Energy
Biden Has Taken More Than 200 Actions Against Domestic Oil, New Report Says

From HeartlandDailyNews
By
President Joe Biden and his administration have taken over 200 actions against the U.S. oil and natural gas industry as energy prices have gone up, according to a new report.
“President Biden and Democrats have a plan for American energy: make it harder to produce and more expensive to purchase,” the Institute for Energy Research states in a new report. “Since Mr. Biden took office, his administration and its allies have taken over 200 actions deliberately designed to make it harder to produce energy here in America.”
The analysis highlights actions Biden took on his first day in office, listing them chronologically through March of this year. The first act was canceling the Keystone XL pipeline, issuing a moratorium on all oil and natural gas leasing activities in the Arctic National Wildlife Refuge and revoking Trump administration executive orders that decreased regulations in order to expand domestic production.
Within a week of being in office, Biden issued additional moratoriums on new oil and gas leases on public lands or in offshore waters and imposed new regulations related to permitting and leasing practices, which were tied up in the courts for years. It was not until last month that a federal court upheld the first oil and natural gas lease sale on federal lands. Last December, the Fifth Circuit also ruled that Gulf lease sales must go forward.
Other actions ahead of the midterm elections include threatening to tax the oil and natural gas industry, blaming them for profiteering. Roughly six months before the general election, his administration has proposed $110 billion tax hikes on oil, natural gas and coal. In response, U.S. Sen. John Barrasso, R-Wyo., led a coalition of 24 senators expressing “grave concern” about his “continued hostility towards American energy production.”
IER published the report after the latest action taken to increase the cost of U.S. oil production and cancel plans to restock the Strategic Petroleum Reserve. The SPR has been depleted to roughly half of what it was when he first took office.
“President Biden had the chance to top up the SPR when prices were still low during the pandemic, but anti-oil-and-gas ideologues within the administration couldn’t bear to do anything that would help out producers when demand was low,” Kathleen Sgamma, president of Western Energy Alliance, told The Center Square. He then drained it “for political reasons and it’s long overdue to fill the SPR back up. Like many other politically driven decisions from this administration that distort energy markets, the government will have to spend more taxpayer money than if it had rational energy policies.”
Ed Longanecker, president of the Texas Independent Producers & Royalty Owners Association, told The Center Square that the Biden administration withdrawing approximately 250 million barrels from the SPR “was another dangerous example of putting politics over national security. The fact that some will believe the decision to cancel contracts to refill the SPR is due to a newly discovered fiscal consciousness is both nonsensical and alarming. Poorly conceived, albeit intentional energy policy results in higher costs for consumers, global emissions, and inflation, while putting our economy and energy security at risk.”
Daniel Turner, Founder and Executive Director for Power The Future, said instead of using American-produced oil to refill the SPR, Biden was “embracing insanity by putting the green agenda ahead of our families and our national security. Only in Joe Biden’s head does it make sense to lower costs by raising fees.” In light of Iran’s recent attacks against Israel, he said, “the world and our allies need a strong America that is fully utilizing our energy strength. Instead, the only things Joe Biden wants to strengthen is Iranian oil and Washington’s tax revenue.”
As the Biden administration imposes more fees on American oil producers, Iran’s oil exports reached $35 billion within the last 12 months, according to Iranian Labour News Agency. “Despite the reimposition of U.S. sanctions on Tehran in 2018, Chinese purchases of Iranian oil have allowed the country to maintain a positive trade balance,” Reuters reported. “Without oil exports, Iran would have registered a $16.8 billion trade deficit.”
U.S. House Republicans last month passed several bills and resolutions to strengthen the U.S. oil and natural gas industry, The Center Square reported. Only a handful of Democrats, largely from Texas, supported them.
Texas leads the U.S. in oil and natural gas production, having broken records in the last few years, The Center Square has reported. Because the majority of oil and natural gas is produced on private land and a bipartisan group of Texas elected officials and regulatory agencies are supportive of the industry, Texas has been able to achieve what most states have not.
Those in the Texas energy industry argue that, without their ingenuity and technological advancement, the U.S. would not be as energy independent as it is and prices would be higher. When the Russian-Ukrainian crisis hit, it was Texas LNG exports that provided a “lifeline” to European countries, a TIPRO analysis found.
“With so much uncertainty in the world, the need for reliable, responsibly produced energy from a stable trading partner has never been more crucial,” Texas Oil & Gas Association President Todd Staples said. “Texas is that trade partner. Our producers, pipelines, refineries, and exporters answer the call to alleviate the global energy crisis, made worse by war.”
He also argues that Texas’ production records “are not guaranteed. We cannot take for granted that this industry can continue to rewrite its record book in the face of federal policies blatantly designed to undermine progress. Delayed permits, canceled pipeline projects, closed and delayed federal leasing programs and incoherent regulations hurt American consumers and stifle our ability to deliver energy freedom and security around the world.”
Bethany Blankley is a contributor to The Center Square.
Originally published by The Center Square. Republished with permission.
Energy
The Carney Government is Hijacking the Phase “Energy Superpower” to Advance Their Agenda

