Economy
Climate researchers show we’re actually “safer than ever from climate” catastrophes
The climate safety denial movement
I and others have documented that we’re safer than ever from climate. Catastrophists can’t refute us, so they’re now saying that disaster deaths don’t matter!
|
|
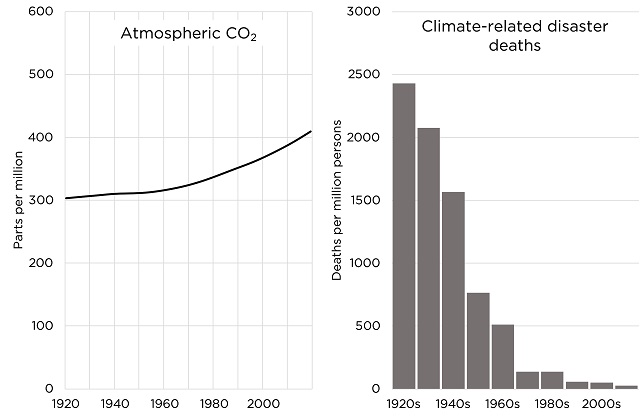
For decades climate catastrophists have portrayed climate disasters as getting deadlier and deadlier.
Now that I and others have documented that we’re safer than ever from climate, catastrophists are saying that disaster deaths don’t matter!
- Reuters says “Drop in climate-related disaster deaths not evidence against climate emergency.”
But a drop in deaths from something—here, a 98% drop—is obvious evidence against it being an emergency.
Would Reuters say: “98% drop in flu deaths not evidence against flu emergency”?¹
- Why is Reuters, along with The New York Times, PolitiFact, and USA Today, claiming that a 98% drop in climate disaster deaths doesn’t contradict their climate emergency narrative? Because it obviously does, and they can only save their narrative by intimidating us into denying the obvious.²
- The central narrative of climate catastrophists is that fossil fuels and their CO2 emissions are killing more and more people via climate disasters.
This narrative has always had a fatal weakness: it totally contradicts the data, which show plummeting climate disaster deaths.³
- Why are climate disaster deaths plummeting as fossil fuel use and CO2 emissions rise?
Because the enormous ability uniquely cost-effective and scalable fossil fuel energy gives us to master climate danger far outweighs any new climate challenges from CO2 emissions.
- An example of fossil-fueled climate mastery overwhelming CO2 impacts is drought.
Any contribution of rising CO2 to drought has been overwhelmed by fossil-fueled irrigation and crop transport, which have helped reduce drought deaths by over 100 times over 100 years as CO2 levels have risen.⁴
- Over the last decade, I and a number of others, including Bjorn Lomborg and Michael Shellenberger, have challenged catastrophism by pointing to declining climate disaster deaths.
Catastrophists couldn’t refute our argument. So instead they pretended it didn’t exist.
Until last year.⁵
- In 2023, climate catastrophists finally felt compelled to address the fact that climate disaster deaths have plummeted (driven by fossil-fueled climate mastery).
Because of honesty? No—because Presidential candidates started bringing it up and persuading people with it.
- Here is Vivek Ramaswamy during his Presidential campaign referring to a 98% decline in climate disaster deaths—and, crucially, giving fossil fuel energy credit.
- Here is Ron DeSantis during his Presidential campaign referring to a 98% decline in climate disaster deaths—and, crucially, giving fossil fuel energy credit.
- The 98% decline in climate disaster deaths, driven by fossil fuels, is a blockbuster fact: it shows that we are experiencing not fossil-fueled climate emergency but fossil-fueled climate safety.
But instead of being happy, catastrophists engage in climate safety denial.
- Here are 3 recent instances of climate safety denial—from Reuters, PolitiFact, and USA Today. All have long portrayed climate deaths as a fast-increasing problem. But now they claim deaths don’t matter.
https://www.reuters.com/fact-check/drop-climate-related- disaster-deaths-not-evidence- against-climate-emergency- 2023-09-19/ - Climate safety denial utilizes 5 main myths to evade the decline in disaster deaths:
1. Fossil fuels don’t deserve credit
2. Weather forecasting deserves the credit
3. 100 years is a misleading period
4. Damages are drastically increasing
5. There’s a major increase in reported disasters - Myth 1: Fossil fuels don’t deserve much credit for plummeting climate disaster deaths; it’s “resilience.”
Truth: Uniquely cost-effective and scalable fossil fuel energy makes us resilient through plentiful infrastructure-building, heating and cooling, irrigation, transportation, etc.⁶
- Myth 2: Storm warning systems deserve the credit for plummeting climate disaster deaths.
Truth: Drought, not storm, deaths are the leading source of reduced climate deaths. And fossil fuels power storm warning and evacuation systems (and more resilient infrastructure).⁷
- Myth 3: 100 years is a misleading period to measure plummeting climate disaster deaths.
Truth: 100 years is a standard, very meaningful period to look at. While we have data going back an additional two decades, those tend to underreport due to less global communication.⁸
- Contrary to the claim that starting analysis of climate disaster deaths in the 1920s overestimates the decline, it actually likely underestimates the decline due to insufficient past reporting; data before WWII extremely likely underreport deaths compared to data after 2000.
