Business
Apple suing British government to stop them from accessing use data

Quick Hit:
Apple is appealing a UK government order that could force it to create a ‘backdoor’ for authorities to access private user data. The move, pushed by Home Secretary Yvette Cooper, threatens the company’s end-to-end encryption protections. President Trump condemned the demand, comparing it to tactics used in China.
Key Details:
- Apple has lodged an appeal with the UK’s Investigatory Powers Tribunal, challenging an order that could weaken its Advanced Data Protection (ADP) encryption.
- The company previously disabled ADP in Britain rather than comply, arguing that a backdoor would compromise user security.
- UK security agencies argue that encryption helps criminals evade law enforcement, while Apple insists it will never create a ‘master key.’
Diving Deeper:
Apple is grappling with the British government over a surveillance order that could force the company to weaken its own security measures. The tech giant filed an appeal with the Investigatory Powers Tribunal, the court responsible for overseeing the UK’s surveillance laws, after Home Secretary Yvette Cooper pushed for the company to provide a ‘backdoor’ to encrypted user data.
The controversy centers around Apple’s Advanced Data Protection (ADP), an encryption system that prevents even Apple from accessing a user’s iCloud backups. In February, the company disabled ADP in the UK rather than comply with the order. Without ADP, Apple can access and hand over certain iCloud backups, such as iMessages, if legally required. However, with full end-to-end encryption enabled, even Apple cannot retrieve the data. The UK order could force Apple to rewrite its security features, something the company strongly opposes.
Apple has made it clear that it will not compromise user privacy. “We have never built a backdoor or master key to any of our products or services and never will,” the company stated. Apple also warned that creating a backdoor for law enforcement would inevitably make millions of users more vulnerable to cyberattacks.
The UK government, however, argues that such encryption hampers law enforcement investigations, particularly into crimes such as child exploitation and terrorism. A Home Office spokesperson defended the order, stating, “The UK has a longstanding position of protecting our citizens from the very worst crimes while ensuring privacy protections.”
President Donald Trump criticized the UK government’s stance, comparing it to authoritarian surveillance practices. “We told them you can’t do this… That’s something, you know, that you hear about with China,” Trump said.
The case also raises concerns about whether the UK’s actions violate the CLOUD Act, a bilateral agreement between the U.S. and the UK that limits government demands for data on foreign citizens. Reports suggest that U.S. officials are now investigating whether Britain breached this agreement by pressuring Apple to create a ‘backdoor.’
Business
Ted Cruz, Jim Jordan Ramp Up Pressure On Google Parent Company To Deal With ‘Censorship’