From Energy Now
By Jim Warren
Lately, the spin doctors in the prime minister’s office (PMO) have been hijacking perfectly good words and altering their meaning in the service of the Liberal agenda.
For budgetary purposes “operating expenses” have become “investments.” Similarly, the term “energy superpower” no longer means what people typically think it means. Back in the day when the concept “energy superpower” was popularized, it was used to describe oil rich countries like Saudi Arabia, the other Gulf states and OPEC members.
Those countries are home to the oil sheiks—the leaders of OPEC who capitalized on their dominant position in global energy markets to affect the global oil supply and prices. They also used their control over oil as a source of leverage in the realm of geopolitics.
Wikipedia, the font of knowledge for lazy columnists, describes the traditional meaning of energy superpower as follows “…a country that supplies large amounts of energy resources (crude oil, natural gas, coal, etc.) to a significant number of other countries – and therefore has the potential to influence world markets for political or economic gains. Energy superpower status might be exercised, for example, by significantly influencing the price on global markets or by withholding supplies.”
During the 2025 election campaign Mark Carney’s notion of what constitutes an energy superpower was aligned with the conventional definition. A CTV news report the day after the federal election reminded viewers that on “April 8 at a campaign stop in Calgary, Carney pledged to position Canada as a ‘world energy superpower,’ calling for new [oil] pipelines, including one to Eastern Canada.”
By September of 2025, Carney and his Energy Minister Timothy Hodgson had obviously adopted a new definition. They still boast about making Canada an energy superpower but no longer referred to oil production and new export pipelines as things integral to that goal.
But wait, on Friday November 7 the prime minister told attendees at Canadian Club event in Toronto not to worry the long sought pipeline “was going to happen.”
Pardon me if I’m not convinced. Over the three months prior to Friday the Liberals had left us to assume becoming an energy superpower could happen without increasing oil production and exports.
We are still left with a riddle—what do the Carney Liberals actually mean when they promise Canadians we will achieve “energy superpower” status if crude oil, Canada’s single most valuable export commodity is no longer one of the key components of the strategy to get us there?
Actually, Canada was well on its way to achieving the status of a world class energy superpower until the Trudeau Liberals assumed office. Our budding superpower ambitions were foreclosed on by the Liberals’ growth killing BANANA* legislation which thwarted efforts to increase oil production and exports. The blue-eyed sheiks of Western Canada have been handcuffed and denounced as authors of the upcoming climate apocalypse.
(*BANANA – Build Absolutely Nothing Anywhere Near Anything)
The communications wizards in the PMO abandoned the traditional definition without actually telling anyone they were doing so. They have quietly adopted a fossil fuel-free version of what it means to be a supremely powerful purveyor of energy, but haven’t explained what that entails.
If they chose to be honest with Canadians they would say what they really mean is “green energy superpower.” But if they came clean, it would probably trigger a national unity crisis. Better to leave things loose until the budget has been approved.
Despite wishful thinking in Ottawa, Canada is a long way from winning the race for medals in the field of clean, green energy production. But, we’re so far behind the leaders that Mark Carney thinks he’s first.
