illegal immigration
UN Budgets Millions for U.S.-Bound Migrants in 2024
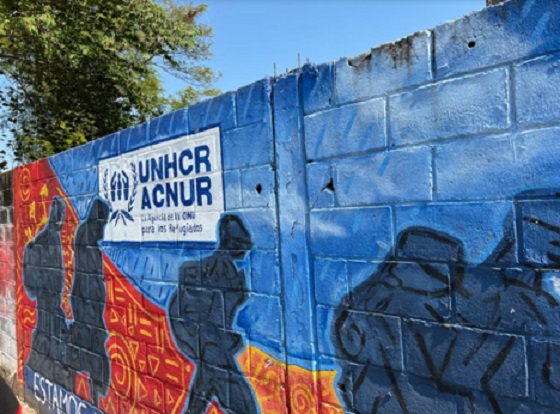

As this mural in Tapachula, Mexico, shows, UN agencies are well aware that their cash aid and assistance helps support illegal immigration over the U.S. southern border. January 2022 photo by Todd Bensman.
From the Center for Immigration Studies
By Todd Bensman
Public docs show cash handouts to help feed, transport, and house people headed for the U.S. border
Early on in America’s historic border crisis, now entering its fourth record-smashing year, some Republican lawmakers named a significant enabling culprit other than the usual Mexican cartel smugglers. They named the U.S. taxpayer-funded United Nations as essentially a co-smuggler after seeing my reports that the UN was handing out debit cards and cash vouchers to aspiring illegal border crossers on their way north.
One outraged group of 21 border-security-minded lawmakers even pitched a bill that would require the United States, the UN’s largest donor, to turn off the taxpayer money spigot. H.R. 6155 never caught fire, though, in no small part because “fact checks” claiming to debunk other reports like mine in the conservative press dissuaded broader media interest and left the American public in the dark.
But now the UN’s 2024 update to the “Regional Refugee and Migrant Response Plan” (RMRP for short), a planning and budget document for handing out nearly $1.6 billion in 17 Latin America countries, can cast a broad confirming light on the cash giveaways and much more aid for 2024 ahead — with the helping hands of 248 named non-governmental organizations. Despite the RMRP plan title naming Venezuelans as recipients of this aid operation, the document’s fine print (footnote on p. 14 and paragraph on p. 43, for instance) says the largesse goes to “all nationalities” and “multiple other nationalities”.

A Haitian shows his UN cash card outside a UN facility in Tapachula. He was there to complain the agency had not deposited money in the depleted card. January 2022 photo by Todd Bensman.
The documents clear up any mystery about what the UN and NGOs are doing on the migrant trails and leave no room for supposedly debunking “fact checks”.
In a nutshell, the UN and its advocacy partners are planning to spread $372 million in “Cash and Voucher Assistance (CVA)”, and “Multipurpose Cash Assistance (MCA)” to some 624,000 immigrants in-transit to the United States during 2024. That money is most often handed out, other UN documents show, as pre-paid, rechargeable debit cards, but also hard “cash in envelopes”, bank transfers, and mobile transfers the U.S. border-bound travelers can use for whatever they want.
The $372 million in planned cash giveaways to the 624,000 immigrants moving north and illegally crossing national borders “represents a significantly greater share of the financial requirements” for 2024, the RMRP says, but it is still only one part of much broader UN hemisphere-wide vision that aims to spend $1.59 billion assisting about three million people in 17 countries who emigrated from their home nations. Most will be “in-destination” recipients already supposedly settled in third countries, albeit in declining numbers, but a rising share of cash will go to the spiking numbers of “in-transit” immigrants launching journeys from those accommodating countries north to the United States.

Cash cards going out to immigrants in long lines at a camp in Reynosa, Mexico, in September 2021, photos that first drew ostensibly debunking fact checks. Photos by Todd Bensman.
Without distinction, both populations get access to UN cash but also “humanitarian transportation”, shelter, food, legal advice, personal hygiene products, health care, and “protection” against threats like human smuggling, and much more besides cash in envelopes or debit cards.
The cash handouts will be in the mix during 2024 as the UN and its private partners incorporate an “increased use of CVA” in, for instance, the $184 million it plans to provide 1.2 million people, $122 million for rent support and also “temporary collective shelter” for 473,000 people, and $25.8 million for “humanitarian transportation” to 129,000 people crossing borders. There’ll also be “expanded use of multi-purpose cash” for those claiming “gender-based violence”.
The UN’s 2024 Game Plan
The 130-page UN-spearheaded RMRP 2024 update went public in December and is readily accessible online, as is the original 2023-2024 plan it revises — sharply upward. It is the latest since the United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees and the UN’s International Organization for Migration started the program in 2018, originally for Venezuelans but now open to anyone in 17 nations of Latin America and the Caribbean. (For the complete list of involved groups, see p. 268, here, and explore their activities further with this handy interactive tool).
Some 57 international organizations would manage the handouts of $273 million, while 132 “national NGOs” and “civil service organizations” would handle $70 million in aid. Fifteen UN agencies would get the lion’s share at $1.2 billion.
The NGOs actively participated in crafting the RMRP 2024 Update, which amends a 2023-2024 plan released back in 2022 that at the time foresaw a decline in illegal immigration after 2023. It increased, instead.

