Alberta
Big bug benefits: Alberta scientist releases guide identifying cow dung insects

Alberta entomologist Kevin Floate is ready to start spreading the news that he has compiled a comprehensive guide into insects that live in cow dung in Canada.
Floate — a scientist with Agriculture and Agri-Food Canada at the Lethbridge Research and Development Centre in southern Alberta — said he started studying insects in cattle dung about 30 years ago.
At the time, he realized he needed one source of information to help get him started.
“It didn’t exist. So, here we are 30 years later, and I’ve written that guide and it’s intended for ranchers and farmers and students and naturalists,” said Floate, who has a doctorate in entomology and penned “Cow Patty Critters: A New Guide on Canada’s Faecal Friends.”
“Anyone who’s ever asked the question ‘What’s in dung?’ This is the guide that I’ve written for you.”
The humble cow turd, sometimes known as a cow patty, cow pie or cow chip, has a soft texture and tends to be deposited in circular shapes, inspiring its various monikers.
Beaver, Okla., has held the World Cow Chip Throwing Contest since 1969 and singer Jim Stafford penned the tongue-in-cheek 1981 hit “Cow Patti.”
Despite the potential for numerous scatological jokes, Floate said he doesn’t mind a bit of ribbing about his profession.
“I embrace it because it’s an unusual topic, yet it’s everywhere, ” Floate said with a laugh. “So, I don’t mind a bad pun, and when you work in cow pies, you get a lot of bad puns.”
Floate said he has spent much of his career looking at the effects of chemicals that end up in cattle dung, and the impact on the insects that live there.
He said an estimated 110 million dung pats are deposited every year in Canada.
He’s identified more than 300 insects in his dung detective’s handbook and only three are considered harmful: horn flies, face flies and stable flies.
He said others, like the dung beetle, can play an important role, especially in the pasture.
“Some of those beetles will put the dung underground in tunnels. The tunnelling increases the permeability of the soil to water and oxygen and the little packages of dung the beetles push underground are like little parcels of fertilizer and help the plants grow,” Floate said.
He said the actions of the beetles also disperse seeds and pollinate plants before they are eventually consumed by birds and smaller mammals higher up the food chain.
Float said the scattering of the fecal matter also reduces the number of pest insects that breed and bother cattle.
This report by The Canadian Press was first published May 13, 2023.
Bill Graveland, The Canadian Press
Alberta
Albertans have contributed $53.6 billion to the retirement of Canadians in other provinces
From the Fraser Institute
By Tegan Hill and Nathaniel Li
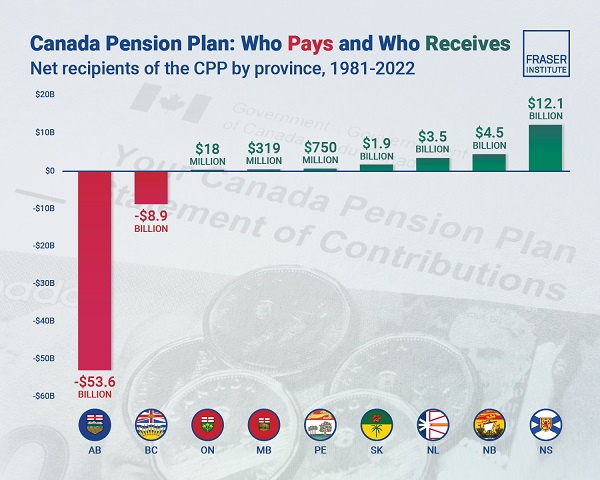
Albertans contributed $53.6 billion more to CPP then retirees in Alberta received from it from 1981 to 2022
Albertans’ net contribution to the Canada Pension Plan —meaning the amount Albertans paid into the program over and above what retirees in Alberta
received in CPP payments—was more than six times as much as any other province at $53.6 billion from 1981 to 2022, finds a new report published today by the Fraser Institute, an independent, non-partisan Canadian public policy think-tank.
“Albertan workers have been helping to fund the retirement of Canadians from coast to coast for decades, and Canadians ought to know that without Alberta, the Canada Pension Plan would look much different,” said Tegan Hill, director of Alberta policy at the Fraser Institute and co-author of Understanding Alberta’s Role in National Programs, Including the Canada Pension Plan.
From 1981 to 2022, Alberta workers contributed 14.4 per cent (on average) of the total CPP premiums paid—Canada’s compulsory, government- operated retirement pension plan—while retirees in the province received only 10.0 per cent of the payments. Alberta’s net contribution over that period was $53.6 billion.
Crucially, only residents in two provinces—Alberta and British Columbia—paid more into the CPP than retirees in those provinces received in benefits, and Alberta’s contribution was six times greater than BC’s.
The reason Albertans have paid such an outsized contribution to federal and national programs, including the CPP, in recent years is because of the province’s relatively high rates of employment, higher average incomes, and younger population.
As such, if Alberta withdrew from the CPP, Alberta workers could expect to receive the same retirement benefits but at a lower cost (i.e. lower payroll tax) than other Canadians, while the payroll tax would likely have to increase for the rest of the country (excluding Quebec) to maintain the same benefits.
“Given current demographic projections, immigration patterns, and Alberta’s long history of leading the provinces in economic growth, Albertan workers will likely continue to pay more into it than Albertan retirees get back from it,” Hill said.
Understanding Alberta’s Role in National Programs, Including the Canada Pension Plan
- Understanding Alberta’s role in national income transfers and other important programs is crucial to informing the broader debate around Alberta’s possible withdrawal from the Canada Pension Plan (CPP).
- Due to Alberta’s relatively high rates of employment, higher average incomes, and younger population, Albertans contribute significantly more to federal revenues than they receive back in federal spending.
- From 1981 to 2022, Alberta workers contributed 14.4 percent (on average) of the total CPP premiums paid while retirees in the province received only 10.0 percent of the payments. Albertans net contribution was $53.6 billion over the period—approximately six times greater than British Columbia’s net contribution (the only other net contributor).
- Given current demographic projections, immigration patterns, and Alberta’s long history of leading the provinces in economic growth and income levels, Alberta’s central role in funding national programs is unlikely to change in the foreseeable future.
- Due to Albertans’ disproportionate net contribution to the CPP, the current base CPP contribution rate would likely have to increase to remain sustainable if Alberta withdrew from the plan. Similarly, Alberta’s stand-alone rate would be lower than the current CPP rate.
Tegan Hill
Director, Alberta Policy, Fraser Institute
Alberta
Alberta Institute urging Premier Smith to follow Saskatchewan and drop Industrial Carbon Tax

