2025 Federal Election
Voters should remember Canada has other problems beyond Trump’s tariffs

From the Fraser Institute
By Jake Fuss and Grady Munro
Canadians will head to the polls on April 28 after Prime Minister Mark Carney called a snap federal election on Sunday. As the candidates make their pitch to try and convince Canadians why they’re best-suited to lead the country, Trump’s tariffs will take centre stage. But while the tariff issue is important, let’s not forget the other important issues Canadians face.
High Taxes: As many Canadians struggle to make ends meet, taxes remain the largest single expense. In 2023, the latest year of available data, the average Canadian family spent 43.0 per cent of its income on taxes compared to 35.6 per cent on food, shelter and clothing combined. High personal income tax rates also make it harder to attract and retain doctors, engineers and other high-skilled workers that contribute to the economy. Tax relief, which delivers savings for families across the income spectrum while also improving Canada’s competitiveness on the world stage, is long overdue.
Government Debt: At the end of March, Canada’s total federal debt will reach a projected $2.2 trillion or $52,094 for every man, woman and child in Canada. The federal government expects to pay $53.7 billion in debt interest costs in fiscal year 2024/25, diverting taxpayer dollars away from programs including health care and social services. The next federal government should rein in spending and stop racking up debt.
Red Tape: Smart regulation is necessary, but the Canadian economy is plagued by a costly and excessive regulatory burden imposed by governments. Regulatory compliance costs the economy approximately $12.2 billion each year, and the average business dedicates an estimated 85 days towards compliance. The next federal government should cut undue red tape and make Canada an easier place to do business.
Housing Affordability: Canadians across the country are struggling with the cost of housing. Indeed, Canada has the largest gap between home prices and incomes among G7 countries, and rents have spiked in recent years in many cities. In short, there’s not enough housing to meet demand. The next federal government should avoid policies that stoke further demand while working with the provinces and municipalities to remove impediments to homebuilding across Canada.
Collapsing Business Investment: Business investment is necessary to equip workers with the tools, technology and training they need to be more productive, yet business investment has collapsed. Specifically, from 2014 to 2021, inflation-adjusted business investment per worker fell from $18,363 to $14,687. Declining investment has helped create Canada’s productivity crisis, which has led to a decline in Canadian living standards. Clearly, Ottawa needs a new policy approach to address this crisis.
Declining Living Standards: According to Statistics Canada, inflation-adjusted per-person GDP—a broad measure of living standards—dropped from the post-pandemic peak of $60,718 in mid-2022 to $58,951 by the end of 2024. The next government should swiftly reverse this trend by enacting meaningful policy reforms that will help promote prosperity. The status quo simply will not suffice.
Tariffs are a clear threat to the Canadian economy and should be discussed at length during this election. But we shouldn’t forget other important issues that arose long before President Trump began this trade war and will continue to hurt Canadians if not addressed.
2025 Federal Election
The “Hardhat Vote” Has Embraced Pierre Poilievre

