Opinion
Can the expanded “Collicutt” parking lot handle the “Dawe” ice rink twinning?

If you start opening up your basement, you may need to rewire the house. Will the twinning of the ice rink at the Dawe Center open up an expensive can of worms?
The Dawe Center is over 40 years old and building codes have changed, pipes have deteriorated, the population has grown and costs have escalated.
When we add the additional structures will we need to upgrade the services, beef up the roofs, upgrade the wiring, the plumbing, the HVAC requirements of the whole complex? The roads, the parking, the lights, and will the costs make it prohibitive?
The city has already mentioned that any plan to twin the ice rink at Dawe would have a structural proviso attached to it. They have already talked about Plan B if the Dawe Centre isn’t capable of allowing expansion. The Collicutt ice rink would be twinned.
The Collicutt with it’s recently expanded parking lot. My bet would see the new rink in the south-east corner with the Collicutt Centre, but I might be wrong. We will see.
Just saying.
Business
China, Mexico, Canada Flagged in $1.4 Billion Fentanyl Trade by U.S. Financial Watchdog
 Sam Cooper
Sam Cooper
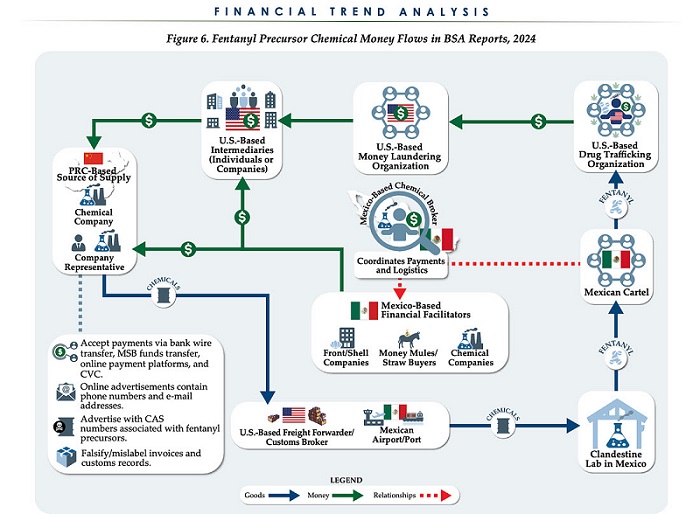
The U.S. Treasury’s Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN) has identified $1.4 billion in fentanyl-linked suspicious transactions, naming China, Mexico, Canada, and India as key foreign touchpoints in the global production and laundering network. The analysis, based on 1,246 Bank Secrecy Act filings submitted in 2024, tracks financial activity spanning chemical purchases, trafficking logistics, and international money laundering operations.
The data reveals that Mexico and the People’s Republic of China were the two most frequently named foreign jurisdictions in financial intelligence gathered by FinCEN. Most of the flagged transactions originated in U.S. cities, the report notes, due to the “domestic nature” of Bank Secrecy Act data collection. Among foreign jurisdictions, Mexico, China, Hong Kong, and Canada were cited most often in fentanyl-related financial activity.
The FinCEN report points to Mexico as the epicenter of illicit fentanyl production, with Mexican cartels importing precursor chemicals from China and laundering proceeds through complex financial routes involving U.S., Canadian, and Hong Kong-based actors.
The findings also align with testimony from U.S. and Canadian law enforcement veterans who have told The Bureau that Chinese state-linked actors sit atop a decentralized but industrialized global fentanyl economy—supplying precursors, pill presses, and financing tools that rely on trade-based money laundering and professional money brokers operating across North America.
“Filers also identified PRC-based subjects in reported money laundering activity, including suspected trade-based money laundering schemes that leveraged the Chinese export sector,” the report says.
A point emphasized by Canadian and U.S. experts—including former U.S. State Department investigator Dr. David Asher—that professional Chinese money laundering networks operating in North America are significantly commanded by Chinese Communist Party–linked Triad bosses based in Ontario and British Columbia—is not explored in detail in this particular FinCEN report.¹
Chinese chemical manufacturers—primarily based in Guangdong, Zhejiang, and Hebei provinces—were repeatedly cited for selling fentanyl precursors via wire transfers and money service businesses. These sales were often facilitated through e-commerce platforms, suggesting that China’s global retail footprint conceals a lethal underground market—one that ultimately fuels a North American public health crisis. In many cases, the logistics were sophisticated: some Chinese companies even offered delivery guarantees and customs clearance for precursor shipments, raising red flags for enforcement officials.