Powering the dream of a net zero world will presumably rely heavily on the approximately 28 critical minerals and rare earths required for wind turbines, advanced electric motors and batteries. Canada makes it to the medals podium for just three of the 28. According to a 2024 report published by Our World in Data, Canada is in third place globally for uranium and aluminum production, and cobalt refining.
Australia, a Western-style capitalist democracy which punches close to our weight by many economic measures is far ahead of Canada when it comes to critical minerals production and proven reserves. China is in a class of its own—clearly the world leader in rare earth production and proven reserves, miles ahead of the rest of the world. When it comes to mining and refining of critical minerals Canada has a lot of catching up to do.
Canada is similarly a long way from superpower status when it comes to the manufacturing of polysilicon, the compound required to produce solar electricity, and wind turbines.
Canada does not have any commercial level producers of polysilicon. China has several firms that manufacture it, one of which GCL-Poly has a 22% share of the global market. Polysilicon is also produced by firms in the US, South Korea, Germany, Japan, Norway and Qatar. There once was a company in Canada which imported polysilicon from China which it then used to make solar panels. Apparently it has moved its operations to the US.
Globally, there are approximately 39 manufacturers of large, grid-scale wind turbines located in some 14 different countries. The world’s largest manufacturer, Vestas, is headquartered in Denmark. No large wind turbines are manufactured in Canada. Our role is limited to installation, operations and maintenance.
And, given recent events it is unlikely Canada is going to become a global superpower for the manufacturing of electric vehicles any time soon.
Canada is in third place globally for the production of hydroelectricity, although our 364.2 terawatt-hours (TWH) of electricity we generate pales in comparison with China’s 4,183.4 TWH of hydroelectric production. While the environmentally virtuous may find grounds for bragging rights with respect to our country’s hydro production, it means little in terms of leverage in a global market place. Sure Canadian producers sell electricity into the US power grid, but they are unable to sell it anywhere else. Ocean spanning transmission lines won’t work, too much power is lost when sending power long distances and selling electricity stored in batteries is not commercially viable—the batteries required are simply too big and insanely expensive.
For the foreseeable future the only way Canada can claim superpower status as a producer of clean energy is if the definition is radically changed. Apparently being identified as a clean green energy superpower can now mean that a country makes use of an impressive level of the stuff—the criteria required to be deemed an “impressive producer” is apparently one of those post-modern woke notions whereby each country is entitled to its own green energy truth.
This echoes the casual way social media mavens award superpower status to supposedly inspiring personal characteristics – my superpower is multi-tasking, or baking sourdough bread, or being an avid recycler. It makes about as much sense as claiming you are a hero because you held a guy’s mitts so he could dial 911 to report an accident.
It is sad, but true, that Canada was well on its way to energy superpower status prior to the federal Liberals coming to office in 2015. Crude oil was then and remains Canada’s single most valuable export product. We currently export approximately 4.2 million barrels per day which was worth 153 billion USD in 2024. Back in 2013 and early 2014 when world prices were good the oil industry was generating as much as three to four percent of Canada’s GDP.
