Alberta
Alberta Health bringing lab services back “in-house”
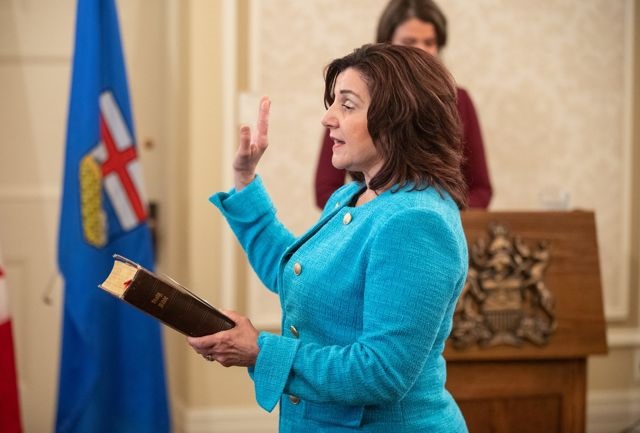

Changes to lab service delivery in Alberta
To improve lab testing and reduce wait times for Albertans, Alberta Precision Laboratories will now deliver community lab services across the province.
Albertans must be able to get the lab tests they need, when and where they need them. Over the past few months, delays and wait times have made accessing lab services very difficult. Since Aug. 3, Alberta Precision Laboratories has provided thousands of additional community lab appointments in Calgary, signifantly reducing wait times. However, it is clear that more needs to be done and Alberta’s government is taking action.
An agreement in principle has been reached with ownership of DynaLIFE to transfer staff, equipment and property in all regions of the province to Alberta Precision Laboratories. This work will be completed in phases with the full transition expected to be completed by December 2023. Albertans will continue to get their lab testing done at the same locations during this transition and additional appointments in Calgary and other areas will continue to be added as planned.
“Lab services are crucial in the diagnosis and treatment of Albertans. It is wholly unacceptable that Albertans had to face long waits and delays to get simple blood work done. I’ve been clear that improving our health care system is a top priority for our government and fixing these delays is one more step we’re taking to ensure Albertans can access the health care they need, when and where they need it, now and into the future.”
Minister LaGrange’s mandate letter from the Premier included direction to resolve unacceptable lab services delays so that Albertans could access timely lab services across the province. As a result, Albertans will have greater access to the lab services they need and end unnecessary delays occurring throughout Calgary and southern Alberta.
“Albertans expect and deserve a world-class health system. This change is an important step to improve and grow lab services, and ensure Albertans have reliable and speedy access to lab testing in their communities, particulary to enable timely diagnosis and treatment. I want to thank all the health care workers who have been providing lab services, I appreciate your efforts to continue meeting the health needs of Albertans during the transition and beyond.”
All existing appointments and lab services will continue to be provided as scheduled and additional capacity will be added in the immediate future. At this time, Albertans can continue to book their lab appointments online or by calling 1-877-702-4486.
“Our focus is on patients and ensuring the safety, accessibility and stability of lab services. We understand and appreciate the challenges that some Albertans have faced with lab services in recent months and we are dedicated to addressing these concerns. We thank all DynaLIFE team members for their continued commitment. We respect their insight and will work closely with them to incorporate feedback and support their transition to Alberta Precision Laboratories.”
Quick facts
- Alberta Precision Laboratories was formed in 2018. Since December 2022, it has operated only in Alberta hospitals, urgent care centres and in rural communities where there are no additional community lab located.
- Since Aug. 3, Alberta Precision Laboratories has taken action to add additional weekly appointments, particularly in the Calgary area, by adding new appointments weekly within their hospital lab system and hiring more staff.
Related links
- Online booking for lab appointments
Alberta
Low oil prices could have big consequences for Alberta’s finances

From the Fraser Institute
By Tegan Hill
Amid the tariff war, the price of West Texas Intermediate oil—a common benchmark—recently dropped below US$60 per barrel. Given every $1 drop in oil prices is an estimated $750 million hit to provincial revenues, if oil prices remain low for long, there could be big implications for Alberta’s budget.
The Smith government already projects a $5.2 billion budget deficit in 2025/26 with continued deficits over the following two years. This year’s deficit is based on oil prices averaging US$68.00 per barrel. While the budget does include a $4 billion “contingency” for unforeseen events, given the economic and fiscal impact of Trump’s tariffs, it could quickly be eaten up.
Budget deficits come with costs for Albertans, who will already pay a projected $600 each in provincial government debt interest in 2025/26. That’s money that could have gone towards health care and education, or even tax relief.
Unfortunately, this is all part of the resource revenue rollercoaster that’s are all too familiar to Albertans.
Resource revenue (including oil and gas royalties) is inherently volatile. In the last 10 years alone, it has been as high as $25.2 billion in 2022/23 and as low as $2.8 billion in 2015/16. The provincial government typically enjoys budget surpluses—and increases government spending—when oil prices and resource revenue is relatively high, but is thrown into deficits when resource revenues inevitably fall.
Fortunately, the Smith government can mitigate this volatility.
The key is limiting the level of resource revenue included in the budget to a set stable amount. Any resource revenue above that stable amount is automatically saved in a rainy-day fund to be withdrawn to maintain that stable amount in the budget during years of relatively low resource revenue. The logic is simple: save during the good times so you can weather the storm during bad times.
Indeed, if the Smith government had created a rainy-day account in 2023, for example, it could have already built up a sizeable fund to help stabilize the budget when resource revenue declines. While the Smith government has deposited some money in the Heritage Fund in recent years, it has not created a dedicated rainy-day account or introduced a similar mechanism to help stabilize provincial finances.
Limiting the amount of resource revenue in the budget, particularly during times of relatively high resource revenue, also tempers demand for higher spending, which is only fiscally sustainable with permanently high resource revenues. In other words, if the government creates a rainy-day account, spending would become more closely align with stable ongoing levels of revenue.
And it’s not too late. To end the boom-bust cycle and finally help stabilize provincial finances, the Smith government should create a rainy-day account.
Alberta
Governments in Alberta should spur homebuilding amid population explosion

