill the government under its safer supply program. The scheme involved pharmacies incentivizing clients to fill prescriptions they did not require by offering them cash or rewards. Some of those clients then sold the drugs on the black market.
An addiction medicine advocacy group is urging B.C. to promptly issue new guidelines for witnessed dosing of drugs dispensed under the province’s controversial safer supply program.
In a March 24 letter to B.C.’s health minister, Addiction Medicine Canada criticized the BC Centre on Substance Use for dragging its feet on delivering the guidelines and downplaying the harms of prescription opioids.
The centre, a government-funded research hub, was tasked by the B.C. government with developing the guidelines after B.C. pledged in February to return to witnessed dosing. The government’s promise followed revelations that many B.C. pharmacies were exploiting rules permitting patients to take safer supply opioids home with them, leading to abuse of the program.
“I think this is just a delay,” said Dr. Jenny Melamed, a Surrey-based family physician and addiction specialist who signed the Addiction Medicine Canada letter. But she urged the centre to act promptly to release new guidelines.
“We’re doing harm and we cannot just leave people where they are.”
Addiction Medicine Canada’s letter also includes recommendations for moving clients off addictive opioids altogether.
“We should go back to evidence-based medicine, where we have medications that work for people in addiction,” said Melamed.
‘Best for patients’
On Feb. 19, the B.C. government said it would return to a witnessed dosing model. This model — which had been in place prior to the pandemic — will require safer supply participants to take prescribed opioids under the supervision of health-care professionals.
The move follows explosive revelations that more than 60 B.C. pharmacies were allegedly participating in a scheme to overbill the government under its safer supply program. The scheme involved pharmacies incentivizing clients to fill prescriptions they did not require by offering them cash or rewards. Some of those clients then sold the drugs on the black market.
In its Feb. 19 announcement, the province said new participants in the safer supply program would immediately be subject to the witnessed dosing requirement. For existing clients of the program, new guidelines would be forthcoming.
“The Ministry will work with the BC Centre on Substance Use to rapidly develop clinical guidelines to support prescribers that also takes into account what’s best for patients and their safety,” Kendra Wong, a spokesperson for B.C.’s health ministry, told Canadian Affairs in an emailed statement on Feb. 27.
More than a month later, addiction specialists are still waiting.
According to Addiction Medicine Canada’s letter, the BC Centre on Substance Use posed “fundamental questions” to the B.C. government, potentially causing the delay.
“We’re stuck in a place where the government publicly has said it’s told BCCSU to make guidance, and BCCSU has said it’s waiting for government to tell them what to do,” Melamed told Canadian Affairs.
This lag has frustrated addiction specialists, who argue the lack of clear guidance is impeding the transition to witnessed dosing and jeopardizing patient care. They warn that permitting take-home drugs leads to more diversion onto the streets, putting individuals at greater risk.
“Diversion of prescribed alternatives expands the number of people using opioids, and dying from hydromorphone and fentanyl use,” reads the letter, which was also co-signed by Dr. Robert Cooper and Dr. Michael Lester. The doctors are founding board members of Addiction Medicine Canada, a nonprofit that advises on addiction medicine and advocates for research-based treatment options.
“We have had people come in [to our clinic] and say they’ve accessed hydromorphone on the street and now they would like us to continue [prescribing] it,” Melamed told Canadian Affairs.
A spokesperson for the BC Centre on Substance Use declined to comment, referring Canadian Affairs to the Ministry of Health. The ministry was unable to provide comment by the publication deadline.
Big challenges
Under the witnessed dosing model, doctors, nurses and pharmacists will oversee consumption of opioids such as hydromorphone, methadone and morphine in clinics or pharmacies.
The shift back to witnessed dosing will place significant demands on pharmacists and patients. In April 2024, an estimated 4,400 people participated in B.C.’s safer supply program.