A Nicaraguan on his way to the U.S. showed his UN cash card in Monterrey, Mexico. January 2022 photo by Todd Bensman.
“Country-level projections of in-transit movements for populations moving north through Central America and Mexico have been revised sharply upwards,” p. 44 explains in updating the 2024 RMRP update.
The reasons given include factors like “xenophobia” leading resettled migrants to leave for the United States. It does, finally, tag the real culprit: U.S. policies that created “newly established opportunities for regular pathways to move to the United States of America” for those who could make their way to northern Mexico.
The document makes clear in writing that the UN and these partners know their endeavor aids, abets, and makes possible the “onward movement” of immigrants who intend to illegally cross borders, especially to get into the United States.
None of them care. Twenty new groups joined the UN endeavor for 2024 for a total of 248.

Their plan frequently acknowledges the illegality, saying for instance, that one in three of the Venezuelan migrants the UN aims to help are in “irregular situations”, including those “who have crossed international borders without complying with all the legal and administrative requirements for entry and may not have the required documentation to do so”, as well as visa overstayers. The original 2023-2024 plan even spelled out that “special attention will be given to the use of [cash and voucher assistance] for in-transit populations, including the need for comprehensive solutions throughout the journey”.
The only expression of apparent concern about supporting people clearly intending to break U.S. law shows up on a page depicting a map with the thin red line of a migration route leading to the U.S. border at about El Paso. Someone took the trouble to add a footnote on that page noting that the map “does not imply official endorsement or acceptance by the UN”.

UN workers help long lines of immigrants apply for aid in Tapachula, Mexico. Photos by Todd Bensman.
Why hand out hundreds of millions of dollars as cash and services to hundreds of thousands planning to illegally follow that red line through UN member states, to include crossing the US border, when those nations don’t like or want it and must bear the political controversies of it?
“To support access to asylum procedures, migratory regularization activities, and socio-economic integration”, the plan says.
The money handout program “has taken on increasing importance”, it explains elsewhere, because it gives growing numbers of immigrants “the flexibility to cover their expenses and needs they deem most urgent, increasing their dignity and autonomy”.
Where It’ll Be Doled Out
Over the past three years, I have visited UN waystations featuring long lines of U.S.-bound immigrants applying for aid from clipboard-wielding workers handing out cash cards and other goodies, from Reynosa and Monterrey in the north of Mexico to Tapachula in the far south. But the waystations also appear everywhere along the trails much farther south.
The RMRP plan calls for distributing most of the cash, cash equivalents, and vouchers to migrants in Colombia and Ecuador, which are launch pads that sent 450,000 people through the Darian Gap jungle passage in Panama. The plan calls for 24 NGO partners to give money to 95,000 in Colombia and 59,000 in Mexico.
Some of the so-called transportation assistance is for local cab rides to stores or doctor appointments. But the UN agencies also know that aid will facilitate “increased onward movements” between countries of the “in-transit population” for 105,000 immigrants in Colombia, 25,000 in Brazil, 13,000 in Panama, and 3,700 in Mexico, to name a few places.
Likewise for “shelter”, $27.5 million is earmarked for 161,000 travelers in Colombia, $22.5 million for 179,000 in Ecuador, $18 million for 165,000 in Peru, and $4.3 million to help 33,000 in Mexico.
Political Fight or Flight
In years one and two of the historic mass migration crisis that President Biden’s let-them-all-in policies triggered, Republicans in the U.S. House of Representatives spoiled for a political fight over UN and NGO activity along the migrant routes because it was funded largely and ironically by the United States. And not just them. In December 2022, Texas Gov. Greg Abbott wrote Attorney General Ken Paxton asking him to investigate whether non-governmental organizations unlawfully assisted mass border crossings that overwhelmed the El Paso region.
Recent Congressional Research Service reporting reminds us that they had some legitimate grounds to complain; the United States has been the largest financial contributor to UN entities since the UN was established in 1945. Congress and the executive branch play key roles; Congress appropriates U.S. funding, while the executive branch shapes where the money will go through the State Department and the U.S. Mission to the United Nations in New York City.
Complaints, questions, and proposed legislation about the UN’s role in all of this may have gone cold, but as the latest RMRP plan reveals, the world body is as hot on the trail as ever.
Prior to his government experience, Bensman worked on staff for The Dallas Morning News, CBS, and Hearst Newspapers, covering the FBI, federal law enforcement and serving on investigative teams. He reported extensively on national security issues after 9/11 and worked from more than 25 countries in Latin America, the Middle East, and Africa. In Texas, he authored long-form investigative stories with emphases on border security related to illegal immigration and Mexico’s drug war. His reporting on human smuggling from Muslim-majority countries, Mexico’s drug war, and cross-border gun smuggling to cartels earned two National Press Club awards and an Inter-American Press Association award, among others.
COVID-19
5 Stories the Media Buried This Week