From the Daily Caller News Foundation
By Andi Shae Napier
Republican Texas Sen. Ted Cruz and Republican Ohio Rep. Jim Jordan are turning their attention to Google over concerns that the tech giant is censoring users and infringing on Americans’ free speech rights.
Google’s parent company Alphabet, which also owns YouTube, appears to be the GOP’s next Big Tech target. Lawmakers seem to be turning their attention to Alphabet after Mark Zuckerberg’s Meta ended its controversial fact-checking program in favor of a Community Notes system similar to the one used by Elon Musk’s X.
Cruz recently informed reporters of his and fellow senators’ plans to protect free speech.
Dear Readers:
As a nonprofit, we are dependent on the generosity of our readers.
Please consider making a small donation of any amount here. Thank you!
“Stopping online censorship is a major priority for the Commerce Committee,” Cruz said, as reported by Politico. “And we are going to utilize every point of leverage we have to protect free speech online.”
Following his meeting with Alphabet CEO Sundar Pichai last month, Cruz told the outlet, “Big Tech censorship was the single most important topic.”
Jordan, Chairman of the House Judiciary Committee, sent subpoenas to Alphabet and other tech giants such as Rumble, TikTok and Apple in February regarding “compliance with foreign censorship laws, regulations, judicial orders, or other government-initiated efforts” with the intent to discover how foreign governments, or the Biden administration, have limited Americans’ access to free speech.
“Throughout the previous Congress, the Committee expressed concern over YouTube’s censorship of conservatives and political speech,” Jordan wrote in a letter to Pichai in March. “To develop effective legislation, such as the possible enactment of new statutory limits on the executive branch’s ability to work with Big Tech to restrict the circulation of content and deplatform users, the Committee must first understand how and to what extent the executive branch coerced and colluded with companies and other intermediaries to censor speech.”
Jordan subpoenaed tech CEOs in 2023 as well, including Satya Nadella of Microsoft, Tim Cook of Apple and Pichai, among others.
Despite the recent action against the tech giant, the battle stretches back to President Donald Trump’s first administration. Cruz began his investigation of Google in 2019 when he questioned Karan Bhatia, the company’s Vice President for Government Affairs & Public Policy at the time, in a Senate Judiciary Committee hearing. Cruz brought forth a presentation suggesting tech companies, including Google, were straying from free speech and leaning towards censorship.
Even during Congress’ recess, pressure on Google continues to mount as a federal court ruled Thursday that Google’s ad-tech unit violates U.S. antitrust laws and creates an illegal monopoly. This marks the second antitrust ruling against the tech giant as a different court ruled in 2024 that Google abused its dominance of the online search market.
Business
China, Mexico, Canada Flagged in $1.4 Billion Fentanyl Trade by U.S. Financial Watchdog
 Sam Cooper
Sam Cooper
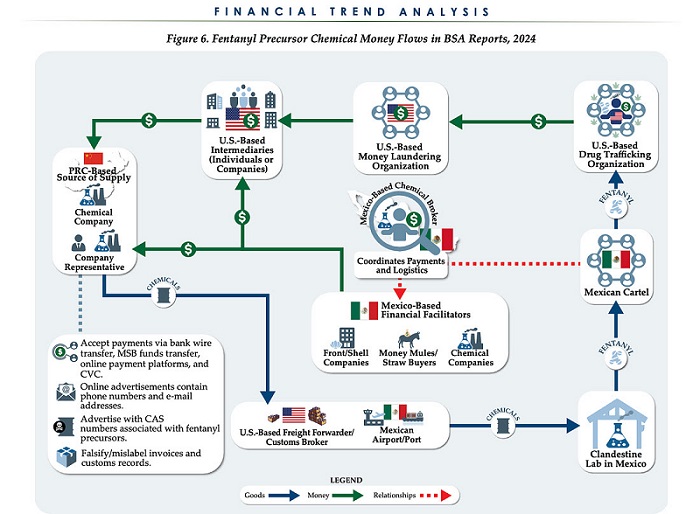
The U.S. Treasury’s Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN) has identified $1.4 billion in fentanyl-linked suspicious transactions, naming China, Mexico, Canada, and India as key foreign touchpoints in the global production and laundering network. The analysis, based on 1,246 Bank Secrecy Act filings submitted in 2024, tracks financial activity spanning chemical purchases, trafficking logistics, and international money laundering operations.
The data reveals that Mexico and the People’s Republic of China were the two most frequently named foreign jurisdictions in financial intelligence gathered by FinCEN. Most of the flagged transactions originated in U.S. cities, the report notes, due to the “domestic nature” of Bank Secrecy Act data collection. Among foreign jurisdictions, Mexico, China, Hong Kong, and Canada were cited most often in fentanyl-related financial activity.
The FinCEN report points to Mexico as the epicenter of illicit fentanyl production, with Mexican cartels importing precursor chemicals from China and laundering proceeds through complex financial routes involving U.S., Canadian, and Hong Kong-based actors.
The findings also align with testimony from U.S. and Canadian law enforcement veterans who have told The Bureau that Chinese state-linked actors sit atop a decentralized but industrialized global fentanyl economy—supplying precursors, pill presses, and financing tools that rely on trade-based money laundering and professional money brokers operating across North America.
“Filers also identified PRC-based subjects in reported money laundering activity, including suspected trade-based money laundering schemes that leveraged the Chinese export sector,” the report says.
A point emphasized by Canadian and U.S. experts—including former U.S. State Department investigator Dr. David Asher—that professional Chinese money laundering networks operating in North America are significantly commanded by Chinese Communist Party–linked Triad bosses based in Ontario and British Columbia—is not explored in detail in this particular FinCEN report.¹
Chinese chemical manufacturers—primarily based in Guangdong, Zhejiang, and Hebei provinces—were repeatedly cited for selling fentanyl precursors via wire transfers and money service businesses. These sales were often facilitated through e-commerce platforms, suggesting that China’s global retail footprint conceals a lethal underground market—one that ultimately fuels a North American public health crisis. In many cases, the logistics were sophisticated: some Chinese companies even offered delivery guarantees and customs clearance for precursor shipments, raising red flags for enforcement officials.
While China’s industrial base dominates the global fentanyl supply chain, Mexican cartels are the next most prominent state-like actors in the ecosystem—but the report emphasizes that Canada and India are rising contributors.
“Subjects in other foreign countries—including Canada, the Dominican Republic, and India—highlight the presence of alternative suppliers of precursor chemicals and fentanyl,” the report says.
