Business
Companies Scrambling To Respond To Trump’s ‘Beautiful’ Tariff Hikes

 From the Daily Caller News Foundation
From the Daily Caller News Foundation
By Adam Pack
Companies are scrambling to respond to President-elect Donald Trump’s “beautiful” tariff proposals that his administration may seek to enact early in his second term.
Proactive steps that companies are taking to evade anticipated price increases include stockpiling inventory in U.S. warehouses and weighing whether they need to completely eliminate China from their supply chains and raise the price of imported goods affected by tariff hikes, whose costs will be passed onto consumers.
Free-trade skeptics are touting companies’ anticipatory actions as delivering a clear sign that Trump’s proposed tariff hikes are already achieving their intended effect of pressuring retailers to eliminate China from their supply chains. However, some policy experts are warning that higher tariffs will be a regressive tax for America’s lower and middle-income families and make inflation worse, according to retailers and economists who spoke to the Daily Caller News Foundation.
On the campaign trail, Trump proposed a universal tariff of up to 20% on all imports coming into the U.S. and a 60% or higher tariff on all imports from China. Trump is considering Robert Lighthizer, the former U.S. trade representative during his administration’s first term who is well-known for favoring high tariffs, to serve as his second administration’s trade czar, the Wall Street Journal first reported.
PRESIDENT TRUMP: "The word tariff to me is a very beautiful word because it can save our country, truly… I saved our steel industries by putting tariffs on steel that China came in and dumped… They had committees that were put in charge of what to do with the money. We were… pic.twitter.com/jj88zenMRP
— Trump War Room (@TrumpWarRoom) October 2, 2024
‘Mitigation Strategies To Lessen The Impact’
Companies are taking preemptive measures, such as stockpiling goods in U.S. warehouses, to work proactively against anticipated price increases that higher tariffs would inflict, Jonathan Gold, vice president of supply chains and customs policy for the National Retail Federation, told the DCNF during an interview.
“They’re looking at different mitigation strategies to lessen the impact that they might feel from the tariffs,” Gold told the DCNF. “One of those strategies is to start looking at potentially bringing in cargo, bringing products earlier to get ahead of potential tariffs that Trump might put in place.”
Importing goods into the U.S. ahead of schedule leads to additional costs for retailers that will likely be passed onto consumers, but waiting to import goods from China after a 60% or higher tariff on Chinese imports goes into effect would be substantially more expensive, according to Gold.
A recent NRF study projected that Trump’s proposed tariff hikes on consumer products would cost American consumers an additional $46 billion to $78 billion a year.
“A tariff is a tax paid by the U.S. importer, not a foreign country or the exporter,” Gold said in a press release accompanying the study. “This tax ultimately comes out of consumers’ pockets through higher prices.”
Decoupling From China
Part of the rationale behind Trump’s tariff proposals is to force manufacturing jobs to return to the United States and pressure companies to completely eliminate China from their supply chains, according to Mark DiPlacido, policy advisor at American Compass.
“I hope in addition to stockpiling, they’re also looking at actually moving their supply chains out of China and ideally back to the United States,” DiPlacido told the DCNF.
“For a long time, the framing has been what is best for just increasing trade flows, regardless of the direction those flows are going. What that’s resulted in for the last 25 years is a flow of manufacturing, a flow of factories and a flow of jobs, especially solid middle class jobs out of the United States and across the world,” DiPlacido added.
But completely shifting production outside of China is not feasible for some retailers even if companies have taken further steps to diversify their supply chain for the past decade, according to Gold.
“It takes a while to make those shifts and not everyone is able to do that, Gold acknowledged. “Nobody has the [production] capacity that China does. Trying to find that within multiple countries is a challenge. And it’s not just the capacity, but the skilled workforce as well.”
In addition, companies who move production out of China to avoid a 60% tariff on imported goods from the nation could still get hit by a 20% across the board tariff if they move their supply chain to countries other than the United States, Gold and several economists told the DCNF.
“They’re talking about tariffs on imports for which there’s not a domestic producer to switch to,” Clark Packard, a research fellow on trade policy at the CATO institute, told the DCNF in an interview. “For example, we don’t make coffee in the United States, so why are we going to impose a tariff on coffee?”
“Who are we trying to protect?” he added.
Some economists are also pessimistic that the president-elect’s planned tariff hikes will ultimately bring jobs that moved overseas to cheaper labor markets back to the United States.
“What we actually saw from the 2018-2019 trade war was a decrease in manufacturing output and employment because of the tariffs,” Erica York, senior economist and research director of the Tax Foundation’s Center for Federal Tax Policy, told the DCNF in an interview. “It played out just like every economist predicted: higher costs for U.S. consumers, reduced output, reduced incomes for American workers, foreign retaliation that’s harmful.”
The president-elect’s proposed tariff hikes could also eliminate more jobs than those saved or created as a result of protecting domestic industries, such as the U.S. steel or solar manufacturing industries, that may benefit from higher tariffs on foreign competitors, Packard told the DCNF.
“It’s disproportionate — the cost that is passed onto the broader economy to protect a very small slice of U.S. employment,” Packard said. Trump’s 25% tariff on imported steel enacted during his first administration slightly increased employment in the U.S. steel industry, but each job that was maintained or created came at a cost of roughly $650,000 that likely killed jobs in other sectors forced to buy more expensive steel, according to Packard.
‘Bipartisan Recognition’
Despite tariffs’ potential to force companies to raise the price of goods they import into the United States, DiPlacido defended Trump’s proposed tariff hikes as essential to eliminating U.S. dependence on China for a variety of strategic goods and consumer products.
“We need to be able to manufacture a broad range of goods in the United States. And we need the job security and the economic security that a strong manufacturing industrial base provides,” DiPlacido said. “That’s going to be important to any future conflict or emergency that the United States may have with China or with anyone else.”
DiPlacido, citing Trump’s dominant electoral performance, also believes Trump has the “mandate” to carry out the tariff proposals he floated during the campaign.
“There’s a sort of a bipartisan recognition of the problem. Even the Biden administration kept almost all of Trump’s tariffs in place,” DiPlacido told the DCNF. “I think he has the political mandate, and that’s often a harder thing to get.”
However, some economists are questioning whether the thousands of dollars of projected costs that American families would be forced to pay as a result of these tariff hikes could create political backlash that has so far failed to materialize against Trump and Biden’s relatively similar trade policies.
“Voters were rightly pretty upset about price increases and inflation,” Packard told the DCNF. “We’re talking about utilizing a tool in tariffs that will increase relative prices.”
“Tariffs as a whole are a regressive tax,” Gold told the DCNF. “They certainly hit low and middle income consumers the hardest.”
Retailers are forecasting a decrease in demand for consumer products as a result of Trump’s tariff proposals, according to Gold.
The incoming Senate Republican leader has also notably criticized Trump’s proposed tariff hikes.
“I get concerned when I hear we just want to uniformly impose a 10% or 20% tariff on everything that comes into the United States,” Republican South Dakota Sen. John Thune, Senate GOP leader, said in August during a panel on agriculture policy in his home state. “Generally, that’s a recipe for increased inflation.”
2025 Federal Election
Canada drops retaliatory tariffs on automakers, pauses other tariffs