 The Vigilant Fox
The Vigilant Fox
“What is likely to happen,” Fauci says, “is the emergence of another respiratory disease.”
“It may be another coronavirus, because we know that coronaviruses, really, mostly in bats, have the capability of binding to receptors that are in humans.”
“It could be another flu,” Fauci continued. “We’re dealing with H5N1 now, which is bird flu, which has taken the somewhat disturbing step of infecting mammals, namely cows and cats and other mammals, which means it’s adapting itself more to a human.”
“So my concern, Walter, is that whenever that happens, the next outbreak will be of a respiratory disease that’s easily transmissible, that has a significant degree of morbidity and mortality,” Fauci said.
When asked if the cuts at HHS and “our attitude towards science” are making the situation “a little bit more dangerous,” Fauci replied, “Oh, absolutely!”
VIDEO: @TheChiefNerd
#4 – Dr. Oz drops bombshells on the massive waste, fraud, and abuse bleeding Medicare and Medicaid.
Oz explained that people are unknowingly signed up for coverage, illegal schemes are funneling taxpayer dollars to those who aren’t eligible, and the same patient can be billed in multiple states with no federal oversight catching it.
It also turns out that 230,000 Americans were enrolled in Obamacare plans without even knowing it.
His reaction at the end of this clip says it all.
VIDEO: @McCulloughFund
While you’re here, don’t forget to subscribe to get this top 10 list emailed to you each week.
#2 – Jenny McCarty reveals chilling encounter after speaking out on vaccine issue.
• After going public about her son’s autism and the vaccine link, Jenny McCarthy received a private visit from a man with a warning.
• He claimed to work for a top-level PR firm and said he was approached by a government agency.
• His job? To create a campaign to discredit her and label her “anti-vaccine.”
• He said he turned down the offer—because his own child had gone through the same thing.
•The man warned her that they would find someone else to do it and use the media to come after her hard.
• McCarthy was stunned and asked him to repeat everything—she said she had chills all over her body.
• When she asked why they’d attack her despite her not being anti-vaccine, he replied, “Doesn’t matter.”
• According to him, they had the media on their side and would do whatever it took to bury her message.
“We gave $13 to $15 billion a year to human traffickers. That’s what this system did,” Antonio Gracias lamented.
Gracias’ team combed through voter rolls in four states and uncovered thousands of non-citizens not only registered to vote, but in many cases, actually voted.
“We looked at the voter rolls in four states, and we found thousands of these people [non-citizens] on the voter rolls, and we found many of those people had voted. In one state in particular, well over a thousand voted.”
His conclusion?
“I think this [Biden’s border policy] was a move to import voters.”
VIDEO: @KanekoaTheGreat
Thanks for reading! This weekly roundup takes time and care to put together—and I do my best to make it your go-to source for the stories that matter most but rarely get the attention they deserve.
If you like my work and want to support me and my family and help keep this page going strong, the most powerful thing you can do is sign up for the email list and become a paid subscriber.
Your monthly subscription goes further than you think. Thank you so much for your support.
illegal immigration
Court attempts to halt Trump deportations, El Salvador president says ‘too late’