 David Krayden
David Krayden
Blue collar and unionized workers are supporting Pierre Poilievre and the CPC
When President Richard Nixon won a landslide in his 1972 reelection, he did so by broadening his own personal popularity and the appeal of the Republican Party to blue collar and unionized workers. It was called the hardhat vote and many working people embraced Nixon because he seemed to be talking the same language as they were. Nixon talked about law and order and getting tough on crime; safer streets and harsher penalties for serious crime. Although unionized workers had traditionally voted for the Democratic Party and seen the Republicans as the party of the wealthy, by 1972 the Democrats had moved far to the left on social issues and were completely out of touch with average Americans who saw Democratic presidential nominee Sen. George McGovern as being soft on crime and approving of the anarchy on the streets.
It’s precisely the language that Conservative Party of Canada leader Pierre Poilievere is speaking in the 2025 federal election. As support for the New Democratic Party has collapsed throughout the election campaign, don’t think most of it is going to the Liberal Party. Poilievre has been targeting blue collar workers for years with his emphasis on the trades and talking about middle class tax cuts and safe streets. A factory or construction worker is middle class and just want an affordable lifestyle for their families. They don’t have a lot of time for the woke underbelly of the Liberals or the NDP and are increasingly reluctant to support either party because both have appealed to elites.
Listen to Karl Lovett, the president of the Local 773 of the International Brotherhood of Electrical Workers, talk about Carney corruption and why he is supporting Poilievre and the CPC in 2025.
“Mark Carney also failed to pay $5 billion in Canadian taxes by hiding his company’s assets in Bermuda above a bike shop. Hard to believe that information comes from Canada’s NDP, or at least who is left of them, because the irony is, Mark Carney has eaten all those people alive. Even the mayor of Lima has warned Canadians not to vote for Mark Carney, and why for ripping him off the poorest of the poor people in Peru. That’s who he ripped off,” Lovett said.
“Listen, there are countless other outrageous examples proving that Mark Carney doesn’t give a damn about the Canadian working man. And now, as prime minister, which he’s not, Carney is promising to put carbon tax and tariff on the auto industry. It’s another rip-off screen that’s right. We’re getting punched by Trump on one side of the border, and Carney plans to punch us on this side of the border, also pretending it’s all about climate change, and now he’s made millions off the workers’ backs. He wants more than money. He wants more power. He wants all of the power to do whatever he wants to do. Mark Carney cannot be trusted with this power. Mark Carney cannot be trusted to protect workers,” Lovett continued.
The union leader told a cheering crowd that “Mark Carney is in it for himself, and when he loses this election, you can bet Mark Carney is going to leave Canada in a New York minute. But there’s hope, there’s hope, there’s our last hope. His name is Pierre Poilievere – the .only hope for Canadian workers. You see Mark Carney fooled Justin Trudeau. We can’t let him keep fooling us.”
“Local 773, which I represent, knows Pierre Poilievre very well. We can proudly tell you that Pierre has our back. Pierre has been putting Canadian people to work and Canadian workers. First, local 773 began working with Pierre Poilievre, the Conservative Member of Parliament Chris Lewis, some years ago, when it became all too clear that the Liberal Party had zero interest in helping out workers. Upon winning the leadership of the party, Pierre made Local 773 his very first priority, he came to my union hall. Pier made the Local 773 Visitor Training Center, and he met all our workers, and he made a pledge to me; he’s not going to turn his back on us, and I believe him,” Lovett said.
Toronto Sun columnist Joe Warmington agreed with me and you can hear that entire interview, below. “Labor wants to work, and they want to, you know, build things, and they want those good, paying jobs, and that’s what Poilievre has always been about, you know.”
“He wants more power. He wants all of the power to do whatever he wants to do. Mark Carney cannot be trusted with this power. Mark Carney cannot be trusted to protect workers,”
“Again, it’s hard to know, but I always felt … and I still think that Poilievre is going to pull this off because of these reasons that you’ve raised today, I never really bought into and again, I’m just one person’s opinion, and I go on the ground. In the air, the polls are saying, I know there’s this main street poll today, maybe it’ll swing differently. But in the air, it says one thing, and on the ground, it says another thing. And that clip you just showed, that’s the ground, that’s where the workers are, that’s where the families are.”
2025 Federal Election
Poilievre will cancel Mark Carney’s new Liberal packaging law and scrap the Liberal plastic ban!

From Conservative Party Communications
Conservative Leader Pierre Poilievre promised today that a new Conservative government will stop Mark Carney’s proposed Liberal food tax and scrap the existing Liberal plastic ban. Poilievre will:
- Stop proposed new labelling and packaging requirements that will raise the cost of fresh produce by as much as 34% and cost the average Canadian household an additional $400 each year.
- Scrap the Liberal plastics ban, including the ban on straws, grocery bags, food containers and cutlery, and other single-use plastics, letting consumers and businesses choose what works for them.
- Protect restaurants, grocers, and low-income Canadians from one-size-fits-all packaging rules that disproportionately affect those who can least afford it.
“After the Lost Liberal Decade, many Canadians can barely afford to put food on the table. And now Mark Carney and the Liberals want to make it even harder with a new food packaging law that will raise the price of food–again,” said Poilievre. “A new Conservative government will keep food prices down by scrapping the Liberal plastic ban and stopping Carney’s new Liberal food tax.”
After a decade of out-of-control spending and massive tax increases, families are spending $800 more on food this year than they did in 2024, and food banks had to handle a record two million visits in a single month. In Montreal, 44 percent of CEGEP students are experiencing some form of food insecurity, while places like Hawkesbury, Kingston, Toronto and Mississauga have all declared food insecurity emergencies.
And food prices are still rocketing upwards, surging by 3.2% over the last year, with no end in sight. In the last month alone, food inflation increased by 1.9 percentage points—the largest monthly jump in food prices in decades.
As if this wasn’t bad enough, Liberals have made life even more expensive and inconvenient for Canadians by banning plastics – including everything from straws to bags to food packaging. The current Liberal ban on single-use plastics will cost Canadians $1.3 billion dollars over the next decade.