- Myth 4: There is an alarming increase in reported disasters, revealing an underlying climate emergency.
Truth: The increase in reported disasters over time is due overwhelmingly to increased global communication. Changes in fundamentals, such as storms, are extremely modest.⁹
- The claim that more reported disasters show an increasingly dangerous climate is absurd in light of the fact that underlying data show massive increases in reporting before significant human climate impacts and the reporting trend also massively goes up for non-climate causes!
- Other biases might inflate the number of reported disasters. E.g., governments of poor countries have an incentive to declare more disasters with increasing international relief.¹⁰
- Using obviously problematic disaster frequency reporting instead of direct climatological evidence to try and show increasing climate danger is a revealing choice by catastrophists. They are making it because the climate change we’ve experienced has been very modest—and masterable.
Do Not Declare a “Climate Emergency”
·AUGUST 17, 2023Read full story - An example of unalarming climate fundamentals: neither the frequency nor the energy in global hurricanes has changed significantly relative to the noisy average. There is also little evidence for more landfalling hurricanes.¹¹
- The catastrophist attempt to undermine the 98% decrease in disaster deaths by pointing to the increased reporting of disasters is actually self-defeating.
If disaster deaths are plummeting despite incomplete past reporting, that means they’ve declined by even more than 98%.
- Myth 5: Climate damages are drastically increasing, revealing an underlying climate emergency.
Truth: Even though there are many incentives for climate damages to go up—preferences for riskier areas, government bailouts—GDP-adjusted damages are flat.¹²
- We often hear that “billion-dollar disasters” have increased significantly. But this is a bogus metric. Of course, as GDP grows we’ll have more billion-dollar disasters because there is more wealth for disasters to strike. But when we adjust for GDP there’s no increase in damage.¹³
- A Reuters “fact check” alarmingly claims a 151% growth in disaster damages from a period starting in 1978 to a period ending in 2017.
But they evade that the global economy grew by over 200% during that period!
(And they evade that disaster and damage reporting increased.)¹⁴
- The stupidest climate safety denial myth (used by The New York Times): 2 million people died from extreme weather in the last 50 years; that’s obviously an emergency.
Truth: 2 million in 50 years is a rate of 40,000 per year—far, far less than 100 years ago, thus confirming today’s climate safety.¹⁵
- The last-gasp climate safety denial myth: Okay, we’re safer than ever from climate disasters, and it is driven by cheap energy from fossil fuels, but we can easily replace fossil fuels with solar and wind.
Truth: For the foreseeable future there is no cheap global energy without fossil fuels.
The ultimate debunking of “solar and wind are cheaper than fossil fuels.”
·JULY 19, 2023Read full story - Observe that all these seemingly scientific outlets, such as The New York Times, Reuters, and PolitiFact are totally unable to refute the death-blow to their “climate emergency” narrative that is the drastic decline in climate disaster deaths.
Science requires that they admit defeat.
Popular links
- EnergyTalkingPoints.com: Hundreds of concise, powerful, well-referenced talking points on energy, environmental, and climate issues.
- My new book Fossil Future: Why Global Human Flourishing Requires More Oil, Coal, and Natural Gas—Not Less.
- Speaking and media inquiries.
“Energy Talking Points by Alex Epstein” is my free Substack newsletter designed to give as many people as possible access to concise, powerful, well-referenced talking points on the latest energy, environmental, and climate issues from a pro-human, pro-energy perspective.
Share Energy Talking Points by Alex Epstein
UC San Diego – The Keeling Curve
For every million people on earth, annual deaths from climate-related causes (extreme temperature, drought, flood, storms, wildfires) declined 98%–from an average of 247 per year during the 1920s to 2.5 per year during the 2010s.
Data on disaster deaths come from EM-DAT, CRED / UCLouvain, Brussels, Belgium – www.emdat.be (D. Guha-Sapir).
Population estimates for the 1920s from the Maddison Database 2010, the Groningen Growth and Development Centre, Faculty of Economics and Business at University of Groningen. For years not shown, population is assumed to have grown at a steady rate.
Population estimates for the 2010s come from World Bank Data
Business
Socialism vs. Capitalism