 MxM News
MxM News
Quick Hit:
Canada has announced it will roll back retaliatory tariffs on automakers and pause several other tariff measures aimed at the United States. The move, unveiled by Finance Minister François-Philippe Champagne, is designed to give Canadian manufacturers breathing room to adjust their supply chains and reduce reliance on American imports.
Key Details:
- Canada will suspend 25% tariffs on U.S. vehicles for automakers that maintain production, employment, and investment in Canada.
- A broader six-month pause on tariffs for other U.S. imports is intended to help Canadian sectors transition to domestic sourcing.
- A new loan facility will support large Canadian companies that were financially stable before the tariffs but are now struggling.
Diving Deeper:
Ottawa is shifting its approach to the escalating trade war with Washington, softening its economic blows in a calculated effort to stabilize domestic manufacturing. On Tuesday, Finance Minister François-Philippe Champagne outlined a new set of trade policies that provide conditional relief from retaliatory tariffs that have been in place since March. Automakers, the hardest-hit sector, will now be eligible to import U.S. vehicles duty-free—provided they continue to meet criteria that include ongoing production and investment in Canada.
“From day one, the government has reacted with strength and determination to the unjust tariffs imposed by the United States on Canadian goods,” Champagne stated. “We’re giving Canadian companies and entities more time to adjust their supply chains and become less dependent on U.S. suppliers.”
The tariff battle, which escalated in April with Canada slapping a 25% tax on U.S.-imported vehicles, had caused severe anxiety within Canada’s auto industry. John D’Agnolo, president of Unifor Local 200, which represents Ford employees in Windsor, warned the BBC the situation “has created havoc” and could trigger a recession.
Speculation about a possible Honda factory relocation to the U.S. only added to the unrest. But Ontario Premier Doug Ford and federal officials were quick to tamp down the rumors. Honda Canada affirmed its commitment to Canadian operations, saying its Alliston facility “will operate at full capacity for the foreseeable future.”
Prime Minister Mark Carney reinforced the message that the relief isn’t unconditional. “Our counter-tariffs won’t apply if they (automakers) continue to produce, continue to employ, continue to invest in Canada,” he said during a campaign event. “If they don’t, they will get 25% tariffs on what they are importing into Canada.”
Beyond the auto sector, Champagne introduced a six-month tariff reprieve on other U.S. imports, granting time for industries to explore domestic alternatives. He also rolled out a “Large Enterprise Tariff Loan Facility” to support big businesses that were financially sound prior to the tariff regime but have since been strained.
While Canada has shown willingness to ease its retaliatory measures, there’s no indication yet that the U.S. under President Donald Trump will reciprocate. Nevertheless, Ottawa signaled its openness to further steps to protect Canadian businesses and workers, noting that “additional measures will be brought forward, as needed.”
Business
DOGE Is Ending The ‘Eternal Life’ Of Government


