Automotive
Canada should get out of EVs before bubble bursts

From the Fraser Institute
A recent article in the The Daily Mail asks, “Is the global EV bubble bursting?” The article then answers the question by looking at electric vehicle (EV) sales figures for six major manufacturers. Sales are down across the industry—Tesla, down 20 per cent in the first quarter this year compared to the same time last year; China’s EV manufacturer, BYD, down 43 per cent; GM down 20.5 per cent; and Volkswagen down 3.3 per cent. Honda saw an anemic uptick of 0.2 per cent. Only BMW experienced a substantial increase in EV sales, up 41 per cent. Not surprisingly, share prices have also dropped across the industry.
An Associated Press article shines more light on EV sales, which in the United States grew only 3.3 per cent in the first quarter of this year, a tiny fraction of the 47 per cent growth that fuelled record sales. The EV share of total U.S. sales fell to 7.15 per cent in the first quarter, down from 7.6 per cent last year. The slowdown, led by Tesla, “confirms automakers’ fears that they moved too quickly to pursue EV buyers.”
In other EV news, Ford has announced it will cut back on EV battery orders, signalling that the company anticipates less EV sales in the future. That would seem to be a good thing for Ford shareholders, as the company also admitted it’s lost $100,000 on every EV it sold in the first quarter of 2024. Ford expects to lose some $5.5 billion from EV sales this year.
So what does it all mean?
Countries that adopted EV sales mandates earlier than Canada are already finding their EV sales targets moving out of reach. In the United Kingdom, which has a 2024 EV sales target of 22 per cent, according to the Society of Motor Manufacturers and Traders, the share of the new car market held by pure battery EVs will be only 19.8 per cent by the end of 2024. The U.K.’s EV sales targets, like Canada’s, require 100 per cent of new vehicle sales to be electric by 2035.
And the rest of Europe is also falling short of EV transition mandates. Forbes reports that current sales of EVs in Europe have flattened at just over 2 million a year, essentially because the continent has run out of early adopters and corporate purchases. Forbes also observes that “other leading market forecasters still expect sales to explode and reach close to 9 million in Europe by 2030,” but that this rate of growth won’t be enough to let the EU and Britain reach target goals of EVs achieving close to an 80 per cent market share.
Meanwhile, the Trudeau government clings to its mandated EV transition, gambling with taxpayer money hand over fist as it pours more than $44 billion into various EV and battery manufacturing operations. And as Andrew Coyne observes in the Globe and Mail, it’s worse than that, as “all of that money will be borrowed, interest costs should also be included. The PBO estimates these at $6.6-billion. All told, that’s $50-billion of other people’s money. For three factories.”
Ottawa’s EV transition policy is deeply misguided, and already shows signs of incipient failure. And likely more failed taxpayer “investments” lie ahead. A smart government would tap the brakes on its EV transition policy. The bubble is growing.
Author:
2025 Federal Election
Trudeau and Carney Have Blown $43B on EVs

 David Krayden
David Krayden
General Motors laid off 500 workers at his Electric Vehicle (EV) plant in Ingersoll, ON.
It had nothing to do with the tariffs.
It had everything to do with the plummeting fascination that Canadians have for EVs. They are selling like used Edsels in the late 1950s. In a useless attempt to create a demand for these “green” vehicles (which aren’t actually green at all because the production of electricity does not result from magic) the governments of former Prime Minister Justin Trudeau and Ontario Premier Doug Ford wasted $42 billions of your tax money. And it was all to bolster an ideology not a demand for cars. There is no demand for these vehicles.
“You just lost 500 jobs. They’ve nuked those jobs. They’re not there anymore.”
-Dan McTeague

Ford, who saw this coming when he called an early provincial election that he knew he probably was going to lose if he waited for the anticipated vote, was actually honest to reporters when he admitted the layoffs had nothing to do with the dreaded Trump tariff but everything to do with public taste.
“What I understand from the president of General Motors that I spoke to, it’s going to be about 500 employees. Has nothing to do with the tariffs. He said, the volume is not there. People are not purchasing like they thought they would. So, they have thousands of vehicles sitting there. We make sure we support the workers and make sure that we get the government, especially Canada Post, to pick up some of these vehicles, because that’s what it’s geared for you.”