People criticize capitalism. A recent Axios-Generation poll says, “College students prefer socialism to capitalism.”
Why?
Because they believe absurd myths. Like the claim that the Soviet Union “wasn’t real socialism.”
Socialism guru Noam Chomsky tells students that. He says the Soviet Union “was about as remote from socialism as you could imagine.”
Give me a break.
The Soviets made private business illegal.
If that’s not socialism, I’m not sure what is.
“Socialism means abolishing private property and … replacing it with some form of collective ownership,” explains economist Ben Powell. “The Soviet Union had an abundance of that.”
Socialism always fails. Look at Venezuela, the richest country in Latin America about 40 years ago. Now people there face food shortages, poverty, misery and election outcomes the regime ignores.
But Al Jazeera claims Venezuela’s failure has “little to do with socialism, and a lot to do with poor governance … economic policies have failed to adjust to reality.”
“That’s the nature of socialism!” exclaims Powell. “Economic policies fail to adjust to reality. Economic reality evolves every day. Millions of decentralized entrepreneurs and consumers make fine tuning adjustments.”
Political leaders can’t keep up with that.
Still, pundits and politicians tell people, socialism does work — in Scandinavia.
“Mad Money’s Jim Cramer calls Norway “as socialist as they come!”
This too is nonsense.
“Sweden isn’t socialist,” says Powell. “Volvo is a private company. Restaurants, hotels, they’re privately owned.”
Norway, Denmark and Sweden are all free market economies.
Denmark’s former prime minister was so annoyed with economically ignorant Americans like Bernie Sanders calling Scandanavia “socialist,” he came to America to tell Harvard students that his country “is far from a socialist planned economy. Denmark is a market economy.”
Powell says young people “hear the preaching of socialism, about equality, but they don’t look on what it actually delivers: poverty, starvation, early death.”
For thousands of years, the world had almost no wealth creation. Then, some countries tried capitalism. That changed everything.
“In the last 20 years, we’ve seen more humans escape extreme poverty than any other time in human history, and that’s because of markets,” says Powell.
Capitalism makes poor people richer.
Former Rep. Jamaal Bowman (D-N.Y.) calls capitalism “slavery by another name.”
Rep. Alexandria Ocasio-Cortez (D-N.Y.) claims, “No one ever makes a billion dollars. You take a billion dollars.”
That’s another myth.
People think there’s a fixed amount of money. So when someone gets rich, others lose.
But it’s not true. In a free market, the only way entrepreneurs can get rich is by creating new wealth.
Yes, Steve Jobs pocketed billions, but by creating Apple, he gave the rest of us even more. He invented technology that makes all of us better off.
“I hope that we get 100 new super billionaires,” says economist Dan Mitchell, “because that means 100 new people figured out ways to make the rest of our lives better off.”
Former Labor Secretary Robert Reich advocates the opposite: “Let’s abolish billionaires,” he says.
He misses the most important fact about capitalism: it’s voluntary.
“I’m not giving Jeff Bezos any money unless he’s selling me something that I value more than that money,” says Mitchell.
It’s why under capitalism, the poor and middle class get richer, too.
“The economic pie grows,” says Mitchell. “We are much richer than our grandparents.”
When the media say the “middle class is in decline,” they’re technically right, but they don’t understand why it’s shrinking.
“It’s shrinking because more and more people are moving into upper income quintiles,” says Mitchell. “The rich get richer in a capitalist society. But guess what? The rest of us get richer as well.”
I cover more myths about socialism and capitalism in my new video.
Business
Residents in economically free states reap the rewards