While China’s industrial base dominates the global fentanyl supply chain, Mexican cartels are the next most prominent state-like actors in the ecosystem—but the report emphasizes that Canada and India are rising contributors.
“Subjects in other foreign countries—including Canada, the Dominican Republic, and India—highlight the presence of alternative suppliers of precursor chemicals and fentanyl,” the report says.
“Canada-based subjects were primarily identified by Bank Secrecy Act filers due to their suspected involvement in drug trafficking organizations allegedly sourcing fentanyl and other drugs from traditional drug source countries, such as Mexico,” it explains, adding that banking intelligence “identified activity indicative of Canada-based individuals and companies purchasing precursor chemicals and laboratory equipment that may be related to the synthesis of fentanyl in Canada. Canada-based subjects were primarily reported with addresses in the provinces of British Columbia and Ontario.”
FinCEN also flagged activity from Hong Kong-based shell companies—often subsidiaries or intermediaries for Chinese chemical exporters. These entities were used to obscure the PRC’s role in transactions and to move funds through U.S.-linked bank corridors.
Breaking down the fascinating and deadly world of Chinese underground banking used to move fentanyl profits from American cities back to producers, the report explains how Chinese nationals in North America are quietly enlisted to move large volumes of cash across borders—without ever triggering traditional wire transfers.
These networks, formally known as Chinese Money Laundering Organizations (CMLOs), operate within a global underground banking system that uses “mirror transfers.” In this system, a Chinese citizen with renminbi in China pays a local broker, while the U.S. dollar equivalent is handed over—often in cash—to a recipient in cities like Los Angeles or New York who may have no connection to the original Chinese depositor aside from their role in the laundering network. The renminbi, meanwhile, is used inside China to purchase goods such as electronics, which are then exported to Mexico and delivered to cartel-linked recipients.
FinCEN reports that US-based money couriers—often Chinese visa holders—were observed depositing large amounts of cash into bank accounts linked to everyday storefront businesses, including nail salons and restaurants. Some of the cash was then used to purchase cashier’s checks, a common method used to obscure the origin and destination of the funds. To banks, the activity might initially appear consistent with a legitimate business. However, modern AI-powered transaction monitoring systems are increasingly capable of flagging unusual patterns—such as small businesses conducting large or repetitive transfers that appear disproportionate to their stated operations.
On the Mexican side, nearly one-third of reports named subjects located in Sinaloa and Jalisco, regions long controlled by the Sinaloa Cartel and Cartel Jalisco Nueva Generación. Individuals in these states were often cited as recipients of wire transfers from U.S.-based senders suspected of repatriating drug proceeds. Others were flagged as originators of payments to Chinese chemical suppliers, raising alarms about front companies and brokers operating under false pretenses.
The report outlines multiple cases where Mexican chemical brokers used generic payment descriptions such as “goods” or “services” to mask wire transfers to China. Some of these transactions passed through U.S.-based intermediaries, including firms owned by Chinese nationals. These shell companies were often registered in unrelated sectors—like marketing, construction, or hardware—and exhibited red flags such as long dormancy followed by sudden spikes in large transactions.
Within the United States, California, Florida, and New York were most commonly identified in fentanyl-related financial filings. These locations serve as key hubs for distribution and as collection points for laundering proceeds. Cash deposits and peer-to-peer payment platforms were the most cited methods for fentanyl-linked transactions, appearing in 54 percent and 51 percent of filings, respectively.
A significant number of flagged transactions included slang terms and emojis—such as “blues,” “ills,” or blue dots—in memo fields. Structured cash deposits were commonly made across multiple branches or ATMs, often linked to otherwise legitimate businesses such as restaurants, salons, and trucking firms.