From The Center Square
By
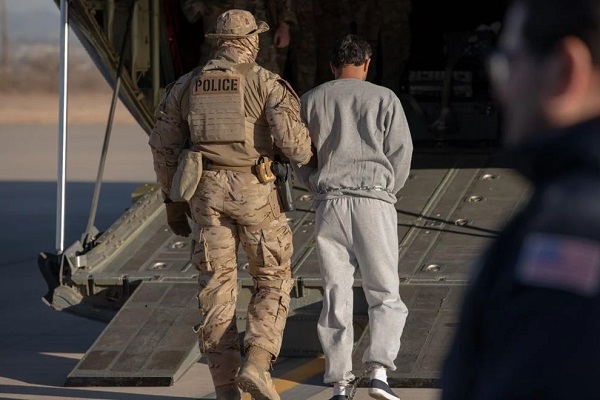
A class action lawsuit was filed on Saturday against the Trump administration after President Donald Trump signed an executive order invoking the Enemy Aliens Act to target, arrest and remove violent Venezuelan prison gang members, Tren de Aragua (TdA), from the U.S.
The lawsuit was filed by the American Civil Liberties Union Foundation on behalf of five Venezuelans illegally in the country who were detained in Texas and New York. The lawsuit was filed in U.S. District Court for the District of Columbia.
On Saturday, nearly 300 violent illegal foreign nationals were removed from the U.S. and arrived in El Salvador with the cooperation of El Salvadoran president Nayib Bukele after reaching an agreement with Secretary of State Marco Rubio.
“The first 238 members of the Venezuelan criminal organization, Tren de Aragua, arrived in our country,” Bukele said in a post on X. “They were immediately transferred to CECOT, the Terrorism Confinement Center, for a period of one year (renewable).”
El Salvador also received 23 MS-13 gang members from the U.S. who were wanted by Salvadoran authorities, Bukele said. They include two ringleaders, one of whom “is a member of the criminal organization’s highest structure.” Those sent to El Salvador by the U.S. will help Bukele’s government “finalize intelligence gathering and go after the last remnants of MS-13, including its former and new members, money, weapons, drugs, hideouts, collaborators and sponsors.
“As always, we continue advancing in the fight against organized crime. But this time, we are also helping our allies, making our prison system self-sustainable, and obtaining vital intelligence to make our country an even safer place. All in a single action. May God bless El Salvador, and may God bless the United States,” he said.
The U.S. government is paying a small fee to detain them, Bukele said, and the prison is also making money because it requires inmates to work. These additional inmates, “combined with the production already being generated by more than 40,000 inmates engaged in various workshops and labor under the Zero Idleness program, will help make our prison system self-sustainable,” he said, noting that it costs $200 million a year to maintain.
In response, Rubio thanked Bukele saying, “El Salvador has agreed to hold the violent criminals “in their very good jails at a fair price that will also save our taxpayer dollars. President Nayib Bukele is not only the strongest security leader in our region, he’s also a great friend of the U.S.”
In an emergency hearing held on Saturday, a federal judge ruled that deportations of violent Venezuelans be temporarily halted and those who were illegally in the country and already removed be returned. The ACLU said the order blocked the administration “from deporting anyone under the Alien Enemies Act while the case proceeds. Flights carrying Venezuelan immigrants the DHS attempted to deport have been ordered to turn around and return to the U.S.”
A U.S. federal judge has no jurisdiction over foreign governments.
In response, Bukele posted on X, “Oopsie … Too late,” with a laughing emoji.
Bukele also posted videos and pictures of them arriving in El Salvador in handcuffs. The video shows them being met by El Salvadoran military wearing riot gear and transported in armored vehicles to CECOT. The videos depict El Salvadoran officials lifting up their shirts to show tattoos of gang member affiliation, officials shaving the heads of kneeling inmates and their admittance as CECOT inmates.
Today, the first 238 members of the Venezuelan criminal organization, Tren de Aragua, arrived in our country. They were immediately transferred to CECOT, the Terrorism Confinement Center, for a period of one year (renewable).
The United States will pay a very low fee for them,… pic.twitter.com/tfsi8cgpD6
— Nayib Bukele (@nayibbukele) March 16, 2025
Cooperation between the U.S. and El Salvador expanded under Trump and Rubio, representing a reversal of Biden administration policy that used taxpayer money and planes to transport illegal foreign nationals into the U.S.
Trump has been aggressively targeting of TdA after a record more than 1 million Venezuelans illegally entered the U.S. under the Biden administration, including TdA members expanding operations in at least 22 states, The Center Square first reported.
Under the Trump administration, Venezuelan repatriation flights also began, paid for by the Venezuelan government, negotiated by the Trump administration, The Center Square reported.
-

 2025 Federal Election1 day ago
2025 Federal Election1 day agoRCMP memo warns of Chinese interference on Canadian university campuses to affect election
-

 2025 Federal Election2 days ago
2025 Federal Election2 days agoConservative Party urges investigation into Carney plan to spend $1 billion on heat pumps
-

 Alberta2 days ago
Alberta2 days agoAlberta takes big step towards shorter wait times and higher quality health care
-

 2025 Federal Election2 days ago
2025 Federal Election2 days agoFifty Shades of Mark Carney
-

 2025 Federal Election19 hours ago
2025 Federal Election19 hours agoResearchers Link China’s Intelligence and Elite Influence Arms to B.C. Government, Liberal Party, and Trudeau-Appointed Senator
-
 2025 Federal Election2 days ago
2025 Federal Election2 days agoCorporate Media Isn’t Reporting on Foreign Interference—It’s Covering for It
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoTrump raises China tariffs to 125%, announces 90-day pause for countries who’ve reached out to negotiate
-

 2025 Federal Election1 day ago
2025 Federal Election1 day agoThe status quo in Canadian politics isn’t sustainable for national unity