Chris Chiew, vice president of pharmacy and health-care innovation at the pharmacy chain London Drugs, told Canadian Affairs that the chain’s pharmacists will supervise consumption in semi-private booths.
Nathan Wong, a B.C.-based pharmacist who left the profession in 2024, fears witnessed dosing will overwhelm already overburdened pharmacists, creating new barriers to care.
“One of the biggest challenges of the retail pharmacy model is that there is a tension between making commercial profit, and being able to spend the necessary time with the patient to do a good and thorough job,” he said.
“Pharmacists often feel rushed to check prescriptions, and may not have the time to perform detailed patient counselling.”
Others say the return to witnessed dosing could create serious challenges for individuals who do not live close to health-care providers.
Shelley Singer, a resident of Cowichan Bay, B.C., on Vancouver Island, says it was difficult to make multiple, daily visits to a pharmacy each day when her daughter was placed on witnessed dosing years ago.
“It was ridiculous,” said Singer, whose local pharmacy is a 15-minute drive from her home. As a retiree, she was able to drive her daughter to the pharmacy twice a day for her doses. But she worries about patients who do not have that kind of support.
“I don’t believe witnessed supply is the way to go,” said Singer, who credits safer supply with saving her daughter’s life.
Melamed notes that not all safer supply medications require witnessed dosing.
“Methadone is under witness dosing because you start low and go slow, and then it’s based on a contingency management program,” she said. “When the urine shows evidence of no other drug, when the person is stable, [they can] take it at home.”
She also noted that Suboxone, a daily medication that prevents opioid highs, reduces cravings and alleviates withdrawal, does not require strict supervision.
Kendra Wong, of the B.C. health ministry, told Canadian Affairs that long-acting medications such as methadone and buprenorphine could be reintroduced to help reduce the strain on health-care professionals and patients.
“There are medications available through the [safer supply] program that have to be taken less often than others — some as far apart as every two to three days,” said Wong.
“Clinicians may choose to transition patients to those medications so that they have to come in less regularly.”
Such an approach would align with Addiction Medicine Canada’s recommendations to the ministry.
The group says it supports supervised dosing of hydromorphone as a short-term solution to prevent diversion. But Melamed said the long-term goal of any addiction treatment program should be to reduce users’ reliance on opioids.
The group recommends combining safer supply hydromorphone with opioid agonist therapies. These therapies use controlled medications to reduce withdrawal symptoms, cravings and some of the risks associated with addiction.
They also recommend limiting unsupervised hydromorphone to a maximum of five 8 mg tablets a day — down from the 30 tablets currently permitted with take-home supplies. And they recommend that doses be tapered over time.
“This protocol is being used with success by clinicians in B.C. and elsewhere,” the letter says.
“Please ensure that the administrative delay of the implementation of your new policy is not used to continue to harm the public.”
This article was produced through the Breaking Needles Fellowship Program, which provided a grant to Canadian Affairs, a digital media outlet, to fund journalism exploring addiction and crime in Canada. Articles produced through the Fellowship are co-published by Break The Needle and Canadian Affairs.
Subscribe to Break The Needle
-

 2025 Federal Election16 hours ago
2025 Federal Election16 hours agoStudy links B.C.’s drug policies to more overdoses, but researchers urge caution
-

 2025 Federal Election2 days ago
2025 Federal Election2 days agoPolice Associations Endorse Conservatives. Poilievre Will Shut Down Tent Cities
-

 conflict2 days ago
conflict2 days agoMarco Rubio says US could soon ‘move on’ from Ukraine conflict: ‘This is not our war’
-

 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoChinese firm unveils palm-based biometric ID payments, sparking fresh privacy concerns
-

 Alberta2 days ago
Alberta2 days agoRed Deer Justice Centre Grand Opening: Building access to justice for Albertans
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoTrump: China’s tariffs to “come down substantially” after negotiations with Xi
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoTrump considers $5K bonus for moms to increase birthrate
-

 Business16 hours ago
Business16 hours agoIs Government Inflation Reporting Accurate?