Clearly Canada could be doing a whole lot better economically if the federal government got behind the oil industry and removed the barriers to growth in production and exports. Danielle Smith has been trying to alert the Canadian government and public to the reality that completion of a single million barrels per day oil pipeline from Alberta to Prince Rupert could contribute $20 to $30 billion in new revenues to Canada’s GDP, depending on world prices.
That would be a giant leap forward on the path to being a real energy superpower.
Alberta
‘Weird and wonderful’ wells are boosting oil production in Alberta and Saskatchewan
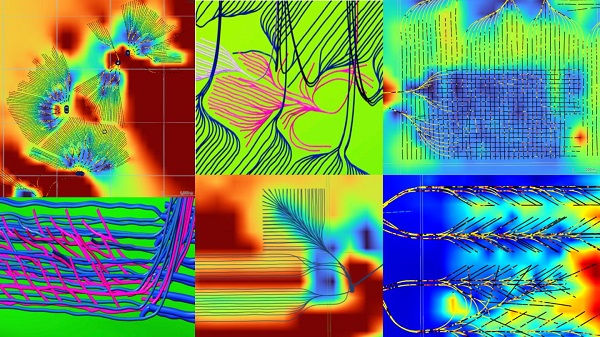
From the Canadian Energy Centre
Multilateral designs lift more energy with a smaller environmental footprint
A “weird and wonderful” drilling innovation in Alberta is helping producers tap more oil and gas at lower cost and with less environmental impact.
With names like fishbone, fan, comb-over and stingray, “multilateral” wells turn a single wellbore from the surface into multiple horizontal legs underground.
“They do look spectacular, and they are making quite a bit of money for small companies, so there’s a lot of interest from investors,” said Calin Dragoie, vice-president of geoscience with Calgary-based Chinook Consulting Services.
Dragoie, who has extensively studied the use of multilateral wells, said the technology takes horizontal drilling — which itself revolutionized oil and gas production — to the next level.
“It’s something that was not invented in Canada, but was perfected here. And it’s something that I think in the next few years will be exported as a technology to other parts of the world,” he said.
Dragoie’s research found that in 2015 less than 10 per cent of metres drilled in Western Canada came from multilateral wells. By last year, that share had climbed to nearly 60 per cent.
Royalty incentives in Alberta have accelerated the trend, and Saskatchewan has introduced similar policy.
Multilaterals first emerged alongside horizontal drilling in the late 1990s and early 2000s, Dragoie said. But today’s multilaterals are longer, more complex and more productive.
The main play is in Alberta’s Marten Hills region, where producers are using multilaterals to produce shallow heavy oil.
Today’s average multilateral has about 7.5 horizontal legs from a single surface location, up from four or six just a few years ago, Dragoie said.
One record-setting well in Alberta drilled by Tamarack Valley Energy in 2023 features 11 legs stretching two miles each, for a total subsurface reach of 33 kilometres — the longest well in Canada.
By accessing large volumes of oil and gas from a single surface pad, multilaterals reduce land impact by a factor of five to ten compared to conventional wells, he said.
The designs save money by skipping casing strings and cement in each leg, and production is amplified as a result of increased reservoir contact.
Here are examples of multilateral well design. Images courtesy Chinook Consulting Services.
Parallel
Fishbone
Fan
Waffle
Stingray
Frankenwells
-

 Uncategorized2 days ago
Uncategorized2 days agoCost of bureaucracy balloons 80 per cent in 10 years: Public Accounts
-

 Daily Caller1 day ago
Daily Caller1 day agoDemocrats Explicitly Tell Spy Agencies, Military To Disobey Trump
-

 Addictions2 days ago
Addictions2 days agoActivists Claim Dealers Can Fix Canada’s Drug Problem
-

 Great Reset1 day ago
Great Reset1 day agoAre climate-obsessed elites losing their grip over global politics?
-

 Indigenous1 day ago
Indigenous1 day agoTop constitutional lawyer slams Indigenous land ruling as threat to Canadian property rights
-

 Carbon Tax2 days ago
Carbon Tax2 days agoCarney fails to undo Trudeau’s devastating energy policies
-

 Daily Caller1 day ago
Daily Caller1 day agoALAN DERSHOWITZ: Can Trump Legally Send Troops Into Our Cities? The Answer Is ‘Wishy-Washy’
-

 Alberta19 hours ago
Alberta19 hours agoAlberta on right path to better health care
