FinCEN also tracked a growing number of trade-based laundering schemes, in which proceeds from fentanyl sales were used to buy electronics and vaping devices. In one case, U.S.-based companies owned by Chinese nationals made outbound payments to Chinese manufacturers, using funds pooled from retail accounts and shell companies. These goods were then shipped to Mexico, closing the laundering loop.
Another key laundering method involved cryptocurrency. Nearly 10 percent of all fentanyl-related reports involved virtual currency, with Bitcoin the most commonly cited, followed by Ethereum and Litecoin. FinCEN flagged twenty darknet marketplaces as suspected hubs for fentanyl distribution and cited failures by some digital asset platforms to catch red-flag activity.
Overall, FinCEN warns that fentanyl-linked funds continue to enter the U.S. financial system through loosely regulated or poorly monitored channels, even as law enforcement ramps up enforcement. The Drug Enforcement Administration reported seizures of over 55 million counterfeit fentanyl pills in 2024 alone.
The broader pattern is unmistakable: precursor chemicals flow from China, manufacturing occurs in Mexico, Canada plays an increasing role in chemical acquisition and potential synthesis, and drugs and proceeds flood into the United States, supported by global financial tools and trade structures. The same infrastructure that enables lawful commerce is being manipulated to sustain the deadliest synthetic drug crisis in modern history.
The Bureau is a reader-supported publication.
To receive new posts and support my work, consider becoming a free or paid subscriber.
Invite your friends and earn rewards
espionage
Ex-NYPD Cop Jailed in Beijing’s Transnational Repatriation Plot, Canada Remains Soft Target

 Sam Cooper
Sam Cooper
A former NYPD sergeant was sentenced to 18 months in prison this week for his role in a shadowy Chinese government operation that sought to coerce a political exile in New Jersey to return to the mainland. The conviction of Michael McMahon marks the first successful prosecution of a current or former American law enforcement officer accused of profiting from Beijing’s covert repatriation campaign, known as Operation Fox Hunt—a global manhunt that has ensnared operatives from Vancouver and Toronto to Los Angeles.
McMahon, 57, was convicted alongside two Chinese-American co-conspirators, Zhu Yong and Congying Zheng, who were previously sentenced to 24 and 16 months in prison, respectively. The trio was found guilty of interstate stalking and acting as unregistered agents of the People’s Republic of China, after a federal jury heard how they aided Beijing’s secret police—using Chinese businessmen and hired thugs based in the Tri-State area and California—to track and psychologically terrorize their target: a former Wuhan official named Xu Jin.
While McMahon’s sentencing concludes one legal chapter, The Bureau’s investigation into court records and national security sources reveals a far broader and ongoing web of espionage, coercion, and transnational repression—directed by senior Chinese Communist Party officials and bolstered by diaspora operatives and criminal proxies across North America.
McMahon and his family have fiercely denied his culpability as a tool of China’s secret police, insisting he was an unwitting pawn in a clandestine war that U.S. authorities failed to warn domestic citizens—including former law enforcement officers—about.
In private messages to The Bureau, following months of in-depth reporting into sealed court documents, McMahon’s wife, Martha Byrne, emphasized their belief that he had done nothing wrong.
“My husband, Michael McMahon, committed no crime,” she wrote. “There’s plenty of media to expose this grave injustice on my family.” She added a stark warning directed at law enforcement and intelligence communities: “It’s extremely important you use your platform to warn private investigators and local law enforcement of these patterns. Our government did nothing to warn us, and they knew my husband was being used. They knew since as early as 2015/16 these Chinese actors were using PIs. They put our family in danger and in turn the security of the entire country.”
But the sentencing judge in Brooklyn emphasized McMahon’s witting participation—and the fact that he profited from the scheme.
The case centered on Xu Jin, a former municipal official from Wuhan who fled China with his wife in 2010, seeking refuge in the United States. By 2015, his face appeared on a China Daily “most wanted” list—alongside dozens of Canada-based targets—part of Beijing’s sweeping Fox Hunt campaign to repatriate ex-officials accused of corruption, dissidents, and political rivals of President Xi Jinping. While Chinese authorities accused Xu of accepting bribes, he maintained he was not a criminal but a political target caught in a purge masked as anti-graft enforcement.
