Business
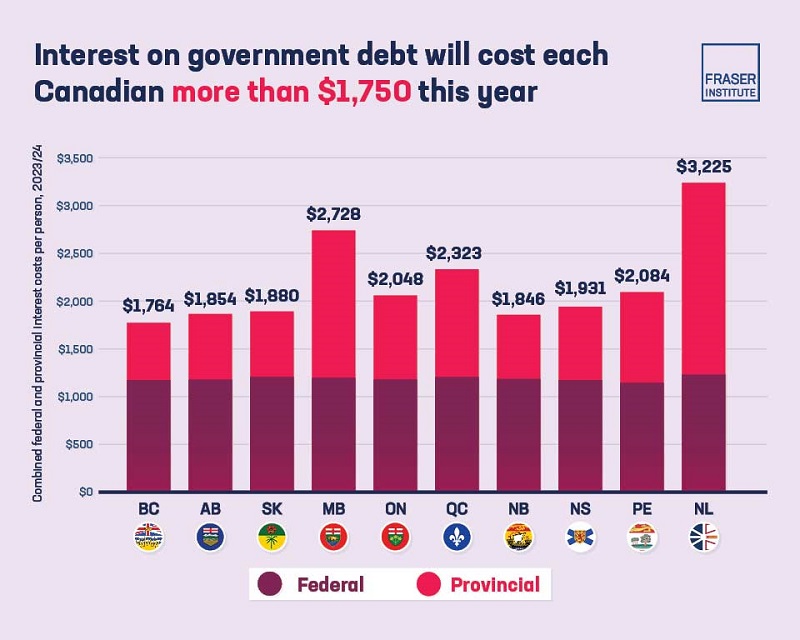
Canadians in every province will pay more than $1,750 per person in 2023-24 on government interest costs amounting to $81.8 billion
From the Fraser Institute
By Jake Fuss and Grady Munro
Canadians in every province will pay more than $1,750 per person in 2023/24 on government interest costs, finds a new study published by the Fraser Institute, an independent, non-partisan Canadian public policy think-tank.
“Interest must be paid on government debt, and the more money governments spend on interest payments the less money is available for the programs and services that matter to Canadians,” said Jake Fuss, director of fiscal studies at the Fraser Institute and author of Federal and Provincial Debt Interest Costs for Canadians, 2024 edition.
The study finds that taxpayers across Canada will pay a total of $81.8 billion on interest payments for the federal and provincial debts this year alone. The federal government will spend $46.5 billion on debt servicing charges in 2023/24, which is more than the government expects to spend on childcare benefits ($31.2 billion) and almost as much as the Canada Health Transfer ($49.4 billion).

Nationally, Newfoundland and Labrador’s combined federal and provincial interest costs is the highest in the country at $3,225 per person. Manitoba is the next highest at $2,728 per person.
Meanwhile, total expenditures on interest costs for Albertans ($8.6 billion) and Ontarians ($31.5 billion) are nearly equivalent to expected spending on K-12 education in their respective provinces this year.
“Even before the COVID-19 pandemic and recession, governments across Canada and in Ottawa were racking up large debts, and this debt imposes real costs on Canadian taxpayers in the form of interest payments,” said Fuss. “Interest payments across the country are substantial, and that takes money away from other important priorities.”
- In recent years, deficit spending and growing government debt have become a trend for many Canadian governments. Like households, governments are required to pay interest on their debt.
- In aggregate, the provinces and federal government are expected to spend $81.8 billion on interest payments in 2023/24.
- Residents in Newfoundland & Labrador face by far the highest combined federal-provincial interest payments per person ($3,225). Manitoba is the next highest at $2,728 per person.
- The federal government will spend $46.5 billion on debt servicing charges in 2023/24, which is nearly what the government expects to spend on the Canada Health Transfer ($49.4 billion), and significantly more than it expects to spend on childcare benefits ($31.2 billion).
- Combined federal-provincial interest costs in Ontario ($31.5 billion), Quebec ($20.3 billion), and Alberta ($8.6 billion) are nearly as much, or more than, what these provinces will spend on K-12 education in 2023/24.
- Meanwhile, combined federal-provincial interest costs for British Columbians ($9.6 billion) are higher than what the province expects to spend on its social services this year.
Authors:
More from this study
The Fraser Institute is an independent Canadian public policy research and educational organization with offices in Vancouver, Calgary, Toronto, and Montreal and ties to a global network of think-tanks in 87 countries. Its mission is to improve the quality of life for Canadians, their families and future generations by studying, measuring and broadly communicating the effects of government policies, entrepreneurship and choice on their well-being. To protect the Institute’s independence, it does not accept grants from governments or contracts for research. Visit www.fraserinstitute.org
Business
Trump: China’s tariffs to “come down substantially” after negotiations with Xi