From the Daily Caller News Foundation
By David Bossie
In his 1964 “A Time For Choosing” speech, Ronald Reagan famously said, “a government bureau is the nearest thing to eternal life we’ll ever see on this earth.” And for more than 60 years, President Reagan’s words have proven to be true. However, with the historic re-election of President Donald Trump and the creation of the Department of Government Efficiency (DOGE) under the leadership of Elon Musk, the Gipper’s contention is finally being challenged – and not a moment too soon.
The Trump Administration inherited a horribly bloated federal government in dire need of common sense streamlining from top to bottom. For decades, the executive branch has expanded at an incomprehensible rate and along with it, so has waste, fraud, and abuse. Presidents on both sides of the aisle have made promises to tighten the government’s belt, shrink the bureaucracy, and return power to the people where it belongs. Those efforts for the most part – however well-intentioned – never got off the ground. The reality is that when politicians have been forced to choose between a legislative priority and cutting government spending, cuts are always the first casualty. But currently, with our $36 trillion national debt spiraling out of control, reining in the size and scope of government is no longer a choice, but a necessity.
President Trump is the perfect leader for these trying times. He’s battletested and fears nothing – and no challenge is too large. Whether it’s securing the border, growing the economy, forging peace in Ukraine and the Middle East, or negotiating fair trade deals, this president is on a mission to save America. And if any chief executive is going to have success at deconstructing the administrative state, it’s Trump the steel-spined change agent. The shadowy deep state doesn’t scare him, the biased liberal media can’t intimidate him, and this time there are no phony partisan investigations aiming to sidetrack him. Trump made a promise to bring fiscal responsibility back to governing, and along with Musk and DOGE, they’re finally conducting the “audit with teeth” that the American people have been waiting for, and their hard work is turning out to be infectious.
Dear Readers:
As a nonprofit, we are dependent on the generosity of our readers.
Please consider making a small donation of any amount here. Thank you!
With each passing day, a different member of the cabinet is announcing a new cut, discovering a duplicative program, or updating an antiquated system to steer us away from the fiscal cliff that’s rapidly approaching. When the president also happens to be a highly successful businessman, making the business operate more smoothly and for less money is the name of the game. Trump has brought this mindset to the White House and according to recent polling 77 percent favor a full review of government spending.
President Trump is going back to the basics that have become taboo in Washington, like asking fundamental questions about whether an agency has been successful in its mission or if a program is still necessary. In the case of the Education Department, Trump sees an emergency and is not willing to kick the can down the road any longer. The president believes that education excellence for our children is essential so America can compete for generations to come. Drastic reform is long overdue and that means moving education decisions back to state and local officials – and parents. That’s why President Trump is taking the steps to confront the failed status quo and close the underperforming department so we can turnaround lackluster public schools and low-test scores.
Similarly, with the decision to end USAID and slash foreign aid, Trump and DOGE are simply putting America first. America is handing out billions upon billions in taxpayer dollars around the globe on programs that should be spent on fixing our own domestic problems. The plan to decentralize and modernize the Agriculture Department is another great example of thinking outside the box. The American people understand the rationale that downtown Washington, D.C. is the last place decisions about farming should be made. Relocating the department to various hubs around the heartland is common sense.
Additionally, the announcement that the Department of Health and Human Services will cut 20,000 full-time employees is part of President Trump’s vision to “right-size the federal government and unleash the private sector again” in the words of Treasury Secretary Scott Bessent. And word that the Trump Administration is planning to work with Congress to finally defund National Public Radio and the Public Broadcasting Service is welcome news to millions of Americans who believe sending taxpayer funds to biased news outlets is wrong.
DOGE is also doing courageous work at the Social Security Administration (SSA). The amazing efforts to identify individuals who are either deceased, in the country illegally, or otherwise ineligible will help stave off the program’s insolvency, which experts predict is only ten years away. When a DOGE official disclosed that 40 percent of the calls made to SSA are from would-be fraudsters trying to exploit the system, it’s become all too obvious that new safeguards must be adopted.
When it comes to the question of how much money DOGE will ultimately end up saving taxpayers, in the context of our $36 trillion debt crisis, the more the better. However, the overall change in mindset – forcing government to operate efficiently and responsibly like businesses and families – and passing that mindset onto future administrations is perhaps the most critical shift that can be made. In fact, in an ideal scenario, every state, county, and city would have its very own DOGE operation. We must get serious about cutting government waste now or we’ll go bankrupt. That’s just the reality of the situation and President Trump knows it.
David Bossie is the president of Citizens United and served as a senior adviser to the Trump-Pence 2020 campaign. In 2016, Bossie served as deputy campaign manager for Donald J. Trump for President and deputy executive director for the Trump-Pence Transition Team.
-
 illegal immigration2 days ago
illegal immigration2 days agoDespite court rulings, the Trump Administration shows no interest in helping Abrego Garcia return to the U.S.
-