By 2017, the Chinese Ministry of Public Security escalated its efforts, dispatching emissaries, threatening Xu’s relatives in China, and launching a North American rendition operation. That’s when Zhu Yong, a 66-year-old Chinese national living in New York, hired McMahon—then working as a private investigator—to locate Xu.
Tapping law enforcement databases and traditional surveillance tactics, McMahon began tracking Xu and his family. The key break came in April 2017, when Xu’s elderly father—who had recently suffered a brain hemorrhage—was flown to the U.S. by the PRC, accompanied by a government doctor. His role: deliver a threatening message in person to his son. If Xu refused to return to China, his family would suffer the consequences.
These same tactics have been deployed in Canada, according to a January 2022 “Special Report” by the Privy Council Office on Chinese Fox Hunt operations, obtained by The Bureau.
McMahon surveilled the father’s arrival at a New Jersey home, then followed him to Xu Jin’s residence. Within days, the Chinese team had the address they needed.
Soon after, Congying Zheng and another associate showed up at Xu’s front door. They pounded on it, peered through the windows, and left a note that read: “If you are willing to go back to the mainland and spend 10 years in prison, your wife and children will be all right. That’s the end of this matter!”
By that point, McMahon’s role had deepened. Text messages recovered by federal investigators confirmed that he understood the objective of the operation. In one exchange with another investigator he had contracted, McMahon acknowledged that the goal was to repatriate the target to China “so they could prosecute him.”
After providing the address of Xu Jin, McMahon told his surveillance partner that he was “waiting for a call” to determine next steps. The partner replied, “Yeah. From NJ State Police about an abduction,” to which McMahon responded: “Lol.”
He later suggested further intimidation tactics to a Chinese co-conspirator, advising: “Park outside his home and let him know we are there.” According to prosecutors, McMahon also conducted background research on the victim’s daughter, including details about her university residence and academic major.
In total, McMahon was paid over $19,000 for his role in the PRC-directed operation. To obscure the origin of the funds, he deposited the payments into his son’s bank account—an arrangement prosecutors noted he had never used with any other client.
Court filings in the case traced troubling connections northward—to Canada—where suspects linked to Fujian-based organized crime networks, long known to Canadian police and senior elected officials, have been under investigation since at least 2022. Yet despite mounting intelligence, no charges have been laid.
The same Interpol “red notice” that named Xu also listed Chinese nationals living in Canada. According to Canadian law enforcement sources who spoke to The Bureau, multiple individuals now targeted by Fox Hunt reside in Vancouver and Toronto—cities with large mainland Chinese communities and a documented history of interference concerns.
“In Canada, we just knock on doors and talk to people,” one RCMP officer told The Bureau. “In the U.S., they go in and make arrests.” The officer pointed to a critical gap in Canadian law: the absence of a foreign agent registry—one of the FBI’s key legal tools in dismantling Fox Hunt cells on U.S. soil.
Beyond McMahon and Zhu Yong, the FBI investigation revealed a sprawling web of operatives functioning as “cutouts”—deniable intermediaries who provide a buffer between Chinese intelligence and the dirty work of coercion.
Even as the New Jersey operation began to falter—after Xu’s ailing father reportedly resisted efforts to pressure his son and Chinese operatives grew wary of U.S. law enforcement closing in—officials in Beijing leveraged McMahon’s surveillance to identify a new target: Xu’s daughter, a university student in Northern California. A second Fox Hunt pressure campaign was soon launched.
In California, the Ministry of Public Security dispatched Rong Jing—a PRC national and permanent U.S. resident—who had operated with apparent impunity across the U.S. as a bounty hunter for Beijing’s global rendition program.
This time, Rong sought to hire a new American private investigator.
On May 22, 2017, Rong met with the PI at a restaurant in Los Angeles. He didn’t know the man was an undercover FBI informant—and agreed to let their four-hour conversation be recorded.
When Rong proposed video surveillance on Xu’s daughter, the informant began to ask probing questions. Rong opened up—not only about the mission, but about the entire Fox Hunt apparatus behind it.