 MxM News
MxM News
Quick Hit:
President Trump said the 145% tariff rate on Chinese imports will drop significantly once a deal is struck with Chinese President Xi Jinping, expressing confidence that a new agreement is on the horizon.
Key Details:
- Trump said the current 145% tariff rate on China “won’t be anywhere near that high” after negotiations.
- He pointed to his relationship with Xi Jinping as a reason for optimism.
- The White House said it is preparing the groundwork for a deal, and Treasury officials expect a “de-escalation” of the trade war.
Diving Deeper:
President Donald Trump on Tuesday told reporters that the steep tariff rate currently imposed on Chinese imports will come down substantially after his administration finalizes a new trade deal with Chinese President Xi Jinping. While the current level stands at 145%, Trump made clear that number was temporary and would be adjusted following talks with Beijing.
“145 percent is very high. It won’t be that high, it’s not going to be that high … it won’t be anywhere near that high,” Trump said from the Oval Office, signaling a shift once a bilateral agreement is reached. “It will come down substantially, but it won’t be zero.”
The tariff, which Trump previously described as “reciprocal,” was maintained on China even after he delayed similar penalties on other trading partners. Those were cut to 10% and paused for 90 days to allow room for further negotiation.
“We’re going to be very nice. They’re going to be very nice, and we’ll see what happens. But ultimately, they have to make a deal because otherwise they’re not going to be able to deal in the United States,” Trump said, reinforcing his view that the U.S. holds the leverage.
Trump’s remarks come as markets remain wary of ongoing trade tensions, though the White House signaled progress, saying it is “setting the stage for a deal with China.” The president cited his personal rapport with Xi Jinping as a key factor in his confidence that an agreement can be reached.
“China was taking us for a ride, and it’s not going to happen,” Trump said. “They would make billions a year off us and build up their military with our money. That’s over. But we’ll still be good to China, and I think we’ll work together.”
Treasury Secretary Scott Bessent also said Tuesday that he expects a cooling of trade hostilities between the two nations, according to several reports from a private meeting with investors.
As the 90-day pause on other reciprocal tariffs nears its end, Trump emphasized that his team is prepared to finalize deals quickly. “We’ve been in talks with many, many world leaders,” he said, expressing confidence that talks will “go pretty quickly.”
White House Press Secretary Karoline Leavitt added that the administration has received 18 formal proposals from other countries engaged in trade negotiations, another sign that momentum is building behind Trump’s broader push to restructure global trade in favor of American workers and businesses.
(Li Xueren/Xinhua via AP)
2025 Federal Election
Next federal government should end corporate welfare for forced EV transition

From the Fraser Institute
By Tegan Hill and Jake Fuss
Corporate welfare simply shifts jobs and investment away from other firms and industries—which are more productive, as they don’t require government funding to be economically viable—to the governments’ preferred industries and firms, circumventing the preferences of consumers and investors. And since politicians spend other people’s money, they have little incentive to be careful investors.
General Motors recently announced the temporary closure of its electric vehicle (EV) manufacturing plant in Ontario, laying off 500 people because its new EV isn’t selling. The plant will shut down for six months despite hundreds of millions in government subsides financed by taxpayers. This is just one more example of corporate welfare—when governments subsidize favoured industries and companies—and it’s time for the provinces and the next federal government to eliminate it.
Between the federal government and Ontario government, GM received about $500 million to help fund its EV transition. But this is just one example of corporate welfare in the auto sector. Stellantis and Volkswagen will receive about $28 billion in government subsidies while Honda is promised $5 billion.
More broadly, from 2007 to 2019, the last pre-COVID year of data, the federal government spent an estimated $84.6 billion (adjusted for inflation) on corporate welfare while provincial and local governments spent another $302.9 billion. And crucially, these numbers exclude other forms of government support such as loan guarantees, direct investments and regulatory privileges, so the actual cost of corporate welfare during this period was much higher.
Of course, politicians claim that corporate welfare benefits workers. Yet according to a significant body of research, corporate welfare fails to generate widespread economic benefit. Think of it this way—if the businesses that received subsidies were viable to begin with, they wouldn’t need government support. So unprofitable companies are kept in business through governments’ support, which can prevent resources, including investment and workers, from moving to profitable companies, hurting overall economic growth.
Put differently, rather than fuelling economic growth, corporate welfare simply shifts jobs and investment away from other firms and industries—which are more productive, as they don’t require government funding to be economically viable—to the governments’ preferred industries and firms, circumventing the preferences of consumers and investors. And since politicians spend other people’s money, they have little incentive to be careful investors.
Governments also must impose higher tax rates on everyone else to pay for corporate welfare. In turn, higher tax rates discourage entrepreneurship and business investment—again, which fuels economic growth. And the higher the tax rates, the more economic activity they discourage.
GM’s EV plant shut down once again proves that when governments try to engineer the economy with corporate welfare, workers will ultimately lose. It’s time for the provinces and the next federal government—whoever it may be—to finally put an end to this costly and ineffective policy approach.
-

 2025 Federal Election1 day ago
2025 Federal Election1 day agoOttawa Confirms China interfering with 2025 federal election: Beijing Seeks to Block Joe Tay’s Election
-

 2025 Federal Election24 hours ago
2025 Federal Election24 hours agoBREAKING: THE FEDERAL BRIEF THAT SHOULD SINK CARNEY
-

 2025 Federal Election1 day ago
2025 Federal Election1 day agoHow Canada’s Mainstream Media Lost the Public Trust
-

 2025 Federal Election1 day ago
2025 Federal Election1 day agoReal Homes vs. Modular Shoeboxes: The Housing Battle Between Poilievre and Carney
-

 2025 Federal Election1 day ago
2025 Federal Election1 day agoCHINESE ELECTION THREAT WARNING: Conservative Candidate Joe Tay Paused Public Campaign
-

 John Stossel1 day ago
John Stossel1 day agoClimate Change Myths Part 2: Wildfires, Drought, Rising Sea Level, and Coral Reefs
-

 Business22 hours ago
Business22 hours ago‘Great Reset’ champion Klaus Schwab resigns from WEF
-

 COVID-191 day ago
COVID-191 day agoNearly Half of “COVID-19 Deaths” Were Not Due to COVID-19 – Scientific Reports Journal








