National
Canadian gov’t budget report targets charitable status of pro-life groups, churches

From LifeSiteNews
A Pre-Budget Consultations in Advance of the 2025 Budget report recommends no longer providing charitable status to anti-abortion organizations and amending the Income Tax Act to remove the privileged status of ‘advancement of religion’ as a charitable purpose.
In 2022, I wrote an essay titled “What is coming next for Canadian churches?” In that essay, as well as in my recent book How We Got Here, I noted that as Canada shifted from being a post-Christian society to an increasingly anti-Christian one, Christian churches and organizations will inevitably lose tax-exempt or charitable status:
Churches and other religious institutions that refuse to bend the knee will likely lose their tax-exempt status at some point. Canadian LGBT activists have been making this case for years, and it is only a matter of time before the idea catches on or — more likely — a progressive politician decides that the time is right. I suspect that a key reason this has not yet been discussed is the awkward fact that many non-Christian institutions hold similar positions on marriage, sexuality, and abortion. That said, I have no doubt that a way to target churches specifically will be worked out. LGBT activists are already asking why the government is “rewarding bigotry” by awarding tax-exempt status to churches with a traditional view of sexuality, and LGBT activists have publicized sermons they disagree with as evidence of hatred. The churches and the state are on a collision course, and it isn’t hard to guess how this will end.
We may be seeing the first move in that direction. With the Christmas season upon us and Ottawa in chaos, few Canadians noticed the government’s publication of “Pre-Budget Consultations In Advance of the 2025 Budget,” the report of the Standing Committee on Finance. The report of annual pre-budget consultations included 462 recommendations that have been tabled and, according to the Standing Committee, will be taken into account by “the Minister of Finance in the development of the 2025 federal budget” (which, if Trudeau is still in power, will be Dominic LeBlanc).
Two recommendations included in that report are deeply concerning, and the Christian Legal Fellowship has written to both the Minister of Finance and the Finance Committee Chair Peter Fonseca to express that concern:
Recommendation 429: No longer provide charitable status to anti-abortion organizations.
Recommendation 430: Amend the Income Tax Act to provide a definition of a charity which would remove the privileged status of ‘advancement of religion’ as a charitable purpose.
Those two recommendations, of course, were buried at the very end of the report. The first is unsurprising — Trudeau’s government is currently targeting crisis pregnancy centers that assist moms and babies in need, so it was inevitable that the government was eventually going to target local Right to Life organizations and other pro-life groups that still have charitable status. More brazen is the recommendation that the Income Tax Act be amended to eliminate “advancement of religion” as a charitable purpose — this could, according to the Christian Legal Fellowship, “have a devastating impact, not only on the 32,000+ religious charities in this country, but the millions of Canadians they serve.” CLF urged the government “to reject any such approach and clarify exactly what is being contemplated.” As CLF noted in their letter:
Religious charities account for nearly 40% of all charities in Canada, including churches, mosques, temples, synagogues, and other faith communities, operating programs such as soup kitchens, shelters, refugee homes, and food banks. They provide indispensable social, economic, and spiritual support, filling a significant gap in our communities and meeting the needs of millions of Canadians.
Suggesting that such organizations must do something other than “advance religion” to be considered charitable ignores the reality that these services are themselves the very manifestation of religious beliefs, inherent to and inextricable from the charity’s religion itself. It also betrays a long-standing recognition of the intrinsic goods provided by religious communities, who offer people hope, encouragement, and belonging in ways that simply cannot be quantified or replaced. Ultimately, any efforts to substitute their much-needed services would place an extraordinary strain on all levels of government.
I have no doubt that the Trudeau government is willing to purse these recommendations regardless; these plans, however, may be thwarted by the next election. Trudeau no doubt remembers the Canada Summer Jobs Program fight, when his government insisted that recipients sign an attestation of support for abortion and LGBT ideology and suddenly found themselves facing angry imams, rabbis, and other religious leaders instead of just the priests and pastors they’d assumed would be impacted. It seems unlikely that going after religious charities is a fight Trudeau wants now.
Trudeau will, however, be campaigning on abortion — it’s the wedge issue he returns to again and again as the PMO increasingly resembles Custer’s Last Stand. Thus, Recommendation 429 may be taken up sooner rather than later. Either way, these two recommendations are essentially a statement of purpose. The Liberals may not get to them just now, but be assured that this is what progressives intend to do just as soon as they get the chance.
2025 Federal Election
Next federal government should recognize Alberta’s important role in the federation
From the Fraser Institute
By Tegan Hill
With the tariff war continuing and the federal election underway, Canadians should understand what the last federal government seemingly did not—a strong Alberta makes for a stronger Canada.
And yet, current federal policies disproportionately and negatively impact the province. The list includes Bill C-69 (which imposes complex, uncertain and onerous review requirements on major energy projects), Bill C-48 (which bans large oil tankers off British Columbia’s northern coast and limits access to Asian markets), an arbitrary cap on oil and gas emissions, numerous other “net-zero” targets, and so on.
Meanwhile, Albertans contribute significantly more to federal revenues and national programs than they receive back in spending on transfers and programs including the Canada Pension Plan (CPP) because Alberta has relatively high rates of employment, higher average incomes and a younger population.
For instance, since 1976 Alberta’s employment rate (the number of employed people as a share of the population 15 years of age and over) has averaged 67.4 per cent compared to 59.7 per cent in the rest of Canada, and annual market income (including employment and investment income) has exceeded that in the other provinces by $10,918 (on average).
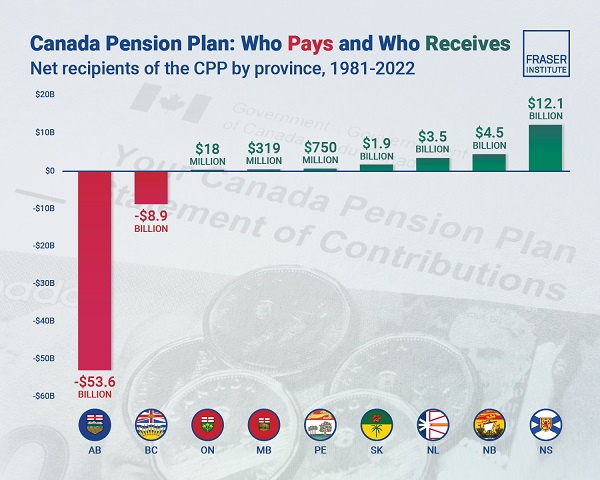
As a result, Alberta’s total net contribution to federal finances (total federal taxes and payments paid by Albertans minus federal money spent or transferred to Albertans) was $244.6 billion from 2007 to 2022—more than five times as much as the net contribution from British Columbians or Ontarians. That’s a massive outsized contribution given Alberta’s population, which is smaller than B.C. and much smaller than Ontario.
Albertans’ net contribution to the CPP is particularly significant. From 1981 to 2022, Alberta workers contributed 14.4 per cent (on average) of total CPP payments paid to retirees in Canada while retirees in the province received only 10.0 per cent of the payments. Albertans made a cumulative net contribution to the CPP (the difference between total CPP contributions made by Albertans and CPP benefits paid to retirees in Alberta) of $53.6 billion over the period—approximately six times greater than the net contribution of B.C., the only other net contributing province to the CPP. Indeed, only two of the nine provinces that participate in the CPP contribute more in payroll taxes to the program than their residents receive back in benefits.
So what would happen if Alberta withdrew from the CPP?
For starters, the basic CPP contribution rate of 9.9 per cent (typically deducted from our paycheques) for Canadians outside Alberta (excluding Quebec) would have to increase for the program to remain sustainable. For a new standalone plan in Alberta, the rate would likely be lower, with estimates ranging from 5.85 per cent to 8.2 per cent. In other words, based on these estimates, if Alberta withdrew from the CPP, Alberta workers could receive the same retirement benefits but at a lower cost (i.e. lower payroll tax) than other Canadians while the payroll tax would have to increase for the rest of the country while the benefits remained the same.
Finally, despite any claims to the contrary, according to Statistics Canada, Alberta’s demographic advantage, which fuels its outsized contribution to the CPP, will only widen in the years ahead. Alberta will likely maintain relatively high employment rates and continue to welcome workers from across Canada and around the world. And considering Alberta recorded the highest average inflation-adjusted economic growth in Canada since 1981, with Albertans’ inflation-adjusted market income exceeding the average of the other provinces every year since 1971, Albertans will likely continue to pay an outsized portion for the CPP. Of course, the idea for Alberta to withdraw from the CPP and create its own provincial plan isn’t new. In 2001, several notable public figures, including Stephen Harper, wrote the famous Alberta “firewall” letter suggesting the province should take control of its future after being marginalized by the federal government.
The next federal government—whoever that may be—should understand Alberta’s crucial role in the federation. For a stronger Canada, especially during uncertain times, Ottawa should support a strong Alberta including its energy industry.
2025 Federal Election
Donald Trump suggests Mark Carney will win Canadian election, touts ‘productive call’ with leader

