Alberta
Canada’s health-care wait times hit 27.7 weeks in 2023—longest ever recorded

From the Fraser Institute
By Mackenzie Moir and Bacchus Barua
Canadian patients waited longer than ever this year for medical treatment, finds a new study released by the Fraser Institute, an independent, non-partisan Canadian public policy think-tank.
The study, an annual survey of physicians across Canada, reports a median wait time of 27.7 weeks—the longest ever recorded, longer than the wait of 27.4 weeks reported in 2022—and 198 per cent higher than the 9.3 weeks Canadians waited in 1993, when the Fraser Institute began tracking wait times.

“COVID-19 and related hospital closures have exacerbated, but are not the cause, of Canada’s historic wait times challenges,” said Bacchus Barua, director of the Fraser Institute’s Centre for Health Policy Studies and co-author of Waiting Your Turn: Wait Times for Health Care in Canada, 2023.
“Previous results revealed that patients waited an estimated 20.9 weeks for medically necessary elective care in 2019—long before the pandemic started.”
The study examines the total wait time faced by patients across 12 medical specialties from referral by a general practitioner (i.e. family doctor) to consultation with a specialist, to when the patient ultimately receives treatment.
More than 1,200 responses were received across the 12 specialties and 10 provinces. Among the provinces, Ontario recorded the shortest wait time at 21.6 weeks—still up from 20.3 weeks in 2022. Nova Scotia recorded the longest wait time in Canada at 56.7 weeks.
Among the various specialties, national wait times were longest between a referral by a GP and plastic (52.4 weeks), orthopedic (44.3) neurosurgery (43.5). Wait times were shortest for radiation (4.4 weeks) and medical oncology treatments (4.8 weeks). Patients also experience significant waiting times for various diagnostic technologies. This year, Canadians could expect to wait 6.6 weeks for a computed tomography (CT) scan, 12.9 weeks for a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan, and 5.3 weeks for an ultrasound.
Crucially, physicians report that their patients are waiting over four and a half weeks longer for treatment (after seeing a specialist) than what they consider to be clinically reasonable.
“Excessively long wait times remain a defining characteristic of Canada’s health-care system” said Mackenzie Moir, Fraser Institute policy analyst and co-author of the report. “And they aren’t simply minor inconveniences, they can result in increased suffering for patients, lost productivity at work, a decreased quality of life, and in the worst cases, disability or death.”
Median wait times by province (in weeks)
PROVINCE 2022 2023
British Columbia 25.8 27.7
Alberta 33.3 33.5
Saskatchewan 30.1 31.0
Manitoba 41.3 29.1
Ontario 20.3 21.6
Quebec 29.4 27.6
New Brunswick 43.3 52.6
Nova Scotia 58.2 56.7
P.E.I. 64.7 55.2
Newfoundland and Labrador 32.1 33.3

Each year, the Fraser Institute surveys physicians across twelve specialties and the ten provinces in order to document the queues for visits to specialists and for diagnostic and surgical procedures in Canada. Waiting Your Turn: Wait Times for Health Care in Canada, 2023 Report reports the results of this year’s survey.
In 2023, physicians report a median wait time of 27.7 weeks between a referral from a general practitioner and receipt of treatment. This represents the longest delay in the survey’s history and is 198% longer than the 9.3 weeks Canadian patients could expect to wait in 1993.
Overall, Ontario reports the shortest wait across Canada (21.6 weeks) while Nova Scotia had the longest (56.7 weeks).
The 27.7 week total wait time that patients face can be examined in two consecutive segments:
- referral by a general practitioner to consultation with a specialist: 14.6 weeks;
- consultation with a specialist to receipt of treatment: 13.1 weeks.
After seeing a specialist, Canadian patients were waiting 4.6 weeks longer than what physicians consider clinically reasonable (8.5 weeks).
Across the ten provinces, the study also estimates that there were 1,209,194 procedures for which patients—3% of the Canadian population—were waiting in 2023.
Patients also face considerable delays for diagnostic technology. This year, Canadians could expect to wait 6.6 weeks for a CT scan, 12.9 for an MRI scan, and 5.3 weeks for an ultrasound.
Survey results suggest that, despite provincial strategies to reduce wait times, Canadian patients continue to wait too long for medically necessary treatment.
Data were collected from the week of January 16 to July 1, 2023, longer than the period of collection in years before the COVID19 pandemic. A total of 1,269 responses were received across the 12 specialties surveyed. However, this year’s response rate was 10.3% (lower than in some previous years). As a result, the findings in this report should be interpreted with caution.
Research has repeatedly indicated that wait times for medically necessary treatment are not benign inconveniences. Wait times can, and do, have serious consequences such as increased pain, suffering, and mental anguish. In certain instances, they can also result in poorer medical outcomes—
transforming potentially reversible illnesses or injuries into chronic, irreversible conditions, or even permanent disabilities. In many instances, patients may also have to forgo their wages while they wait for treatment, resulting in an economic cost to the individuals themselves and the economy in general.
The results of this year’s survey indicate that despite provincial strategies to reduce wait times and high levels of health expenditure, it is clear that patients in Canada continue to wait too long to receive medically necessary treatment.
Waiting Your Turn: Wait Times for Health Care in Canada, 2023 Report
By Mackenzie Moir and Bacchus Barua, with Hani Wannamaker
www.fraserinstitute.org
Authors:
Alberta
Made in Alberta! Province makes it easier to support local products with Buy Local program