So, Ford expects Canada Post, another government agency on its last legs, to come to the rescue and pick up all these excess EVs? Sounds like it. The irony is that Ford came into office largely because the previous Liberal government had gone hog wild with its green energy program and hydro rates were among the highest in North America. Ford used to say that a industrialized province like Ontario can’t possibly prosper or even subsist on the energy provided by windmills and solar panels. He was right then but over the years he became firmly ensconced in the pocket of Trudeau and the Liberals, just as he is today with Mark Carney.

I spoke to my old friend Dan McTeague on Saturday about this mess. McTeague is a former Liberal MP from the GTA who is the president of Canadians for Affordable Energy today and well known for predicting gas prices across Canada as the @ gaspricewizard on X. As an MP, he always put principal above expediency, and he is no different today. McTeague is anxious for a Conservative Party of Canada (CPC) victory in this federal election and he is actively campaigning for a CPC nominee.

McTeague was not surprised over the dismal outlook for EVs.
“This is about Pierre Poilievre saying your policies are garbage. They’ve hurt Canadians. They’ve undermined the financial feasibility and sustainability of the federal government and the provincial government, and we’re going to get rid of them, just like we’re going to get rid of the CBC.”
-Dan McTeague
“Well, on the 22nd of March after having gone to the Ingersoll plant. I just tweeted a little while ago. I actually went there, filmed what was there in inventory. There were thousands of these vehicles just sitting there doing nothing. Obviously, Doug Ford didn’t get it on the 22nd of March. I said it says a lot about why the Ford nation is giddy about supporting Carney, he’s committed billions in world EV and battery manufacturing like this one in Ingersoll, where the provincial Feds kicked in over half a billion for bright drops. Was supposed to sell 100,000 units. Only sold 2100 actually, it got wrong. It was 2500 they might have probably given that a few away there. But look, this is anticipating what was there. It’s pretty obvious. I mean, I don’t just predict gas prices. Pretty good idea policies, EV mandates, the entire nets,” McTeague said.
McTeague explained that the “EV mandates are toast,” not just because President Donald Trump eliminated them but because they simply never had traction with consumers. He noted that Carney is playing games with the consumer carbon tax – because he hasn’t eliminated it but merely reduced it temporarily to zero – and has continued to keep emissions caps in place.
“Why are they doubling down on forcing us to have California-style appliances, which are extraordinarily costly to consumers. There are thousands of these things that are coming up. GFANZ, the Glasgow Financial Alliance for Net Zero that Mark Carney put forward, is now subject to antitrust review in the United States. This guy could be charged and billions of dollars taken away from the GFANZ organization,” McTeague said, adding that “anybody who hopped on the bandwagon a few years ago on net zero is now looking pretty damn foolish, and it’s amazing to see so many stunned Canadians falling in for this.”
“You just lost 500 jobs. They’ve nuked those jobs. They’re not there anymore.”