“Canada-based subjects were primarily identified by Bank Secrecy Act filers due to their suspected involvement in drug trafficking organizations allegedly sourcing fentanyl and other drugs from traditional drug source countries, such as Mexico,” it explains, adding that banking intelligence “identified activity indicative of Canada-based individuals and companies purchasing precursor chemicals and laboratory equipment that may be related to the synthesis of fentanyl in Canada. Canada-based subjects were primarily reported with addresses in the provinces of British Columbia and Ontario.”
FinCEN also flagged activity from Hong Kong-based shell companies—often subsidiaries or intermediaries for Chinese chemical exporters. These entities were used to obscure the PRC’s role in transactions and to move funds through U.S.-linked bank corridors.
Breaking down the fascinating and deadly world of Chinese underground banking used to move fentanyl profits from American cities back to producers, the report explains how Chinese nationals in North America are quietly enlisted to move large volumes of cash across borders—without ever triggering traditional wire transfers.
These networks, formally known as Chinese Money Laundering Organizations (CMLOs), operate within a global underground banking system that uses “mirror transfers.” In this system, a Chinese citizen with renminbi in China pays a local broker, while the U.S. dollar equivalent is handed over—often in cash—to a recipient in cities like Los Angeles or New York who may have no connection to the original Chinese depositor aside from their role in the laundering network. The renminbi, meanwhile, is used inside China to purchase goods such as electronics, which are then exported to Mexico and delivered to cartel-linked recipients.
FinCEN reports that US-based money couriers—often Chinese visa holders—were observed depositing large amounts of cash into bank accounts linked to everyday storefront businesses, including nail salons and restaurants. Some of the cash was then used to purchase cashier’s checks, a common method used to obscure the origin and destination of the funds. To banks, the activity might initially appear consistent with a legitimate business. However, modern AI-powered transaction monitoring systems are increasingly capable of flagging unusual patterns—such as small businesses conducting large or repetitive transfers that appear disproportionate to their stated operations.
On the Mexican side, nearly one-third of reports named subjects located in Sinaloa and Jalisco, regions long controlled by the Sinaloa Cartel and Cartel Jalisco Nueva Generación. Individuals in these states were often cited as recipients of wire transfers from U.S.-based senders suspected of repatriating drug proceeds. Others were flagged as originators of payments to Chinese chemical suppliers, raising alarms about front companies and brokers operating under false pretenses.
The report outlines multiple cases where Mexican chemical brokers used generic payment descriptions such as “goods” or “services” to mask wire transfers to China. Some of these transactions passed through U.S.-based intermediaries, including firms owned by Chinese nationals. These shell companies were often registered in unrelated sectors—like marketing, construction, or hardware—and exhibited red flags such as long dormancy followed by sudden spikes in large transactions.
Within the United States, California, Florida, and New York were most commonly identified in fentanyl-related financial filings. These locations serve as key hubs for distribution and as collection points for laundering proceeds. Cash deposits and peer-to-peer payment platforms were the most cited methods for fentanyl-linked transactions, appearing in 54 percent and 51 percent of filings, respectively.
A significant number of flagged transactions included slang terms and emojis—such as “blues,” “ills,” or blue dots—in memo fields. Structured cash deposits were commonly made across multiple branches or ATMs, often linked to otherwise legitimate businesses such as restaurants, salons, and trucking firms.
FinCEN also tracked a growing number of trade-based laundering schemes, in which proceeds from fentanyl sales were used to buy electronics and vaping devices. In one case, U.S.-based companies owned by Chinese nationals made outbound payments to Chinese manufacturers, using funds pooled from retail accounts and shell companies. These goods were then shipped to Mexico, closing the laundering loop.
Another key laundering method involved cryptocurrency. Nearly 10 percent of all fentanyl-related reports involved virtual currency, with Bitcoin the most commonly cited, followed by Ethereum and Litecoin. FinCEN flagged twenty darknet marketplaces as suspected hubs for fentanyl distribution and cited failures by some digital asset platforms to catch red-flag activity.
Overall, FinCEN warns that fentanyl-linked funds continue to enter the U.S. financial system through loosely regulated or poorly monitored channels, even as law enforcement ramps up enforcement. The Drug Enforcement Administration reported seizures of over 55 million counterfeit fentanyl pills in 2024 alone.
The broader pattern is unmistakable: precursor chemicals flow from China, manufacturing occurs in Mexico, Canada plays an increasing role in chemical acquisition and potential synthesis, and drugs and proceeds flood into the United States, supported by global financial tools and trade structures. The same infrastructure that enables lawful commerce is being manipulated to sustain the deadliest synthetic drug crisis in modern history.
The Bureau is a reader-supported publication.
To receive new posts and support my work, consider becoming a free or paid subscriber.
Invite your friends and earn rewards
-

 espionage1 day ago
espionage1 day agoEx-NYPD Cop Jailed in Beijing’s Transnational Repatriation Plot, Canada Remains Soft Target
-

 2025 Federal Election2 days ago
2025 Federal Election2 days agoNeil Young + Carney / Freedom Bros
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoDOGE Is Ending The ‘Eternal Life’ Of Government
-

 2025 Federal Election2 days ago
2025 Federal Election2 days agoCanada drops retaliatory tariffs on automakers, pauses other tariffs
-

 2025 Federal Election2 days ago
2025 Federal Election2 days agoTucker Carlson Interviews Maxime Bernier: Trump’s Tariffs, Mass Immigration, and the Oncoming Canadian Revolution
-

 2025 Federal Election1 day ago
2025 Federal Election1 day agoBREAKING from THE BUREAU: Pro-Beijing Group That Pushed Erin O’Toole’s Exit Warns Chinese Canadians to “Vote Carefully”
-
 Daily Caller1 day ago
Daily Caller1 day agoDOJ Releases Dossier Of Deported Maryland Man’s Alleged MS-13 Gang Ties
-

 Health2 days ago
Health2 days agoWHO member states agree on draft of ‘pandemic treaty’ that could be adopted in May