Uncategorized
Amazon’s exit could scare off tech companies from New York

NEW YORK — Amazon jilted New York City on Valentine’s Day, scrapping plans to build a massive headquarters campus in Queens amid fierce opposition from politicians angry about nearly $3 billion in tax breaks and the company’s anti-union stance.
With millions of jobs and a bustling economy, New York can withstand the blow, but experts say the decision by the e-commerce giant to walk away and take with it 25,000 promised jobs could scare off other companies considering moving to or expanding in the city, which wants to be seen as the Silicon Valley of the East Coast.
“One of the real risks here is the message we send to companies that want to come to New York and expand to New York,” said Julie Samuels, the executive director of industry group Tech: NYC. “We’re really playing with fire right now.”
In November, Amazon selected New York City and Crystal City, Virginia, as the winners of a secretive, yearlong process in which more than 230 North American cities bid to become the home of the Seattle-based company’s second headquarters.
New York Mayor Bill de Blasio and Gov. Andrew Cuomo heralded the city’s selection at the time as the biggest boon yet to its burgeoning tech economy and underscored that the deal would generate billions of dollars for improving transit, schools and housing.
Opposition came swiftly though, as details started to emerge.
Critics complained about public subsidies that were offered to Amazon and chafed at some of the conditions of the deal, such as the company’s demand for access to a helipad. Some pleaded for the deal to be renegotiated or scrapped altogether.
“We knew this was going south from the moment it was announced,” said Thomas Stringer, a site selection adviser for big companies. “If this was done right, all the elected officials would have been out there touting how great it was. When you didn’t see that happen, you knew something was wrong.”
Stringer, a managing director of the consulting firm BDO USA LLP, said city and state officials need to rethink the secrecy with which they approached the negotiations. Community leaders and potential critics were kept in the dark, only to be blindsided when details became public.
“It’s time to hit the reset button and say, ‘What did we do wrong?'” Stringer said. “This is fumbling at the 1-yard line.”
Amazon said in a statement Thursday that its commitment to New York City required “positive, collaborative relationships” with state and local officials and that a number of them had “made it clear that they oppose our presence and will not work with us to build the type of relationships that are required to go forward.”
Not that Amazon is blameless, experts say.
Joe Parilla, a fellow at the Brookings Institution’s Metropolitan Policy Program, said the company’s high-profile bidding process may have stoked the backlash. Companies usually search for new locations quietly, in part to avoid the kind of opposition Amazon received.
“They had this huge competition, and the media covered it really aggressively, and a bunch of cities responded,” Parilla said. “What did you expect? It gave the opposition a much bigger platform.”
Richard Florida, an urban studies professor and critic of Amazon’s initial search process, said the company should have expected to feel the heat when it selected New York, a city known for its
“At the end of the day, this is going to hurt Amazon,” said Florida, head of the University of Toronto’s Martin Prosperity Institute. “This is going to embolden people who don’t like corporate welfare across the country.”
Other tech companies have been keeping New York City’s tech economy churning without making much of a fuss.
Google is spending $2.4 billion to build up its Manhattan campus. Cloud-computing company Salesforce has plastered its name on Verizon’s former headquarters in midtown, and music streaming service Spotify is gobbling up space at the World Trade Center complex.
Despite higher costs, New York City remains attractive to tech companies because of its vast, diverse talent pool, world-class educational and cultural institutions and access to other industries, such as Wall Street capital and Madison Avenue ad dollars.
No other metropolitan area in the U.S. has as many computer-related jobs as New York City, which has 225,600, according to the Bureau of Labor Statistics. But San Francisco, San Jose, Seattle, Washington, Boston, Atlanta and Dallas each have a greater concentration of their workers in tech.
In the New York area, the average computer-related job pays roughly $104,000 a year, about $15,000 above the national average. Still, that’s about $20,000 less than in San Francisco.
Even after cancelling its headquarters project, Amazon still has 5,000 employees in New York City, not counting Whole Foods.
“New York has actually done a really great job of growing and supporting its tech ecosystem, and I’m confident that will continue,” Samuels said. “Today we took a step back, but I would not but the nail in the coffin of tech in New York City.”
___
Follow Sisak at www.twitter.com/mikesisak and Boak at www.twitter.com/joshboak .
___
Boak reported from Washington. Associated Press writers Bernard Condon in New York and Chris Rugaber in Washington contributed to this report.
Michael R. Sisak And Josh Boak, The Associated Press
Uncategorized
Trump Admin Establishing Council To Make Buildings Beautiful Again