The former Liberal MP said the EV program is just one example of a failed economic record from the Trudeau-Carney regime. “However you slice it, the Liberals have had 10 years of failed policies. Net Zero has laid an egg. It’s not doing anything. And what they’re going to try to do is use a lot more public money and hopefully put enough wool over everyone’s eyes, so that we continue to go down this road of more recklessness as a result of what we’ve seen on EVs.
“Anybody who hopped on the bandwagon a few years ago on net zero is now looking pretty damn foolish, and it’s amazing to see so many stunned Canadians falling in for this.”
McTeague also wondered how the Ontario premier has moved from a commonsense politician on green energy to a cheerleader for Trudeau’s environmental authoritarianism. “For Doug Ford to have signed onto this. I mean, Shame on him, but it probably explains why he doesn’t want to support Pierre Poilievre.”
Said McTeague: “This is about Pierre Poilievre saying your policies are garbage. They’ve hurt Canadians. They’ve undermined the financial feasibility and sustainability of the federal government and the provincial government, and we’re going to get rid of them, just like we’re going to get rid of the CBC.”
“And so, for those reasons, you’re going to see why people are not supporting Pierre Poilievre, because they know, you know, they know which side of the bread is going to get buttered and for guys like Doug Ford, Bad mistake, back the wrong horse, and now we’re holding the bag. That’s why he called the election early.”
McTeague said the federal election is a watershed moment for people to decide what kind of future they want: prosperity or poverty. “If Canadians can’t get their head out of the sand and realize that they’re being duped that they can’t afford, you know, the saddling of the debts that these things are incurring for generations to come, and they think that somehow crapping on pipelines or putting emission caps that won’t allow us to make any more oil or gas to send these pipelines that they now suddenly have discovered are important … If we don’t wake up real soon, next two weeks, I can say confidently the next four years is basically cutting people.”
The energy expert predicted that the worst if yet to come if Carney wins a mandate to govern from the voters. “Nothing has changed, if anything, Mr. Carney and his company, as we well know, has lied on so many fronts. And here’s the big one that I’m going to say it here now, because I’ve said it many places before, but to be absolutely clear, you’re going to get a carbon tax, and that 20 cents you think you’re getting off. It’s going to be 40 cents by 2030, likely by the end of another government, “should they form a majority government.”
McTeague cautioned against Canadians becoming deluded and declaring, “Oh, we’re not worried about the future; we just don’t like Donald Trump, and we think Pierre Poilievre is like him.” Give your head a shake — because you know what, I’m going to spend a lot of time over the next few years, pointing back to the stupidity and frivolity of people. And make no mistake, David, these people know what they’re doing. They’re just trying to be cool and friendly because they made mistakes in 2015, 2019 and again in 2021 and they want to somehow think that they can justify bad decisions. What’s coming at the expense of the country? Coming at the expense of our economic sustainability? It’s likely coming at the expense of what concerns me even more so: the future of the federation of this country.”
“I’ve said it many places before, but to be absolutely clear, you’re going to get a carbon tax, and that 20 cents you think you’re getting off. It’s going to be 40 cents by 2030.”
Dan and I also discussed how he has discovered that much of the polling being conducted during this campaign is over-sampling people over 60, which comprise at least 50 percent of the respondents included in the surveys. This bodes well for Poilievre and the Conservatives.
Tomorrow I will be examining how the Consevatives are appealing to working class Canadians, labor union leaders and blue collar workers. Seeking and winning the “hard hat vote” worked for President Richard Nixon in 1972 and President Ronald Reagan in 1984. It can work for Poilevre too in 2025 — and somehow I think he realizes that.
WATCH: The Ugly Truth About Carney: Trudeau Subsidies Fail
CHECK OUT OUR KR NEWS INVESTIGATIVE SERIES ON MARK CARNEY

Rich Banker Man Mark Carney Caught by CBC & CTV Dodging Taxes

Liberal MP Encouraged the Abduction of Conservative Rival for Chinese Bounty

KR NEWSLETTER: Mark Carney to “Fold” “After the vote.” Carney’s Wife’s Eurasia Group Boss Spills the Beans on the Liberals’ “Elbows Up” Master Plan

GFANZ, Mark Carney’s Climate Cabal That Won’t Leave Us Alone

Mark Carney’s is China’s Man

KRN NEWSLETTER: Mark Carney Deep Dive + Disastrous Liberal Leadership Debates
Automotive
Tesla Vandals Keep Running Into The Same Problem … Cameras