From the Fraser Institute
By Tegan Hill and Austin Thompson
In 2024, construction started on 47,827 housing units—the most since 48,336 units in 2007 when population growth was less than half of what it was in 2024.
Alberta has long been viewed as an oasis in Canada’s overheated housing market—a refuge for Canadians priced out of high-cost centres such as Vancouver and Toronto. But the oasis is starting to dry up. House prices and rents in the province have spiked by about one-third since the start of the pandemic. According to a recent Maru poll, more than 70 per cent of Calgarians and Edmontonians doubt they will ever be able to afford a home in their city. Which raises the question: how much longer can this go on?
Alberta’s housing affordability problem reflects a simple reality—not enough homes have been built to accommodate the province’s growing population. The result? More Albertans competing for the same homes and rental units, pushing prices higher.
Population growth has always been volatile in Alberta, but the recent surge, fuelled by record levels of immigration, is unprecedented. Alberta has set new population growth records every year since 2022, culminating in the largest-ever increase of 186,704 new residents in 2024—nearly 70 per cent more than the largest pre-pandemic increase in 2013.
Homebuilding has increased, but not enough to keep pace with the rise in population. In 2024, construction started on 47,827 housing units—the most since 48,336 units in 2007 when population growth was less than half of what it was in 2024.
Moreover, from 1972 to 2019, Alberta added 2.1 new residents (on average) for every housing unit started compared to 3.9 new residents for every housing unit started in 2024. Put differently, today nearly twice as many new residents are potentially competing for each new home compared to historical norms.
While Alberta attracts more Canadians from other provinces than any other province, federal immigration and residency policies drive Alberta’s population growth. So while the provincial government has little control over its population growth, provincial and municipal governments can affect the pace of homebuilding.
For example, recent provincial amendments to the city charters in Calgary and Edmonton have helped standardize building codes, which should minimize cost and complexity for builders who operate across different jurisdictions. Municipal zoning reforms in Calgary, Edmonton and Red Deer have made it easier to build higher-density housing, and Lethbridge and Medicine Hat may soon follow suit. These changes should make it easier and faster to build homes, helping Alberta maintain some of the least restrictive building rules and quickest approval timelines in Canada.
There is, however, room for improvement. Policymakers at both the provincial and municipal level should streamline rules for building, reduce regulatory uncertainty and development costs, and shorten timelines for permit approvals. Calgary, for instance, imposes fees on developers to fund a wide array of public infrastructure—including roads, sewers, libraries, even buses—while Edmonton currently only imposes fees to fund the construction of new firehalls.
It’s difficult to say how long Alberta’s housing affordability woes will endure, but the situation is unlikely to improve unless homebuilding increases, spurred by government policies that facilitate more development.
-

 2025 Federal Election1 day ago
2025 Federal Election1 day agoColumnist warns Carney Liberals will consider a home equity tax on primary residences
-

 2025 Federal Election1 day ago
2025 Federal Election1 day agoNine Dead After SUV Plows Into Vancouver Festival Crowd, Raising Election-Eve Concerns Over Public Safety
-

 2025 Federal Election1 day ago
2025 Federal Election1 day agoMark Carney: Our Number-One Alberta Separatist
-

 International1 day ago
International1 day agoJeffrey Epstein accuser Virginia Giuffre reportedly dies by suicide
-

 COVID-1910 hours ago
COVID-1910 hours agoFormer Australian state premier accused of lying about justification for COVID lockdowns
-

 2025 Federal Election1 day ago
2025 Federal Election1 day agoCanada is squandering the greatest oil opportunity on Earth
-

 International21 hours ago
International21 hours agoU.S. Army names new long-range hypersonic weapon ‘Dark Eagle’
-
 Business20 hours ago
Business20 hours agoTrump demands free passage for American ships through Panama, Suez