From LifeSiteNews
‘It was an extremely productive call, we agree on many things, and will be meeting immediately after Canada’s upcoming Election,’ Trump wrote about Carney on Friday.
U.S. President Donald Trump says he had “an extremely productive call” with Prime Minister Mark Carney and implied that the World Economic Forum-linked politician will win Canada’s upcoming federal election.
“I just finished speaking with Prime Minister Mark Carney, of Canada,” Trump wrote on Truth Social Friday. “It was an extremely productive call, we agree on many things, and will be meeting immediately after Canada’s upcoming Election to work on elements of Politics, Business, and all other factors, that will end up being great for both the United States of America and Canada. Thank you for your attention to this matter!”
Reacting to the post, LifeSiteNews editor-in-chief John-Henry Westen wrote on X:

Trump’s comments come just weeks before Canadians head to the polls on April 28 for a federal election. Carney called the snap-election just nine days after taking over for Justin Trudeau as leader of the Liberal Party and prime minister.
Carney, an admitted “globalist” and “elitist,” formerly served as head of the Bank of Canada and Bank of England, and has extensive ties to globalist groups like the World Economic Forum and the United Nations.
Trump’s comments regarding Carney may prove significant as much of the debate in the mainstream media ahead of the election has been about how the prospective leaders will handle tariff threats and trade deals with America.
-

 Alberta2 days ago
Alberta2 days agoAlberta Institute urging Premier Smith to follow Saskatchewan and drop Industrial Carbon Tax
-
 Alberta1 day ago
Alberta1 day agoAlbertans have contributed $53.6 billion to the retirement of Canadians in other provinces
-

 Energy1 day ago
Energy1 day agoPoll: Majority says energy independence more important than fighting climate change
-

 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoFeds Spent Roughly $1 Billion To Conduct Survey That Could’ve Been Done For $10,000, Musk Says
-

 2025 Federal Election2 days ago
2025 Federal Election2 days agoFool Me Once: The Cost of Carney–Trudeau Tax Games
-

 Addictions2 days ago
Addictions2 days agoShould fentanyl dealers face manslaughter charges for fatal overdoses?
-

 Health2 days ago
Health2 days agoHow the once-blacklisted Dr. Jay Bhattacharya could help save healthcare
-

 Energy1 day ago
Energy1 day agoEnergy, climate, and economics — A smarter path for Canada