From the Alberta Institute
Axe Alberta’s Industrial Carbon Tax
Aside from tariffs, carbon taxes have been the key topic of the election campaign so far, with Mark Carney announcing that the Liberals would copy the Conservatives’ long-standing policy to axe the tax – but with a big caveat.
You see, it’s misleading to talk about the carbon tax as if it were a single policy.
In fact, that’s what the Liberals would like you to think because it helps them hide all the other carbon taxes they’ve forced on Canadians and on the Provinces.
Broadly speaking, there are actually four types of carbon taxes in place in Canada:
- A federal consumer carbon tax
- A federal industrial carbon tax
- Various provincial consumer carbon taxes
- Various provincial industrial carbon taxes
Alberta was actually the first jurisdiction anywhere in North America to introduce a carbon tax in 2007, when Premier Ed Stelmach introduced a provincial industrial carbon tax.
Then, as we all know, the Alberta NDP introduced a provincial consumer carbon tax in 2017.
The provincial consumer carbon tax was short-lived, as the UCP repealed it in 2019.
But, unfortunately, the UCP failed to repeal the provincial industrial carbon tax at the same time.
Worse, by then, the federal Liberals had introduced a federal consumer carbon tax and a federal industrial carbon tax as well!
Flash forward to 2025, and the political calculus has changed dramatically.
Mark Carney might only be promising to get rid of the federal consumer carbon tax, but Pierre Poilievre is promising to get rid of both the federal consumer carbon tax and the federal industrial carbon tax.
This is a clear opportunity, and yesterday, Scott Moe jumped on it.
He announced that Saskatchewan will also be repealing its provincial industrial carbon tax.
Saskatchewan never had a provincial consumer carbon tax, which means that, within just a few weeks, people in Saskatchewan could be paying ZERO carbon tax of ANY kind.
Alberta needs to follow Saskatchewan’s lead.
The Alberta government should immediately repeal Alberta’s provincial industrial carbon tax.
There’s no excuse for our provincial government to continue burdening our industries with unnecessary costs that hurt competitiveness and deter investment.
These taxes make it harder for businesses to thrive, grow, and create jobs, especially when other provinces are taking action to eliminate similar policies.
Premier Danielle Smith must act now and eliminate the provincial industrial carbon tax in Alberta.
If you agree, please sign our petition calling on the Alberta government to Axe Alberta’s Industrial Carbon Tax today:
After you’ve signed, please send the petition to your friends, family, and wider network, so that every Albertan can have their voice heard!
– The Alberta Institute Team
-

 2025 Federal Election1 day ago
2025 Federal Election1 day agoPoilievre refuses to bash Trump via trick question, says it’s possible to work with him and be ‘firm’
-

 International2 days ago
International2 days agoVice President Vance, Second Lady to visit Greenland on Friday
-
 Community2 days ago
Community2 days agoSupport local healthcare while winning amazing prizes!
-

 Daily Caller2 days ago
Daily Caller2 days agoCover up of a Department of Energy Study Might Be The Biggest Stain On Biden Admin’s Legacy
-

 COVID-191 day ago
COVID-191 day ago17-year-old died after taking COVID shot, but Ontario judge denies his family’s liability claim
-

 2025 Federal Election19 hours ago
2025 Federal Election19 hours agoFool Me Once: The Cost of Carney–Trudeau Tax Games
-

 2025 Federal Election2 days ago
2025 Federal Election2 days agoVoters should remember Canada has other problems beyond Trump’s tariffs
-

 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoWhile “Team Canada” attacks Trump for election points, Premier Danielle Smith advocates for future trade relations