Show your Alberta side. Buy Local. |
When the going gets tough, Albertans stick together. That’s why Alberta’s government is launching a new campaign to benefit hard-working Albertans.
Global uncertainty is threatening the livelihoods of hard-working Alberta farmers, ranchers, processors and their families. The ‘Buy Local’ campaign, recently launched by Alberta’s government, encourages consumers to eat, drink and buy local to show our unified support for the province’s agriculture and food industry.
The government’s ‘Buy Local’ campaign encourages consumers to buy products from Alberta’s hard-working farmers, ranchers and food processors that produce safe, nutritious food for Albertans, Canadians and the world.
“It’s time to let these hard-working Albertans know we have their back. Now, more than ever, we need to shop local and buy made-in-Alberta products. The next time you are grocery shopping or go out for dinner or a drink with your friends or family, support local to demonstrate your Alberta pride. We are pleased tariffs don’t impact the ag industry right now and will keep advocating for our ag industry.”
Alberta’s government supports consumer choice. We are providing tools to help folks easily identify Alberta- and Canadian-made foods and products. Choosing local products keeps Albertans’ hard-earned dollars in our province. Whether it is farm-fresh vegetables, potatoes, honey, craft beer, frozen food or our world-renowned beef, Alberta has an abundance of fresh foods produced right on our doorstep.
Quick facts
- This summer, Albertans can support local at more than 150 farmers’ markets across the province and meet the folks who make, bake and grow our food.
- In March 2023, the Alberta government launched the ‘Made in Alberta’ voluntary food and beverage labelling program to support local agriculture and food sectors.
- Through direct connections with processors, the program has created the momentum to continue expanding consumer awareness about the ‘Made in Alberta’ label to help shoppers quickly identify foods and beverages produced in our province.
- Made in Alberta product catalogue website
Related information
Alberta
Province to expand services provided by Alberta Sheriffs: New policing option for municipalities

Expanding municipal police service options |
Proposed amendments would help ensure Alberta’s evolving public safety needs are met while also giving municipalities more options for local policing.
As first announced with the introduction of the Public Safety Statutes Amendment Act, 2024, Alberta’s government is considering creating a new independent agency police service to assume the police-like duties currently performed by Alberta Sheriffs. If passed, Bill 49 would lay additional groundwork for the new police service.
Proposed amendments to the Police Act recognize the unique challenges faced by different communities and seek to empower local governments to adopt strategies that effectively respond to their specific safety concerns, enhancing overall public safety across the province.
If passed, Bill 49 would specify that the new agency would be a Crown corporation with an independent board of directors to oversee its day-to-day operations. The new agency would be operationally independent from the government, consistent with all police services in Alberta. Unlike the Alberta Sheriffs, officers in the new police service would be directly employed by the police service rather than by the government.
“With this bill, we are taking the necessary steps to address the unique public safety concerns in communities across Alberta. As we work towards creating an independent agency police service, we are providing an essential component of Alberta’s police framework for years to come. Our aim is for the new agency is to ensure that Albertans are safe in their communities and receive the best possible service when they need it most.”
Additional amendments would allow municipalities to select the new agency as their local police service once it becomes fully operational and the necessary standards, capacity and frameworks are in place. Alberta’s government is committed to ensuring the new agency works collaboratively with all police services to meet the province’s evolving public safety needs and improve law enforcement response times, particularly in rural communities. While the RCMP would remain the official provincial police service, municipalities would have a new option for their local policing needs.
Once established, the agency would strengthen Alberta’s existing policing model and complement the province’s current police services, which include the RCMP, Indigenous police services and municipal police. It would help fill gaps and ensure law enforcement resources are deployed efficiently across the province.
Related information
-
 illegal immigration2 days ago
illegal immigration2 days agoDespite court rulings, the Trump Administration shows no interest in helping Abrego Garcia return to the U.S.
-

 2025 Federal Election2 days ago
2025 Federal Election2 days agoEuthanasia is out of control in Canada, but nobody is talking about it on the campaign trail
-

 2025 Federal Election2 days ago
2025 Federal Election2 days agoConservative MP Leslyn Lewis warns Canadian voters of Liberal plan to penalize religious charities
-
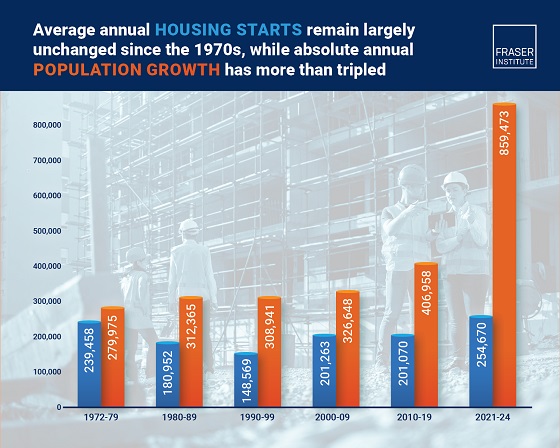
 2025 Federal Election2 days ago
2025 Federal Election2 days agoHousing starts unchanged since 1970s, while Canadian population growth has more than tripled
-

 Education2 days ago
Education2 days agoSchools should focus on falling math and reading grades—not environmental activism
-

 2025 Federal Election21 hours ago
2025 Federal Election21 hours agoRCMP Whistleblowers Accuse Members of Mark Carney’s Inner Circle of Security Breaches and Surveillance
-

 Autism1 day ago
Autism1 day agoAutism Rates Reach Unprecedented Highs: 1 in 12 Boys at Age 4 in California, 1 in 31 Nationally
-

 Bjorn Lomborg2 days ago
Bjorn Lomborg2 days agoGlobal Warming Policies Hurt the Poor