From the Daily Caller News Foundation
By Jason Hopkins
The Trump administration is creating a first-of-its-kind task force aimed at ushering in a new “Golden Age” of beautiful infrastructure across the U.S.
The Department of Transportation (DOT) will announce the establishment of the Beautifying Transportation Infrastructure Council (BTIC) on Thursday, the Daily Caller News Foundation exclusively learned. The BTIC seeks to advise Transportation Secretary Sean Duffy on design and policy ideas for key infrastructure projects, including highways, bridges and transit hubs.
“What happened to our country’s proud tradition of building great, big, beautiful things?” Duffy said in a statement shared with the DCNF. “It’s time the design for America’s latest infrastructure projects reflects our nation’s strength, pride, and promise.”
“We’re engaging the best and brightest minds in architectural design and engineering to make beautiful structures that move you and bring about a new Golden Age of Transportation,” Duffy continued.
Mini scoop – here is the DOT’s rollout of its Beautifying Transportation Infrastructure Council, which will be tasked with making our buildings beautiful again. pic.twitter.com/
9iV2xSxdJM — Jason Hopkins (@jasonhopkinsdc) October 23, 2025
The DOT is encouraging nominations of the country’s best architects, urban planners, artists and others to serve on the council, according to the department. While ensuring that efficiency and safety remain a top priority, the BTIC will provide guidance on projects that “enhance” public areas and develop aesthetic performance metrics.
The new council aligns with an executive order signed by President Donald Trump in August 2025 regarding infrastructure. The “Making Federal Architecture Beautiful Again” order calls for federal public buildings in the country to “respect regional architectural heritage” and aims to prevent federal construction projects from using modernist and brutalist architecture styles, instead returning to a classical style.
“The Founders, in line with great societies before them, attached great importance to Federal civic architecture,” Trump’s order stated. “They wanted America’s public buildings to inspire the American people and encourage civic virtue.”
“President George Washington and Secretary of State Thomas Jefferson consciously modeled the most important buildings in Washington, D.C., on the classical architecture of ancient Athens and Rome,” the order continued. “Because of their proven ability to meet these requirements, classical and traditional architecture are preferred modes of architectural design.”
The DOT invested millions in major infrastructure projects since Trump’s return to the White House. Duffy announced in August a $43 million transformation initiative of the New York Penn Station in New York City and in September unveiledmajor progress in the rehabilitation and modernization of Washington Union Station in Washington, D.C.
The BTIC will comprise up to 11 members who will serve two-year terms, with the chance to be reappointed, according to the DOT. The task force will meet biannually. The deadline for nominations will end Nov. 21.
Uncategorized
New report warns WHO health rules erode Canada’s democracy and Charter rights

The Justice Centre for Constitutional Freedoms has released a new report titled Canada’s Surrender of Sovereignty: New WHO health regulations undermine Canadian democracy and Charter freedoms. Authored by Nigel Hannaford, a veteran journalist and researcher, the report warns that Canada’s acceptance of the World Health Organization’s (WHO) revised International Health Regulations (IHR) represents a serious erosion of national independence and democratic accountability.
The IHR amendments, which took effect on September 19, 2025, authorize the WHO Director-General to declare global “health emergencies” that could require Canada to follow directives from bureaucrats in Geneva, bypassing the House of Commons and the will of Canadian voters.
The WHO regards these regulations as “binding,” despite having no ability or legal authority to impose such regulations. Even so, Canada is opting to accept the regulations as binding.
By accepting the WHO’s revised IHR, the report explains, Canada has relinquished its own control over future health crises and instead has agreed to let the WHO determine when a “pandemic emergency” exists and what Canada must do to respond to it, after which Canada must report back to the WHO.
In fact, under these International Health Regulations, the WHO could demand countries like Canada impose stringent freedom-violating health policies, such as lockdowns, vaccine mandates, or travel restrictions without debate, evidence review, or public accountability, the report explains.
Once the WHO declares a “Pandemic Emergency,” member states are obligated to implement such emergency measures “without delay” for a minimum of three months.
Importantly, following these WHO directives would undermine government accountability as politicians may hide behind international “commitments” to justify their actions as “simply following international rules,” the report warns.
Canada should instead withdraw from the revised IHR, following the example of countries like Germany, Austria, Italy, Czech Republic, and the United States. The report recommends continued international cooperation without surrendering control over domestic health policies.
Constitutional lawyer Allison Pejovic said, “[b]y treating WHO edicts as binding, the federal government has effectively placed Canadian sovereignty on loan to an unelected international body.”
“Such directives, if enforced, would likely violate Canadians’ Charter rights and freedoms,” she added.
Mr. Hannaford agreed, saying, “Canada’s health policies must be made in Canada. No free and democratic nation should outsource its emergency powers to unelected bureaucrats in Geneva.”
The Justice Centre urges Canadians to contact their Members of Parliament and demand they support withdrawing from the revised IHR to restore Canadian sovereignty and reject blind compliance with WHO directives.
-

 International2 days ago
International2 days agoIs America drifting toward civil war? Joe Rogan thinks so
-

 Business19 hours ago
Business19 hours agoParliamentary Budget Officer begs Carney to cut back on spending
-

 International2 days ago
International2 days agoBondi and Patel deliver explosive “Clinton Corruption Files” to Congress
-

 International1 day ago
International1 day agoState Department designates European Antifa groups foreign terror organizations
-

 International1 day ago
International1 day agoUS announces Operation Southern Spear, targeting narco-terrorists
-

 Censorship Industrial Complex1 day ago
Censorship Industrial Complex1 day agoEU’s “Democracy Shield” Centralizes Control Over Online Speech
-
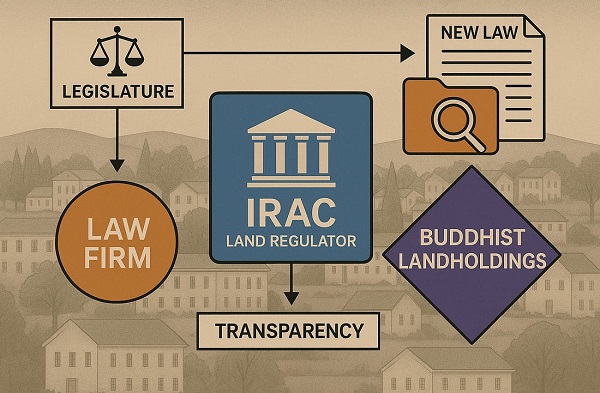
 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoP.E.I. Moves to Open IRAC Files, Forcing Land Regulator to Publish Reports After The Bureau’s Investigation
-
 COVID-192 days ago
COVID-192 days agoMajor new studies link COVID shots to kidney disease, respiratory problems