Asked how payment would be arranged, Rong said it would depend on what the PRC decided to do once the daughter was located. “Say, if the next step somebody asks me to catch [Xu’s] daughter,” he speculated. “When we get there, they wouldn’t feel comfortable to arrest her… So we need to be there on their behalf.”
According to Rong, successful Fox Hunt collaborators could submit for reward money—paid out inside China and split with U.S.-based operatives. The funds, he said, were controlled by Party officials, with the Communist Party overseeing all payments.
Rong contrasted his own freelance status with another class of agents—PRC “lobbyists” sent abroad as salaried civil servants. These operatives, he said, traveled under false names and work visas, sometimes posing as academics or trade representatives. Their job was to persuade overseas Chinese to return “voluntarily.”
“These lobbyists explain the advantages of returning to the PRC,” Rong said, euphemistically.
And then he pointed north.
Rong told the informant he had personally met one such PRC lobbyist in Canada. Though he did not name the individual, he described the tactic: use false identities, operate under official cover, and insulate the PRC government from any legal risk.
As the conversation turned back to Xu’s daughter, the informant asked the most pressing question: would she be safe?
“If there was an accident,” Rong replied, “in truth, you could claim that you were just investigating her.”
The Bureau is a reader-supported publication.
To receive new posts and support my work, consider becoming a free or paid subscriber.
Invite your friends and earn rewards
-

 2025 Federal Election2 days ago
2025 Federal Election2 days agoEuthanasia is out of control in Canada, but nobody is talking about it on the campaign trail
-

 2025 Federal Election1 day ago
2025 Federal Election1 day agoRCMP Whistleblowers Accuse Members of Mark Carney’s Inner Circle of Security Breaches and Surveillance
-

 Autism1 day ago
Autism1 day agoAutism Rates Reach Unprecedented Highs: 1 in 12 Boys at Age 4 in California, 1 in 31 Nationally
-

 Health1 day ago
Health1 day agoTrump admin directs NIH to study ‘regret and detransition’ after chemical, surgical gender transitioning
-

 Education2 days ago
Education2 days agoSchools should focus on falling math and reading grades—not environmental activism
-
 2025 Federal Election2 days ago
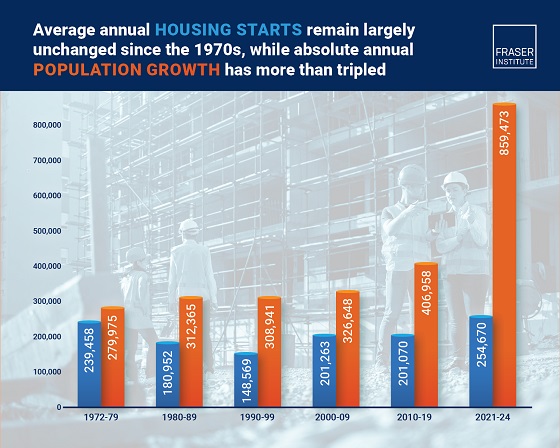
2025 Federal Election2 days agoHousing starts unchanged since 1970s, while Canadian population growth has more than tripled
-

 Bjorn Lomborg2 days ago
Bjorn Lomborg2 days agoGlobal Warming Policies Hurt the Poor
-
 Autism21 hours ago
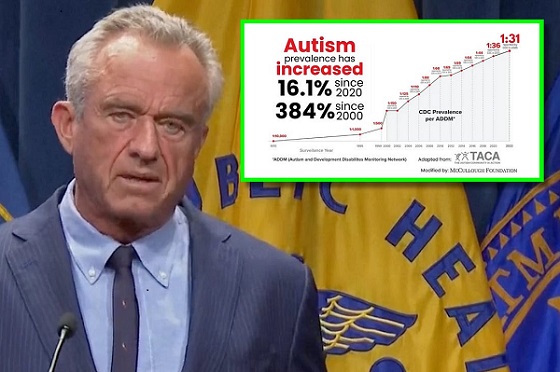
Autism21 hours agoRFK Jr. Exposes a Chilling New Autism Reality