Now Mark Carney wants to make it worse by adding complicated and costly new food packaging rules that will drive up the price of food even more–in effect, a new Liberal food tax. Plastic food packaging makes up 1/3 of all plastic packaging in Canada. The proposed Liberal food tax will cost the average Canadian household an additional $400 each year, waste half a million tonnes of food, decrease access to imported fruit and produce, and increase food inflation. The Chemistry Industry Association of Canada has also warned that this tax will put up to 60,000 Canadians out of work.
“The Liberals’ ideological crusade against convenience has already driven up food prices and the last thing Canadians need is Mark Carney’s new food tax added directly to your grocery bill,” said Poilievre. “The choice for Canadians is clear, a fourth Liberal term that will make food even more expensive or a new Conservative government that will axe the food tax and bring back straws, grocery bags and other items, to make life more affordable and convenient for Canadians – For a Change.”
-

 Daily Caller2 days ago
Daily Caller2 days agoTrump Executive Orders ensure ‘Beautiful Clean’ Affordable Coal will continue to bolster US energy grid
-

 2025 Federal Election2 days ago
2025 Federal Election2 days agoBREAKING from THE BUREAU: Pro-Beijing Group That Pushed Erin O’Toole’s Exit Warns Chinese Canadians to “Vote Carefully”
-
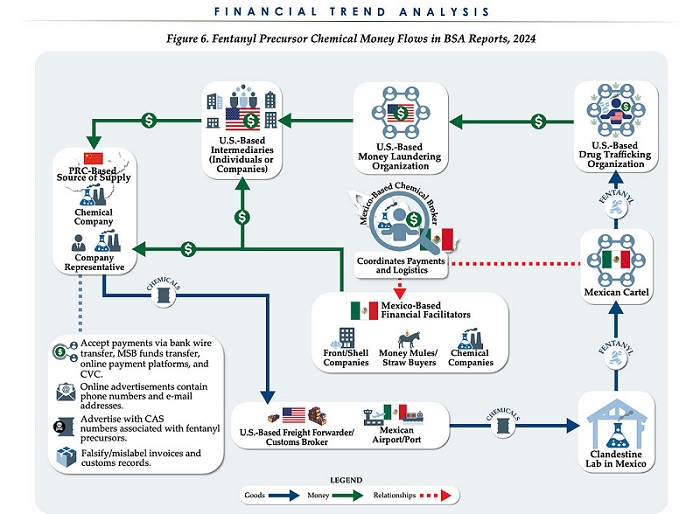
 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoChina, Mexico, Canada Flagged in $1.4 Billion Fentanyl Trade by U.S. Financial Watchdog
-

 COVID-191 day ago
COVID-191 day agoTamara Lich and Chris Barber trial update: The Longest Mischief Trial of All Time continues..
-

 Energy1 day ago
Energy1 day agoStraits of Mackinac Tunnel for Line 5 Pipeline to get “accelerated review”: US Army Corps of Engineers
-

 2025 Federal Election1 day ago
2025 Federal Election1 day agoAllegations of ethical misconduct by the Prime Minister and Government of Canada during the current federal election campaign
-

 Daily Caller24 hours ago
Daily Caller24 hours agoDaily Caller EXCLUSIVE: Trump’s Broad Ban On Risky Gain-Of-Function Research Nears Completion
-
 Daily Caller2 days ago
Daily Caller2 days agoDOJ Releases Dossier Of Deported Maryland Man’s Alleged MS-13 Gang Ties