From the Daily Caller News Foundation
By Hudson Crozier
People damaging Teslas in anger toward their owners and Elon Musk aren’t picking up on the fact that the vehicles have multiple cameras capable of catching them in the act.
At least nine perpetrators have been caught on video keying, writing graffiti or otherwise defacing Tesla vehicles in parking lots across the U.S. in the month of March alone. Most have led to an arrest or warrant based partly on the footage, which Tesla’s “Sentry Mode” automatically films from the side of the unattended vehicle when it detects human activity nearby.
“Smile, you’re on camera,” Tesla warned in a March 20 X post about its Sentry Mode feature. Musk’s company has been working to upgrade Sentry Mode so that the vehicles will soon blast music at full volume when vandals attack it. The camera system, however, has not stopped an increasing number of vandals from singling out Tesla owners, usually in protest of Musk’s work in the Trump administration for the Department of Government Efficiency (DOGE).
One incident happened on March 29, the same day leftists coordinated protests around the country for a “Global Day of Action” against Musk. That Saturday also saw alleged instances of violence at protests. The demonstrations stemmed from an online call to action by groups such as the Disruption Project, which encourages activists to foment “uprisings,” find a “target’s” home address and other confrontational tactics.
Tesla’s press team did not respond to a request for comment.
One man allegedly caught on camera keying a Tesla SUV on March 24 apologized to the owner who confronted him in a parking lot in Pennsylvania, police and media reports said. The man faces charges of criminal mischief, harassment and disorderly conduct for allegedly carving a swastika onto the vehicle.
“I have nothing against your car, and I have nothing against you,” the suspect said while the owner filmed him in the parking lot. “Obviously, I have something against Elon Musk.” The man called his own behavior “misguided.”
The defendant’s lawyer told Fox News his “client is a proud father, long-time resident, and is currently undergoing cancer treatment” and that he would not comment publicly “pending the outcome of the case.”
One of the most aggressive acts caught by Sentry Mode was in the case of a man who drove an ATV-style vehicle into a Tesla on March 25. Texas police identified the man as Demarqeyun Marquize Cox, arrested him and said he allegedly gave two other nearby Teslas the same treatment while also writing “Elon” on them. The public defender office representing Cox did not respond to a voicemail from the Daily Caller News Foundation.
Tesla cameras also caught three other people in Florida, Texas and Arizona keying and smearing bubble gum on the vehicles in March. The three suspects named by police do not have attorneys listed in county records available for contact.
Many of the vandalism cases since Trump’s return have reportedly caused thousands of dollars in damage for individual owners. For example, the bubble gum incident in Florida brought $2,623.66 in costs, while another keying incident in Minnesota brought $3,200.
Some reported attacks on Tesla vehicles and chargers have gotten the attention of federal law enforcement, including cases of alleged firebombing or shooting.
Two other suspected vandals in New York, one in Minnesota and one in Mississippi have reportedly avoided arrest for now — with one owner declining to press charges — but were all seen on the Teslas’ cameras scratching up the vehicles. Police identified the Mississippi suspect as an illegal migrant from Cuba.
One Tesla owner in North Dakota ridiculed a man who allegedly carved the letter “F” into his Cybertruck in a Costco parking lot — as seen on the Cybertruck’s camera. The defendant faces charges of criminal mischief, and county records say he is representing himself in court.
“I can’t believe this guy is potentially ruining his life to follow a political ideology,” the owner told WDAY News.
“If you’re going to vandalize these vehicles, you’re going to get caught,” the owner said.
-
 Business2 days ago
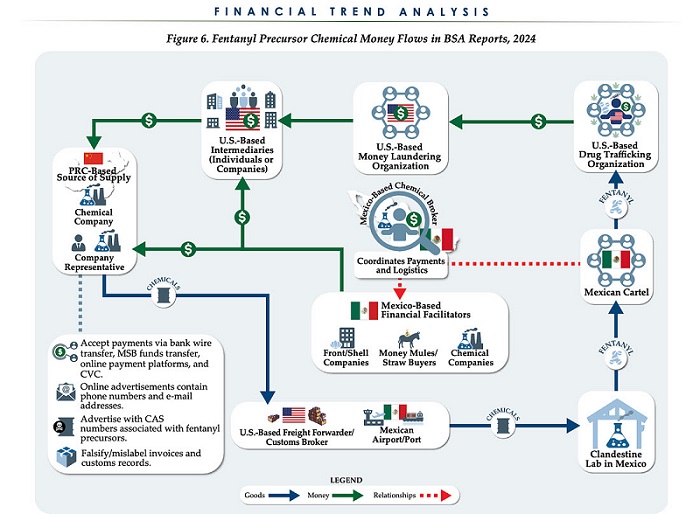
Business2 days agoChina, Mexico, Canada Flagged in $1.4 Billion Fentanyl Trade by U.S. Financial Watchdog
-

 2025 Federal Election2 days ago
2025 Federal Election2 days agoTucker Carlson Interviews Maxime Bernier: Trump’s Tariffs, Mass Immigration, and the Oncoming Canadian Revolution
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoDOGE Is Ending The ‘Eternal Life’ Of Government
-

 espionage2 days ago
espionage2 days agoEx-NYPD Cop Jailed in Beijing’s Transnational Repatriation Plot, Canada Remains Soft Target
-

 2025 Federal Election1 day ago
2025 Federal Election1 day agoBREAKING from THE BUREAU: Pro-Beijing Group That Pushed Erin O’Toole’s Exit Warns Chinese Canadians to “Vote Carefully”
-

 2025 Federal Election2 days ago
2025 Federal Election2 days agoCanada drops retaliatory tariffs on automakers, pauses other tariffs
-
 Daily Caller1 day ago
Daily Caller1 day agoDOJ Releases Dossier Of Deported Maryland Man’s Alleged MS-13 Gang Ties
-

 Daily Caller1 day ago
Daily Caller1 day agoTrump Executive Orders ensure ‘Beautiful Clean’ Affordable Coal will continue to bolster US energy grid