From the Fraser Institute
A report published by the Fraser Institute reaffirms just how much more economically free some states are compared with others. These are places where citizens are allowed to make more of their economic choices. Their taxes are lighter, and their regulatory burdens are easier. The benefits for workers, consumers and businesses have been clear for a long time.
There’s another group of states to watch: “movers” that have become much freer in recent decades. These are states that may not be the freest, but they have been cutting taxes and red tape enough to make a big difference.
How do they fare?
I recently explored this question using 22 years of data from the same Economic Freedom of North America index. The index uses 10 variables encompassing government spending, taxation and labour regulation to assess the degree of economic freedom in each of the 50 states.
Some states, such as New Hampshire, have long topped the list. It’s been in the top five for three decades. With little room to grow, the Granite State’s level of economic freedom hasn’t budged much lately. Others, such as Alaska, have significantly improved economic freedom over the last two decades. Because it started so low, it remains relatively unfree at 43rd out of 50.
Three states—North Carolina, North Dakota and Idaho—have managed to markedly increase and rank highly on economic freedom.
In 2000, North Carolina was the 19th most economically free state in the union. Though its labour market was relatively unhindered by the state’s government, its top marginal income tax rate was America’s ninth-highest, and it spent more money than most states.
From 2013 to 2022, North Carolina reduced its top marginal income tax rate from 7.75 per cent to 4.99 per cent, reduced government employment and allowed the minimum wage to fall relative to per-capita income. By 2022, it had the second-freest labour market in the country and was ninth in overall economic freedom.
North Dakota took a similar path, reducing its 5.54 per cent top income tax rate to 2.9 per cent, scaling back government employment, and lowering its minimum wage to better reflect local incomes. It went from the 27th most economically free state in the union in 2000 to the 10th freest by 2022.
Idaho saw the most significant improvement. The Gem State has steadily improved spending, taxing and labour market freedom, allowing it to rise from the 28th most economically free state in 2000 to the eighth freest in 2022.
We can contrast these three states with a group that has achieved equal and opposite distinction: California, Delaware, New Jersey and Maryland have managed to decrease economic freedom and end up among the least free overall.
What was the result?
The economies of the three liberating states have enjoyed almost twice as much economic growth. Controlling for inflation, North Carolina, North Dakota and Idaho grew an average of 41 per cent since 2010. The four repressors grew by just 24 per cent.
Among liberators, statewide personal income grew 47 per cent from 2010 to 2022. Among repressors, it grew just 26 per cent.
In fact, when it comes to income growth per person, increases in economic freedom seem to matter even more than a state’s overall, long-term level of freedom. Meanwhile, when it comes to population growth, placing highly over longer periods of time matters more.
The liberators are not unique. There’s now a large body of international evidence documenting the freedom-prosperity connection. At the state level, high and growing levels of economic freedom go hand-in-hand with higher levels of income, entrepreneurship, in-migration and income mobility. In economically free states, incomes tend to grow faster at the top and bottom of the income ladder.
These states suffer less poverty, homelessness and food insecurity and may even have marginally happier, more philanthropic and more tolerant populations.
In short, liberation works. Repression doesn’t.
-

 Haultain Research6 hours ago
Haultain Research6 hours agoSweden Fixed What Canada Won’t Even Name
-

 Business1 day ago
Business1 day ago“Magnitude cannot be overstated”: Minnesota aid scam may reach $9 billion
-

 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoLargest fraud in US history? Independent Journalist visits numerous daycare centres with no children, revealing massive scam
-

 Censorship Industrial Complex1 day ago
Censorship Industrial Complex1 day agoUS Under Secretary of State Slams UK and EU Over Online Speech Regulation, Announces Release of Files on Past Censorship Efforts
-

 Energy2 days ago
Energy2 days agoCanada’s debate on energy levelled up in 2025
-

 Business5 hours ago
Business5 hours agoWhat Do Loyalty Rewards Programs Cost Us?
-

 Daily Caller2 days ago
Daily Caller2 days agoIs Ukraine Peace Deal Doomed Before Zelenskyy And Trump Even Meet At Mar-A-Lago?