 2025 Federal Election2 days ago
2025 Federal Election2 days agoEuthanasia is out of control in Canada, but nobody is talking about it on the campaign trail
-

 2025 Federal Election2 days ago
2025 Federal Election2 days agoConservative MP Leslyn Lewis warns Canadian voters of Liberal plan to penalize religious charities
-
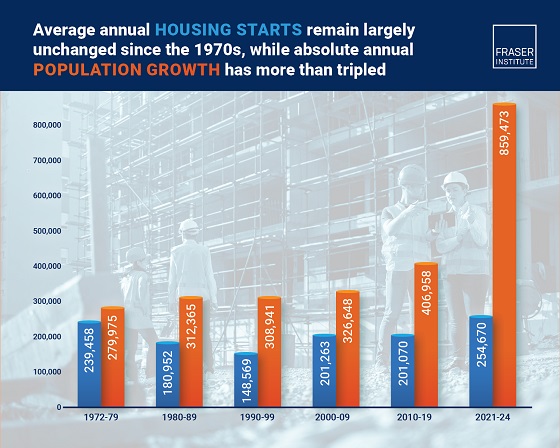
 2025 Federal Election2 days ago
2025 Federal Election2 days agoHousing starts unchanged since 1970s, while Canadian population growth has more than tripled
-

 2025 Federal Election19 hours ago
2025 Federal Election19 hours agoRCMP Whistleblowers Accuse Members of Mark Carney’s Inner Circle of Security Breaches and Surveillance
-

 Education2 days ago
Education2 days agoSchools should focus on falling math and reading grades—not environmental activism
-

 Autism1 day ago
Autism1 day agoAutism Rates Reach Unprecedented Highs: 1 in 12 Boys at Age 4 in California, 1 in 31 Nationally
-

 Bjorn Lomborg1 day ago
Bjorn Lomborg1 day agoGlobal Warming Policies Hurt the Poor






